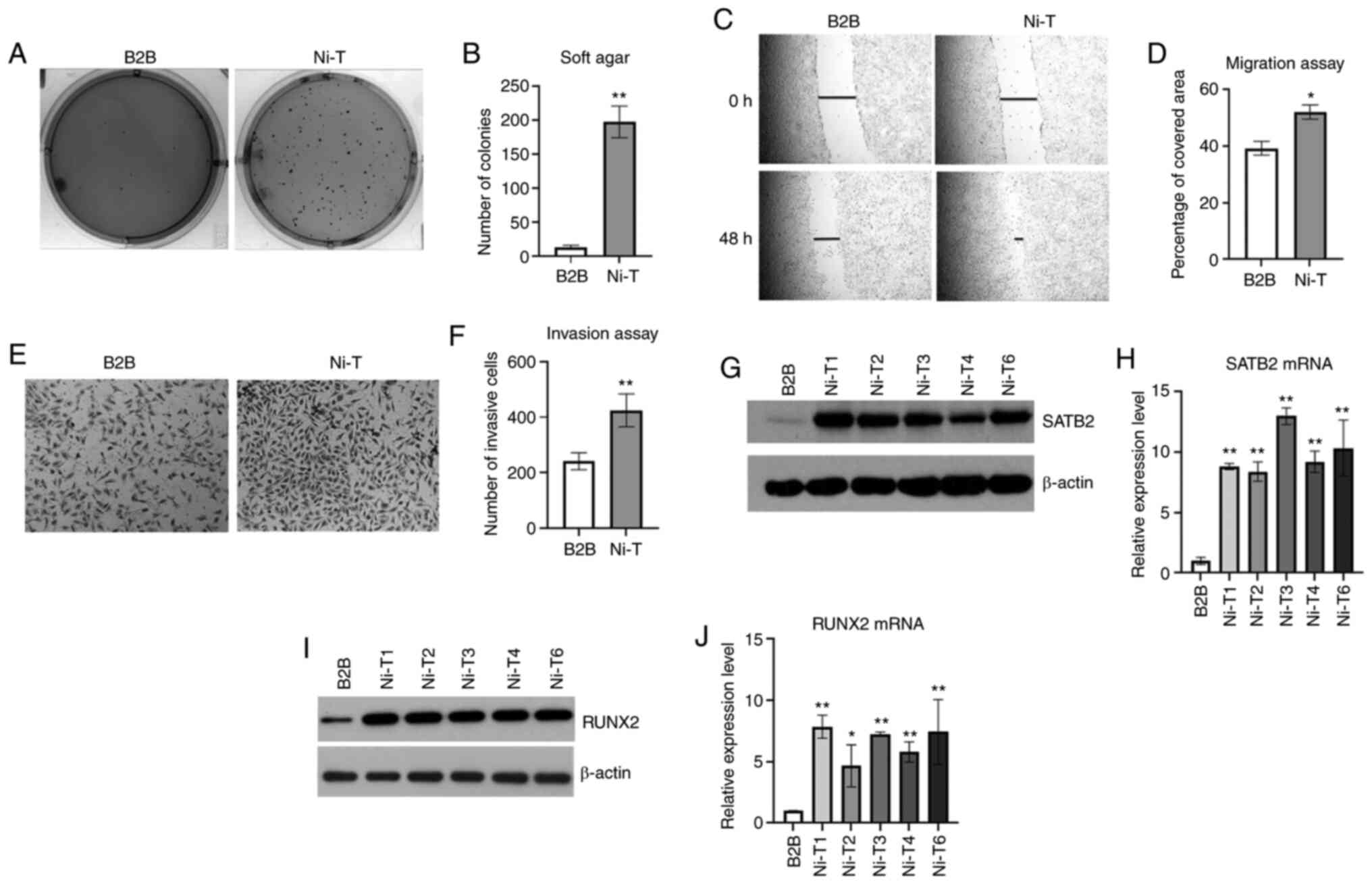
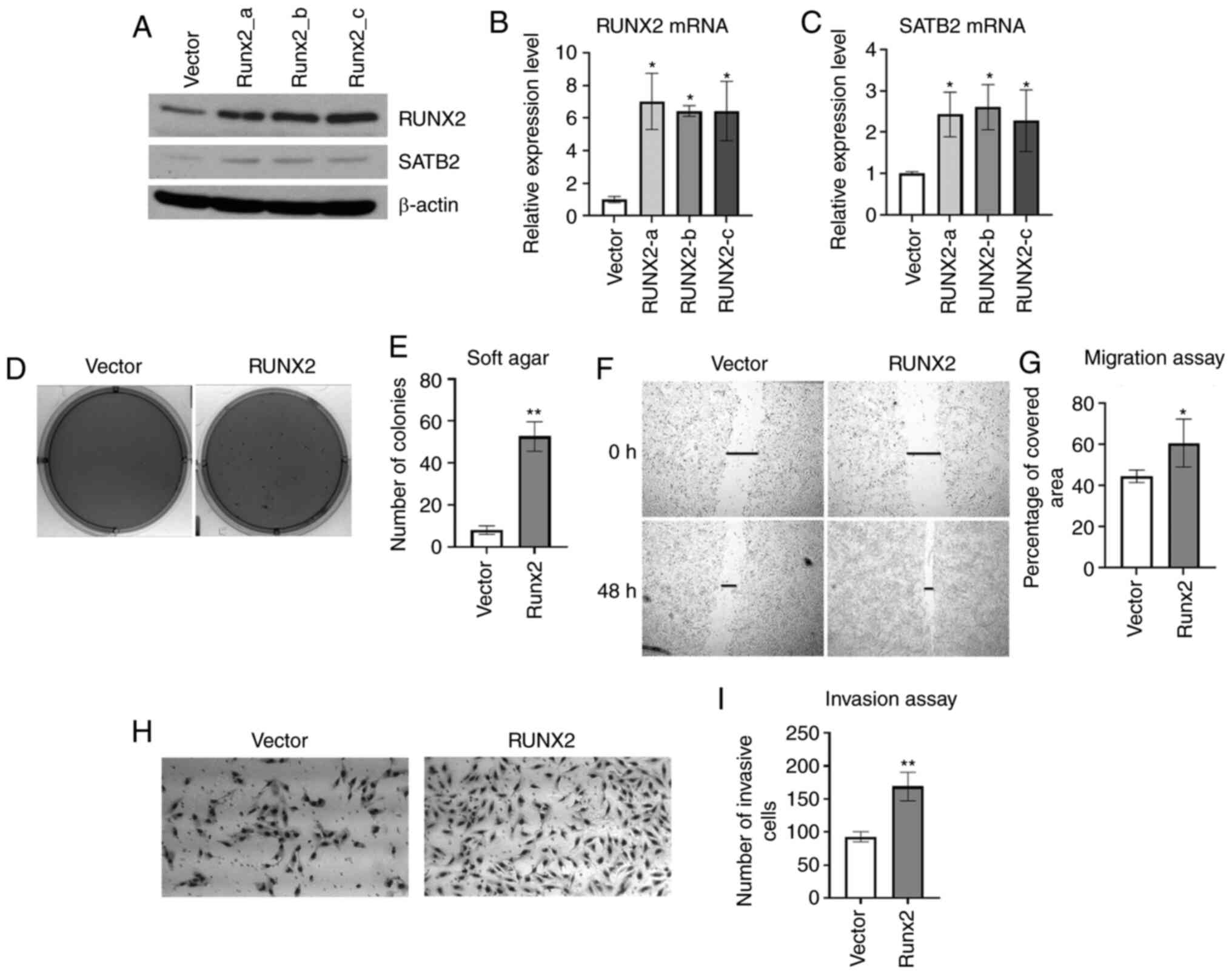
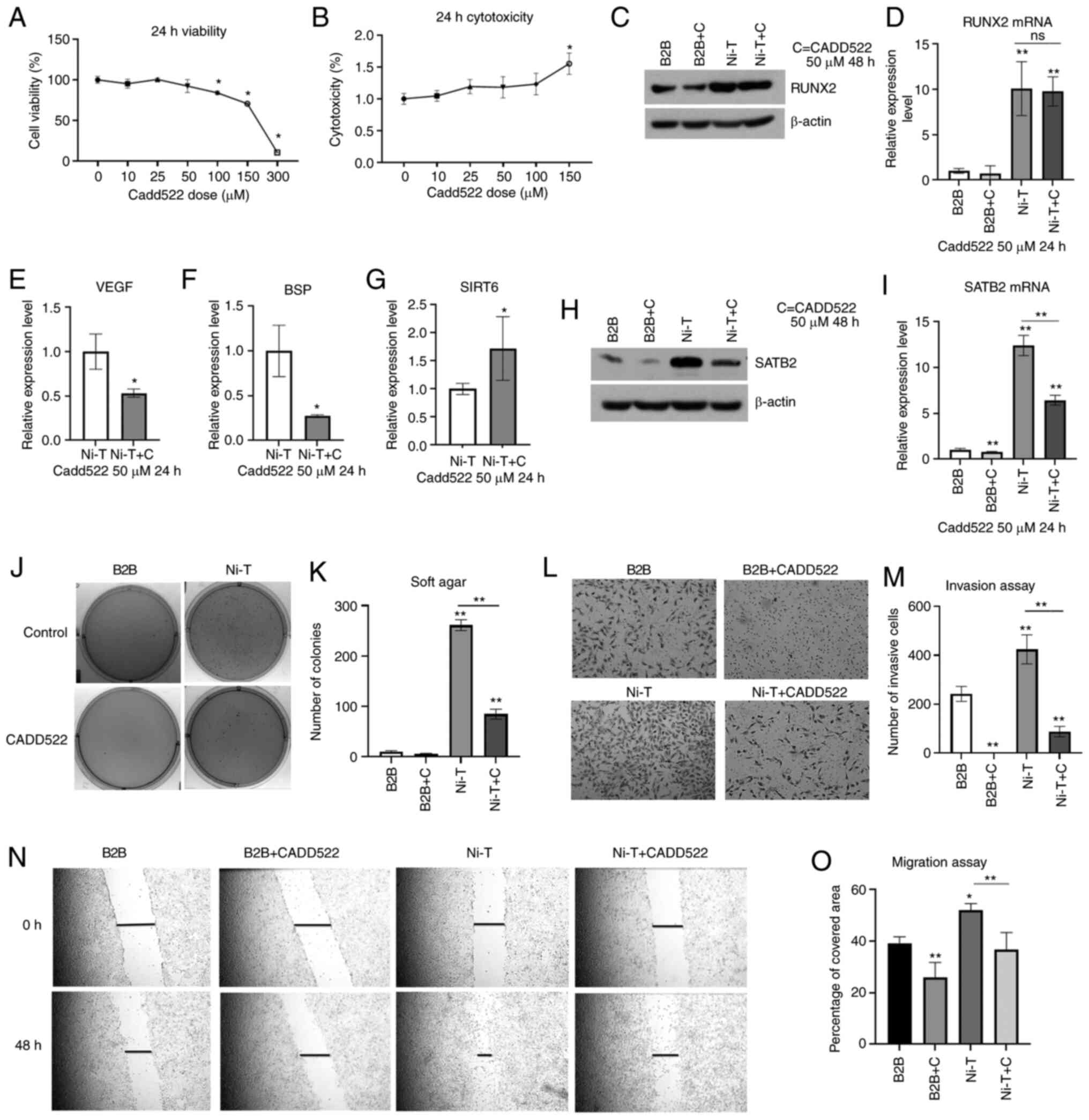
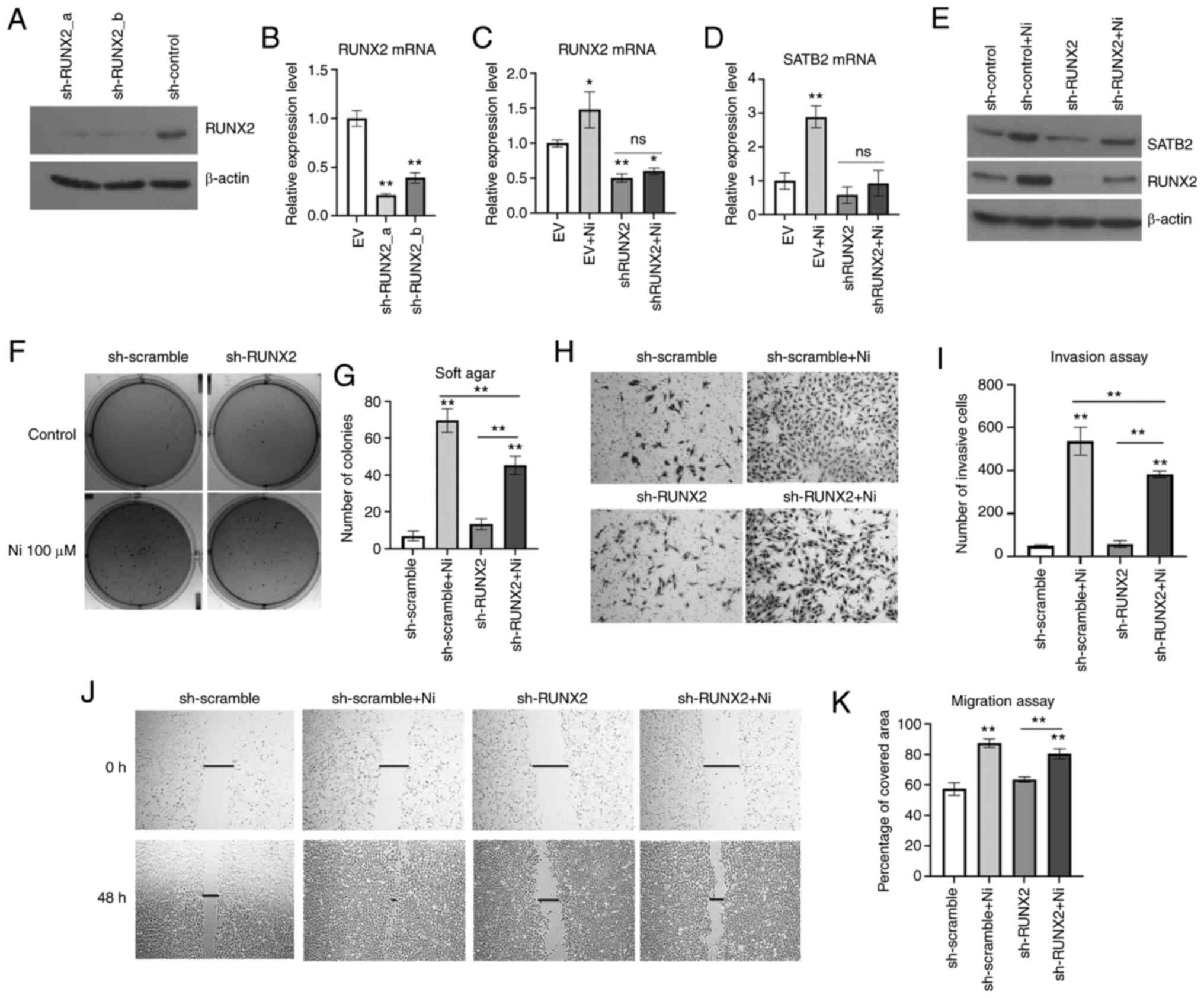
|
1
|
Huvinen M and Pukkala E: Cancer incidence
among Finnish ferrochromium and stainless steel production workers
in 1967–2011: A cohort study. BMJ Open. 3:e0038192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grimsrud TK and Andersen A: Evidence of
carcinogenicity in humans of water-soluble nickel salts. J Occup
Med Toxicol. 5:72010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Andersen A, Berge SR, Engeland A and
Norseth T: Exposure to nickel compounds and smoking in relation to
incidence of lung and nasal cancer among nickel refinery workers.
Occup Environ Med. 53:708–713. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seilkop SK and Oller AR: Respiratory
cancer risks associated with low-level nickel exposure: An
integrated assessment based on animal, epidemiological, and
mechanistic data. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 37:173–190. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anttila A, Pukkala E, Aitio A, Rantanen T
and Karjalainen S: Update of cancer incidence among workers at a
copper/nickel smelter and nickel refinery. Int Arch Occup Environ
Health. 71:245–250. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moulin JJ, Clavel T, Roy D, Dananche B,
Marquis N, Fevotte J and Fontana JM: Risk of lung cancer in workers
producing stainless steel and metallic alloys. Int Arch Occup
Environ Health. 73:171–180. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clancy HA, Sun H, Passantino L, Kluz T,
Munoz A, Zavadil J and Costa M: Gene expression changes in human
lung cells exposed to arsenic, chromium, nickel or vanadium
indicate the first steps in cancer. Metallomics. 4:784–793. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Savarese F, Davila A, Nechanitzky R, De La
Rosa-Velazquez I, Pereira CF, Engelke R, Takahashi K, Jenuwein T,
Kohwi-Shigematsu T, Fisher AG and Grosschedl R: Satb1 and Satb2
regulate embryonic stem cell differentiation and Nanog expression.
Genes Dev. 23:2625–2638. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Magnusson K, de Wit M, Brennan DJ, Johnson
LB, McGee SF, Lundberg E, Naicker K, Klinger R, Kampf C, Asplund A,
et al: SATB2 in combination with cytokeratin 20 identifies over 95%
of all colorectal carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 35:937–948. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang G, Cui Y, Yu X, Wu Z, Ding G and Cao
L: miR-211 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating
SATB2. Oncotarget. 6:9457–9466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cartularo L, Kluz T, Cohen L, Shen SS and
Costa M: Molecular mechanisms of malignant transformation by low
dose cadmium in normal human bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS One.
11:e01550022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fukuhara M, Agnarsdottir M, Edqvist PH,
Coter A and Ponten F: SATB2 is expressed in Merkel cell carcinoma.
Arch Dermatol Res. 308:449–454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu W, Ma Y, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
SATB2/β-catenin/TCF-LEF pathway induces cellular transformation by
generating cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep.
7:109392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bae T, Rho K, Choi JW, Horimoto K, Kim W
and Kim S: Identification of upstream regulators for prognostic
expression signature genes in colorectal cancer. BMC Syst Biol.
7:862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu W, Ma Y, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Role of SATB2 in human pancreatic cancer: Implications in
transformation and a promising biomarker. Oncotarget.
7:57783–57797. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu F, Jordan A, Kluz T, Shen S, Sun H,
Cartularo LA and Costa M: SATB2 expression increased
anchorage-independent growth and cell migration in human bronchial
epithelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 293:30–36. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao X, Qu Z, Tickner J, Xu J, Dai K and
Zhang X: The role of SATB2 in skeletogenesis and human disease.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 25:35–44. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Komori T: Regulation of skeletal
development by the Runx family of transcription factors. J Cell
Biochem. 95:445–453. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, Zhang Z,
Deng JM, Behringer RR and de Crombrugghe B: The novel zinc
finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for
osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 108:17–29.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang W, Li Y, Osimiri L and Zhang C:
Osteoblast-specific transcription factor Osterix (Osx) is an
upstream regulator of Satb2 during bone formation. J Biol Chem.
286:32995–33002. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu L, Xu Y, Qu H, Yu Y, Li W, Zhao Y and
Qiu G: Decrease of miR-31 induced by TNF-α inhibitor activates
SATB2/RUNX2 pathway and promotes osteogenic differentiation in
ethanol-induced osteonecrosis. J Cell Physiol. 234:4314–4326. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deng Y, Wu S, Zhou H, Bi X, Wang Y, Hu Y,
Gu P and Fan X: Effects of a miR-31, Runx2, and Satb2 regulatory
loop on the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cells Dev. 22:2278–2286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hassan MQ, Gordon JA, Beloti MM, Croce CM,
van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS and Lian JB: A network connecting
Runx2, SATB2, and the miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster regulates the
osteoblast differentiation program. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:19879–19884. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dobreva G, Chahrour M, Dautzenberg M,
Chirivella L, Kanzler B, Farinas I, Karsenty G and Grosschedl R:
SATB2 is a multifunctional determinant of craniofacial patterning
and osteoblast differentiation. Cell. 125:971–986. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dowrey T, Schwager EE, Duong J, Merkuri F,
Zarate YA and Fish JL: Satb2 regulates proliferation and nuclear
integrity of pre-osteoblasts. Bone. 127:488–498. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Tu Q, Grosschedl R, Kim MS,
Griffin T, Drissi H, Yang P and Chen J: Roles of SATB2 in
osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration. Tissue Eng Part
A. 17:1767–1776. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kayed H, Jiang X, Keleg S, Jesnowski R,
Giese T, Berger MR, Esposito I, Lohr M, Friess H and Kleeff J:
Regulation and functional role of the Runt-related transcription
factor-2 in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 97:1106–1115. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pratap J, Lian JB, Javed A, Barnes GL, van
Wijnen AJ, Stein JL and Stein GS: Regulatory roles of Runx2 in
metastatic tumor and cancer cell interactions with bone. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 25:589–600. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Niu DF, Kondo T, Nakazawa T, Oishi N,
Kawasaki T, Mochizuki K, Yamane T and Katoh R: Transcription factor
Runx2 is a regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
invasion in thyroid carcinomas. Lab Invest. 92:1181–1190. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thomas DM, Johnson SA, Sims NA, Trivett
MK, Slavin JL, Rubin BP, Waring P, McArthur GA, Walkley CR,
Holloway AJ, et al: Terminal osteoblast differentiation, mediated
by runx2 and p27KIP1, is disrupted in osteosarcoma. J Cell Biol.
167:925–934. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Akech J, Wixted JJ, Bedard K, van der Deen
M, Hussain S, Guise TA, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Languino LR,
Altieri DC, et al: Runx2 association with progression of prostate
cancer in patients: Mechanisms mediating bone osteolysis and
osteoblastic metastatic lesions. Oncogene. 29:811–821. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun X, Wei L, Chen Q and Terek RM: HDAC4
represses vascular endothelial growth factor expression in
chondrosarcoma by modulating RUNX2 activity. J Biol Chem.
284:21881–21890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Papachristou DJ, Papachristou GI,
Papaefthimiou OA, Agnantis NJ, Basdra EK and Papavassiliou AG: The
MAPK-AP-1/-Runx2 signalling axes are implicated in chondrosarcoma
pathobiology either independently or via up-regulation of VEGF.
Histopathology. 47:565–574. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Inman CK and Shore P: The osteoblast
transcription factor Runx2 is expressed in mammary epithelial cells
and mediates osteopontin expression. J Biol Chem. 278:48684–48689.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Baniwal SK, Khalid O, Gabet Y, Shah RR,
Purcell DJ, Mav D, Kohn-Gabet AE, Shi Y, Coetzee GA and Frenkel B:
Runx2 transcriptome of prostate cancer cells: Insights into
invasiveness and bone metastasis. Mol Cancer. 9:2582010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuen HF, Kwok WK, Chan KK, Chua CW, Chan
YP, Chu YY, Wong YC, Wang X and Chan KW: TWIST modulates prostate
cancer cell-mediated bone cell activity and is upregulated by
osteogenic induction. Carcinogenesis. 29:1509–1518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aprelikova O, Yu X, Palla J, Wei BR, John
S, Yi M, Stephens R, Simpson RM, Risinger JI, Jazaeri A and
Niederhuber J: The role of miR-31 and its target gene SATB2 in
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 9:4387–4398. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang MH, Yu J, Chen N, Wang XY, Liu XY,
Wang S and Ding YQ: Elevated microRNA-31 expression regulates
colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene SATB2.
PLoS One. 8:e853532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Xie RL, Croce CM, Stein JL, Lian
JB, van Wijnen AJ and Stein GS: A program of microRNAs controls
osteogenic lineage progression by targeting transcription factor
Runx2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:9863–9868. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen QY, Li J, Sun H, Wu F, Zhu Y, Kluz T,
Jordan A, DesMarais T, Zhang X, Murphy A and Costa M: Role of
miR-31 and SATB2 in arsenic-induced malignant BEAS-2B cell
transformation. Mol Carcinog. 57:968–977. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ge J, Guo S, Fu Y, Zhou P, Zhang P, Du Y,
Li M, Cheng J and Jiang H: Dental follicle cells participate in
tooth eruption via the RUNX2-miR-31-SATB2 Loop. J Dent Res.
94:936–944. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li Z, Hassan MQ, Volinia S, van Wijnen AJ,
Stein JL, Croce CM, Lian JB and Stein GS: A microRNA signature for
a BMP2-induced osteoblast lineage commitment program. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:13906–13911. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li Z, Hassan MQ, Jafferji M, Aqeilan RI,
Garzon R, Croce CM, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS and Lian JB:
Biological functions of miR-29b contribute to positive regulation
of osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 284:15676–15684. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pawlicki JM and Steitz JA: Nuclear
networking fashions pre-messenger RNA and primary microRNA
transcripts for function. Trends Cell Biol. 20:52–61. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhu Y, Chen QY, Li AH and Costa M: The
role of non-coding RNAs involved in nickel-induced lung
carcinogenic mechanisms. Inorganics. 7:812019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chen QY, Des Marais T and Costa M:
Deregulation of SATB2 in carcinogenesis with emphasis on
miRNA-mediated control. Carcinogenesis. 40:393–402. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tian W, Wang G, Liu Y, Huang Z, Zhang C,
Ning K, Yu C, Shen Y, Wang M, Li Y, et al: The miR-599 promotes
non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion via SATB2. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 485:35–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
El Bezawy R, Cominetti D, Fenderico N,
Zuco V, Beretta GL, Dugo M, Arrighetti N, Stucchi C, Rancati T,
Valdagni R, et al: miR-875-5p counteracts epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and enhances radiation response in prostate cancer
through repression of the EGFR-ZEB1 axis. Cancer Lett. 395:53–62.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gu J, Wang G, Liu H and Xiong C: SATB2
targeted by methylated miR-34c-5p suppresses proliferation and
metastasis attenuating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
colorectal cancer. Cell Prolif. 51:e124552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sun X, Liu S, Chen P, Fu D, Hou Y, Hu J,
Liu Z, Jiang Y, Cao X, Cheng C, et al: miR-449a inhibits colorectal
cancer progression by targeting SATB2. Oncotarget. 8:100975–100988.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Luo LJ, Yang F, Ding JJ, Yan DL, Wang DD,
Yang SJ, Ding L, Li J, Chen D, Ma R, et al: miR-31 inhibits
migration and invasion by targeting SATB2 in triple negative breast
cancer. Gene. 594:47–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gong Y, Xu F, Zhang L, Qian Y, Chen J,
Huang H and Yu Y: MicroRNA expression signature for Satb2-induced
osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 387:227–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ratnadiwakara M and Änkö ML: mRNA
stability assay using transcription inhibition by actinomycin D in
mouse pluripotent stem cells. Bio-Protocol. 8:e30722018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Costa M: Molecular mechanisms of nickel
carcinogenesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 31:321–337. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen QY and Costa M: A comprehensive
review of metal-induced cellular transformation studies. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 331:33–40. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Huang H, Zhu J, Li Y, Zhang L, Gu J, Xie
Q, Jin H, Che X, Li J, Huang C, et al: Upregulation of SQSTM1/p62
contributes to nickel-induced malignant transformation of human
bronchial epithelial cells. Autophagy. 12:1687–1703. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pang Y, Li W, Ma R, Ji W, Wang Q, Li D,
Xiao Y, Wei Q, Lai Y, Yang P, et al: Development of human cell
models for assessing the carcinogenic potential of chemicals.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 232:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Rani AS, Qu DQ, Sidhu MK, Panagakos F,
Shah V, Klein KM, Brown N, Pathak S and Kumar S: Transformation of
immortal, non-tumorigenic osteoblast-like human osteosarcoma cells
to the tumorigenic phenotype by nickel sulfate. Carcinogenesis.
14:947–953. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang L, Fan J, Hitron JA, Son YO, Wise JT,
Roy RV, Kim D, Dai J, Pratheeshkumar P, Zhang Z and Shi X: Cancer
stem-like cells accumulated in nickel-induced malignant
transformation. Toxicol Sci. 151:376–387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang Q, Salnikow K, Kluz T, Chen LC, Su
WC and Costa M: Inhibition and reversal of nickel-induced
transformation by the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 192:201–211. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Borowicz S, Van Scoyk M, Avasarala S,
Karuppusamy Rathinam MK, Tauler J, Bikkavilli RK and Winn RA: The
soft agar colony formation assay. J Vis Exp. e519982014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jiang WG, Sanders AJ, Katoh M, Ungefroren
H, Gieseler F, Prince M, Thompson SK, Zollo M, Spano D, Dhawan P,
et al: Tissue invasion and metastasis: Molecular, biological and
clinical perspectives. Semin Cancer Biol. 35 Suppl:S244–S275. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sahai E: Mechanisms of cancer cell
invasion. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 15:87–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A,
Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao YH, Inada M, et al:
Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone
formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell.
89:755–764. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Valenti MT, Serafini P, Innamorati G, Gili
A, Cheri S, Bassi C and Dalle Carbonare L: Runx2 expression: A
mesenchymal stem marker for cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:4167–4172. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Thomas DM, Carty SA, Piscopo DM, Lee JS,
Wang WF, Forrester WC and Hinds PW: The retinoblastoma protein acts
as a transcriptional coactivator required for osteogenic
differentiation. Mol Cell. 8:303–316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Bai X, Meng L, Sun H, Li Z, Zhang X and
Hua S: MicroRNA-196b Inhibits cell growth and metastasis of lung
cancer cells by targeting Runx2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:757–767.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Herreno AM, Ramirez AC, Chaparro VP,
Fernandez MJ, Canas A, Morantes CF, Moreno OM, Bruges RE, Mejia JA,
Bustos FJ, et al: Role of RUNX2 transcription factor in epithelial
mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer lung cancer:
Epigenetic control of the RUNX2 P1 promoter. Tumour Biol.
41:10104283198510142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li H, Zhou RJ, Zhang GQ and Xu JP:
Clinical significance of RUNX2 expression in patients with nonsmall
cell lung cancer: A 5-year follow-up study. Tumour Biol.
34:1807–1812. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Underwood KF, D'Souza DR, Mochin-Peters M,
Pierce AD, Kommineni S, Choe M, Bennett J, Gnatt A, Habtemariam B,
MacKerell AD Jr and Passaniti A: Regulation of RUNX2 transcription
factor-DNA interactions and cell proliferation by vitamin D3
(cholecalciferol) prohormone activity. J Bone Miner Res.
27:913–925. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Underwood KF, Mochin MT, Brusgard JL, Choe
M, Gnatt A and Passaniti A: A quantitative assay to study protein:
DNA interactions, discover transcriptional regulators of gene
expression, and identify novel anti-tumor agents. J Vis Exp.
78:e505122013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kim MS, Gernapudi R, Choi EY, Lapidus RG
and Passaniti A: Characterization of CADD522, a small molecule that
inhibits RUNX2-DNA binding and exhibits antitumor activity.
Oncotarget. 8:70916–70940. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Dobreva G, Dambacher J and Grosschedl R:
SUMO modification of a novel MAR-binding protein, SATB2, modulates
immunoglobulin mu gene expression. Genes Dev. 17:3048–3061. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4022018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Flynt AS and Lai EC: Biological principles
of microRNA-mediated regulation: Shared themes amid diversity. Nat
Rev Genet. 9:831–842. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cameron KS, Buchner V and Tchounwou PB:
Exploring the molecular mechanisms of nickel-induced genotoxicity
and carcinogenicity: A literature review. Rev Environ Health.
26:81–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lee JW, Bae SH, Jeong JW, Kim SH and Kim
KW: Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: Its protein stability
and biological functions. Exp Mol Med. 36:1–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ke Q and Costa M: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol. 70:1469–1480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Li Q, Chen H, Huang X and Costa M: Effects
of 12 metal ions on iron regulatory protein 1 (IRP-1) and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-regulated
genes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 213:245–255. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Davidson TL, Chen H, Di Toro DM, D'Angelo
G and Costa M: Soluble nickel inhibits HIF-prolyl-hydroxylases
creating persistent hypoxic signaling in A549 cells. Mol Carcinog.
45:479–489. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lee SH, Che X, Jeong JH, Choi JY, Lee YJ,
Lee YH, Bae SC and Lee YM: Runx2 protein stabilizes
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α through competition with von
Hippel-Lindau protein (pVHL) and stimulates angiogenesis in growth
plate hypertrophic chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 287:14760–14771.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kwon TG, Zhao X, Yang Q, Li Y, Ge C, Zhao
G and Franceschi RT: Physical and functional interactions between
Runx2 and HIF-1α induce vascular endothelial growth factor gene
expression. J Cell Biochem. 112:3582–3593. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Dong W, Chen Y, Qian N, Sima G, Zhang J,
Guo Z and Wang C: SATB2 knockdown decreases hypoxia-induced
autophagy and stemness in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
20:794–802. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ali T, Mushtaq I, Maryam S, Farhan A, Saba
K, Jan MI, Sultan A, Anees M, Duygu B, Hamera S, et al: Interplay
of N acetyl cysteine and melatonin in regulating oxidative
stress-induced cardiac hypertrophic factors and microRNAs. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 661:56–65. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Clemens F, Verma R, Ramnath J and Landolph
JR: Amplification of the Ect2 proto-oncogene and over-expression of
Ect2 mRNA and protein in nickel compound and
methylcholanthrene-transformed 10T1/2 mouse fibroblast cell lines.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 206:138–149. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chiocca SM, Sterner DA, Biggart NW and
Murphy EC Jr: Nickel mutagenesis: Alteration of the MuSVts110
thermosensitive splicing phenotype by a nickel-induced duplication
of the 3′ splice site. Mol Carcinog. 4:61–71. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhang YJ, Chen JW, He XS, Zhang HZ, Ling
YH, Wen JH, Deng WH, Li P, Yun JP, Xie D and Cai MY: SATB2 is a
promising biomarker for identifying a colorectal origin for liver
metastatic adenocarcinomas. EBioMedicine. 28:62–69. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Dragomir A, de Wit M, Johansson C, Uhlen M
and Ponten F: The role of SATB2 as a diagnostic marker for tumors
of colorectal origin: Results of a pathology-based clinical
prospective study. Am J Clin Pathol. 141:630–638. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Eberhard J, Gaber A, Wangefjord S, Nodin
B, Uhlen M, Ericson Lindquist K and Jirstrom K: A cohort study of
the prognostic and treatment predictive value of SATB2 expression
in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:931–938. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Lin F, Shi J, Zhu S, Chen Z, Li A, Chen T,
Wang HL and Liu H: Cadherin-17 and SATB2 are sensitive and specific
immunomarkers for medullary carcinoma of the large intestine. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 138:1015–1026. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Moh M, Krings G, Ates D, Aysal A, Kim GE
and Rabban JT: SATB2 Expression distinguishes ovarian metastases of
colorectal and appendiceal origin from primary ovarian tumors of
mucinous or endometrioid type. Am J Surg Pathol. 40:419–432. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yu W, Ma Y, Ochoa AC, Shankar S and
Srivastava RK: Cellular transformation of human mammary epithelial
cells by SATB2. Stem Cell Res. 19:139–147. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Shin MH, He Y, Marrogi E, Piperdi S, Ren
L, Khanna C, Gorlick R, Liu C and Huang J: A RUNX2-Mediated
epigenetic regulation of the survival of p53 defective cancer
cells. PLoS Genet. 12:e10058842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Tang W, Yang F, Li Y, de Crombrugghe B,
Jiao H, Xiao G and Zhang C: Transcriptional regulation of Vascular
Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) by osteoblast-specific
transcription factor Osterix (Osx) in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem.
287:1671–1678. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Efe JA and Ding S: The evolving biology of
small molecules: Controlling cell fate and identity. Philos Trans R
Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 366:2208–2221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ma YN, Zhang HY, Fei LR, Zhang MY, Wang
CC, Luo Y and Han YC: SATB2 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer
invasiveness by G9a. Clin Exp Med. 18:37–44. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wei MM and Zhou GB: Long non-coding RNAs
and their roles in non-small-cell lung cancer. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 14:280–288. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
siRNAs. Genes Dev. 20:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Stepicheva NA and Song JL: Function and
regulation of microRNA-31 in development and disease. Mol Reprod
Dev. 83:654–674. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Asangani IA, Harms PW, Dodson L, Pandhi M,
Kunju LP, Maher CA, Fullen DR, Johnson TM, Giordano TJ, Palanisamy
N and Chinnaiyan AM: Genetic and epigenetic loss of microRNA-31
leads to feed-forward expression of EZH2 in melanoma. Oncotarget.
3:1011–1025. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Augoff K, Das M, Bialkowska K, McCue B,
Plow EF and Sossey-Alaoui K: miR-31 is a broad regulator of
β1-integrin expression and function in cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Res. 9:1500–1508. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Yamagishi M, Nakano K, Miyake A, Yamochi
T, Kagami Y, Tsutsumi A, Matsuda Y, Sato-Otsubo A, Muto S,
Utsunomiya A, et al: Polycomb-mediated loss of miR-31 activates
NIK-dependent NF-κB pathway in adult T cell leukemia and other
cancers. Cancer Cell. 21:121–135. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ling H, Fabbri M and Calin GA: MicroRNAs
and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug
development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 12:847–865. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Kim HS, Lee KS, Bae HJ, Eun JW, Shen Q,
Park SJ, Shin WC, Yang HD, Park M, Park WS, et al: MicroRNA-31
functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell cycle and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory proteins in liver
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:8089–8102. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Sakai T, Toguchida J, Ohtani N, Yandell
DW, Rapaport JM and Dryja TP: Allele-specific hypermethylation of
the retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor gene. Am J Hum Genet.
48:880–888. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Lee YW, Klein CB, Kargacin B, Salnikow K,
Kitahara J, Dowjat K, Zhitkovich A, Christie NT and Costa M:
Carcinogenic nickel silences gene expression by chromatin
condensation and DNA methylation: A new model for epigenetic
carcinogens. Mol Cell Biol. 15:2547–2557. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Ohtani-Fujita N, Fujita T, Aoike A,
Osifchin NE, Robbins PD and Sakai T: CpG methylation inactivates
the promoter activity of the human retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor
gene. Oncogene. 8:1063–1067. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Sutcliffe JS, Nelson DL, Zhang F, Pieretti
M, Caskey CT, Saxe D and Warren ST: DNA methylation represses FMR-1
transcription in fragile X syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1:397–400.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Greger V, Debus N, Lohmann D, Hopping W,
Passarge E and Horsthemke B: Frequency and parental origin of
hypermethylated RB1 alleles in retinoblastoma. Hum Genet.
94:491–496. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Hansen RS, Gartler SM, Scott CR, Chen SH
and Laird CD: Methylation analysis of CGG sites in the CpG island
of the human FMR1 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1:571–578. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|