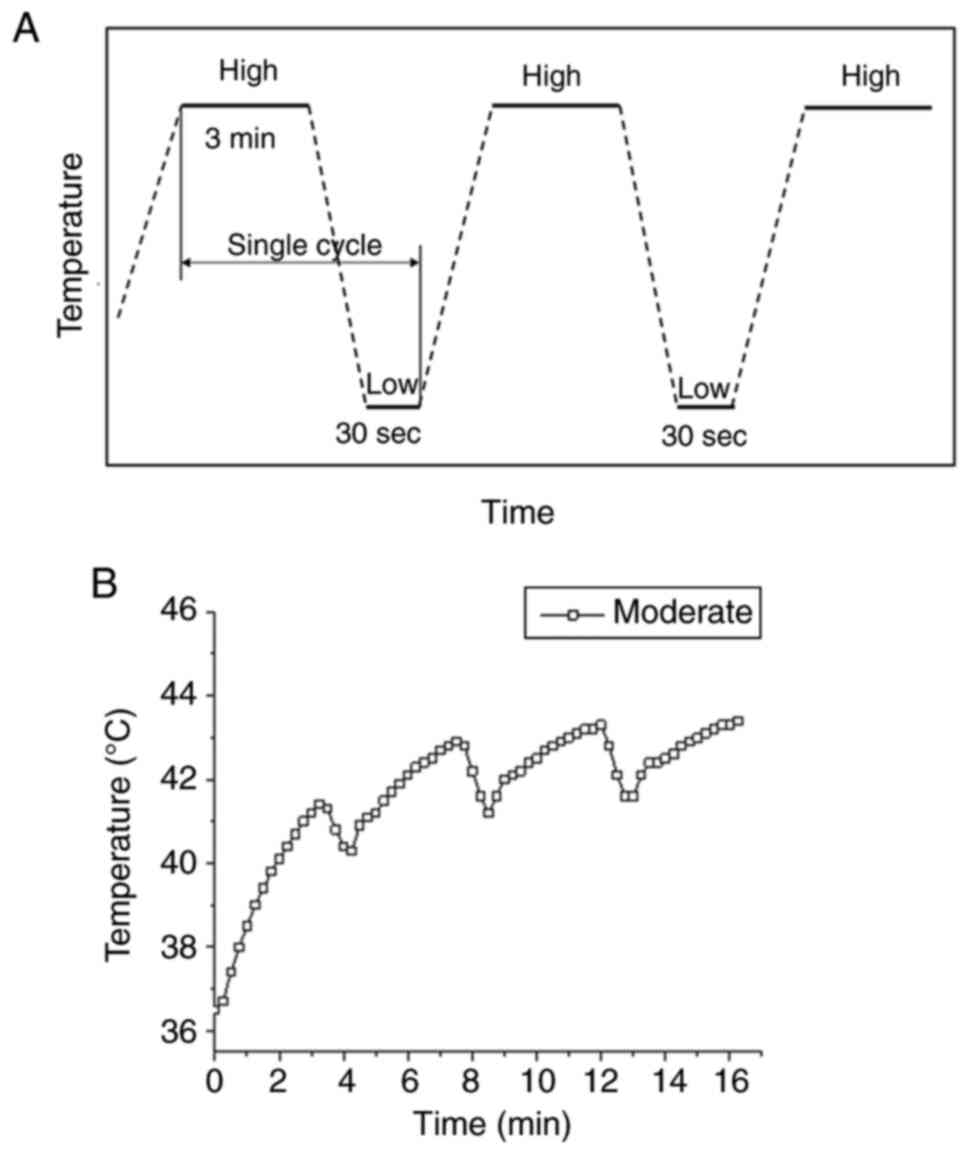
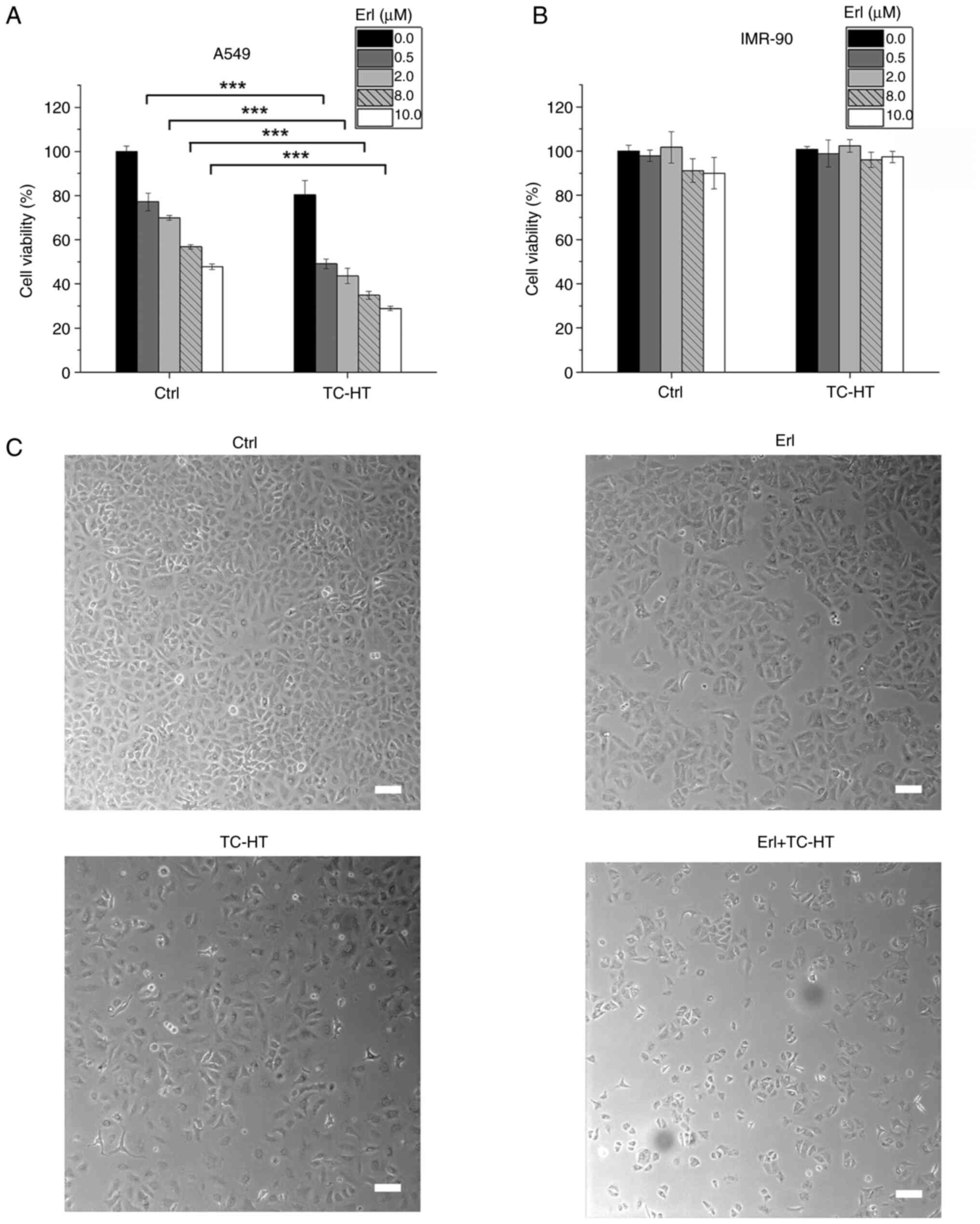
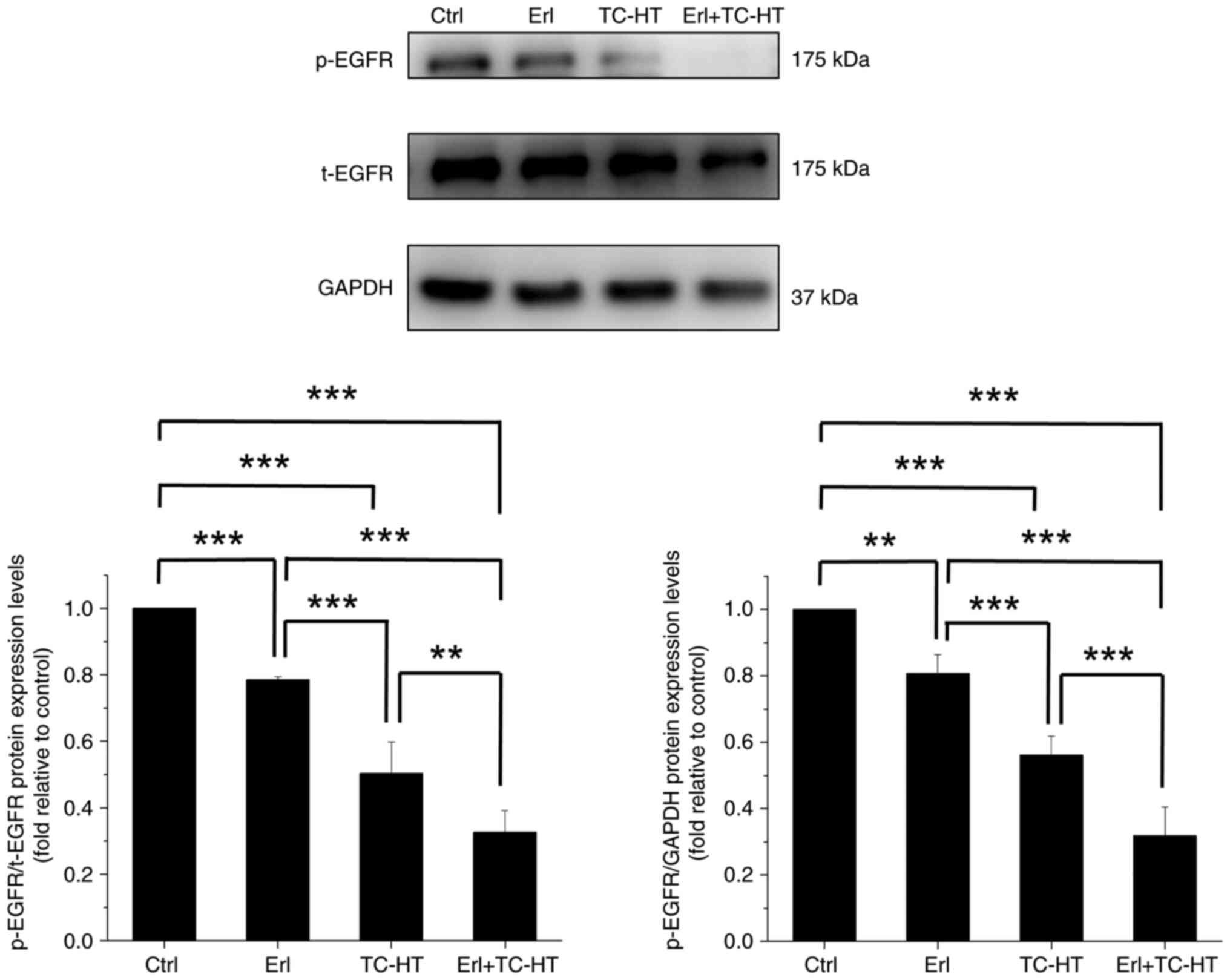
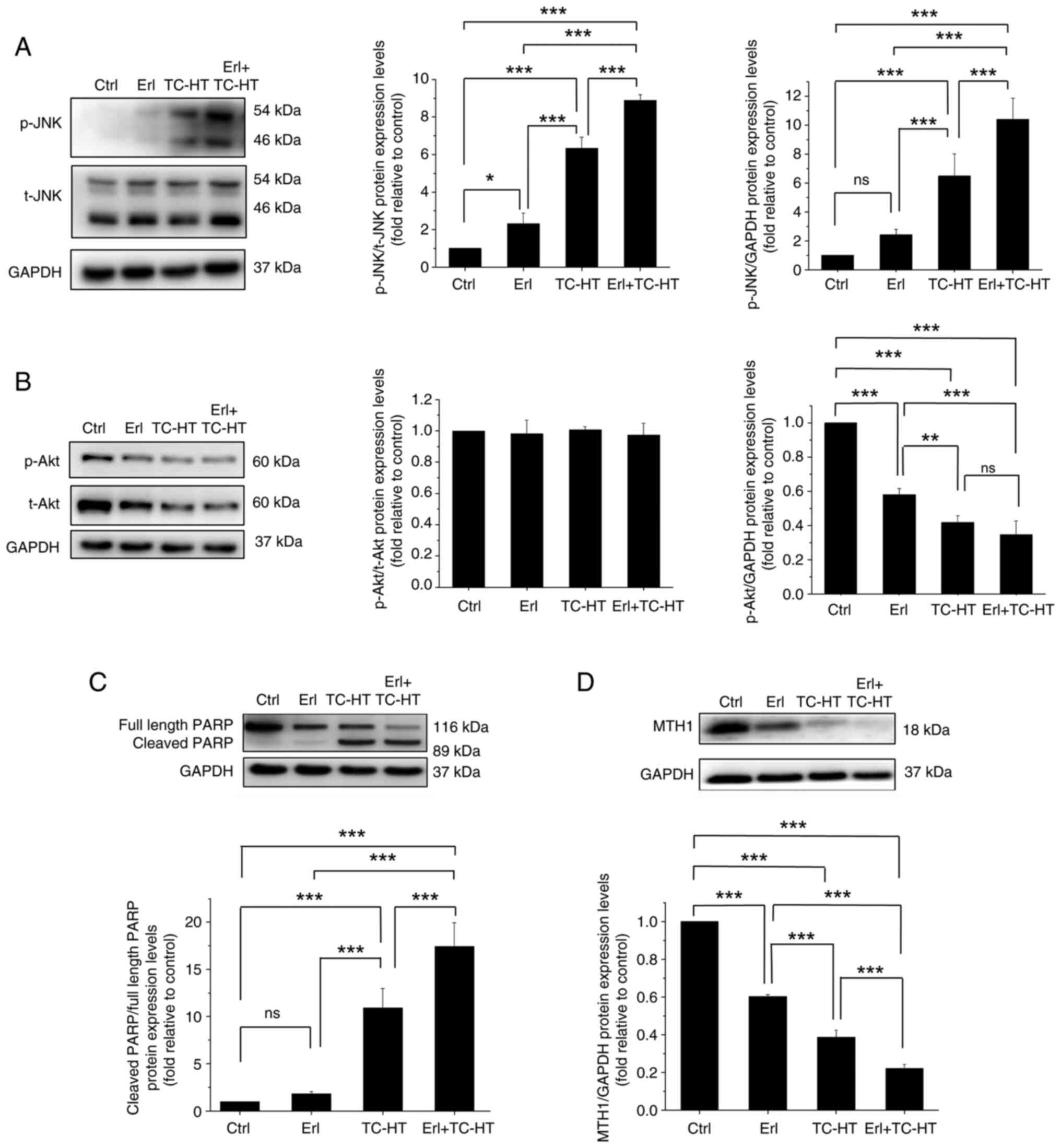
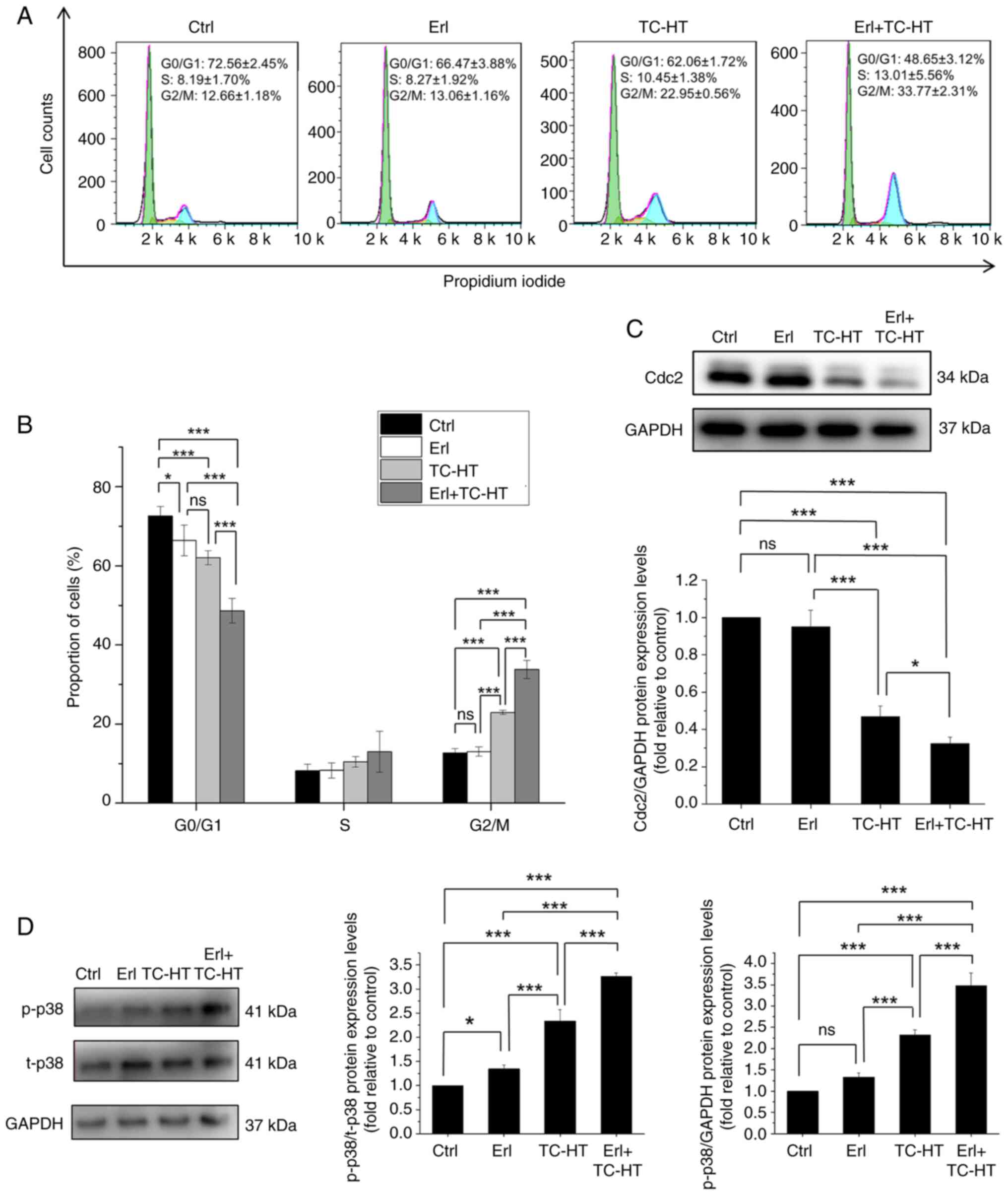
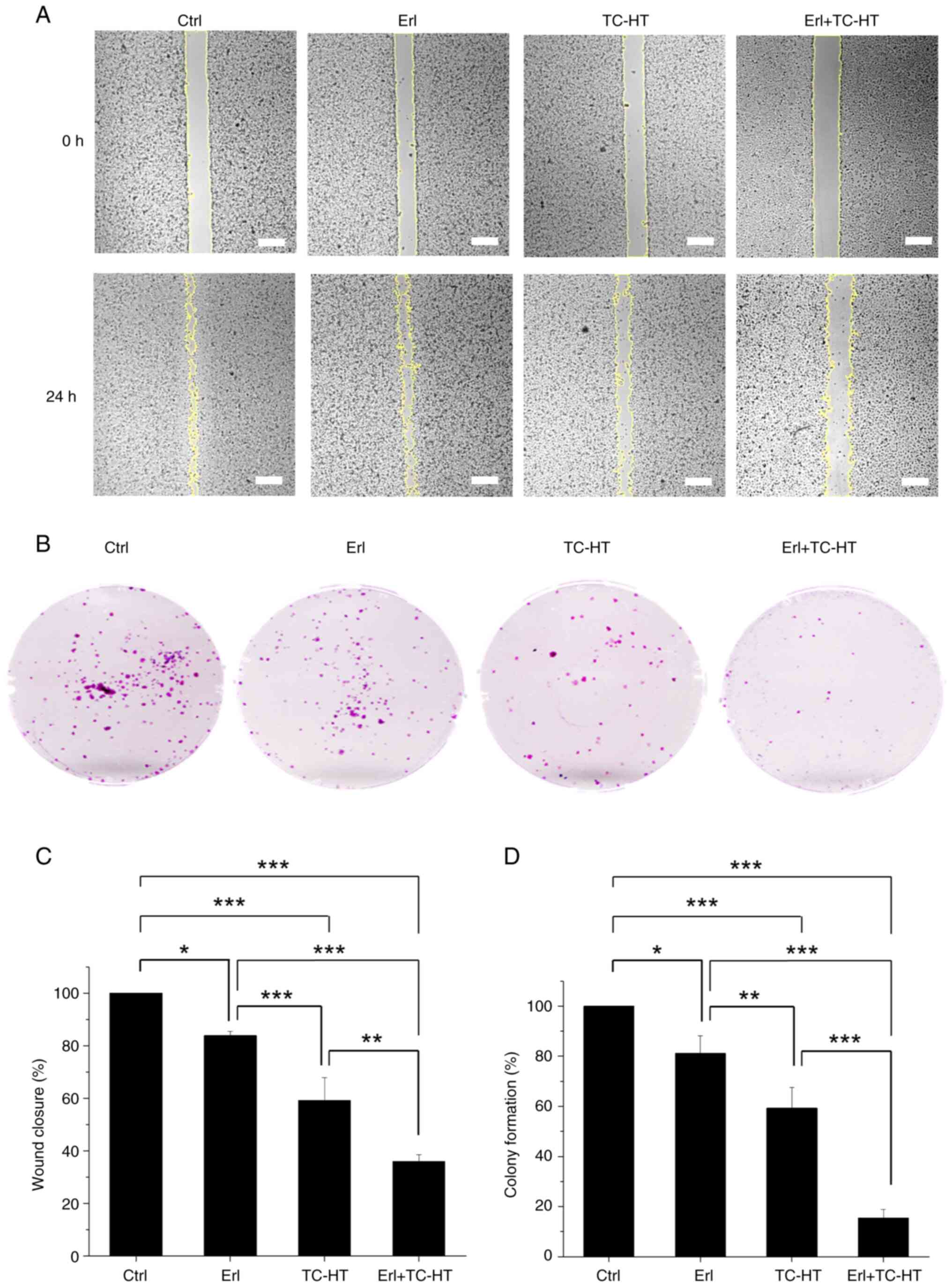
|
1
|
World Health Organization, . WHO report on
cancer: Setting priorities, investing wisely and providing care for
all. World Health Organization; 2020
|
|
2
|
Balani C, Goss G and Blumenschein G Jr:
Recent clinical developments and rationale for combining targeted
agents in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer Treat Rev.
38:174–184. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Imyanitov EN, Iyevleva AG and Levchenko
EV: Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung
cancer: Current status and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hemat.
157:1031942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wieduwilt MJ and Moasser MM: The epidermal
growth factor receptor family: Biology driving targeted
therapeutics. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:1566–1584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yewale C, Baradia D, Vhora I, Patil S and
Misra A: Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer: A
review of trends and strategies. Biomaterials. 34:8690–8707. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wee P and Wang Z: Epidermal growth factor
receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers (Basel).
29:522017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ciardiello F, De Vita F, Orditura M and
Tortora G: The role of EGFR inhibitors in nonsmall cell lung
cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 16:130–135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gridelli C, Maione P, Bareschino MA,
Schettino C, Sacco PC, Ambrosio R, Barbato V, Falanga M and Rossi
A: Erlotinib in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer:
Current status and future developments. Anticancer Res.
30:1301–1310. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin Y, Wang X and Jin H: EGFR-TKI
resistance in NSCLC patients: Mechanisms and strategies. Am J
Cancer Res. 4:411–435. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Melosky B: Supportive care treatments for
toxicities of anti-EGFR and other targeted agents. Curr Oncol.
19:59–63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu CQ, da Cunha Santos G, Ding K,
Sakurada A, Cutz JC, Liu N, Zhang T, Marrano P, Whitehead M, Squire
JA, et al: Role of KRAS and EGFR as biomarkers of response to
erlotinib in National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials
Group Study BR.21. J Clin Oncol. 26:4268–4275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calvo E and Baselga J: Ethnic differences
in response to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 24:2158–2163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garassino MC, Martelli O, Broggini M,
Farina G, Veronese S, Rulli E, Bianchi F, Bettini A, Longo F,
Moscetti L, et al: Erlotinib versus docetaxel as second-line
treatment of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and
wild-type EGFR tumours (TAILOR): A randomised controlled trial.
Lancet Oncol. 14:981–988. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Raimbourg J, Joalland MP, Cabart M, de
Plater L, Bouquet F, Savina A, Decaudin D, Bennouna J, Vallette FM
and Lalier L: Sensitization of EGFR wild-type non-small cell lung
cancer cells to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib. Mol
Cancer Ther. 16:1634–1644. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li T, Ling YH, Goldman ID and Perez-Soler
R: Schedule-dependent cytotoxic synergism of pemetrexed and
erlotinib in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:3413–3422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Almanric K, Marceau N, Cantin A and Bertin
É: Risk factors for nephrotoxicity associated with cisplatin. Can J
Hosp Pharm. 70:99–106. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oei AL, Vriend LE, Crezee J, Franken NA
and Krawczyk PM: Effects of hyperthermia on DNA repair pathways:
One treatment to inhibit them all. Radiat Oncol. 10:1652015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaur P, Hurwitz MD, Krishnan S and Asea A:
Combined hyperthermia and radiotherapy for the treatment of cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 3:3799–3823. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kwon S, Jung S and Baek SH: Combination
therapy of radiation and hyperthermia, focusing on the synergistic
Anti-cancer effects and research trends. Antioxidants. 12:9242023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang WH, Xie J, Lai ZY, Yang MD, Zhang GH,
Li Y, Mu JB and Xu J: Radiofrequency deep hyperthermia combined
with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced Non-small cell lung
cancer. Chin Med J. 132:922–927. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Beik J, Abed Z, Ghoreishi FS,
Hosseini-Nami S, Mehrzadi S, Shakeri-Zadeh A and Kamrava SK:
Nanotechnology in hyperthermia cancer therapy: From fundamental
principles to advanced applications. J Control Release.
235:205–221. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen WT, Sun YK, Lu CH and Chao CY:
Thermal cycling as a novel thermal therapy to synergistically
enhance the anticancer effect of propolis on PANC-1 cells. Int J
Oncol. 55:617–628. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu CH, Chen WT, Hsieh CH, Kuo YY and Chao
CY: Thermal cycling-hyperthermia in combination with polyphenols,
epigallocatechin gallate and chlorogenic acid, exerts synergistic
anticancer effect against human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells.
PLoS One. 14:e02176762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kuo YY, Chen WT, Lin GB, Lu CH and Chao
CY: Study on the effect of a triple cancer treatment of propolis,
thermal cycling-hyperthermia, and low-intensity ultrasound on
PANC-1 cells. Aging. 15:7496–7512. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu CH, Kuo YY, Lin GB, Chen WT and Chao
CY: Application of non-invasive low-intensity pulsed electric field
with thermal cycling-hyperthermia for synergistically enhanced
anticancer effect of chlorogenic acid on PANC-1 cells. PLoS One.
15:e02221262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsieh CH, Lu CH, Chen WT, Ma BL and Chao
CY: Application of non-invasive low strength pulsed electric field
to EGCG treatment synergistically enhanced the inhibition effect on
PANC-1 cells. PLoS One. 12:e01888852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ruttanapattanakul J, Wikan N, Potikanond S
and Nimlamool W: Combination of pinocembrin and epidermal growth
factor enhances the proliferation and survival of human
keratinocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 24:124502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zou Y, Ling YH, Sironi J, Schwartz EL,
Perez-Soler R and Piperdi B: The autophagy inhibitor chloroquine
overcomes the innate resistance of Wild-type EGFR Non-small-cell
lung cancer cells to erlotinib. J Thorac Oncol. 8:693–702. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Otahal A, Aydemir D, Tomasich E and
Minichsdorfer C: Delineation of cell death mechanisms induced by
synergistic effects of statins and erlotinib in non-small cell lung
cancer cell (NSCLC) lines. Sci Rep. 10:9592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li YL, Hu X, Li QY, Wang F, Zhang B, Ding
K, Tan BQ, Lin NM and Zhang C: Shikonin sensitizes wild type EGFR
NSCLC cells to erlotinib and gefitinib therapy. Mol Med Rep.
18:3882–3890. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Howe GA, Xiao B, Zhao H, Al-Zahrani KN,
Hasim MS, Villeneuve J, Sekhon HS, Goss GD, Sabourin LA,
Dimitroulakos J and Addison CL: Focal adhesion kinase inhibitors in
combination with erlotinib demonstrate enhanced Anti-tumor activity
in Non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01505672016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Greve G, Schiffmann I, Pfeifer D, Pantic
M, Schüler J and Lübbert M: The pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat
acts as a sensitizer for erlotinib activity in EGFR-mutated and
-wildtype non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 15:9472015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Atalay G, Cardoso F, Awada A and Piccart
MJ: Novel therapeutic strategies targeting the epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) family and its downstream effectors in
breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 14:1346–1363. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takeuchi K and Ito F: EGF receptor in
relation to tumor development: Molecular basis of responsiveness of
cancer cells to EGFR-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitors. FEBS J.
277:316–326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Akca H, Tani M, Hishida T, Matsumoto S and
Yokota J: Activation of the AKT and STAT3 pathways and prolonged
survival by a mutant EGFR in human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer.
54:25–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Matsuyama S and Reed JC:
Mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and cellular pH regulation. Cell
Death Differ. 7:1155–1165. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yi M, Dong B, Qin S, Chu Q, Wu K and Luo
S: Advances and perspectives of PARP inhibitors. Exp Hematol Oncol.
8:445732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gad H, Koolmeister T, Jemth AS, Eshtad S,
Jacques SA, Ström CE, Svensson LM, Schultz N, Lundbäck T,
Einarsdottir BO, et al: MTH1 inhibition eradicates cancer by
preventing sanitation of the dNTP pool. Nature. 508:215–221. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li DN, Yang CC, Li J, Ou Yang QG, Zeng LT,
Fan GQ, Liu TH, Tian XY, Wang JJ, Zhang H, et al: The high
expression of MTH1 and NUDT5 promotes tumor metastasis and
indicates a poor prognosis in patients with non-small-cell lung
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1868:1188952021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dorée M and Hunt T: From Cdc2 to Cdk1:
When did the cell cycle kinase join its cyclin partner? J Cell Sci.
115:2461–2464. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lim S and Kaldis P: Cdks, cyclins and
CKIs: Roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development.
140:3079–3093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chang CC, Heller JD, Kuo J and Huang RC:
Tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid induces growth arrest and
cellular apoptosis by inhibiting Cdc2 and survivin expression. Proc
Natl Acad USA Sci. 101:13239–13244. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Senju M, Sueoka N, Sato A, Iwanaga K,
Sakao Y, Tomimitsu S, Tominaga M, Irie K, Hayashi S and Sueoka E:
Hsp90 inhibitors cause G2/M arrest associated with the reduction of
Cdc25C and Cdc2 in lung cancer cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
132:150–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoshida M, Matsui Y, Iizuka A and Ikarashi
Y: G2-phase arrest through p21(WAF1/Cip1) induction and cdc2
repression by gnidimacrin in human hepatoma HLE cells. Anticancer
Res. 29:1349–1354. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Su JC, Lin KL, Chien CM, Lu CM, Chen YL,
Chang LS and Lin SR: Novel indoloquinoline derivative, IQDMA,
induces G(2)/M phase arrest and apoptosis in A549 cells through
JNK/p38 MAPK signaling activation. Life Sci. 85:505–516. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pai JT, Hsu MW, Leu YL, Chang KT and Weng
MS: Induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest via
p38/p21Waf1/Cip1-dependent signaling pathway activation by
bavachinin in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Molecules.
26:51612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Luo YH, Wang C, Xu WT, Zhang Y, Zhang T,
Xue H, Li YN, Fu ZR, Wang Y and Jin CH: 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid has
Anti-cancer effects via inducing apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle
arrest, and inhibiting migration of A549 lung cancer cells. Onco
Targets Ther. 14:5131–5144. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tamura T, Kurishima K, Nakazawa K,
Kagohashi K, Ishikawa H, Satoh H and Hizawa N: Specific organ
metastases and survival in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer.
Mol Clin Oncol. 3:217–221. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Uramoto H and Tanaka F: Recurrence after
surgery in patients with NSCLC. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
4:2422014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Passaro A, Jänne PA, Mok T and Peters S:
Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat
Cancer. 2:377–391. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tong CW, Wu WK, Loong HH, Cho WC and To
KK: Drug combination approach to overcome resistance to EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Lett.
405:100–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cavazzoni A, Alfieri RR, Cretella D,
Saccani F, Ampollini L, Galetti M, Quaini F, Graiani G, Madeddu D,
Mozzoni P, et al: Combined use of anti-ErbB monoclonal antibodies
and erlotinib enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of
wild-type erlotinib-sensitive NSCLC cell lines. Mol Cancer.
11:912012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hu X, Wu LW, Weng X, Lin NM and Zhang C:
Synergistic antitumor activity of aspirin and erlotinib: Inhibition
of p38 enhanced aspirin plus Erlotinib-induced suppression of
metastasis and promoted cancer cell apoptosis. Oncol Lett.
16:2715–2724. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen JC, Ko JC, Yen TC, Chen TY, Lin YC,
Ma PF and Lin YW: Capsaicin enhances erlotinib-induced cytotoxicity
via AKT inactivation and excision repair cross-complementary 1
(ERCC1) down-regulation in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol Res.
8:459–470. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bing C, Cheng B, Staruch RM, Nofiele J,
Wodzak Staruch M, Szczepanski D, Farrow-Gillespie A, Yang A,
Laetsch TW and Chopra R: Breath-hold MR-HIFU hyperthermia: Phantom
and in vivo feasibility. Int J Hyperthermia. 36:1084–1097. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sadhukha T, Wiedmann TS and Panyam J:
Inhalable magnetic nanoparticles for targeted hyperthermia in lung
cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 34:5163–5171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Park J and Baek SH: Combination therapy
with cinnamaldehyde and hyperthermia induces apoptosis of A549
Non-small cell lung carcinoma cells via regulation of reactive
oxygen species and mitogen-Activated protein kinase family. Int J
Mol Sci. 21:62292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Heo J, Jo Y and Yoon M: Synergistic
effects of combined hyperthermia and electric fields treatment in
non-small cell lung-cancer (NSCLC) cell lines. Clin Transl Oncol.
Oct 22–2024.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03760-6.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Cheng H, An SJ, Dong S, Zhang YF, Zhang
XC, Chen ZH, Jian-Su and Wu YL: Molecular mechanism of the
schedule-dependent synergistic interaction in EGFR-mutant non-small
cell lung cancer cell lines treated with paclitaxel and gefitinib.
J Hematol Oncol. 4:52011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Volman Y, Hefetz R, Galun E and
Rachmilewitz J: DNA damage alters EGFR signaling and reprograms
cellular response via Mre-11. Sci Rep. 12:57602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Feng YB, Chen L, Chen FX, Yang Y, Chen GH,
Zhou ZH and Xu CF: Immunopotentiation effects of apigenin on NK
cell proliferation and killing pancreatic cancer cells. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 37:39463202311611742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xu J, Jiao W, Wu DB, Yu JH, Liu LJ, Zhang
MY and Chen GX: Yishen Tongbi decoction attenuates inflammation and
bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis by regulating
JAK/STAT3/SOCS3 pathway. Front Immunol. 15:13818022024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Steen NV, Potze L, Giovannetti E,
Cavazzoni A, Ruijtenbeek R, Rolfo C, Pauwels P and Peters GJ:
Molecular mechanism underlying the pharmacological interactions of
the protein kinase C-β inhibitor enzastaurin and erlotinib in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 7:816–830.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cheng F, Peng X, Meng G, Pu Y, Luo K and
He B: Poly(ester-thioether) microspheres co-loaded with erlotinib
and α-tocopheryl succinate for combinational therapy of non-small
cell lung cancer. J Mater Chem B. 8:1728–1738. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wust P, Hildebrandt B, Sreenivasa G, Rau
B, Gellermann J, Riess H, Felix R and Schlag PM: Hyperthermia in
combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 3:487–497. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Belhadj Slimen I, Najar T, Ghram A,
Dabbebi H, Ben Mrad M and Abdrabbah M: Reactive oxygen species,
heat stress and oxidative-induced mitochondrial damage. A review.
Int J Hyperthermia. 30:513–523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Panieri E and Santoro M: ROS homeostasis
and metabolism: A dangerous liason in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Van der Zee J: Heating the patient: A
promising approach? Ann Oncol. 13:1173–1184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Salem A, Asselin MC, Reymen B, Jackson A,
Lambin P, West CML, O'Connor JPB and Faivre-Finn C: Targeting
hypoxia to improve non-Small cell lung cancer outcome. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 110:14–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Gerweck LE, Nygaard TG and Burlett M:
Response of cells to hyperthermia under acute and chronic hypoxic
conditions. Cancer Res. 39:966–972. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bicher HI, Hetzel FW, Sandhu TS, Frinak S,
Vaupel P, O'Hara MD and O'Brien T: Effects of hyperthermia on
normal and tumor microenvironment. Radiology. 137:523–530. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Overgaard J: Effect of hyperthermia on the
hypoxic fraction in an experimental mammary carcinoma in vivo. Br J
Radiol. 54:245–249. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Elming PB, Sørensen BS, Oei AL, Franken
NAP, Crezee J, Overgaard J and Horsman MR: Hyperthermia: The
optimal treatment to overcome radiation resistant hypoxia. Cancers.
11:602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kabakov AE and Yakimova AO:
Hypoxia-induced cancer cell responses driving radioresistance of
hypoxic tumors: Approaches to targeting and radiosensitizing.
Cancers. 13:11022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hu C, Yang J, Qi Z, Wu H, Wang B, Zou F,
Mei H, Liu J, Wang W and Liu Q: Heat shock proteins: Biological
functions, pathological roles, and therapeutic opportunities.
MedComm. 3:e1612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ahmed K, Zaidi SF, Mati-Ur-Rehman Rehman R
and Kondo T: Hyperthermia and protein homeostasis: Cytoprotection
and cell death. J Therm Biol. 91:1026152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Scutigliani EM, Liang Y, Crezee H, Kanaar
R and Krawczyk PM: Modulating the heat stress response to improve
Hyperthermia-Based anticancer treatments. Cancers. 13:12432021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Karar J and Maity A: Modulating the tumor
microenvironment to increase radiation responsiveness. Cancer Biol
Ther. 8:1994–2001. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Nijkamp MM, Span PN, Bussink J and
Kaanders JH: Interaction of EGFR with the tumour microenvironment:
Implications for radiation treatment. Radiother Oncol. 108:17–23.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang T, Chen L, Zhang S, Xu Y, Fan Y and
Zhang L: Effects of high-intensity focused ultrasound on
Cisplatin-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 49:1092–1098. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Qin Y, Sun Y, Liu Y, Luo Y and Zhu J:
Pilot study of radiofrequency hyperthermia in combination with
gefitinib in gefitinib-effective patients with advanced NSCLC.
Thorac Cancer. 7:422–427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sekins KM, Leeper DB, Hoffman JK, Keilman
GW, Ziskin MC, Wolfson MR and Shaffer TH: Feasibility of lung
cancer hyperthermia using breathable perfluorochemical (PFC)
liquids. Part II: Ultrasound hyperthermia. Int J Hyperthermia.
20:278–299. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|