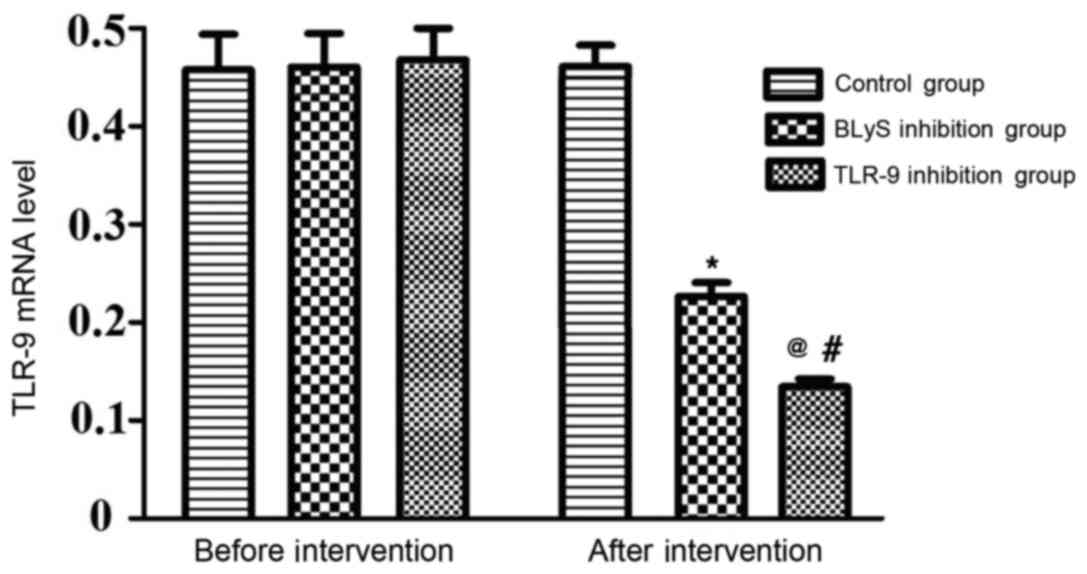
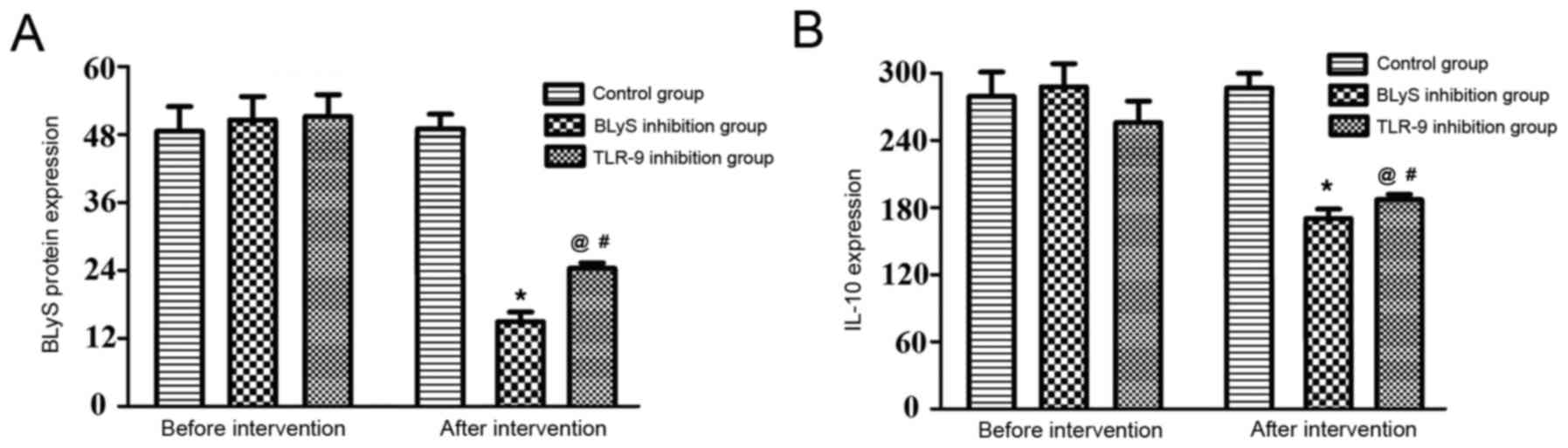
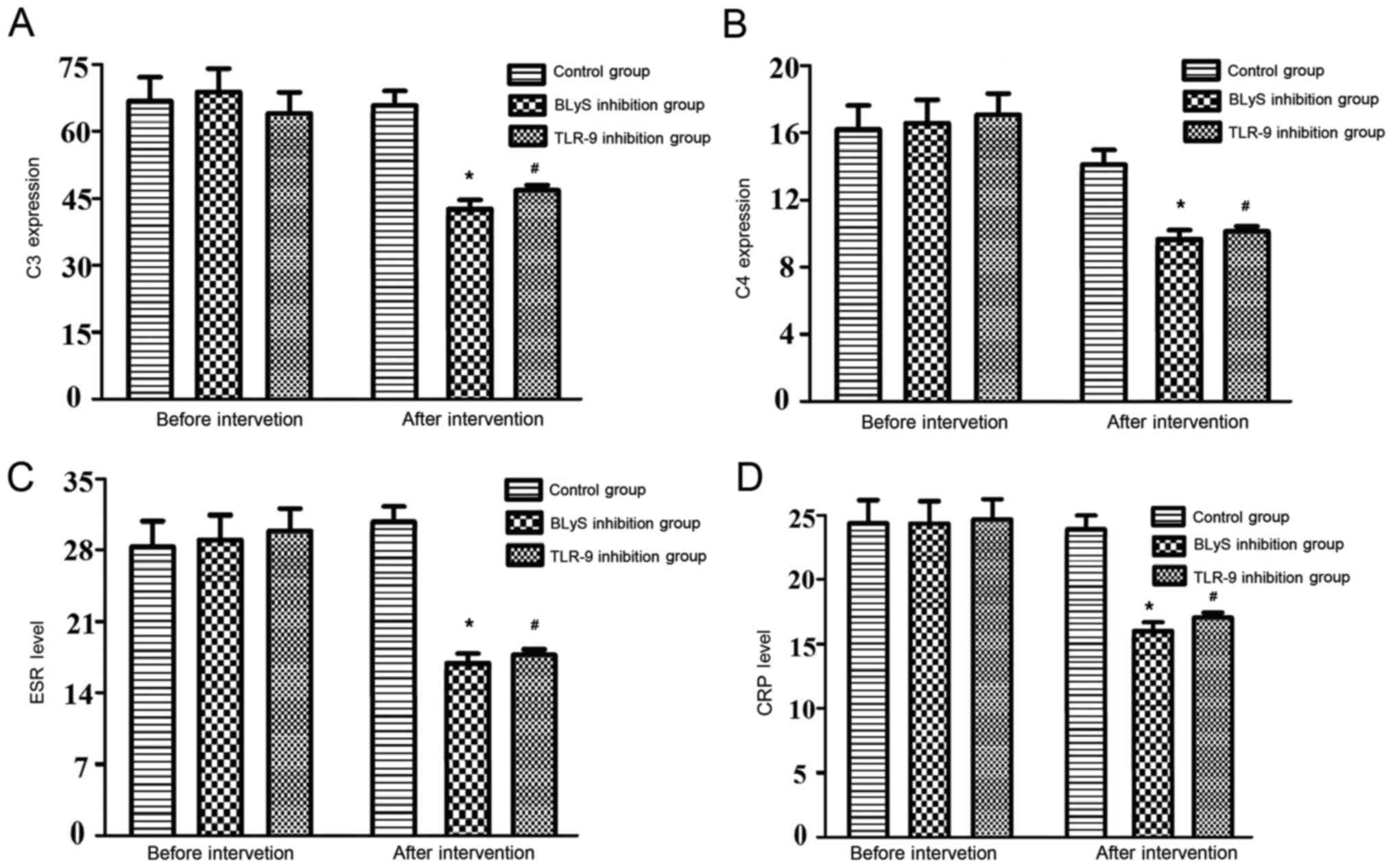
|
1
|
Thong B and Olsen NJ: Systemic lupus
erythematosus diagnosis and management. Rheumatology (Oxford).
56(suppl_1): i3–i13. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Golder V and Hoi A: Systemic lupus
erythematosus: An update. Med J Aust. 206:215–220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murphy G and Isenberg D: Effect of gender
on clinical presentation in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 52:2108–2115. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sebastiani GD, Prevete I, Iuliano A and
Minisola G: The importance of an early diagnosis in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Isr Med Assoc J. 18:212–215. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu A, Li H, Niu J, Wu S, Xue G, Yao X, Guo
Q, Wan N, Abliz P, Yang G, et al: Hyperactivation of the NLRP3
inflammasome in myeloid cells leads to severe organ damage in
experimental lupus. J Immunol. 198:1119–1129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zahran AM, Elsayh KI, Saad K, Eloseily EM,
Osman NS, Alblihed MA, Badr G and Mahmoud MH: Effects of royal
jelly supplementation on regulatory T cells in children with SLE.
Food Nutr Res. 60:329632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambrose N, Morgan TA, Galloway J, Ionnoau
Y, Beresford MW and Isenberg DA; UK JSLE Study Group, : Differences
in disease phenotype and severity in SLE across age groups. Lupus.
25:1542–1550. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Narang T, Sharma M, Gulati N and Kaur A:
Extensive hypertrophic lupus erythematosus: Atypical presentatio.
Indian J Dermatol. 57:5042012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tunnicliffe DJ, Singh-Grewal D, Kim S,
Craig JC and Tong A: Diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of
systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review of clinical
practice guidelines. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 67:1440–1452.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z,
Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, Ruiz-Irastorza G and Hughes G:
Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160392016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aringer M and Voll RE: Lupus
erythematosus-Update 2016. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 141:1785–1788.
2016.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin WY, Gong Q, Seshasayee D, Lin Z, Ou Q,
Ye S, Suto E, Shu J, Lee WP, Lee CW, et al: Anti-BR3 antibodies: A
new class of B-cell immunotherapy combining cellular depletion and
survival blockade. Blood. 110:3959–3967. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Furie R, Petri M, Zamani O, Cervera R,
Wallace DJ, Tegzová D, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Schwarting A, Merrill
JT, Chatham WW, et al: A phase III, randonlized, placebo-controlled
study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B
lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus
erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 63:3918–3930. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ko GJ, Zakaria A, Womer KL and Rabb H:
Immunologic research in kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury at johns
hopkins university. Immunol Res. 47:78–85. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo Y, Chai Q, Zhao Y, Li P, Qiao J and
Huang J: Increased activation of toll-like receptors-7 and −8 of
peripheral blood mononuclear cells and upregulated serum cytokines
in patients with pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:20472–20480. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khoryati L, Augusto JF, Shipley E,
Contin-Bordes C, Douchet I, Mitrovic S, Truchetet ME, Lazaro E,
Duffau P, Couzi L, Jacquemin C, et al: IgE inhibits Toll-like
receptor 7- and Toll-like receptor 9 mediated expression of
interferon-α by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in systemic lupus
patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:2221–2231. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Medzhitov R, Kashgarian M, Shlomchik MJ,
Teichmann LL and Schenten D: Signals via the adaptor MyD88 in B
cells and DCs make distinct and synergistic contributions to immune
activation and tissue damage in lupus. Immunity. 38:528–540. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cancro MP, D'Cruz DP and Khamashta MA: The
role of B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) in systemic lupus
erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 119:1066–1073. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramanujam M and Davidson A: BAFF blockade
for systemic lupus erythematosus: Will the promise be fulfilled?
Immunol Rev. 223:156–174. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ritterhouse LL, Crown SR, Niewold TB,
Merrill JT, Roberts VC, Dedeke AB, Neas BR, Thompson LF, Guthridge
JM and James JA: B lymphocyte stimulator levels in systemic lupus
erythematosus: Higher circulating levels in African American
patients and increased production after influenza vaccination in
patients with low baseline levels. Arthritis Rheum. 63:3931–3941.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stohl W: Biologic differences between
various inhibitors of the BLyS/BAFF pathway: Should we expect
differences between belimumab and other inhibitors in development?
Curr Rheumatol Rep. 14:303–309. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ju S, Zhang D, Wang Y, Ni H, Kong X and
Zhong R: Correlation of the expression levels of BLyS and its
receptors mRNA in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin
Biochem. 39:1131–1137. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scholz JL, Oropallo MA, Sindhava V, Goenka
R and Cancro MP: The role of B lymphocyte stimulator in B cell
biology: Implications for the treatment of lupus. Lupus.
22:350–360. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Treml LS, Carlesso G, Hoek KL, Stadanlick
JE, Kambayashi T, Bram RJ, Cancro MP and Khan WN: TLR stimulation
modifies BLyS receptor expression in follicular and marginal zone B
cells. J Immunol. 178:7531–7539. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cargill EJ and Womack JE: Detection of
polymorphisms in bovine toll-like receptors 3, 7, 8 and 9.
Genomics. 89:745–755. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park BS and Lee JO: Recognition of
lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Exp Mol Med.
45:e662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Castellano G, Stasi A, Intini A, Gigante
M, Di Palma AM, Divella C, Netti GS, Prattichizzo C, Pontrelli P,
Crovace A, et al: Endothelial dysfunction and renal fibrosis in
endotoxemia-induced oliguric kidney injury: Possible role of
LPS-binding protein. Crit Care. 18:5202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim BM, Jeong CB, Rhee JS and Lee JS:
Transcriptional profiles of Rel/NF-κB, inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) and
lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α factor (LITAF) in the
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and two Vibrio sp.-exposed intertidal
copepod, Tigriopus japonicus. Dev Comp Immunol. 42:229–239. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thompson JS, Bixler SA, Qian F, Vora K,
Scott ML, Cachero TG, Hession C, Schneider P, Sizing ID, Mullen C,
et al: BAFF-R, a newly identified TNF receptor that specifically
interacts with BAFF. Science. 293:2108–2111. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pone EJ, Lou Z, Lam T, Greenberg ML, Wang
R, Xu Z and Casali P: B cell TLR1/2, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 interact
in induction of class switch DNA recombination: Modulation by BCR
and CD40 and relevance to T-independent antibody responses.
Autoimmunity. 48:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu K and Mohan C: Altered B-cell
signaling in lupus. Autoimmun Rev. 8:214–218. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marshak-Rothstein A, Viglianti GA, Moody
KL, Uccellini MB and Avalos AM: Toll-like receptor-dependent immune
complex activation of B cells and dendritic cells. Methods Mol
Biol. 1390:249–272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Morimoto S, Nakano S, Watanabe T, Tamayama
Y, Mitsuo A, Nakiri Y, Suzuki J, Nozawa K, Amano H, Tokano Y, et
al: Expression of B-cell activating factor of the tumour necrosis
factor family (BAFF) in T cells in active systemic lupus
erythematosus: The role of BAFF inT cell-dependent B cell
pathogenic autoantibody production. Rheumatology. 46:1083–1086.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hua Z and Hou B: TLR signaling in B-cell
development and activation. Cell Mol Immunol. 10:103–106. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD and Song GG:
Association between toll-like receptor polymorphisms and systemic
lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis update. Lupus. 25:593–601.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bao Y and Cao X: The immune potential and
immunopathology of cytokine-producing B cell subsets: A
comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 55:10–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abdallah E, Waked E and Abdelwahab MA:
Evaluating the association of interleukin-10 gene promoter-592 A/C
polymorphism with lupus nephritis susceptibility. Kidney Res Clin
Pract. 35:29–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Timóteo RP, Micheli DC, Teodoro RB, Freire
M, Bertoncello D, Murta EF and Tavares-Murta BM: Characterization
of inflammatory markers associated with systemic lupus
erythematosus patients undergoing treatment. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl
Ed. 56:497–503. 2016.(In English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Heinemann K, Wilde B, Hoerning A, Tebbe B,
Kribben A, Witzke O and Dolff S: Decreased IL-10(+) regulatory B
cells (Bregs) in lupus nephritis patients. Scand J Rheumatol.
45:312–316. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Steiman AJ, Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Noamani
B, Landolt-Marticorena C, Urowitz MB and Wither JE: Lack of
interferon and proinflammatory cyto/chemokines in serologically
active clinically quiescent systemic lupus erythematosus. J
Rheumatol. 42:2318–2326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu Y, Zeumer L, Reeves WH and Morel L:
Induced murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Methods Mol
Biol. 1134:103–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Davison LM and Jørgensen TN: Sialic
acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin H-positive plasmacytoid
dendritic cells drive spontaneous lupus-like disease development in
B6. Nba2 mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:1012–1022. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jain S, Park G, Sproule TJ, Christianson
GJ, Leeth CM, Wang H, Roopenian DC and Morse HC III: Interleukin 6
accelerates mortality by promoting the progression of the systemic
lupus erythematosus-like disease of BXSB. Yaa Mice. PLoS One.
11:e01530592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee HY, Kim YI, Lee JW, Byun JY, Park MS
and Yeo SG: Decreased expression of TLR-9 and cytokines in the
presence of bacteria in patients with otitis media with effusion.
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 6:195–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Capobianco MP, Cassiano GC, Furini AA,
Storti-Melo LM, Pavarino EC, Galbiatti AL, Fraga VD, Conceição LM,
Couto VS, Couto AA and Machado RL: No evidence for association of
the CD40, CD40L and BLYS polymorphisms, B-cell co-stimulatory
molecules, with Brazilian endemic Plasmodium vivax malaria. Trans R
Soc Trop Med Hyg. 107:377–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tan X, Fujiu K, Manabe I, Nishida J,
Yamagishi R, Nagai R and Yanagi Y: Choroidal neovascularization is
inhibited via an intraocular decrease of inflammatory cells in mice
lacking complement component C3. Sci Rep. 5:157022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Taylor SH, Ripley BS, Martin T, De-Wet LA,
Woodward FI and Osborne CP: Physiological advantages of C4 grasses
in the field: A comparative experiment demonstrating the importance
of drought. Glob Chang Biol. 20:1992–2003. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|