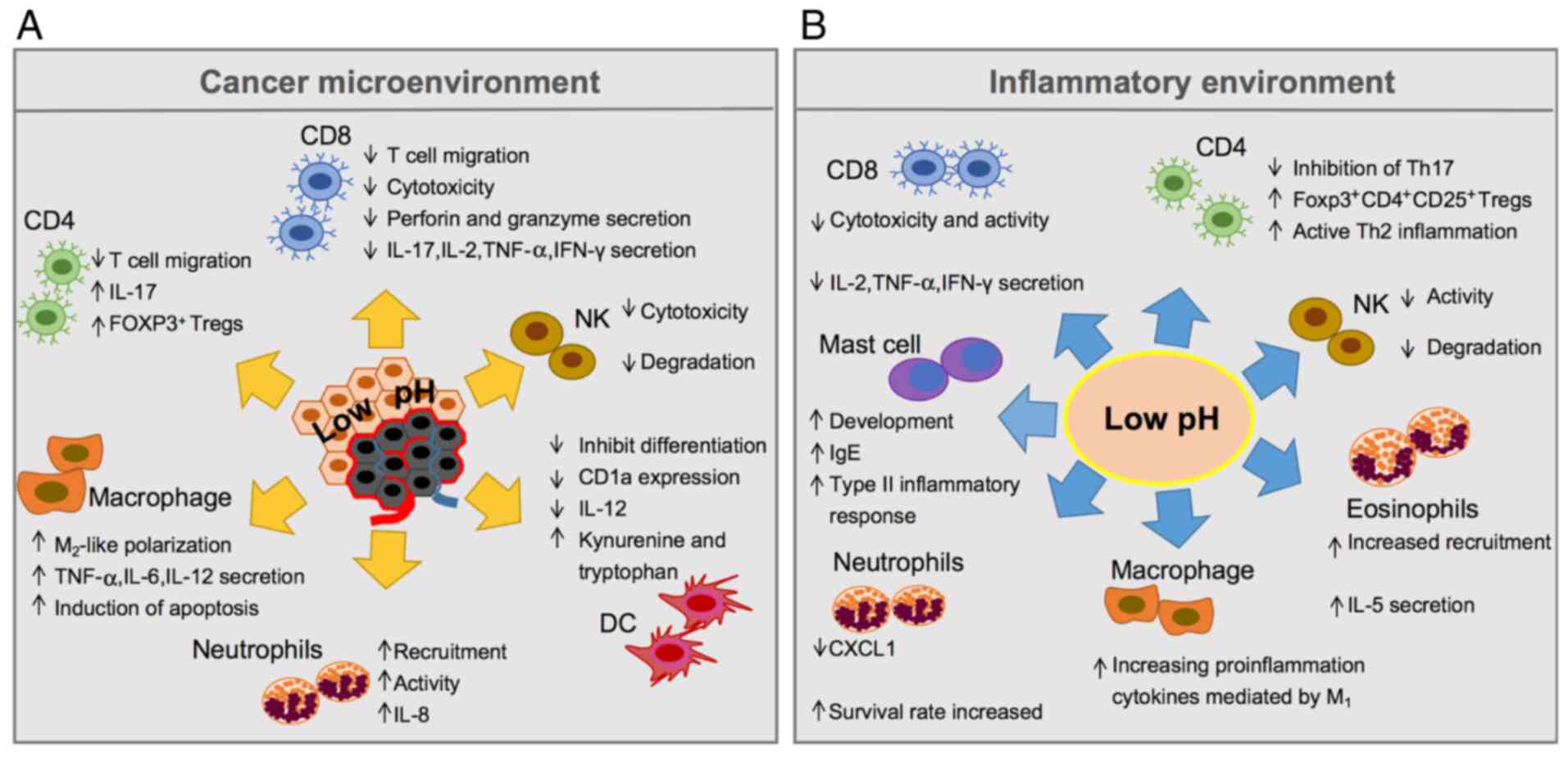
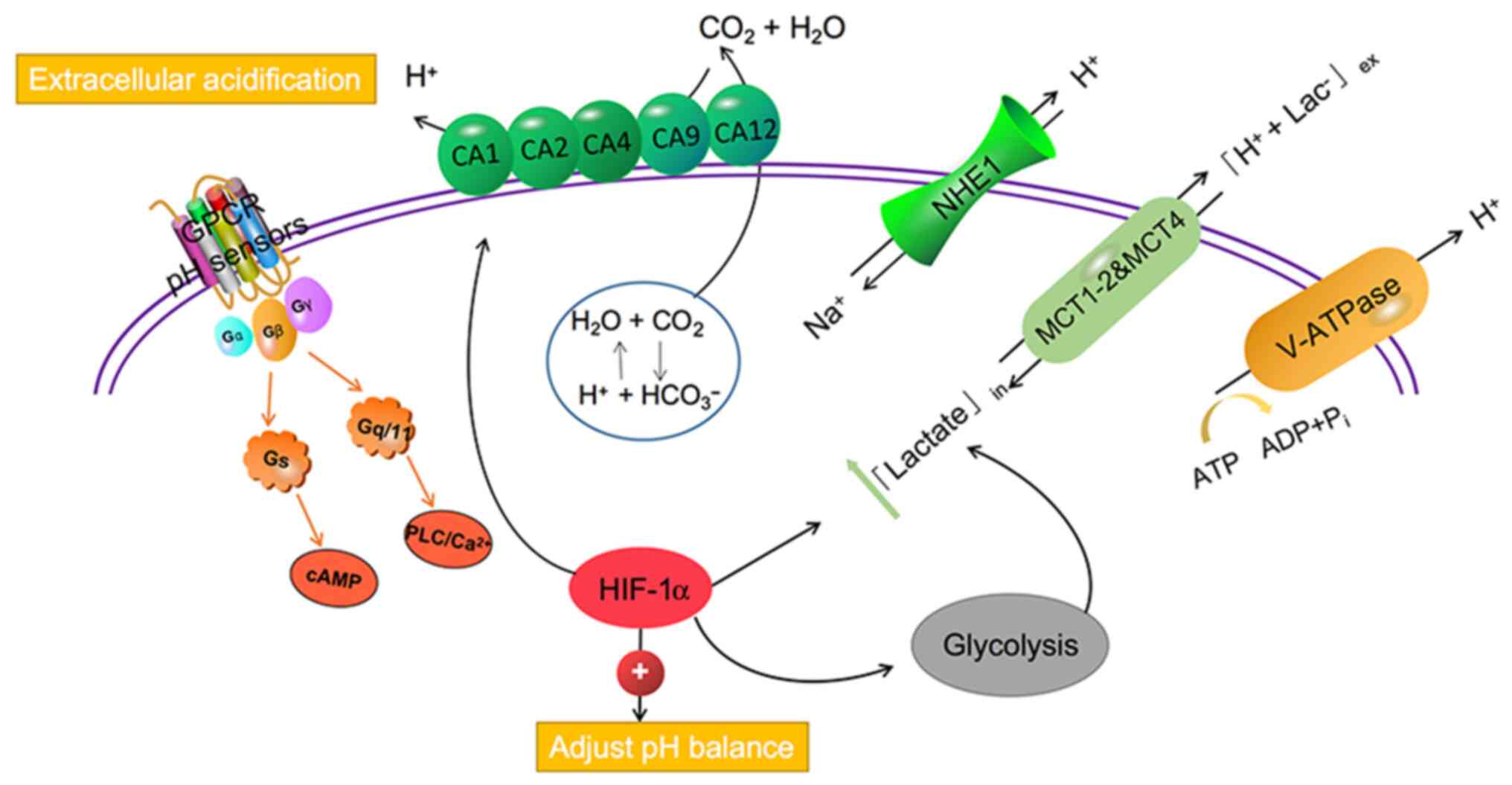
|
1
|
Imtiyaz HZ and Simon MC: Hypoxia-inducible
factors as essential regulators of inflammation. Curr Top Microbiol
Immunol. 345:105–120. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen
H and Shu Y: Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the
tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 18:1572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Koltai T: The Ph paradigm in cancer. Eur J
Clin Nutr. 74 (Suppl 1):S14–S19. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jancic CC, Cabrini M, Gabelloni ML,
Rodríguez Rodrigues C, Salamone G, Trevani AS and Geffner J: Low
extracellular pH stimulates the production of IL-1beta by human
monocytes. Cytokine. 57:258–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang CH, Curtis JD, Maggi LB Jr, Faubert
B, Villarino AV, O'Sullivan D, Huang SC, van der Windt GJ, Blagih
J, Qiu J, et al: Posttranscriptional control of T cell effector
function by aerobic glycolysis. Cell. 153:1239–1251. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakagawa Y, Negishi Y, Shimizu M,
Takahashi M, Ichikawa M and Takahashi H: Effects of extracellular
pH and hypoxia on the function and development of antigen-specific
cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunol Lett. 167:72–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chalmin F, Bruchard M, Vegran F and
Ghiringhelli F: Regulation of T cell antitumor immune response by
tumor induced metabolic stress. Cell Stress. 3:9–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gardner A and Ruffell B: Dendritic cells
and cancer immunity. Trends Immunol. 37:855–865. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hargadon KM: Tumor-altered dendritic cell
function: Implications for anti-tumor immunity. Front Immunol.
4:1922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Förster
I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, Haase VH, Jaenisch R, Corr M, Nizet V,
et al: HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated
inflammation. Cell. 112:645–657. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee JH, Elly C, Park Y and Liu YC: E3
ubiquitin ligase VHL regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α to
maintain regulatory T cell stability and suppressive capacity.
Immunity. 42:1062–1074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martínez D, Vermeulen M, Trevani A,
Ceballos A, Sabatté J, Gamberale R, Alvarez ME, Salamone G, Tanos
T, Coso OA and Geffner J: Extracellular acidosis induces neutrophil
activation by a mechanism dependent on activation of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and ERK pathways. J Immunol.
176:1163–1171. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Franklin RA, Liao W, Sarkar A, Kim MV,
Bivona MR, Liu K, Pamer EG and Li MO: The cellular and molecular
origin of tumor-associated macrophages. Science. 344:921–925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Erra Díaz F, Dantas E and Geffner J:
Unravelling the interplay between extracellular acidosis and immune
cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2018:12182972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roma-Rodrigues C, Mendes R, Baptista PV
and Fernandes AR: Targeting tumor microenvironment for cancer
therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 20:8402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huber V, Camisaschi C, Berzi A, Ferro S,
Lugini L, Triulzi T, Tuccitto A, Tagliabue E, Castelli C and
Rivoltini L: Cancer acidity: An ultimate frontier of tumor immune
escape and a novel target of immunomodulation. Semin Cancer Biol.
43:74–89. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McDonald PC, Chafe SC and Dedhar S:
Overcoming hypoxia-mediated tumor progression: Combinatorial
approaches targeting pH regulation, angiogenesis and immune
dysfunction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 4:272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Guo B, Wang J, Cheng X, Xu Y and
Sang J: Ovarian cancer G protein coupled receptor 1 suppresses cell
migration of MCF7 breast cancer cells via a Gα12/13-Rho-Rac1
pathway. J Mol Signal. 8:62013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wiley SZ, Sriram K, Liang W, Chang SE,
French R, McCann T, Sicklick J, Nishihara H, Lowy AM and Insel PA:
GPR68, a proton-sensing GPCR, mediates interaction of
cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer cells. FASEB J.
32:1170–1183. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pérez-Escuredo J, Van Hée VF, Sboarina M,
Falces J, Payen VL, Pellerin L and Sonveaux P: Monocarboxylate
transporters in the brain and in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2481–2497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Halestrap AP and Wilson MC: The
monocarboxylate transporter family-role and regulation. IUBMB Life.
64:109–119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alfarouk KO: Tumor metabolism, cancer cell
transporters, and microenvironmental resistance. J Enzyme Inhib Med
Chem. 31:859–866. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Merezhinskaya N, Ogunwuyi SA, Mullick FG
and Fishbein WN: Presence and localization of three lactic acid
transporters (MCT1, −2, and −4) in separated human granulocytes,
lymphocytes, and monocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 52:1483–1493.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Merezhinskaya N, Ogunwuyi SA and Fishbein
WN: Expression of monocarboxylate transporter 4 in human platelets,
leukocytes, and tissues assessed by antibodies raised against
terminal versus pre-terminal peptides. Mol Genet Metab. 87:152–161.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Long Y, Gao Z, Hu X, Xiang F, Wu Z, Zhang
J, Han X, Yin L, Qin J, Lan L, et al: Downregulation of MCT4 for
lactate exchange promotes the cytotoxicity of NK cells in breast
carcinoma. Cancer Med. 7:4690–4700. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sukumar M, Liu J, Ji Y, Subramanian M,
Crompton JG, Yu Z, Roychoudhuri R, Palmer DC, Muranski P, Karoly
ED, et al: Inhibiting glycolytic metabolism enhances CD8+ T cell
memory and antitumor function. J Clin Invest. 123:4479–4488. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fischer K, Hoffmann P, Voelkl S,
Meidenbauer N, Ammer J, Edinger M, Gottfried E, Schwarz S, Rothe G,
Hoves S, et al: Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid
on human T cells. Blood. 109:3812–3819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murray CM, Hutchinson R, Bantick JR,
Belfield GP, Benjamin AD, Brazma D, Bundick RV, Cook ID, Craggs RI,
Edwards S, et al: Monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 is a target for
immunosuppression. Nat Chem Biol. 1:371–376. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Végran F, Boidot R, Michiels C, Sonveaux P
and Feron O: Lactate influx through the endothelial cell
monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 supports an NF-κB/IL-8 pathway
that drives tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 71:2550–2560. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang T, Feng Q, Wang Z, Li W, Sun Z,
Wilhelm J, Huang G, Vo T, Sumer BD and Gao J: Tumor-targeted
inhibition of monocarboxylate transporter 1 improves T-cell
immunotherapy of solid tumors. Adv Healthc Mater. 10:e20005492021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raychaudhuri D, Bhattacharya R, Sinha BP,
Liu CSC, Ghosh AR, Rahaman O, Bandopadhyay P, Sarif J, D'Rozario R,
Paul S, et al: Lactate induces pro-tumor reprogramming in
intratumoral plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Front Immunol.
10:18782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gottfried E, Kunz-Schughart LA, Ebner S,
Mueller-Klieser W, Hoves S, Andreesen R, Mackensen A and Kreutz M:
Tumor-derived lactic acid modulates dendritic cell activation and
antigen expression. Blood. 107:2013–2021. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bonuccelli G, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Fatatis A, Witkiewicz AK,
Vander Heiden MG, Migneco G, Chiavarina B, et al: The reverse
Warburg effect: Glycolysis inhibitors prevent the tumor promoting
effects of caveolin-1 deficient cancer associated fibroblasts. Cell
Cycle. 9:1960–1971. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wei L, Zhou Y, Yao J, Qiao C, Ni T, Guo R,
Guo Q and Lu N: Lactate promotes PGE2 synthesis and gluconeogenesis
in monocytes to benefit the growth of inflammation-associated
colorectal tumor. Oncotarget. 6:16198–16214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Colegio OR, Chu NQ, Szabo AL, Chu T,
Rhebergen AM, Jairam V, Cyrus N, Brokowski CE, Eisenbarth SC,
Phillips GM, et al: Functional polarization of tumour-associated
macrophages by tumour-derived lactic acid. Nature. 513:559–563.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tan Z, Xie N, Banerjee S, Cui H, Fu M,
Thannickal VJ and Liu G: The monocarboxylate transporter 4 is
required for glycolytic reprogramming and inflammatory response in
macrophages. J Biol Chem. 290:46–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang L and Li S: Lactic acid promotes
macrophage polarization through MCT-HIF1α signaling in gastric
cancer. Exp Cell Res. 388:1118462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stone SC, Rossetti RA, Alvarez KL,
Carvalho JP, Margarido PF, Baracat EC, Tacla M, Boccardo E, Yokochi
K, Lorenzi NP and Lepique AP: Lactate secreted by cervical cancer
cells modulates macrophage phenotype. J Leukoc Biol. 105:1041–1054.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kong L, Wang Z, Liang X, Wang Y, Gao L and
Ma C: Monocarboxylate transporter 1 promotes classical microglial
activation and pro-inflammatory effect via
6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2, 6-biphosphatase 3. J
Neuroinflammation. 16:2402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Silva LS, Poschet G, Nonnenmacher Y,
Becker HM, Sapcariu S, Gaupel AC, Schlotter M, Wu Y, Kneisel N,
Seiffert M, et al: Branched-chain ketoacids secreted by
glioblastoma cells via MCT1 modulate macrophage phenotype. EMBO
Rep. 18:2172–2185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Contreras-Baeza Y, Sandoval PY, Alarcón R,
Galaz A, Cortés-Molina F, Alegría K, Baeza-Lehnert F, Arce-Molina
R, Guequén A, Flores CA, et al: Monocarboxylate transporter 4
(MCT4) is a high affinity transporter capable of exporting lactate
in high-lactate microenvironments. J Biol Chem. 294:20135–20147.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mikkilineni L, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Domingo-Vidal M, Sprandio J, Avena P, Cotzia P, Dulau-Florea A,
Gong J, Uppal G, Zhan T, et al: Hodgkin lymphoma: A complex
metabolic ecosystem with glycolytic reprogramming of the tumor
microenvironment. Semin Oncol. 44:218–225. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Afonso J, Pinto T, Simões-Sousa S, Schmitt
F, Longatto-Filho A, Pinheiro C, Marques H and Baltazar F: Clinical
significance of metabolism-related biomarkers in non-Hodgkin
lymphoma-MCT1 as potential target in diffuse large B cell lymphoma.
Cell Oncol (Dordr). 42:303–318. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Beloueche-Babari M, Casals Galobart T,
Delgado-Goni T, Wantuch S, Parkes HG, Tandy D, Harker JA and Leach
MO: Monocarboxylate transporter 1 blockade with AZD3965 inhibits
lipid biosynthesis and increases tumour immune cell infiltration.
Br J Cancer. 122:895–903. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Noble RA, Bell N, Blair H, Sikka A, Thomas
H, Phillips N, Nakjang S, Miwa S, Crossland R, Rand V, et al:
Inhibition of monocarboxyate transporter 1 by AZD3965 as a novel
therapeutic approach for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt
lymphoma. Haematologica. 102:1247–1257. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Braga M, Kaliszczak M, Carroll L, Schug
ZT, Heinzmann K, Baxan N, Benito A, Valbuena GN, Stribbling S,
Beckley A, et al: Tracing nutrient flux following monocarboxylate
transporter-1 inhibition with AZD3965. Cancers (Basel).
12:17032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Draoui N, Schicke O, Seront E, Bouzin C,
Sonveaux P, Riant O and Feron O: Antitumor activity of
7-aminocarboxycoumarin derivatives, a new class of potent
inhibitors of lactate influx but not efflux. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:1410–1418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Quanz M, Bender E, Kopitz C, Grünewald S,
Schlicker A, Schwede W, Eheim A, Toschi L, Neuhaus R, Richter C, et
al: Preclinical efficacy of the novel monocarboxylate transporter 1
inhibitor BAY-8002 and associated markers of resistance. Mol Cancer
Ther. 17:2285–2296. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Renner K, Bruss C, Schnell A, Koehl G,
Becker HM, Fante M, Menevse AN, Kauer N, Blazquez R, Hacker L, et
al: Restricting glycolysis preserves T cell effector functions and
augments checkpoint therapy. Cell Rep. 29:135–150.e9. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Cho KS, Yamada T, Wynn C, Behanna HA, Hong
IC, Manaves V, Nakanishi T, Hirose J, Abe Y, Jiang H, et al:
Mechanism analysis of long-term graft survival by monocarboxylate
transporter-1 inhibition. Transplantation. 90:1299–1306. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kondapalli KC, Prasad H and Rao R: An
inside job: How endosomal Na(+)/H(+) exchangers link to autism and
neurological disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:1722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
De Vito P: The sodium/hydrogen exchanger:
A possible mediator of immunity. Cell Immunol. 240:69–85. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Vereninov AA, Vassilieva IO, Yurinskaya
VE, Matveev VV, Glushankova LN, Lang F and Matskevitch JA:
Differential transcription of ion transporters, NHE1, ATP1B1, NKCC1
in human peripheral blood lymphocytes activated to proliferation.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 11:19–26. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chang CP, Wang SW, Huang ZL, Wang OY,
Huang MI, Lu LM, Tarng DC, Chien CH and Chien EJ: Non-genomic rapid
inhibition of Na+/H+-exchange 1 and apoptotic
immunosuppression in human T cells by glucocorticoids. J Cell
Physiol. 223:679–686. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chien EJ, Hsu CH, Chang VH, Lin EP, Kuo
TP, Chien CH and Lin HY: In human T cells mifepristone antagonizes
glucocorticoid non-genomic rapid responses in terms of
Na(+)/H(+)-exchange 1 activity, but not ezrin/radixin/moesin
phosphorylation. Steroids. 111:29–36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xing K, Gu B, Zhang P and Wu X:
Dexamethasone enhances programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) expression
during T cell activation: An insight into the optimum application
of glucocorticoids in anti-cancer therapy. BMC Immunol. 16:392015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lai JN, Wang OY, Lin VH, Liao CF, Tarng DC
and Chien EJ: The non-genomic rapid acidification in peripheral T
cells by progesterone depends on intracellular calcium increase and
not on Na+/H+-exchange inhibition. Steroids.
77:1017–1024. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Singh Y, Zhou Y, Shi X, Zhang S, Umbach
AT, Salker MS, Lang KS and Lang F: Alkaline cytosolic pH and high
sodium hydrogen exchanger 1 (NHE1) activity in Th9 cells. J Biol
Chem. 291:23662–23671. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rotte A, Pasham V, Eichenmüller M, Yang W,
Bhandaru M and Lang F: Influence of dexamethasone on
Na+/H+ exchanger activity in dendritic cells.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 28:305–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang W, Bhandaru M, Pasham V, Bobbala D,
Zelenak C, Jilani K, Rotte A and Lang F: Effect of thymoquinone on
cytosolic pH and Na+/H+ exchanger activity in
mouse dendritic cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 29:21–30. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhou Y, Pasham V, Chatterjee S, Rotte A,
Yang W, Bhandaru M, Singh Y and Lang F: Regulation of
Na+/H+ exchanger in dendritic cells by Akt1.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1237–1249. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhu W, Carney KE, Pigott VM, Falgoust LM,
Clark PA, Kuo JS and Sun D: Glioma-mediated microglial activation
promotes glioma proliferation and migration: Roles of Na+/H+
exchanger isoform 1. Carcinogenesis. 37:839–851. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Song S, Wang S, Pigott VM, Jiang T, Foley
LM, Mishra A, Nayak R, Zhu W, Begum G, Shi Y, et al: Selective role
of Na+/H+ exchanger in Cx3cr1+
microglial activation, white matter demyelination, and post-stroke
function recovery. Glia. 66:2279–2298. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Liu CL, Zhang X, Liu J, Wang Y, Sukhova
GK, Wojtkiewicz GR, Liu T, Tang R, Achilefu S, Nahrendorf M, et al:
Na+-H+ exchanger 1 determines atherosclerotic
lesion acidification and promotes atherogenesis. Nat Commun.
10:39782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Takakuwa S, Mizuno N, Takano T, Asakawa S,
Sato T, Hiratsuka M and Hirasawa N: Down-regulation of
Na+/H+ exchanger 1 by Toll-like receptor
stimulation in macrophages. Immunobiology. 222:176–182. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Provost JJ and Wallert MA: Inside out:
Targeting NHE1 as an intracellular and extracellular regulator of
cancer progression. Chem Biol Drug Des. 81:85–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Asgharzadeh MR, Barar J, Pourseif MM,
Eskandani M, Jafari Niya M, Mashayekhi MR and Omidi Y: Molecular
machineries of pH dysregulation in tumor microenvironment:
Potential targets for cancer therapy. Bioimpacts. 7:115–133. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shi Y, Chanana V, Watters JJ, Ferrazzano P
and Sun D: Role of sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 1 in
microglial activation and proinflammatory responses in ischemic
brains. J Neurochem. 119:124–135. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu CL, Liu X, Wang Y, Deng Z, Liu T,
Sukhova GK, Wojtkiewicz GR, Tang R, Zhang JY, Achilefu S, et al:
Reduced Nhe1 (Na+-H+ Exchanger-1) function
protects ApoE-deficient mice From Ang II (Angiotensin II)-induced
abdominal aortic aneurysms. Hypertension. 76:87–100. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Guan X, Hasan MN, Begum G, Kohanbash G,
Carney KE, Pigott VM, Persson AI, Castro MG, Jia W and Sun D:
Blockade of Na/H exchanger stimulates glioma tumor immunogenicity
and enhances combinatorial TMZ and anti-PD-1 therapy. Cell Death
Dis. 9:10102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jin W, Li Q, Wang J, Chang G, Lin Y, Li H,
Wang L, Gao W and Pang T: Na+/H+ exchanger 1
inhibition contributes to K562 leukaemic cell differentiation. Cell
Biol Int. 36:739–745. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Fliegel L: Structural and functional
changes in the Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1,
induced by Erk1/2 phosphorylation. Int J Mol Sci. 20:23782019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Smith AN, Lovering RC, Futai M, Takeda J,
Brown D and Karet FE: Revised nomenclature for mammalian
vacuolar-type H+ -ATPase subunit genes. Mol Cell.
12:801–803. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Forgac M: Vacuolar ATPases: Rotary proton
pumps in physiology and pathophysiology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:917–929. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
McGuire C, Stransky L, Cotter K and Forgac
M: Regulation of V-ATPase activity. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
22:609–622. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kulshrestha A, Katara GK, Ginter J,
Pamarthy S, Ibrahim SA, Jaiswal MK, Sandulescu C, Periakaruppan R,
Dolan J, Gilman-Sachs A and Beaman KD: Selective inhibition of
tumor cell associated Vacuolar-ATPase ‘a2’ isoform overcomes
cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Mol Oncol.
10:789–805. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Smith GA, Howell GJ, Phillips C, Muench
SP, Ponnambalam S and Harrison MA: Extracellular and luminal pH
regulation by vacuolar H+-ATPase isoform expression and
targeting to the plasma membrane and endosomes. J Biol Chem.
291:8500–8515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Stransky L, Cotter K and Forgac M: The
function of V-ATPases in cancer. Physiol Rev. 96:1071–1091. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rao Z, Jordan PM, Wang Y, Menche D, Pace
S, Gerstmeier J and Werz O: Differential role of vacuolar
(H+)-ATPase in the expression and activity of
cyclooxygenase-2 in human monocytes. Biochem Pharmacol.
175:1138582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sahoo M, Katara GK, Bilal MY, Ibrahim SA,
Kulshrestha A, Fleetwood S, Suzue K and Beaman KD: Hematopoietic
stem cell specific V-ATPase controls breast cancer progression and
metastasis via cytotoxic T cells. Oncotarget. 9:33215–33231. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Peterson TV, Jaiswal MK, Beaman KD and
Reynolds JM: Conditional deletion of the V-ATPase a2-subunit
disrupts intrathymic T cell development. Front Immunol.
10:19112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Rothenberg EV, Ungerbäck J and Champhekar
A: Forging T-lymphocyte identity: Intersecting networks of
transcriptional control. Adv Immunol. 129:109–174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
McGuire C, Cotter K, Stransky L and Forgac
M: Regulation of V-ATPase assembly and function of V-ATPases in
tumor cell invasiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1857:1213–1218.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ibrahim SA, Kulshrestha A, Katara GK, Amin
MA and Beaman KD: Cancer derived peptide of vacuolar ATPase ‘a2’
isoform promotes neutrophil migration by autocrine secretion of
IL-8. Sci Rep. 6:368652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Katara GK, Jaiswal MK, Kulshrestha A,
Kolli B, Gilman-Sachs A and Beaman KD: Tumor-associated vacuolar
ATPase subunit promotes tumorigenic characteristics in macrophages.
Oncogene. 33:5649–5654. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Katara GK, Kulshrestha A, Mao L, Wang X,
Sahoo M, Ibrahim S, Pamarthy S, Suzue K, Shekhawat GS, Gilman-Sachs
A and Beaman KD: Mammary epithelium-specific inactivation of
V-ATPase reduces stiffness of extracellular matrix and enhances
metastasis of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 12:208–223. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ibrahim SA, Kulshrestha A, Katara GK,
Riehl V, Sahoo M and Beaman KD: Cancer-associated V-ATPase induces
delayed apoptosis of protumorigenic neutrophils. Mol Oncol.
14:590–610. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gilman-Sachs A, Tikoo A, Akman-Anderson L,
Jaiswal M, Ntrivalas E and Beaman K: Expression and role of a2
vacuolar-ATPase (a2V) in trafficking of human neutrophil granules
and exocytosis. J Leukoc Biol. 97:1121–1131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Xia Y, Liu N, Xie X, Bi G, Ba H, Li L,
Zhang J, Deng X, Yao Y, Tang Z, et al: The macrophage-specific
V-ATPase subunit ATP6V0D2 restricts inflammasome activation and
bacterial infection by facilitating autophagosome-lysosome fusion.
Autophagy. 15:960–975. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Murase M, Kawasaki T, Hakozaki R, Sueyoshi
T, Putri DD, Kitai Y, Sato S, Ikawa M and Kawai T: Intravesicular
acidification regulates lipopolysaccharide inflammation and
tolerance through TLR4 trafficking. J Immunol. 200:2798–2808. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Kimura T, Nada S, Takegahara N, Okuno T,
Nojima S, Kang S, Ito D, Morimoto K, Hosokawa T, Hayama Y, et al:
Polarization of M2 macrophages requires Lamtor1 that integrates
cytokine and amino-acid signals. Nat Commun. 7:131302016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Rao Z, Pace S, Jordan PM, Bilancia R,
Troisi F, Börner F, Andreas N, Kamradt T, Menche D, Rossi A, et al:
Vacuolar (H+)-ATPase critically regulates specialized
proresolving mediator pathways in human M2-like monocyte-derived
macrophages and has a crucial role in resolution of inflammation. J
Immunol. 203:1031–1043. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kuchuk O, Tuccitto A, Citterio D, Huber V,
Camisaschi C, Milione M, Vergani B, Villa A, Alison MR, Carradori
S, et al: pH regulators to target the tumor immune microenvironment
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoImmunology. 7:e14454522018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Thomas L, Rao Z, Gerstmeier J, Raasch M,
Weinigel C, Rummler S, Menche D, Müller R, Pergola C, Mosig A and
Werz O: Selective upregulation of TNFα expression in
classically-activated human monocyte-derived macrophages (M1)
through pharmacological interference with V-ATPase. Biochem
Pharmacol. 130:71–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Bowman EJ, Graham LA, Stevens TH and
Bowman BJ: The bafilomycin/concanamycin binding site in subunit c
of the V-ATPases from Neurospora crassa and Saccharomyces
cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 279:33131–33138. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Lu X, Chen L, Chen Y, Shao Q and Qin W:
Bafilomycin A1 inhibits the growth and metastatic potential of the
BEL-7402 liver cancer and HO-8910 ovarian cancer cell lines and
induces alterations in their microRNA expression. Exp Ther Med.
10:1829–1834. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Halcrow P, Khan N, Datta G, Ohm JE, Chen X
and Geiger JD: Importance of measuring endolysosome, cytosolic, and
extracellular pH in understanding the pathogenesis of and possible
treatments for glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Rep.
2:e11932019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Yuan N, Song L, Zhang S, Lin W, Cao Y, Xu
F, Fang Y, Wang Z, Zhang H, Li X, et al: Bafilomycin A1 targets
both autophagy and apoptosis pathways in pediatric B-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 100:345–356. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Emruli VK, Olsson R, Ek F and Ek S:
Identification of V-ATPase as a molecular sensor of SOX11-levels
and potential therapeutic target for mantle cell lymphoma. BMC
Cancer. 16:4932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Fais S: Proton pump inhibitor-induced
tumour cell death by inhibition of a detoxification mechanism. J
Intern Med. 267:515–525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
De Milito A, Canese R, Marino ML, Borghi
M, Iero M, Villa A, Venturi G, Lozupone F, Iessi E, Logozzi M, et
al: pH-dependent antitumor activity of proton pump inhibitors
against human melanoma is mediated by inhibition of tumor acidity.
Int J Cancer. 127:207–219. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Denny WA and Wilson WR: Considerations for
the design of nitrophenyl mustards as agents with selective
toxicity for hypoxic tumor cells. J Med Chem. 29:879–887. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Luciani F, Spada M, De Milito A, Molinari
A, Rivoltini L, Montinaro A, Marra M, Lugini L, Logozzi M, Lozupone
F, et al: Effect of proton pump inhibitor pretreatment on
resistance of solid tumors to cytotoxic drugs. J Natl Cancer Inst.
96:1702–1713. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Corbet C and Feron O: Tumour acidosis:
From the passenger to the driver's seat. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:577–593. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Neri D and Supuran CT: Interfering with pH
regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 10:767–777. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Fan J, Kamphorst JJ, Mathew R, Chung MK,
White E, Shlomi T and Rabinowitz JD: Glutamine-driven oxidative
phosphorylation is a major ATP source in transformed mammalian
cells in both normoxia and hypoxia. Mol Syst Biol. 9:7122013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Sedlakova O, Svastova E, Takacova M,
Kopacek J, Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX, a
hypoxia-induced catalytic component of the pH regulating machinery
in tumors. Front Physiol. 4:4002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Hunt JF, Fang K, Malik R, Snyder A,
Malhotra N, Platts-Mills TA and Gaston B: Endogenous airway
acidification. Implications for asthma pathophysiology. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 161((3 Pt 1)): 694–699. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Wen T, Mingler MK, Wahl B, Khorki ME,
Pabst O, Zimmermann N and Rothenberg ME: Carbonic anhydrase IV is
expressed on IL-5-activated murine eosinophils. J Immunol.
192:5481–5489. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Pulendran B and Artis D: New paradigms in
type 2 immunity. Science. 337:431–435. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Henry EK, Sy CB, Inclan-Rico JM, Espinosa
V, Ghanny SS, Dwyer DF, Soteropoulos P, Rivera A and Siracusa MC:
Carbonic anhydrase enzymes regulate mast cell-mediated
inflammation. J Exp Med. 213:1663–1673. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Noti M, Kim BS, Siracusa MC, Rak GD, Kubo
M, Moghaddam AE, Sattentau QA, Comeau MR, Spergel JM and Artis D:
Exposure to food allergens through inflamed skin promotes
intestinal food allergy through the thymic stromal
lymphopoietin-basophil axis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 133:1390–1399,
1399.e1-6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Winum JY: Carbonic anhydrase enzymes for
regulating mast cell hematopoiesis and type-2 inflammation: A
patent evaluation (WO2017/058370). Expert Opin Ther Pat.
28:741–743. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Supuran CT: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
and their potential in a range of therapeutic areas. Expert Opin
Ther Pat. 28:709–712. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Supuran CT, Altamimi ASA and Carta F:
Carbonic anhydrase inhibition and the management of glaucoma: A
literature and patent review 2013–2019. Expert Opin Ther Pat.
29:781–792. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Borenshtein D, Schlieper KA, Rickman BH,
Chapman JM, Schweinfest CW, Fox JG and Schauer DB: Decreased
expression of colonic Slc26a3 and carbonic anhydrase iv as a cause
of fatal infectious diarrhea in mice. Infect Immun. 77:3639–3650.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Mori K, Yamanishi H, Ikeda Y, Kumagi T,
Hiasa Y, Matsuura B, Abe M and Onji M: Oral administration of
carbonic anhydrase I ameliorates murine experimental colitis
induced by Foxp3-CD4+CD25-T cells. J Leukoc Biol. 93:963–972. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Lavin Y, Winter D, Blecher-Gonen R, David
E, Keren-Shaul H, Merad M, Jung S and Amit I: Tissue-resident
macrophage enhancer landscapes are shaped by the local
microenvironment. Cell. 159:1312–1326. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Lounnas N, Rosilio C, Nebout M, Mary D,
Griessinger E, Neffati Z, Chiche J, Spits H, Hagenbeek TJ, Asnafi
V, et al: Pharmacological inhibition of carbonic anhydrase XII
interferes with cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in
T-cell lymphomas. Cancer Lett. 333:76–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Ibrahim-Hashim A and Estrella V: Acidosis
and cancer: From mechanism to neutralization. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 38:149–155. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Chafe SC, McDonald PC, Saberi S,
Nemirovsky O, Venkateswaran G, Burugu S, Gao D, Delaidelli A, Kyle
AH, Baker JHE, et al: Targeting hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase
IX enhances immune-checkpoint blockade locally and systemically.
Cancer Immunol Res. 7:1064–1078. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
McDonald PC, Chia S, Bedard PL, Chu Q,
Lyle M, Tang L, Singh M, Zhang Z, Supuran CT, Renouf DJ and Dedhar
S: A phase 1 study of SLC-0111, a novel inhibitor of carbonic
anhydrase IX, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Am J Clin
Oncol. 43:484–490. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Nasu K, Yamaguchi K, Takanashi T, Tamai K,
Sato I, Ine S, Sasaki O, Satoh K, Tanaka N, Tanaka Y, et al:
Crucial role of carbonic anhydrase IX in tumorigenicity of
xenotransplanted adult T-cell leukemia-derived cells. Cancer Sci.
108:435–443. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Chen LQ, Howison CM, Spier C, Stopeck AT,
Malm SW, Pagel MD and Baker AF: Assessment of carbonic anhydrase IX
expression and extracellular pH in B-cell lymphoma cell line
models. Leuk Lymphoma. 56:1432–1439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Mei Y, Zhao L, Liu Y, Gong H, Song Y, Lei
L, Zhu Y, Jin Z, Ma S, Hu B, et al: Combining DNA vaccine and
AIDA-1 in attenuated Salmonella activates tumor-specific
CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses. Cancer
Immunol Res. 5:503–514. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Sun YY, Peng S, Han L, Qiu J, Song L, Tsai
Y, Yang B, Roden RB, Trimble CL, Hung CF and Wu TC: Local HPV
Recombinant vaccinia boost following priming with an HPV DNA
vaccine enhances local HPV-specific CD8+ T-cell-mediated
tumor control in the genital tract. Clin Cancer Res. 22:657–669.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Duan Y, Yang C, Zhang Z, Liu J, Zheng J
and Kong D: Poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted polyethylenimine modified
with G250 monoclonal antibody for tumor gene therapy. Hum Gene
Ther. 21:191–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zhao Y, Wei Z, Yang H, Li X, Wang Q, Wang
L and Li S: Enhance the anti-renca carcinoma effect of a DNA
vaccine targeting G250 gene by co-expression with cytotoxic
T-lymphocyte associated antigen-4(CTLA-4). Biomed Pharmacother.
90:147–152. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Chai D, Shan H, Wang G, Zhang Q, Li H,
Fang L, Song J, Liu N, Zhang Q, Yao H and Zheng J: Combining DNA
vaccine and AIM2 in H1 nanoparticles exert anti-renal carcinoma
effects via enhancing tumor-specific multi-functional
CD8+ T-cell responses. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:323–334.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zhang Q, Xu J, Ding J, Liu H, Li H, Li H,
Lu M, Miao Y, Wang Z, Fu Q and Zheng J: Bortezomib improves
adoptive carbonic anhydrase IX-specific chimeric antigen
receptor-modified NK92 cell therapy in mouse models of human renal
cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 40:3714–3724. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Li H, Ding J, Lu M, Liu H, Miao Y, Li L,
Wang G, Zheng J, Pei D and Zhang Q: CAIX-specific CAR-T cells and
sunitinib show synergistic effects against metastatic renal cancer
models. J Immunother. 43:16–28. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Lau J, Liu Z, Lin KS, Pan J, Zhang Z,
Vullo D, Supuran CT, Perrin DM and Bénard F: Trimeric
radiofluorinated sulfonamide derivatives to achieve in vivo
selectivity for carbonic anhydrase IX-targeted PET imaging. J Nucl
Med. 56:1434–1440. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Dubois LJ, Niemans R, van Kuijk SJ, Panth
KM, Parvathaneni NK, Peeters SG, Zegers CM, Rekers NH, van
Gisbergen MW, Biemans R, et al: New ways to image and target tumour
hypoxia and its molecular responses. Radiother Oncol. 116:352–357.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Justus CR, Dong L and Yang LV: Acidic
tumor microenvironment and pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors.
Front Physiol. 4:3542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Liu JP, Nakakura T, Tomura H, Tobo M, Mogi
C, Wang JQ, He XD, Takano M, Damirin A, Komachi M, et al: Each one
of certain histidine residues in G-protein-coupled receptor GPR4 is
critical for extracellular proton-induced stimulation of multiple
G-protein-signaling pathways. Pharmacol Res. 61:499–505. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Ludwig MG, Vanek M, Guerini D, Gasser JA,
Jones CE, Junker U, Hofstetter H, Wolf RM and Seuwen K:
Proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 425:93–98.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Damaghi M, Wojtkowiak JW and Gillies RJ:
pH sensing and regulation in cancer. Front Physiol. 4:3702013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Pilon-Thomas S, Kodumudi KN, El-Kenawi AE,
Russell S, Weber AM, Luddy K, Damaghi M, Wojtkowiak JW, Mulé JJ,
Ibrahim-Hashim A and Gillies RJ: Neutralization of tumor acidity
improves antitumor responses to immunotherapy. Cancer Res.
76:1381–1390. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Wiley SZ, Sriram K, Salmerón C and Insel
PA: GPR68: An emerging drug target in cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
20:5592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Lardner A: The effects of extracellular pH
on immune function. J Leukoc Biol. 69:522–530. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
de Vallière C, Wang Y, Eloranta JJ, Vidal
S, Clay I, Spalinger MR, Tcymbarevich I, Terhalle A, Ludwig MG,
Suply T, et al: G Protein-coupled pH-sensing receptor OGR1 is a
regulator of intestinal inflammation. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
21:1269–1281. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Wang Y, de Vallière C, Imenez Silva PH,
Leonardi I, Gruber S, Gerstgrasser A, Melhem H, Weber A, Leucht K,
Wolfram L, et al: The proton-activated receptor GPR4 modulates
intestinal inflammation. J Crohn's Colitis. 12:355–368. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Frasch SC, McNamee EN, Kominsky D,
Jedlicka P, Jakubzick C, Zemski Berry K, Mack M, Furuta GT, Lee JJ,
Henson PM, et al: G2A signaling dampens colitic inflammation via
production of IFN-γ. J Immunol. 197:1425–1434. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Li HM, Jang JH, Jung JS, Shin J, Park CO,
Kim YJ, Ahn WG, Nam JS, Hong CW, Lee J, et al: G2A protects mice
against sepsis by modulating kupffer cell activation: Cooperativity
with adenosine receptor 2b. J Immunol. 202:527–538. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Su YS, Huang YF, Wong J, Lee CW, Hsieh WS
and Sun WH: G2A as a Threshold regulator of inflammatory
hyperalgesia modulates chronic hyperalgesia. J Mol Neurosci.
64:39–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Osthues T, Zimmer B, Rimola V, Klann K,
Schilling K, Mathoor P, Angioni C, Weigert A, Geisslinger G, Münch
C, et al: The lipid receptor G2A (GPR132) mediates macrophage
migration in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Cells.
9:17402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Kern K, Schäfer SMG, Cohnen J, Pierre S,
Osthues T, Tarighi N, Hohmann S, Ferreiros N, Brüne B, Weigert A,
et al: The G2A receptor controls polarization of macrophage by
determining their localization within the inflamed tissue. Front
Immunol. 9:22612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Kung CC, Dai SP, Chiang H, Huang HS and
Sun WH: Temporal expression patterns of distinct cytokines and
M1/M2 macrophage polarization regulate rheumatoid arthritis
progression. Mol Biol Rep. 47:3423–3437. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Dai SP, Hsieh WS, Chen CH, Lu YH, Huang
HS, Chang DM, Huang SL and Sun WH: TDAG8 deficiency reduces
satellite glial number and pro-inflammatory macrophage number to
relieve rheumatoid arthritis disease severity and chronic pain. J
Neuroinflammation. 17:1702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Tsurumaki H, Mogi C, Aoki-Saito H, Tobo M,
Kamide Y, Yatomi M, Sato K, Dobashi K, Ishizuka T, Hisada T, et al:
Protective role of proton-sensing TDAG8 in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Int J Mol Sci.
16:28931–28942. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Tcymbarevich I, Richards SM, Russo G,
Kühn-Georgijevic J, Cosin-Roger J, Baebler K, Lang S, Bengs S,
Atrott K, Bettoni C, et al: Lack of the pH-sensing receptor TDAG8
[GPR65] in macrophages plays a detrimental role in murine models of
inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 13:245–258. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Chen P, Zuo H, Xiong H, Kolar MJ, Chu Q,
Saghatelian A, Siegwart DJ and Wan Y: Gpr132 sensing of lactate
mediates tumor-macrophage interplay to promote breast cancer
metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:580–585. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Yan L, Singh LS, Zhang L and Xu Y: Role of
OGR1 in myeloid-derived cells in prostate cancer. Oncogene.
33:157–164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Holgate ST: Innate and adaptive immune
responses in asthma. Nat Med. 18:673–683. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Aoki H, Mogi C, Hisada T, Nakakura T,
Kamide Y, Ichimonji I, Tomura H, Tobo M, Sato K, Tsurumaki H, et
al: Proton-sensing ovarian cancer G protein-coupled receptor 1 on
dendritic cells is required for airway responses in a murine asthma
model. PLoS One. 8:e799852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Kottyan LC, Collier AR, Cao KH, Niese KA,
Hedgebeth M, Radu CG, Witte ON, Khurana Hershey GK, Rothenberg ME
and Zimmermann N: Eosinophil viability is increased by acidic pH in
a cAMP- and GPR65-dependent manner. Blood. 114:2774–2782. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Sanderlin EJ, Marie M, Velcicky J,
Loetscher P and Yang LV: Pharmacological inhibition of GPR4
remediates intestinal inflammation in a mouse colitis model. Eur J
Pharmacol. 852:218–230. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Velcicky J, Miltz W, Oberhauser B, Orain
D, Vaupel A, Weigand K, Dawson King J, Littlewood-Evans A, Nash M,
Feifel R and Loetscher P: Development of selective, orally active
GPR4 antagonists with modulatory effects on nociception,
inflammation, and angiogenesis. J Med Chem. 60:3672–3683. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Miltz W, Velcicky J, Dawson J,
Littlewood-Evans A, Ludwig MG, Seuwen K, Feifel R, Oberhauser B,
Meyer A, Gabriel D, et al: Design and synthesis of potent and
orally active GPR4 antagonists with modulatory effects on
nociception, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Bioorg Med Chem.
25:4512–4525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Fukuda H, Ito S, Watari K, Mogi C, Arisawa
M, Okajima F, Kurose H and Shuto S: Identification of a potent and
selective GPR4 antagonist as a drug lead for the treatment of
myocardial infarction. ACS Med Chem Lett. 7:493–497. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Lengacher S, Nehiri-Sitayeb T, Steiner N,
Carneiro L, Favrod C, Preitner F, Thorens B, Stehle JC, Dix L,
Pralong F, et al: Resistance to diet-induced obesity and associated
metabolic perturbations in haploinsufficient monocarboxylate
transporter 1 mice. PLoS One. 8:e825052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Draoui N, Schicke O, Fernandes A, Drozak
X, Nahra F, Dumont A, Douxfils J, Hermans E, Dogné JM, Corbau R, et
al: Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of carboxycoumarins as
a new antitumor treatment targeting lactate transport in cancer
cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 21:7107–7117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Reshkin SJ, Cardone RA and Harguindey S:
Na+-H+ exchanger, pH regulation and cancer.
Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov. 8:85–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Ferrari S, Perut F, Fagioli F, Brach Del
Prever A, Meazza C, Parafioriti A, Picci P, Gambarotti M, Avnet S,
Baldini N and Fais S: Proton pump inhibitor chemosensitization in
human osteosarcoma: From the bench to the patients' bed. J Transl
Med. 11:2682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Mentzer RM Jr, Bartels C, Bolli R, Boyce
S, Buckberg GD, Chaitman B, Haverich A, Knight J, Menasché P, Myers
ML, et al: Sodium-hydrogen exchange inhibition by cariporide to
reduce the risk of ischemic cardiac events in patients undergoing
coronary artery bypass grafting: Results of the EXPEDITION study.
Ann Thorac Surg. 85:1261–1270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Zeymer U, Suryapranata H, Monassier JP,
Opolski G, Davies J, Rasmanis G, Linssen G, Tebbe U, Schröder R,
Tiemann R, et al: The Na(+)/H(+) exchange inhibitor eniporide as an
adjunct to early reperfusion therapy for acute myocardial
infarction. Results of the evaluation of the safety and
cardioprotective effects of eniporide in acute myocardial
infarction (ESCAMI) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 38:1644–1650. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Théroux P, Chaitman BR, Danchin N, Erhardt
L, Meinertz T, Schroeder JS, Tognoni G, White HD, Willerson JT and
Jessel A: Inhibition of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger with
cariporide to prevent myocardial infarction in high-risk ischemic
situations. Main results of the GUARDIAN trial. Guard during
ischemia against necrosis (GUARDIAN) Investigators. Circulation.
102:3032–3038. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Atwal KS, O'Neil SV, Ahmad S, Doweyko L,
Kirby M, Dorso CR, Chandrasena G, Chen BC, Zhao R and Zahler R:
Synthesis and biological activity of
5-aryl-4-(4-(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)piperidin-1-yl)pyrimidine
analogs as potent, highly selective, and orally bioavailable NHE-1
inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:4796–4799. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Harguindey S, Arranz JL, Polo Orozco JD,
Rauch C, Fais S, Cardone RA and Reshkin SJ: Cariporide and other
new and powerful NHE1 inhibitors as potentially selective
anticancer drugs-an integral
molecular/biochemical/metabolic/clinical approach after one hundred
years of cancer research. J Transl Med. 11:2822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Huber V, De Milito A, Harguindey S,
Reshkin SJ, Wahl ML, Rauch C, Chiesi A, Pouysségur J, Gatenby RA,
Rivoltini L and Fais S: Proton dynamics in cancer. J Transl Med.
8:572010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Spugnini EP, Sonveaux P, Stock C,
Perez-Sayans M, De Milito A, Avnet S, Garcìa AG, Harguindey S and
Fais S: Proton channels and exchangers in cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1848:2715–2726. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Chiche J, Ilc K, Laferrière J, Trottier E,
Dayan F, Mazure NM, Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur J:
Hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase IX and XII promote tumor cell
growth by counteracting acidosis through the regulation of the
intracellular pH. Cancer Res. 69:358–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Salmon H, Remark R, Gnjatic S and Merad M:
Host tissue determinants of tumour immunity. Nat Rev Cancer.
19:215–227. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|