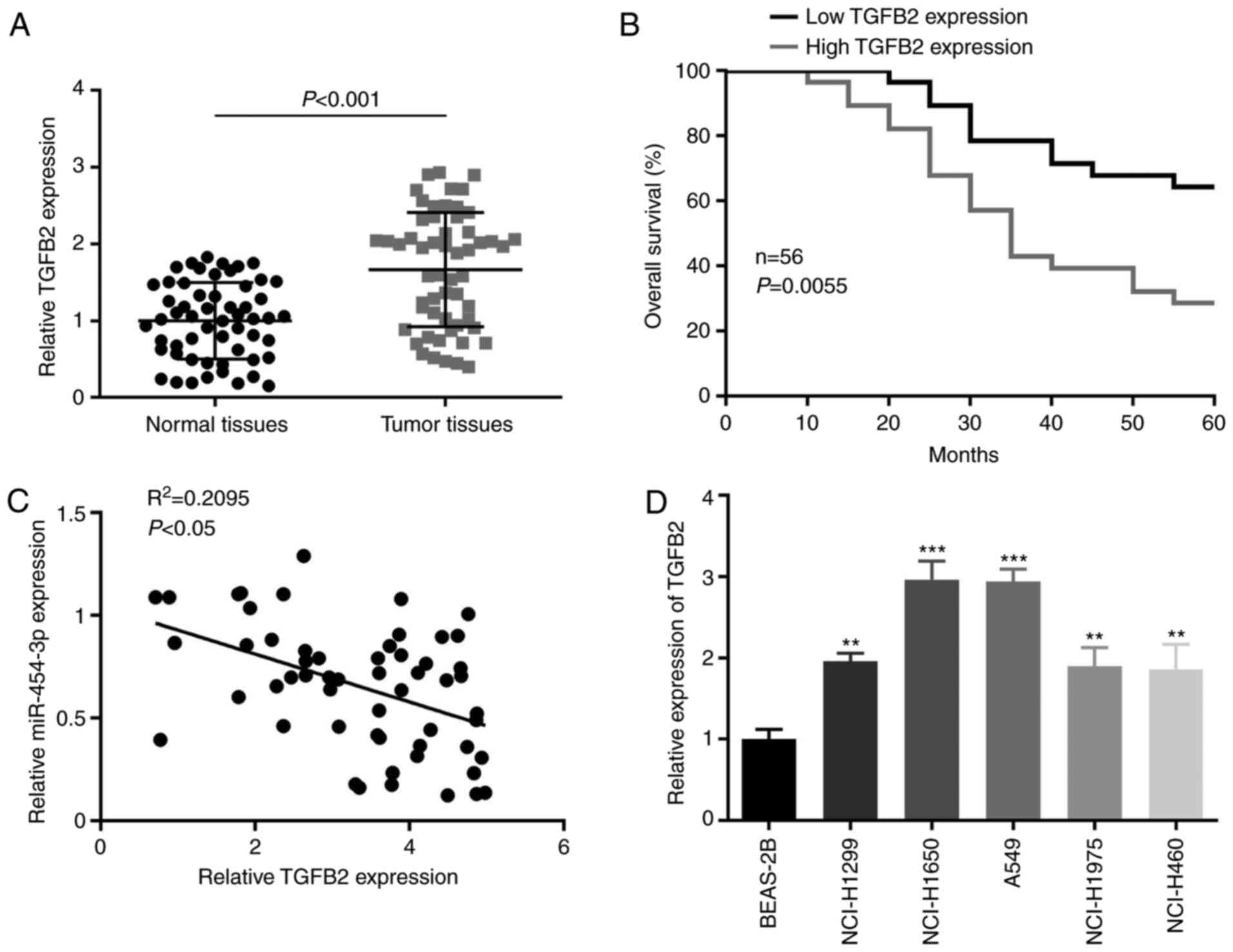
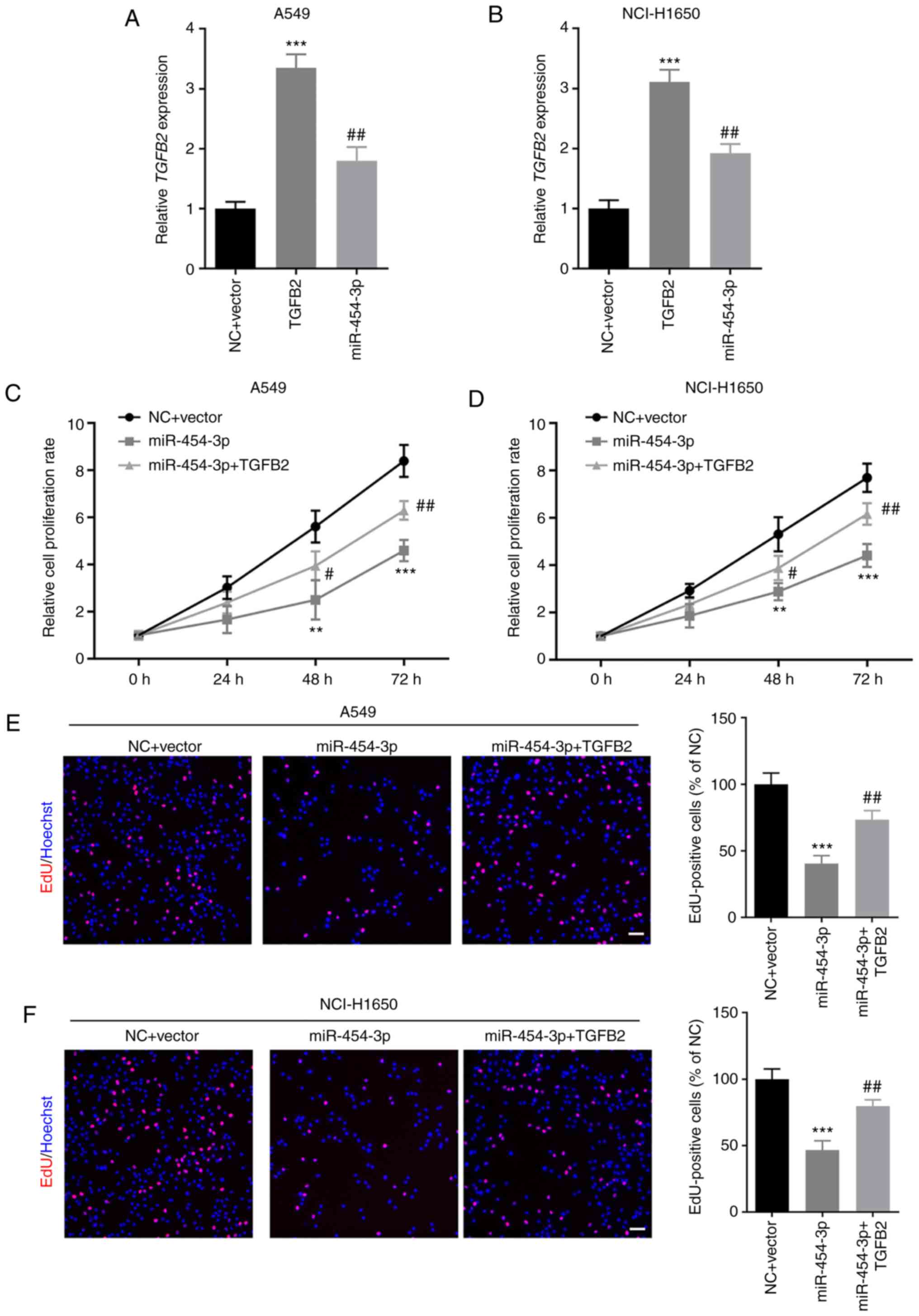
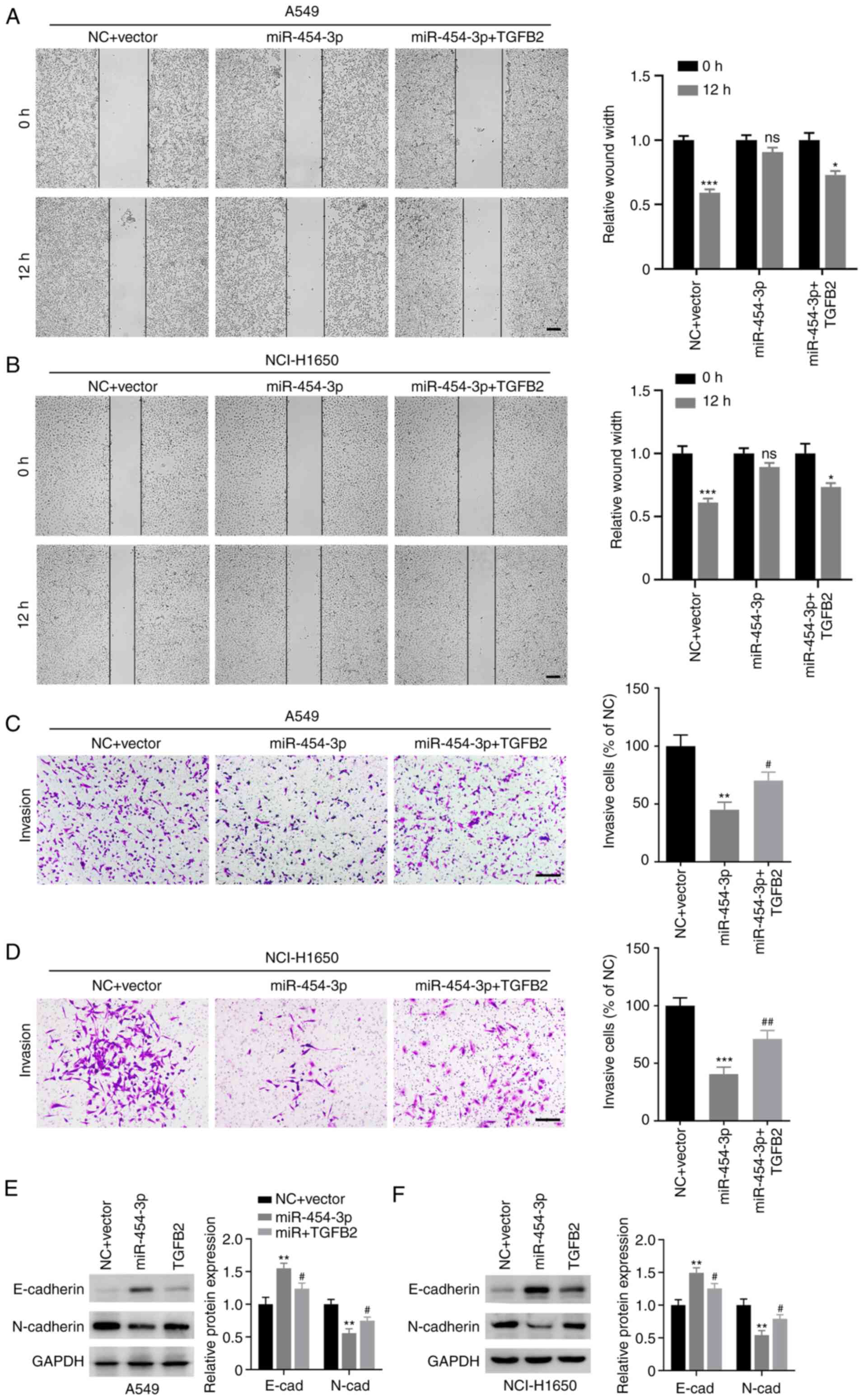
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Didkowska J, Wojciechowska U, Mańczuk M
and Łobaszewski J: Lung cancer epidemiology: Contemporary and
future challenges worldwide. Ann Transl Med. 4:1502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jonna S and Subramaniam DS: Molecular
diagnostics and targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): An update. Discov Med. 27:167–170. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Foster CC, Pitroda SP and Weichselbaum RR:
Beyond palliation: The rationale for metastasis-directed therapy
for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
14:1510–1512. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galagali H and Kim JK: The multifaceted
roles of microRNAs in differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
67:118–140. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee TJ, Yuan X, Kerr K, Yoo JY, Kim DH,
Kaur B and Eltzschig HK: Strategies to modulate MicroRNA functions
for the treatment of cancer or organ injury. Pharmacol Rev.
72:639–667. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu M, Wang G, Tian W, Deng Y and Xu Y:
miRNA-based therapeutics for lung cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
23:5989–5996. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan Y, Liao H, Pu Q, Ke X, Hu X, Ma Y,
Luo X, Jiang Q, Gong Y, Wu M, et al: miR-410 induces both
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance through
activation of the PI3K/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun X, Xu M, Liu H and Ming K:
MicroRNA-219 is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and
inhibits cell growth and metastasis by targeting HMGA2. Mol Med
Rep. 16:3557–3564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xing F, Song Z and He Y: miR-219-5p
inhibits growth and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells by targeting
HMGA2. Biol Res. 51:502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shao Y, Liang B, Long F and Jiang SJ:
Diagnostic MicroRNA biomarker discovery for non-small-cell lung
cancer adenocarcinoma by integrative bioinformatics analysis.
Biomed Res Int. 2017:25630852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zuo J, Yu H, Xie P, Liu W, Wang K and Ni
H: miR-454-3p exerts tumor-suppressive functions by down-regulation
of NFATc2 in glioblastoma. Gene. 710:233–239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jin C, Lin T and Shan L: Downregulation of
calbindin 1 by miR-454-3p suppresses cell proliferation in nonsmall
cell lung cancer in vitro. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 34:119–127.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang S, Zhang G, Zheng W, Xue Q, Wei D,
Zheng Y and Yuan J: miR-454-3p and miR-374b-5p suppress migration
and invasion of bladder cancer cells through targetting ZEB2.
Biosci Rep. 38:BSR201814362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan Y, Shi C, Li T and Kuang T:
microRNA-454 shows anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic activity in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting LRP6. Am J Cancer
Res. 7:139–147. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abraham CG, Ludwig MP, Andrysik Z, Pandey
A, Joshi M, Galbraith MD, Sullivan KD and Espinosa JM: ΔNp63α
suppresses TGFB2 expression and RHOA activity to drive cell
proliferation in squamous cell carcinomas. Cell Rep. 24:3224–3236.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang B, Bai J, Shi R, Shao X, Yang Y, Jin
Y, Che X, Zhang Y, Qu X, Liu Y and Li Z: TGFB2 serves as a link
between epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor mutation burden
in gastric cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 84:1065322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dave H, Trivedi S, Shah M and Shukla S:
Transforming growth factor beta 2: A predictive marker for breast
cancer. Indian J Exp Biol. 49:879–887. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bruna A, Darken RS, Rojo F, Ocaña A,
Peñuelas S, Arias A, Paris R, Tortosa A, Mora J, Baselga J and
Seoane J: High TGFbeta-Smad activity confers poor prognosis in
glioma patients and promotes cell proliferation depending on the
methylation of the PDGF-B gene. Cancer Cell. 11:147–160. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mittal V: Epithelial mesenchymal
transition in aggressive lung cancers. Adv Exp Med Biol. 890:37–56.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Singh M, Yelle N, Venugopal C and Singh
SK: EMT: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther.
182:80–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang H, Brown CW and Matzuk MM: Genetic
analysis of the mammalian transforming growth factor-beta
superfamily. Endocr Rev. 23:787–823. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rodriguez LG, Wu X and Guan JL:
Wound-healing assay. Methods Mol Biol. 294:23–29. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hung JJ, Jeng WJ, Hsu WH, Chou TY, Huang
BS and Wu YC: Predictors of death, local recurrence, and distant
metastasis in completely resected pathological stage-I
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 7:1115–1123. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee WC, Reuben A, Hu X, McGranahan N, Chen
R, Jalali A, Negrao MV, Hubert SM, Tang C, Wu CC, et al: Multiomics
profiling of primary lung cancers and distant metastases reveals
immunosuppression as a common characteristic of tumor cells with
metastatic plasticity. Genome Biol. 21:2712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lim ZF and Ma PC: Emerging insights of
tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms in lung cancer
targeted therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 12:1342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Diaz-Lagares A, Mendez-Gonzalez J, Hervas
D, Saigi M, Pajares MJ, Garcia D, Crujerias AB, Pio R, Montuenga
LM, Zulueta J, et al: A novel epigenetic signature for early
diagnosis in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:3361–3371. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duruisseaux M and Esteller M: Lung cancer
epigenetics: From knowledge to applications. Semin Cancer Biol.
51:116–128. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Iqbal MA, Arora S, Prakasam G, Calin GA
and Syed MA: MicroRNA in lung cancer: Role, mechanisms, pathways
and therapeutic relevance. Mol Aspects Med. 70:3–20. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu KL, Tsai YM, Lien CT, Kuo PL and Hung
AJ: The roles of MicroRNA in lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
20:16112019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jiang D, Li H, Xiang H, Gao M, Yin C, Wang
H, Sun Y and Xiong M: Long chain non-coding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR
knockdown increases miR-454-3p to suppress gastric cancer growth by
targeting STAT3/cyclin D1. Med Sci Monit. 25:1537–1548. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hui X, Zhang S and Wang Y: miR-454-3p
suppresses cell migration and invasion by targeting CPEB1 in human
glioblastoma. Mol Med Rep. 18:3965–3972. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yan A, Wang C, Zheng L, Zhou J and Zhang
Y: MicroRNA-454-3p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in
esophageal cancer by targeting insulin-like growth factor 2
mRNA-binding protein 1. Oncol Lett. 20:3592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ren L, Chen H, Song J, Chen X, Lin C,
Zhang X, Hou N, Pan J, Zhou Z, Wang L, et al: miR-454-3p-mediated
Wnt/β-catenin signaling antagonists suppression promotes breast
cancer metastasis. Theranostics. 9:449–465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song Y, Guo Q, Gao S and Hua K: miR-454-3p
promotes proliferation and induces apoptosis in human cervical
cancer cells by targeting TRIM3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
516:872–879. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Strauss J, Heery CR, Schlom J, Madan RA,
Cao L, Kang Z, Lamping E, Marté JL, Donahue RN, Grenga I, et al:
Phase I trial of M7824 (MSB0011359C), a bifunctional fusion protein
targeting PD-L1 and TGFβ, in advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer
Res. 24:1287–1295. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A:
TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat
Genet. 29:117–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Mechanisms of
TGFβ-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Med.
5:632016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Vagenas K, Spyropoulos C, Gavala V and
Tsamandas AC: TGFbeta1, TGFbeta2, and TGFbeta3 protein expression
in gastric carcinomas: Correlation with prognostics factors and
patient survival. J Surg Res. 139:182–188. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schlingensiepen KH, Schlingensiepen R,
Steinbrecher A, Hau P, Bogdahn U, Fischer-Blass B and Jachimczak P:
Targeted tumor therapy with the TGF-beta 2 antisense compound AP
12009. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17:129–139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao L, Lin L, Pan C, Shi M, Liao Y, Bin J
and Liao W: Flotillin-2 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma
metastasis and is necessary for the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition induced by transforming growth factor-β. Oncotarget.
6:9781–9793. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang X, Zhang L, Chen M and Liu D:
miR-324-5p inhibits gallbladder carcinoma cell metastatic
behaviours by downregulation of transforming growth factor beta 2
expression. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 48:315–324. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lu R, Ji Z, Li X, Qin J, Cui G, Chen J,
Zhai Q, Zhao C, Zhang W and Yu Z: Tumor suppressive microRNA-200a
inhibits renal cell carcinoma development by directly targeting
TGFB2. Tumour Biol. 36:6691–6700. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jaschinski F, Rothhammer T, Jachimczak P,
Seitz C, Schneider A and Schlingensiepen KH: The antisense
oligonucleotide trabedersen (AP 12009) for the targeted inhibition
of TGF-β2. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 12:2203–2213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bogdahn U, Hau P, Stockhammer G,
Venkataramana NK, Mahapatra AK, Suri A, Balasubramaniam A, Nair S,
Oliushine V, Parfenov V, et al: Targeted therapy for high-grade
glioma with the TGF-β2 inhibitor trabedersen: Results of a
randomized and controlled phase IIb study. Neuro Oncol. 13:132–142.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|