|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. Feb 4–2021.(Epub ahead
of print). doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM
and Wallace MB: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 394:1467–1480. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
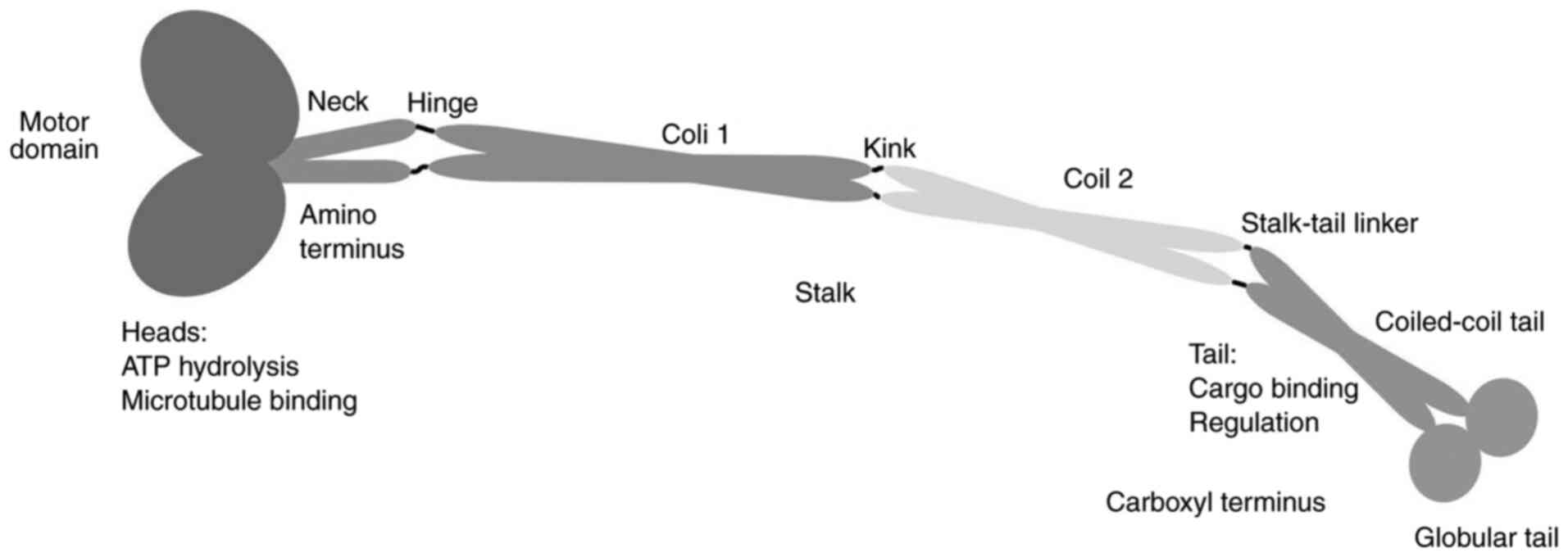
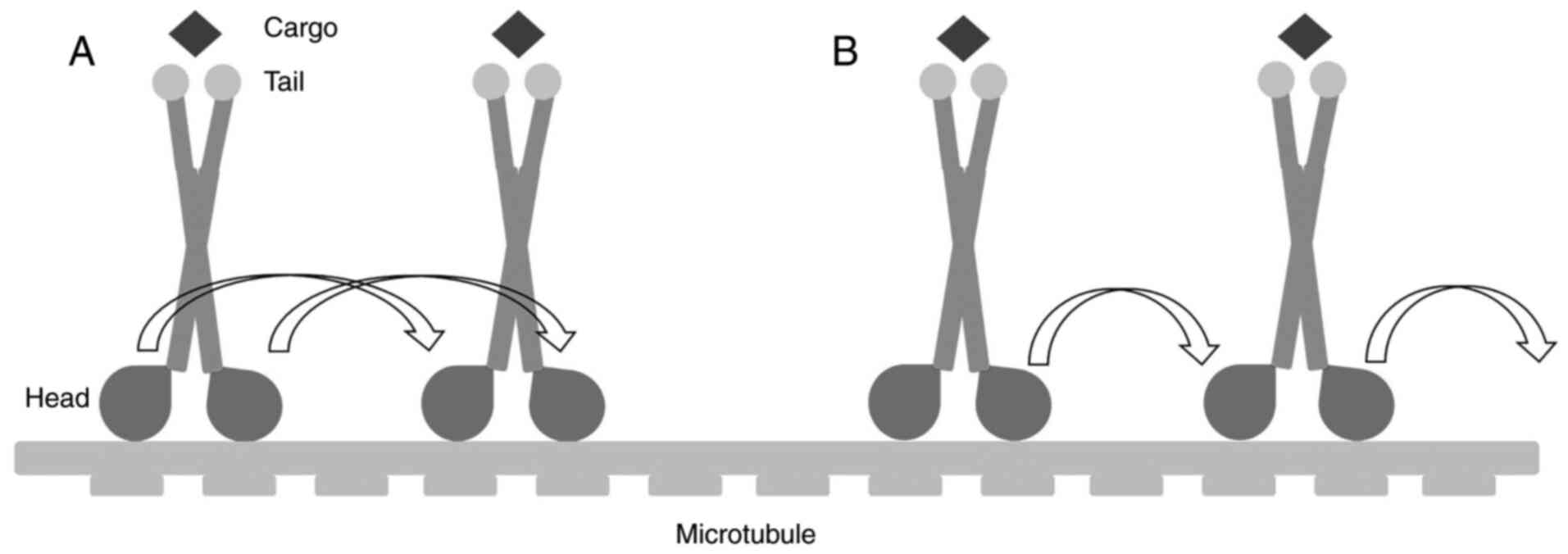
Vale RD and Milligan RA: The way things
move: Looking under the hood of molecular motor proteins. Science.
288:88–95. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nonaka S, Tanaka Y, Okada Y, Takeda S,
Harada A, Kanai Y, Kido M and Hirokawa N: Randomization of
left-right asymmetry due to loss of nodal cilia generating leftward
flow of extraembryonic fluid in mice lacking KIF3B motor protein.
Cell. 95:829–837. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goldstein LS: Kinesin molecular motors:
Transport pathways, receptors, and human disease. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 98:6999–7003. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Morel M, Héraud C, Nicaise C, Suain V and
Brion JP: Levels of kinesin light chain and dynein intermediate
chain are reduced in the frontal cortex in Alzheimer's disease:
Implications for axoplasmic transport. Acta neuropathol. 123:71–84.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan X, Wang X, Zhu H, Wang W, Zhang S and
Wang Z: KIF2A overexpression and its association with
clinicopathologic characteristics and unfavorable prognosis in
colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:8895–8902. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsumoto Y, Saito M, Saito K, Kanke Y,
Watanabe Y, Onozawa H, Hayase S, Sakamoto W, Ishigame T, Momma T,
et al: Enhanced expression of KIF4A in colorectal cancer is
associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncol Lett. 15:2188–2194.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
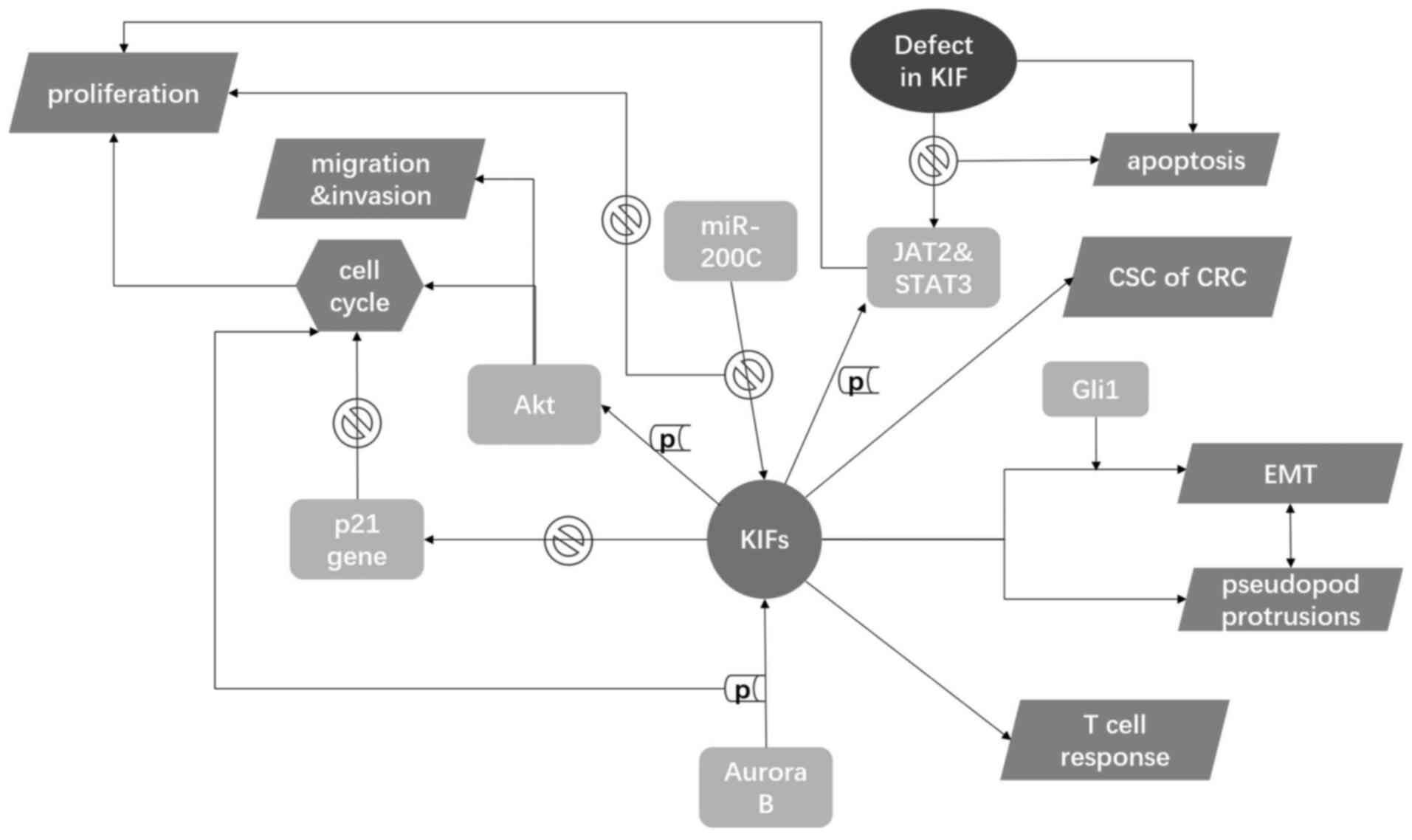
Hou PF, Jiang T, Chen F, Shi PC, Li HQ,
Bai J and Song J: KIF4A facilitates cell proliferation via
induction of p21-mediated cell cycle progression and promotes
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 9:4772018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagahara M, Nishida N, Iwatsuki M,
Ishimaru S, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Nakagawa T, Sato T, Sugihara K,
Hoon DS and Mori M: Kinesin 18A expression: Clinical relevance to
colorectal cancer progression. Int J Cancer. 129:2543–2552. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ishikawa K, Kamohara Y, Tanaka F,
Haraguchi N, Mimori K, Inoue H and Mori M: Mitotic
centromere-associated kinesin is a novel marker for prognosis and
lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer.
98:1824–1829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin WF, Lin XL, Fu SW, Yang L, Tang CT,
Gao YJ, Chen HY and Ge ZZ: Pseudopod-associated protein KIF20B
promotes Gli1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition modulated
by pseudopodial actin dynamic in human colorectal cancer. Mol
Carcinog. 57:911–925. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Cui F, Wang X, Xue Y, Chen J, Yu
Y, Lu H, Zhang M, Tang H and Peng Z: Elevated kinesin family member
26B is a prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target
for colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li B, Zhu FC, Yu SX, Liu SJ and Li BY:
Suppression of KIF22 inhibits cell proliferation and xenograft
tumor growth in colon cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:50–57.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiong M, Zhuang K, Luo Y, Lai Q, Luo X,
Fang Y, Zhang Y, Li A and Liu S: KIF20A promotes cellular malignant
behavior and enhances resistance to chemotherapy in colorectal
cancer through regulation of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Aging
(Albany NY). 11:11905–11921. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Imai T, Oue N, Sentani K, Sakamoto N,
Uraoka N, Egi H, Hinoi T, Ohdan H, Yoshida K and Yasui W: KIF11 is
required for spheroid formation by oesophageal and colorectal
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 37:47–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
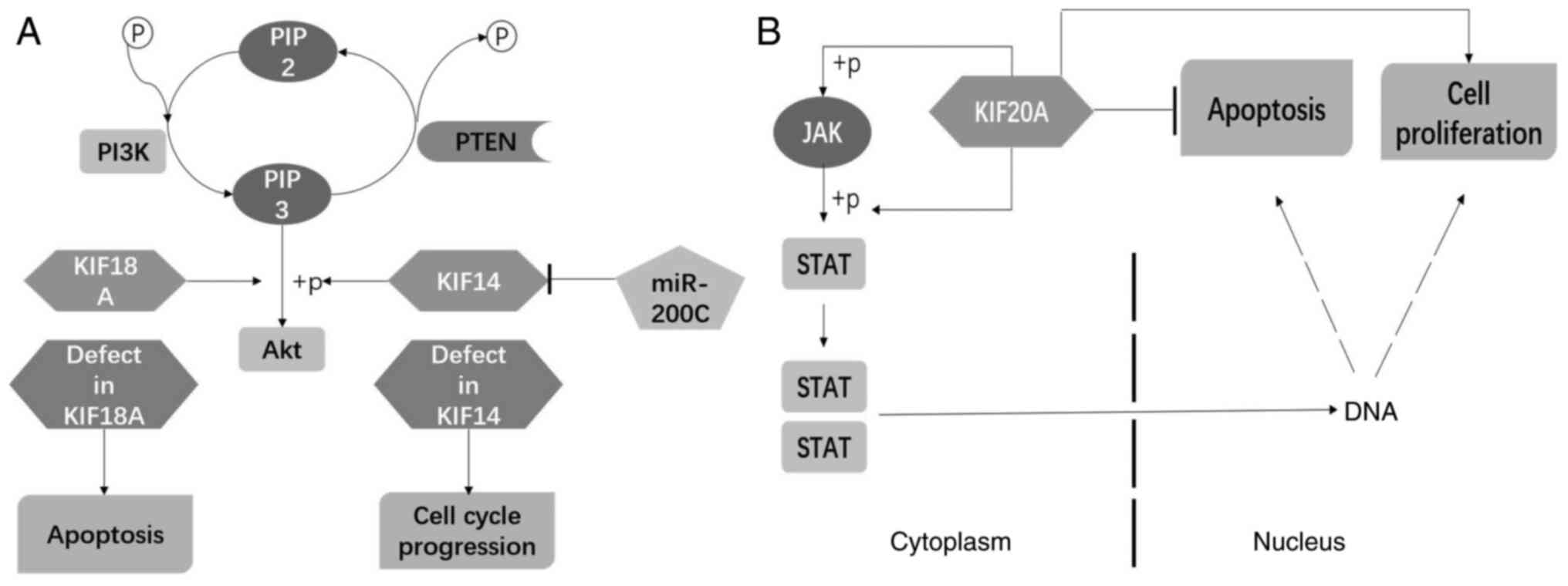
Wang ZZ, Yang J, Jiang BH, Di JB, Gao P,
Peng L and Su XQ: KIF14 promotes cell proliferation via activation
of Akt and is directly targeted by miR-200c in colorectal cancer.
Int J Oncol. 53:1939–1952. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ritter A, Sanhaji M, Friemel A, Roth S,
Rolle U, Louwen F and Yuan J: Functional analysis of
phosphorylation of the mitotic centromere-associated kinesin by
Aurora B kinase in human tumor cells. Cell cycle. 14:3755–3767.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lawrence CJ, Dawe RK, Christie KR,
Cleveland DW, Dawson SC, Endow SA, Goldstein LS, Goodson HV,
Hirokawa N, Howard J, et al: A standardized kinesin nomenclature. J
Cell Biol. 167:19–22. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hirokawa N, Noda Y, Tanaka Y and Niwa S:
Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:682–696. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Woehlke G and Schliwa M: Walking on two
heads: The many talents of kinesin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 1:50–58.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sack S, Kull FJ and Mandelkow E: Motor
proteins of the kinesin family. Structures, variations, and
nucleotide binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 262:1–11. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hua W, Chung J and Gelles J:
Distinguishing inchworm and hand-over-hand processive kinesin
movement by neck rotation measurements. Science. 295:844–848. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vale RD: The molecular motor toolbox for
intracellular transport. Cell. 112:467–480. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ruane PT, Gumy LF, Bola B, Anderson B,
Wozniak MJ, Hoogenraad CC and Allan VJ: Tumour suppressor
adenomatous polyposis Coli (APC) localisation is regulated by both
Kinesin-1 and Kinesin-2. Sci Rep. 6:274562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin R, Duan Z, Sun H, Fung ML, Chen H,
Wang J, Lau CF, Yang D, Liu Y, Ni Y, et al: Kinesin-1 regulates
extrasynaptic targeting of NMDARs and neuronal vulnerability toward
excitotoxicity. iScience. 13:82–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hirokawa N, Niwa S and Tanaka Y: Molecular
motors in neurons: Transport mechanisms and roles in brain
function, development, and disease. Neuron. 68:610–638. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cui J, Wang Z, Cheng Q, Lin R, Zhang XM,
Leung PS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Yao KM and Huang JD: Targeted
inactivation of kinesin-1 in pancreatic β-cells in vivo leads to
insulin secretory deficiency. Diabetes. 60:320–330. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cui J, Pang J, Lin YJ, Gong H, Wang ZH, Li
YX, Li J, Wang Z, Jiang P, Dai DP, et al: Adipose-specific deletion
of Kif5b exacerbates obesity and insulin resistance in a mouse
model of diet-induced obesity. FASEB J. 31:2533–2547. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tanaka Y, Kanai Y, Okada Y, Nonaka S,
Takeda S, Harada A and Hirokawa N: Targeted disruption of mouse
conventional kinesin heavy chain, kif5B, results in abnormal
perinuclear clustering of mitochondria. Cell. 93:1147–1158. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tigchelaar W, de Jong AM, Bloks VW, van
Gilst WH, de Boer RA and Silljé HH: Hypertrophy induced KIF5B
controls mitochondrial localization and function in neonatal rat
cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 97:70–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu C, Zhao J, Bibikova M, Leverson JD,
Bossy-Wetzel E, Fan JB, Abraham RT and Jiang W: Functional analysis
of human microtubule-based motor proteins, the kinesins and
dyneins, in mitosis/cytokinesis using RNA interference. Mol Biol
Cell. 16:3187–3199. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lukong KE and Richard S: Breast tumor
kinase BRK requires kinesin-2 subunit KAP3A in modulation of cell
migration. Cell Signal. 20:432–442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Corson TW, Zhu CQ, Lau SK, Shepherd FA,
Tsao MS and Gallie BL: KIF14 messenger RNA expression is
independently prognostic for outcome in lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:3229–3234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miki H, Okada Y and Hirokawa N: Analysis
of the kinesin superfamily: Insights into structure and function.
Trends Cell Biol. 15:467–476. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Siddiqui N and Straube A: Intracellular
cargo transport by Kinesin-3 motors. Biochemistry (Mosc).
82:803–815. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Corson TW, Huang A, Tsao MS and Gallie BL:
KIF14 is a candidate oncogene in the 1q minimal region of genomic
gain in multiple cancers. Oncogene. 24:4741–4753. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mazumdar M, Sundareshan S and Misteli T:
Human chromokinesin KIF4A functions in chromosome condensation and
segregation. J Cell Biol. 166:613–620. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y and Yousefi B:
Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and
transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst).
42:63–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Waitzman JS and Rice SE: Mechanism and
regulation of kinesin-5, an essential motor for the mitotic
spindle. Biol Cell. 106:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang M, Zhuang H, Xia R, Gan L, Wu Y, Ma
J, Sun Y and Zhuang Z: KIF11 is required for proliferation and
self-renewal of docetaxel resistant triple negative breast cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:92106–92118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Takaishi S, Okumura T and Wang TC: Gastric
cancer stem cells. J Clin Oncol. 26:2876–2882. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Imai T, Oue N, Nishioka M, Mukai S, Oshima
T, Sakamoto N, Sentani K, Matsusaki K, Yoshida K and Yasui W:
Overexpression of KIF11 in gastric cancer with intestinal mucin
phenotype. Pathobiology. 84:16–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cesario JM, Jang JK, Redding B, Shah N,
Rahman T and McKim KS: Kinesin 6 family member Subito participates
in mitotic spindle assembly and interacts with mitotic regulators.
J Cell Sci. 119:4770–4780. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Imai K, Hirata S, Irie A, Senju S, Ikuta
Y, Yokomine K, Harao M, Inoue M, Tomita Y, Tsunoda T, et al:
Identification of HLA-A2-restricted CTL epitopes of a novel
tumour-associated antigen, KIF20A, overexpressed in pancreatic
cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:300–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang C, Wang Y, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Ji B,
Wang S and Sun Y, Zhu C, Zhang D and Sun Y: Gli1 promotes
colorectal cancer metastasis in a Foxm1-dependent manner by
activating EMT and PI3K-AKT signaling. Oncotarget. 7:86134–86147.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pinder C, Matsuo Y, Maurer SP and Toda T:
Kinesin-8 and Dis1/TOG collaborate to limit spindle elongation from
prophase to anaphase A for proper chromosome segregation in fission
yeast. J Cell Sci. 132:jcs2323062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Edzuka T and Goshima G: Drosophila
kinesin-8 stabilizes the kinetochore-microtubule interaction. J
Cell Biol. 218:474–488. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gardner MK, Odde DJ and Bloom K: Kinesin-8
molecular motors: Putting the brakes on chromosome oscillations.
Trends Cell Biol. 18:307–310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mayr MI, Hümmer S, Bormann J, Grüner T,
Adio S, Woehlke G and Mayer TU: The human kinesin Kif18A is a
motile microtubule depolymerase essential for chromosome
congression. Curr Biol. 17:488–498. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhu H, Xu W, Zhang H, Liu J, Xu H, Lu S,
Dang S, Kuang Y, Jin X and Wang Z: Targeted deletion of Kif18a
protects from colitis-associated colorectal (CAC) tumors in mice
through impairing Akt phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
438:97–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Levesque AA and Compton DA: The
chromokinesin Kid is necessary for chromosome arm orientation and
oscillation, but not congression, on mitotic spindles. J Cell Biol.
154:1135–1146. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tahara K, Takagi M, Ohsugi M, Sone T,
Nishiumi F, Maeshima K, Horiuchi Y, Tokai-Nishizumi N, Imamoto F,
Yamamoto T, et al: Importin-beta and the small guanosine
triphosphatase Ran mediate chromosome loading of the human
chromokinesin Kid. J Cell Biol. 180:493–506. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tokai N, Fujimoto-Nishiyama A, Toyoshima
Y, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Inoue J and Yamamota T: Kid, a novel
kinesin-like DNA binding protein, is localized to chromosomes and
the mitotic spindle. EMBO J. 15:457–467. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yu Y, Wang XY, Sun L, Wang YL, Wan YF, Li
XQ and Feng YM: Inhibition of KIF22 suppresses cancer cell
proliferation by delaying mitotic exit through upregulating CDC25C
expression. Carcinogenesis. 35:1416–1425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhou R, Niwa S, Homma N, Takei Y and
Hirokawa N: KIF26A is an unconventional kinesin and regulates
GDNF-Ret signaling in enteric neuronal development. Cell.
139:802–813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Orellana C, Roselló M, Monfort S, Oltra S,
Quiroga R, Ferrer I and Martínez F: Corpus callosum abnormalities
and the controversy about the candidate genes located in 1q44.
Cytogenet Genome Res. 127:5–8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Miyamoto T, Hosoba K, Ochiai H, Royba E,
Izumi H, Sakuma T, Yamamoto T, Dynlacht BD and Matsuura S: The
Microtubule-Depolymerizing activity of a mitotic kinesin protein
KIF2A drives primary cilia disassembly coupled with cell
proliferation. Cell Rep. 10:664–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Vasudevan KK, Jiang YY, Lechtreck KF,
Kushida Y, Alford LM, Sale WS, Hennessey T and Gaertig J:
Kinesin-13 regulates the quantity and quality of tubulin inside
cilia. Mol Biol Cell. 26:478–494. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wordeman L and Mitchison TJ:
Identification and partial characterization of mitotic
centromere-associated kinesin, a kinesin-related protein that
associates with centromeres during mitosis. J Cell Biol.
128:95–104. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Helenius J, Brouhard G, Kalaidzidis Y,
Diez S and Howard J: The depolymerizing kinesin MCAK uses lattice
diffusion to rapidly target microtubule ends. Nature. 441:115–119.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kumar A, Rajendran V, Sethumadhavan R and
Purohit R: Evidence of colorectal cancer-associated mutation in
MCAK: A computational report. Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:837–851.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Aoki S, Ohta K, Yamazaki T, Sugawara F and
Sakaguchi K: Mammalian mitotic centromere-associated kinesin
(MCAK): A new molecular target of sulfoquinovosylacylglycerols
novel antitumor and immunosuppressive agents. FEBS J.
272:2132–2140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Scanlan MJ, Welt S, Gordon CM, Chen YT,
Gure AO, Stockert E, Jungbluth AA, Ritter G, Jäger D, Jäger E, et
al: Cancer-related serological recognition of human colon cancer:
Identification of potential diagnostic and immunotherapeutic
targets. Cancer Res. 62:4041–4047. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gnjatic S, Cao Y, Reichelt U, Yekebas EF,
Nölker C, Marx AH, Erbersdobler A, Nishikawa H, Hildebrandt Y,
Bartels K, et al: NY-CO-58/KIF2C is overexpressed in a variety of
solid tumors and induces frequent T cell responses in patients with
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:381–393. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Carpenter RL and Lo HW: STAT3 target genes
relevant to human cancers. Cancers (Basel). 6:897–925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kramer HB, Lai CF, Patel H, Periyasamy M,
Lin ML, Feller SM, Fuller-Pace FV, Meek DW, Ali S and Buluwela L:
LRH-1 drives colon cancer cell growth by repressing the expression
of the CDKN1A gene in a p53-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:582–594. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lim S and Kaldis P: Cdks, cyclins and
CKIs: Roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development.
140:3079–3093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Braun A, Dang K, Buslig F, Baird MA,
Davidson MW, Waterman CM and Myers KA: Rac1 and Aurora A regulate
MCAK to polarize microtubule growth in migrating endothelial cells.
J Cell Biol. 206:97–112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Shimo A, Tanikawa C, Nishidate T, Lin ML,
Matsuda K, Park JH, Ueki T, Ohta T, Hirata K, Fukuda M, et al:
Involvement of kinesin family member 2C/mitotic
centromere-associated kinesin overexpression in mammary
carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 99:62–70. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yamada Y, Takahari D, Matsumoto H, Baba H,
Nakamura M, Yoshida K, Yoshida M, Iwamoto S, Shimada K, Komatsu Y,
et al: Leucovorin, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin plus bevacizumab
versus S-1 and oxaliplatin plus bevacizumab in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer (SOFT): An open-label,
non-inferiority, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
14:1278–1286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J,
Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, Humblet Y, Bodoky G, Cunningham
D, Jassem J, et al: Randomized, phase III trial of panitumumab with
infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4)
versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with
previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: The PRIME study.
J Clin Oncol. 28:4697–4705. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lucanus AJ and Yip GW: Kinesin
superfamily: Roles in breast cancer, patient prognosis and
therapeutics. Oncogene. 37:833–838. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Rath O and Kozielski F: Kinesins and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:527–539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang W, Zhai L, Lu W, Boohaker RJ,
Padmalayam I and Li Y: Discovery of novel allosteric Eg5 Inhibitors
through structure-based virtual screening. Chem Biol Drug Des.
88:178–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nakai R, Iida S, Takahashi T, Tsujita T,
Okamoto S, Takada C, Akasaka K, Ichikawa S, Ishida H, Kusaka H, et
al: K858, a novel inhibitor of mitotic kinesin Eg5 and antitumor
agent, induces cell death in cancer cells. Cancer Res.
69:3901–3909. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zong H, Carnes SK, Moe C, Walczak CE and
Ems-McClung SC: The far C-terminus of MCAK regulates its
conformation and spindle pole focusing. Mol Biol Cell.
27:1451–1464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|