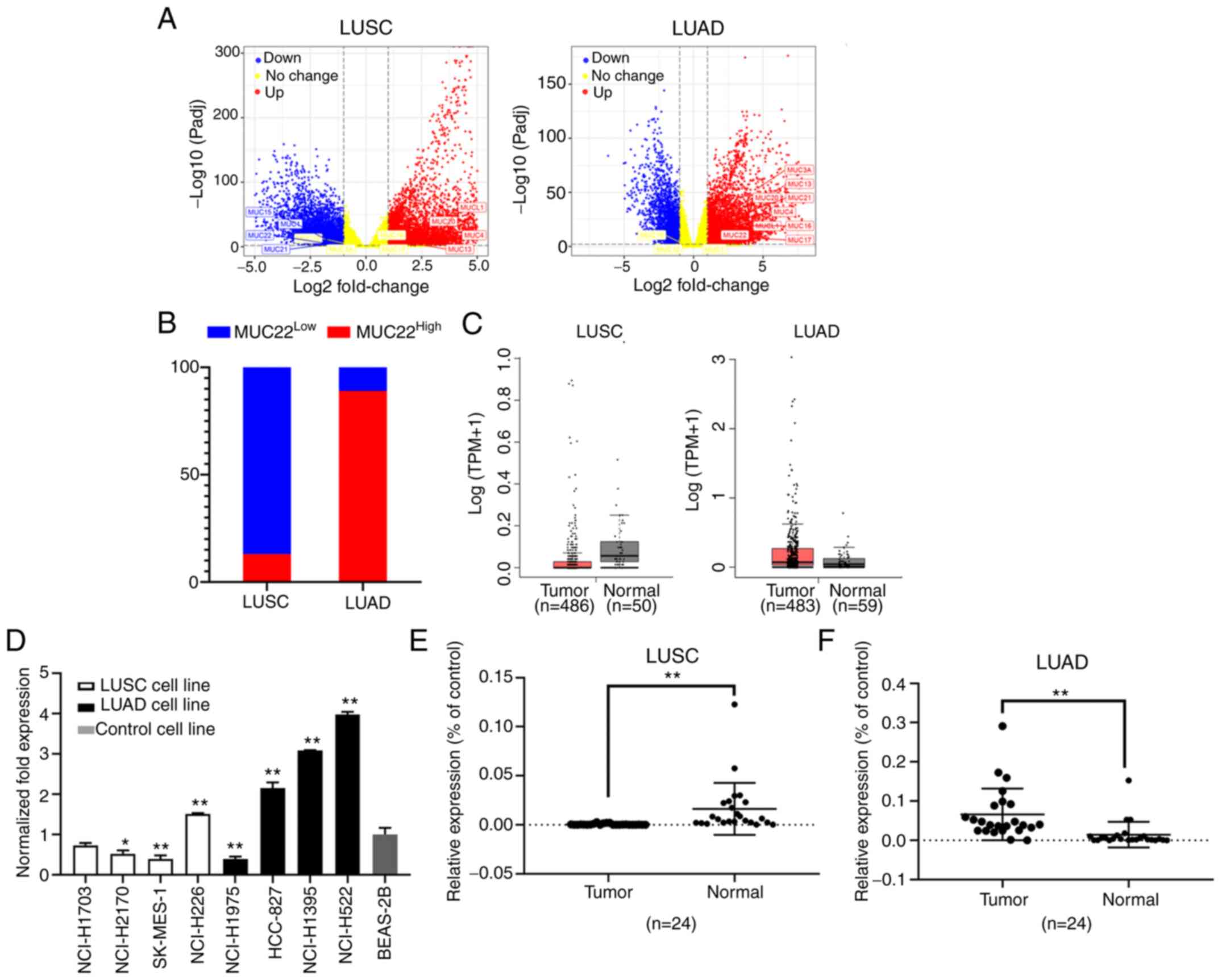
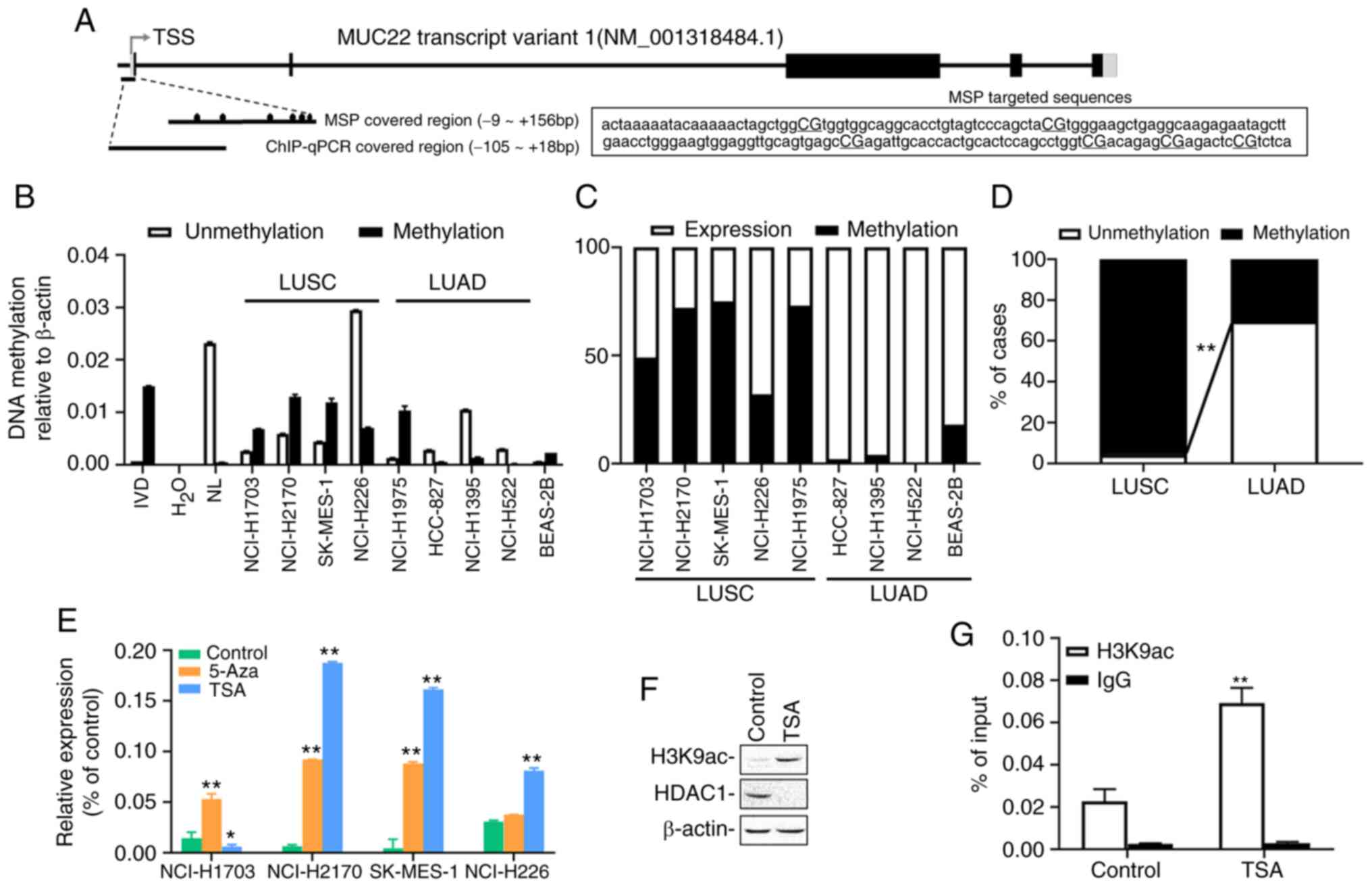
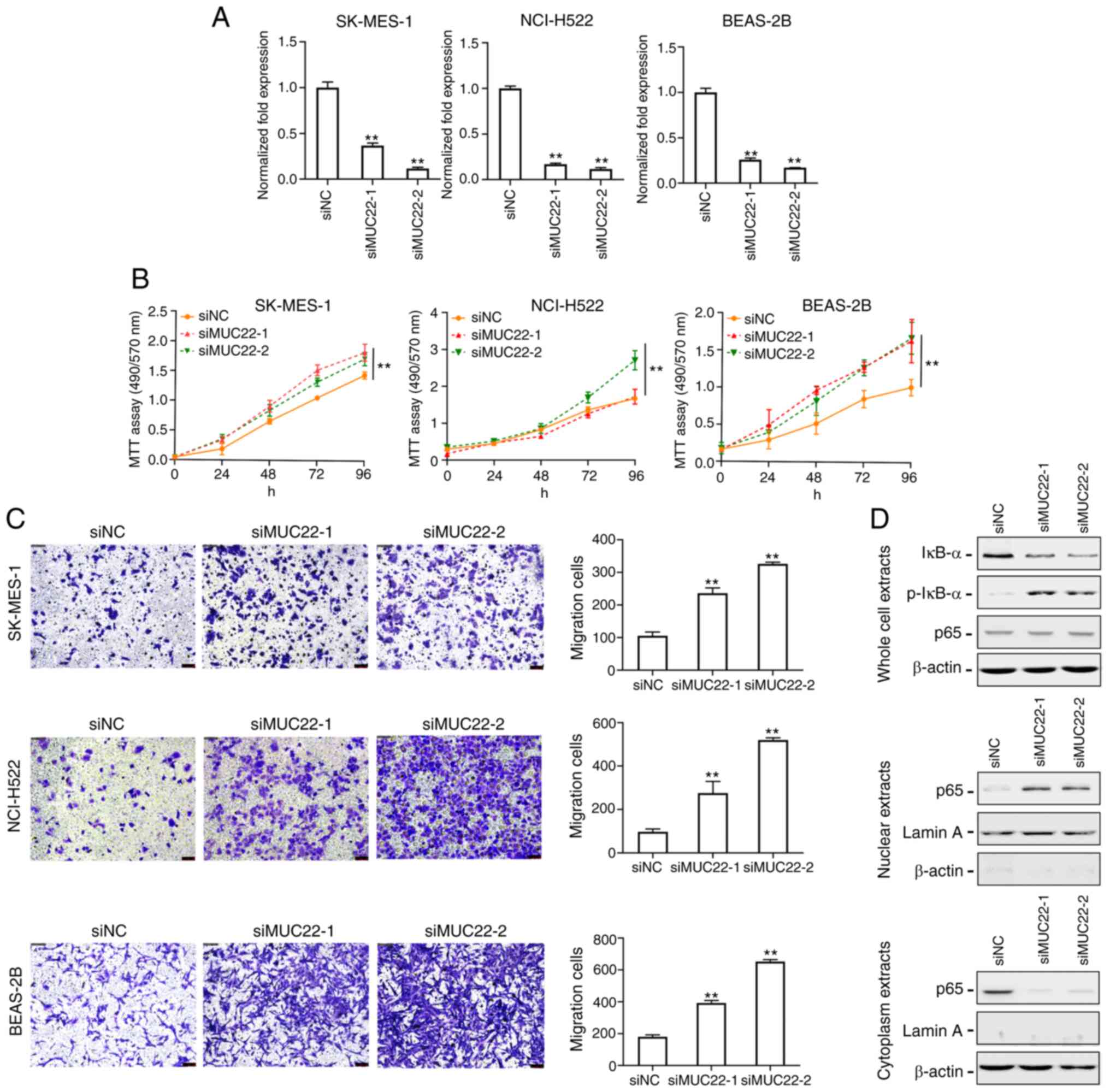
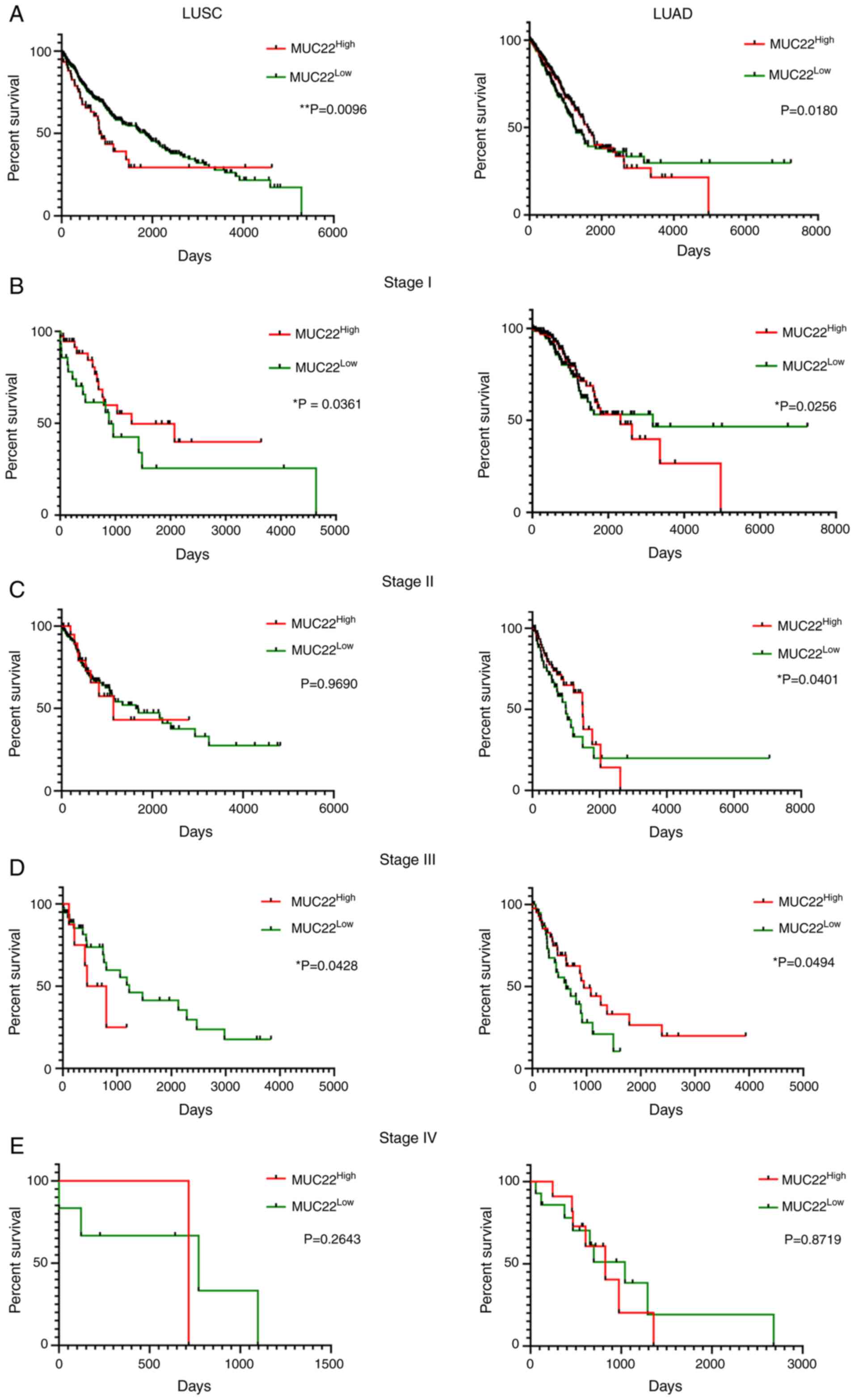
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Skoulidis F and Heymach JV: Co-occurring
genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:495–509. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Z, Fillmore CM, Hammerman PS, Kim CF
and Wong KK: Non-small-cell lung cancers: A heterogeneous set of
diseases. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:535–546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Quintanal-Villalonga Á and Molina-Pinelo
S: Epigenetics of lung cancer: A translational perspective. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 42:739–756. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Travis WD: Lung cancer pathology: Current
concepts. Clin Chest Med. 41:67–85. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bustamante-Marin XM and Ostrowski LE:
Cilia and mucociliary clearance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
9:a0282412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Relli V, Trerotola M, Guerra E and Alberti
S: Abandoning the notion of non-small cell lung cancer. Trends Mol
Med. 25:585–594. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abbosh C, Birkbak NJ, Wilson GA,
Jamal-Hanjani M, Constantin T, Salari R, Le Quesne J, Moore DA,
Veeriah S, Rosenthal R, et al: Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts
early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature. 545:446–451. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rotow J and Bivona TG: Understanding and
targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:637–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Poirier JT,
Mermel CH, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, Katayama R, Costa C, Ross KN,
Moran T, et al: RB loss in resistant EGFR mutant lung
adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer. Nat
Commun. 6:63772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roca E, Pozzari M, Vermi W, Tovazzi V,
Baggi A, Amoroso V, Nonnis D, Intagliata S and Berruti A: Outcome
of EGFR-mutated adenocarcinoma NSCLC patients with changed
phenotype to squamous cell carcinoma after tyrosine kinase
inhibitors: A pooled analysis with an additional case. Lung Cancer.
127:12–18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dhanisha SS, Guruvayoorappan C, Drishya S
and Abeesh P: Mucins: Structural diversity, biosynthesis, its role
in pathogenesis and as possible therapeutic targets. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 122:98–122. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kufe DW: Mucins in cancer: Function,
prognosis and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:874–885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu M, Wang DC, Wang X and Zhang Y:
Correlation between mucin biology and tumor heterogeneity in lung
cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 64:73–78. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lucchetta M, da Piedade I, Mounir M,
Vabistsevits M, Terkelsen T and Papaleo E: Distinct signatures of
lung cancer types: Aberrant mucin O-glycosylation and compromised
immune response. BMC Cancer. 19:8242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hollingsworth MA and Swanson BJ: Mucins in
cancer: Protection and control of the cell surface. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:45–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, McGranahan N,
Birkbak NJ, Watkins TBK, Veeriah S, Shafi S, Johnson DH, Mitter R,
Rosenthal R, et al: Tracking the evolution of non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 376:2109–2121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamada N, Kitamoto S, Yokoyama S, Hamada
T, Goto M, Tsutsumida H, Higashi M and Yonezawa S: Epigenetic
regulation of mucin genes in human cancers. Clin Epigenetics.
2:85–96. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin S, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Yang B, Cui J, Huang
J, Wang JM, Xing R and Lu Y: Epigenetic downregulation of MUC17 by
H. pylori infection facilitates NF-κB-mediated expression of
CEACAM1-3S in human gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 22:941–954.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pan Y, Lin S, Xing R, Zhu M, Lin B, Cui J,
Li W, Gao J, Shen L, Zhao Y, et al: Epigenetic upregulation of
metallothionein 2A by diallyl trisulfide enhances chemosensitivity
of human gastric cancer cells to docetaxel through attenuating
NF-κB activation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 24:839–854. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin B, Zhou X, Lin S, Wang X, Zhang M, Cao
B, Dong Y, Yang S, Wang JM, Guo M and Huang J: Epigenetic silencing
of PRSS3 provides growth and metastasis advantage for human
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Mol Med (Berl). 95:1237–1249. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin S, Wang X, Pan Y, Tian R, Lin B, Jiang
G, Chen K, He Y, Zhang L, Zhai W, et al: Transcription factor
myeloid zinc-finger 1 suppresses human gastric carcinogenesis by
interacting with metallothionein 2A. Clin Cancer Res. 25:1050–1062.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Uhlen M, Zhang C, Lee S, Sjöstedt E,
Fagerberg L, Bidkhori G, Benfeitas R, Arif M, Liu Z, Edfors F, et
al: A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science.
357:eaan25072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ghandi M, Huang FW, Jané-Valbuena J,
Kryukov GV, Lo CC, McDonald ER III, Barretina J, Gelfand ET,
Bielski CM, Li H, et al: Next-generation characterization of the
cancer cell line encyclopedia. Nature. 569:503–508. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Masser DR, Hadad N, Porter H, Stout MB,
Unnikrishnan A, Stanford DR and Freeman WM: Analysis of DNA
modifications in aging research. Geroscience. 40:11–29. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jonckheere N and Van Seuningen I:
Integrative analysis of the cancer genome atlas and cancer cell
lines encyclopedia large-scale genomic databases: MUC4/MUC16/MUC20
signature is associated with poor survival in human carcinomas. J
Transl Med. 16:2592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Atanasova KR and Reznikov LR: Strategies
for measuring airway mucus and mucins. Respir Res. 20:2612019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yonezawa S, Higashi M, Yamada N, Yokoyama
S, Kitamoto S, Kitajima S and Goto M: Mucins in human neoplasms:
Clinical pathology, gene expression and diagnostic application.
Pathol Int. 61:697–716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nath S and Mukherjee P: MUC1: A
multifaceted oncoprotein with a key role in cancer progression.
Trends Mol Med. 20:332–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Quoix E, Lena H, Losonczy G, Forget F,
Chouaid C, Papai Z, Gervais R, Ottensmeier C, Szczesna A,
Kazarnowicz A, et al: TG4010 immunotherapy and first-line
chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (TIME):
Results from the phase 2b part of a randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 17:212–223.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hall PE, Ready N, Johnston A, Bomalaski
JS, Venhaus RR, Sheaff M, Krug L and Szlosarek PW: Phase II study
of arginine deprivation therapy with pegargiminase in patients with
relapsed sensitive or refractory small cell lung cancer. Clin Lung
Cancer. 21:527–533. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Taherali F, Varum F and Basit AW: A
slippery slope: On the origin, role and physiology of mucus. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 124:16–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fini ME, Jeong S, Gong H,
Martinez-Carrasco R, Laver NMV, Hijikata M, Keicho N and Argüeso P:
Membrane-associated mucins of the ocular surface: New genes, new
protein functions and new biological roles in human and mouse. Prog
Retin Eye Res. 75:1007772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hijikata M, Matsushita I, Tanaka G,
Tsuchiya T, Ito H, Tokunaga K, Ohashi J, Homma S, Kobashi Y,
Taguchi Y, et al: Molecular cloning of two novel mucin-like genes
in the disease-susceptibility locus for diffuse panbronchiolitis.
Hum Genet. 129:117–128. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim YK, Shin DH, Kim KB, Shin N, Park WY,
Lee JH, Choi KU, Kim JY, Lee CH, Sol MY and Kim MH: MUC5AC and
MUC5B enhance the characterization of mucinous adenocarcinomas of
the lung and predict poor prognosis. Histopathology. 67:520–528.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee HK, Kwon MJ, Seo J, Kim JW, Hong M,
Park HR, Min SK, Choe JY, Ra YJ, Jang SH, et al: Expression of
mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) in ALK-positive lung cancer:
Comparison with EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Pathol Res Pract.
215:459–465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kai Y, Amatya VJ, Kushitani K, Kambara T,
Suzuki R, Tsutani Y, Miyata Y, Okada M and Takeshima Y: Mucin 21 is
a novel, negative immunohistochemical marker for epithelioid
mesothelioma for its differentiation from lung adenocarcinoma.
Histopathology. 74:545–554. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yoshimoto T, Matsubara D, Soda M, Ueno T,
Amano Y, Kihara A, Sakatani T, Nakano T, Shibano T, Endo S, et al:
Mucin 21 is a key molecule involved in the incohesive growth
pattern in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 110:3006–3011. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lakshmanan I, Rachagani S, Hauke R, Krishn
SR, Paknikar S, Seshacharyulu P, Karmakar S, Nimmakayala RK,
Kaushik G, Johansson SL, et al: MUC5AC interactions with integrin
β4 enhances the migration of lung cancer cells through FAK
signaling. Oncogene. 35:4112–4121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Qu J, Yu H, Li F, Zhang C, Trad A, Brooks
C, Zhang B, Gong T, Guo Z, Li Y, et al: Molecular basis of antibody
binding to mucin glycopeptides in lung cancer. Int J Oncol.
48:587–594. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Itoh Y, Kamata-Sakurai M, Denda-Nagai K,
Nagai S, Tsuiji M, Ishii-Schrade K, Okada K, Goto A, Fukayama M and
Irimura T: Identification and expression of human
epiglycanin/MUC21: A novel transmembrane mucin. Glycobiology.
18:74–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang DC, Wang W, Zhu B and Wang X: Lung
cancer heterogeneity and new strategies for drug therapy. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 58:531–546. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yamada N, Nishida Y, Tsutsumida H, Hamada
T, Goto M, Higashi M, Nomoto M and Yonezawa S: MUC1 expression is
regulated by DNA methylation and histone H3 lysine 9 modification
in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 68:2708–2716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yokoyama S, Higashi M, Kitamoto S, Oeldorf
M, Knippschild U, Kornmann M, Maemura K, Kurahara H, Wiest E,
Hamada T, et al: Aberrant methylation of MUC1 and MUC4 promoters
are potential prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinomas. Oncotarget. 7:42553–42565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Okudaira K, Kakar S, Cun L, Choi E, Wu
Decamillis R, Miura S, Sleisenger MH, Kim YS and Deng G: MUC2 gene
promoter methylation in mucinous and non-mucinous colorectal cancer
tissues. Int J Oncol. 36:765–775. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yokoyama S, Higashi M, Tsutsumida H,
Wakimoto J, Hamada T, Wiest E, Matsuo K, Kitazono I, Goto Y, Guo X,
et al: TET1-mediated DNA hypomethylation regulates the expression
of MUC4 in lung cancer. Genes Cancer. 8:517–527. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kitamoto S, Yamada N, Yokoyama S, Houjou
I, Higashi M, Goto M, Batra SK and Yonezawa S: DNA methylation and
histone H3-K9 modifications contribute to MUC17 expression.
Glycobiology. 21:247–256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Vincent A, Perrais M, Desseyn JL, Aubert
JP, Pigny P and Van Seuningen I: Epigenetic regulation (DNA
methylation, histone modifications) of the 11p15 mucin genes (MUC2,
MUC5AC, MUC5B, MUC6) in epithelial cancer cells. Oncogene.
26:6566–6576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xu F, Lin H, He P, He L, Chen J, Lin L and
Chen Y: A TP53-associated gene signature for prediction of
prognosis and therapeutic responses in lung squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncoimmunology. 9:17319432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yamada N, Hamada T, Goto M, Tsutsumida H,
Higashi M, Nomoto M and Yonezawa S: MUC2 expression is regulated by
histone H3 modification and DNA methylation in pancreatic cancer.
Int J Cancer. 119:1850–1857. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lakshminarasimhan R and Liang G: The role
of DNA methylation in cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 945:151–172. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|