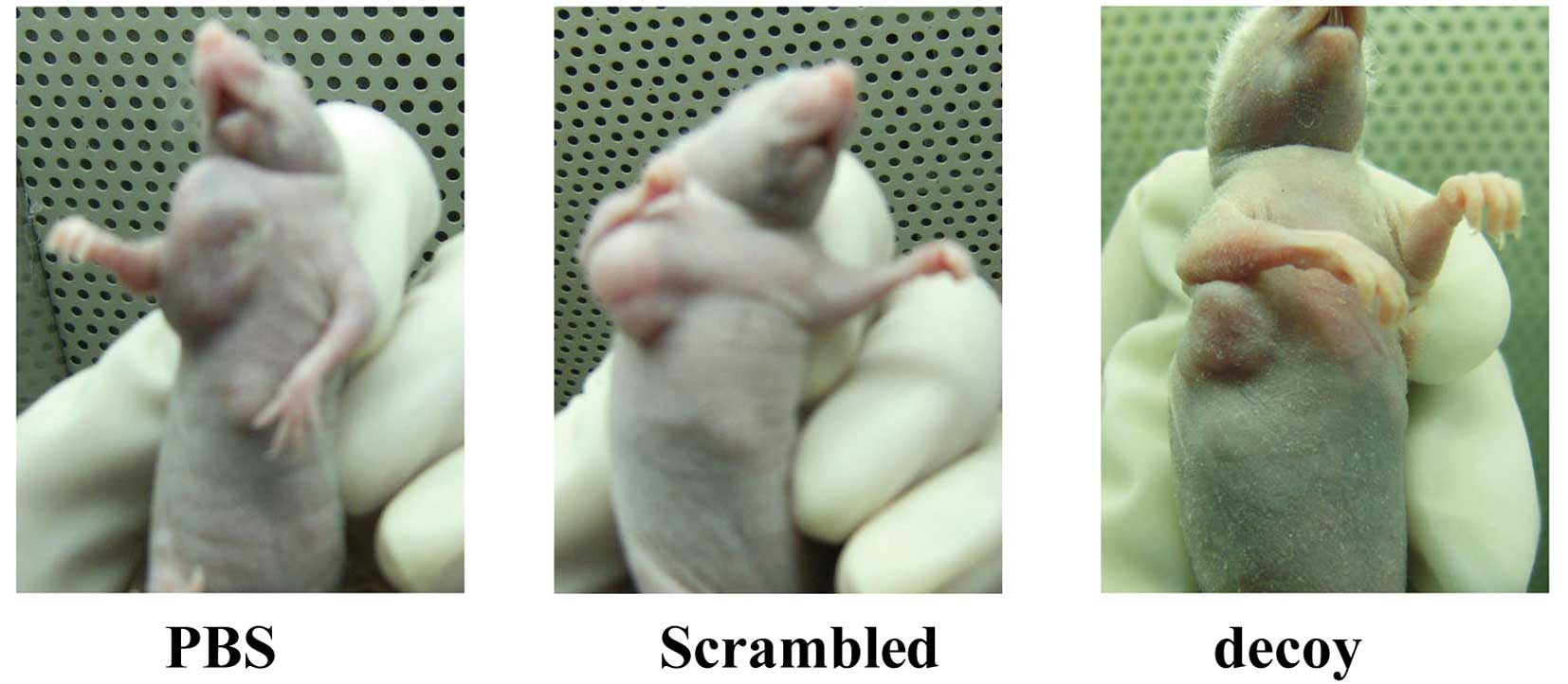
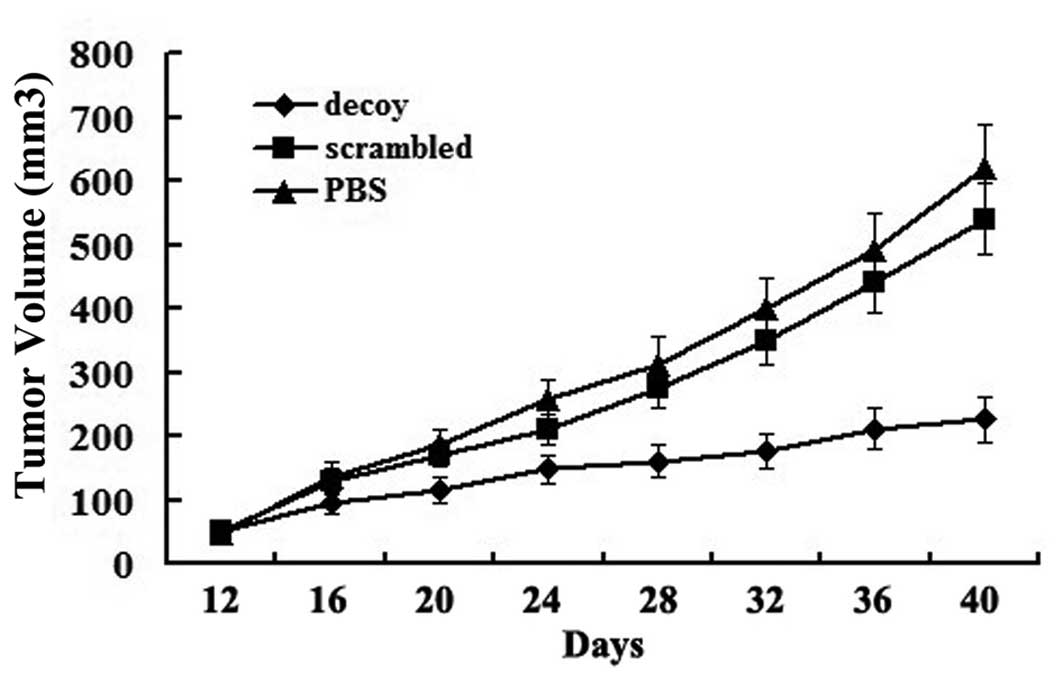
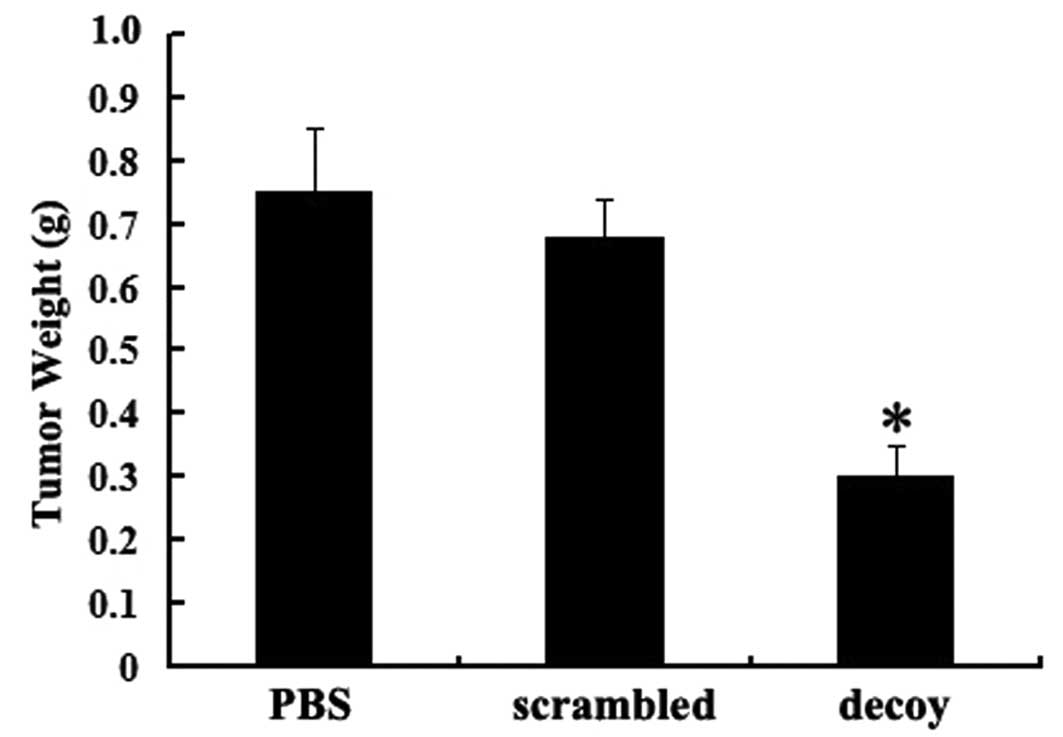
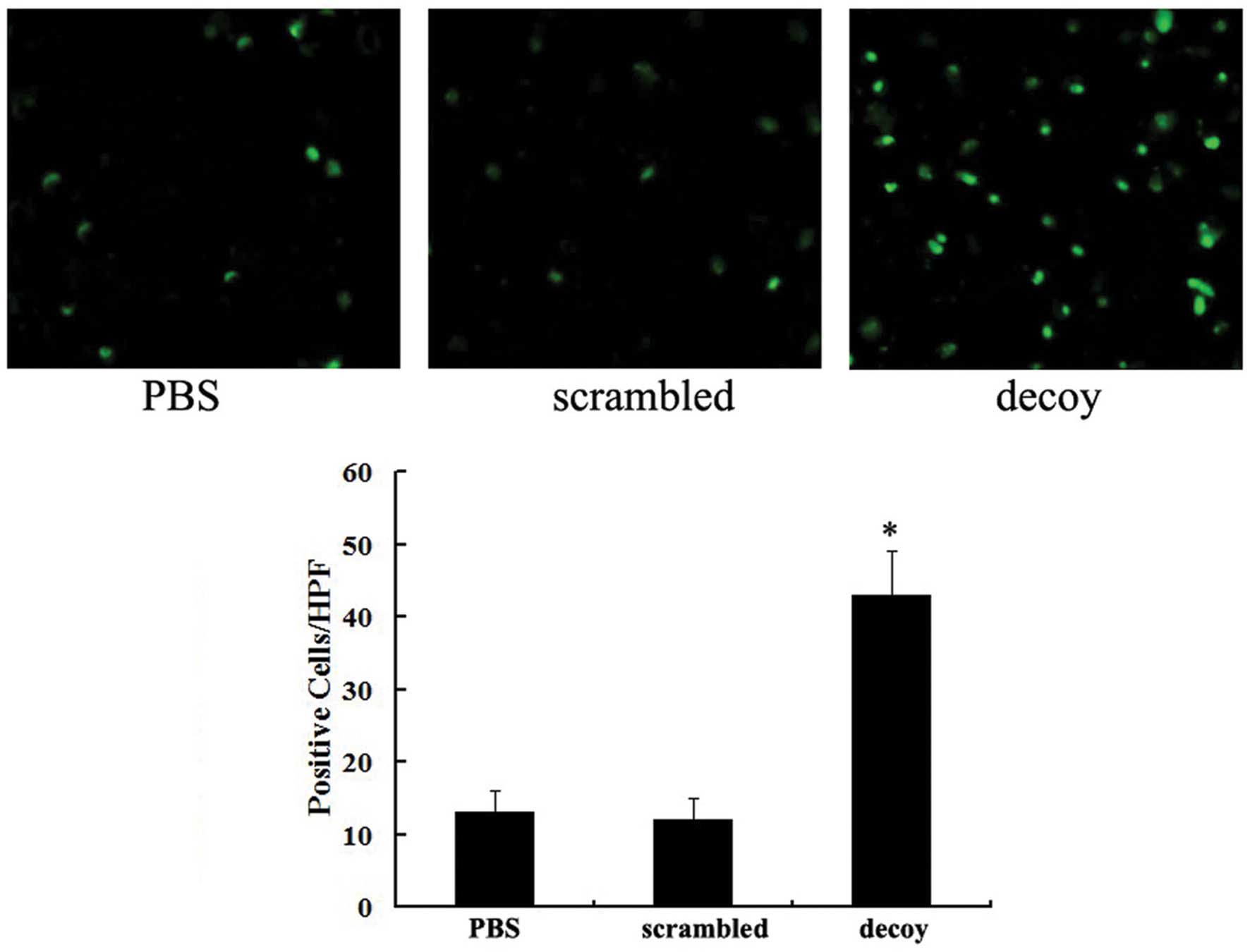
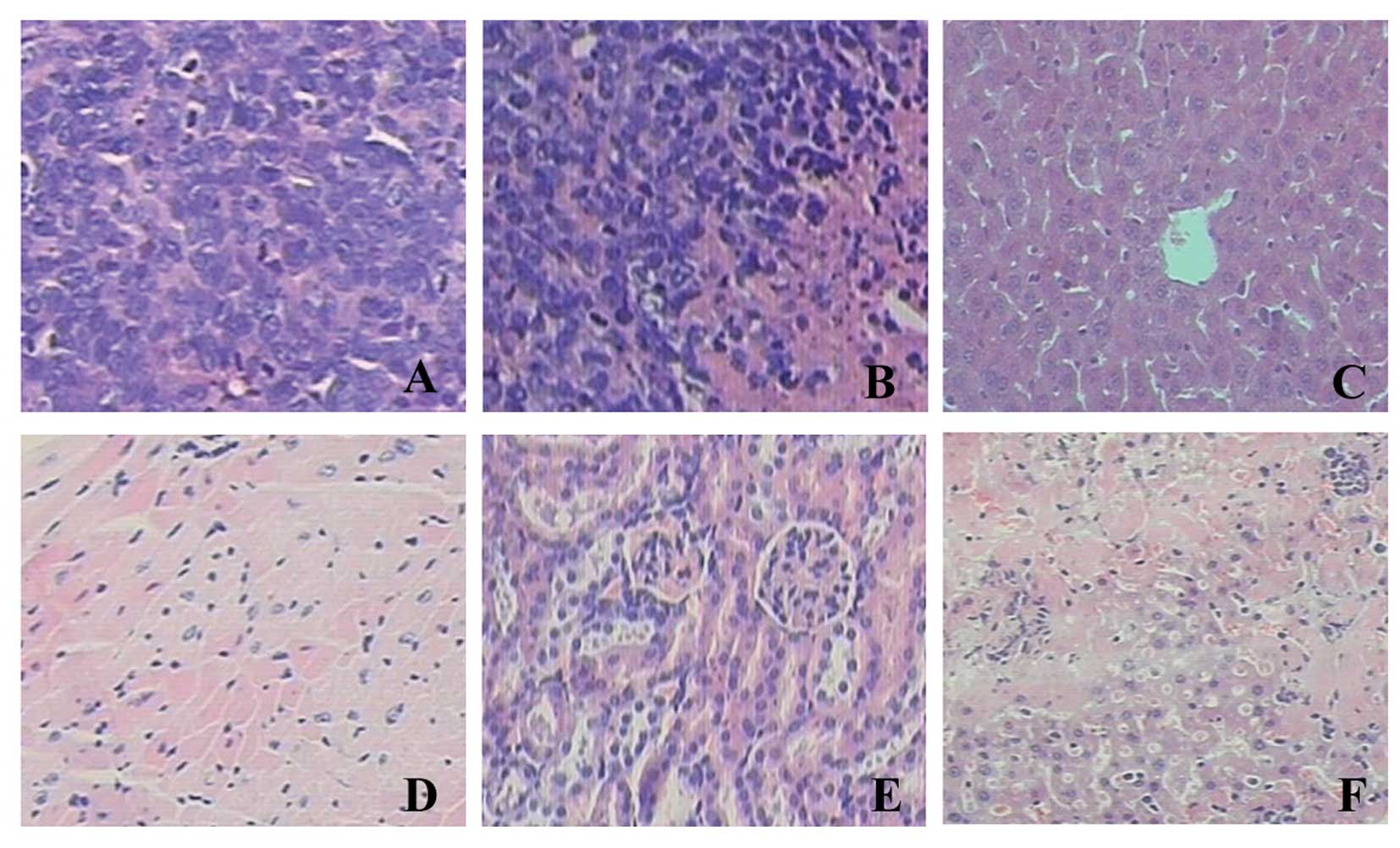
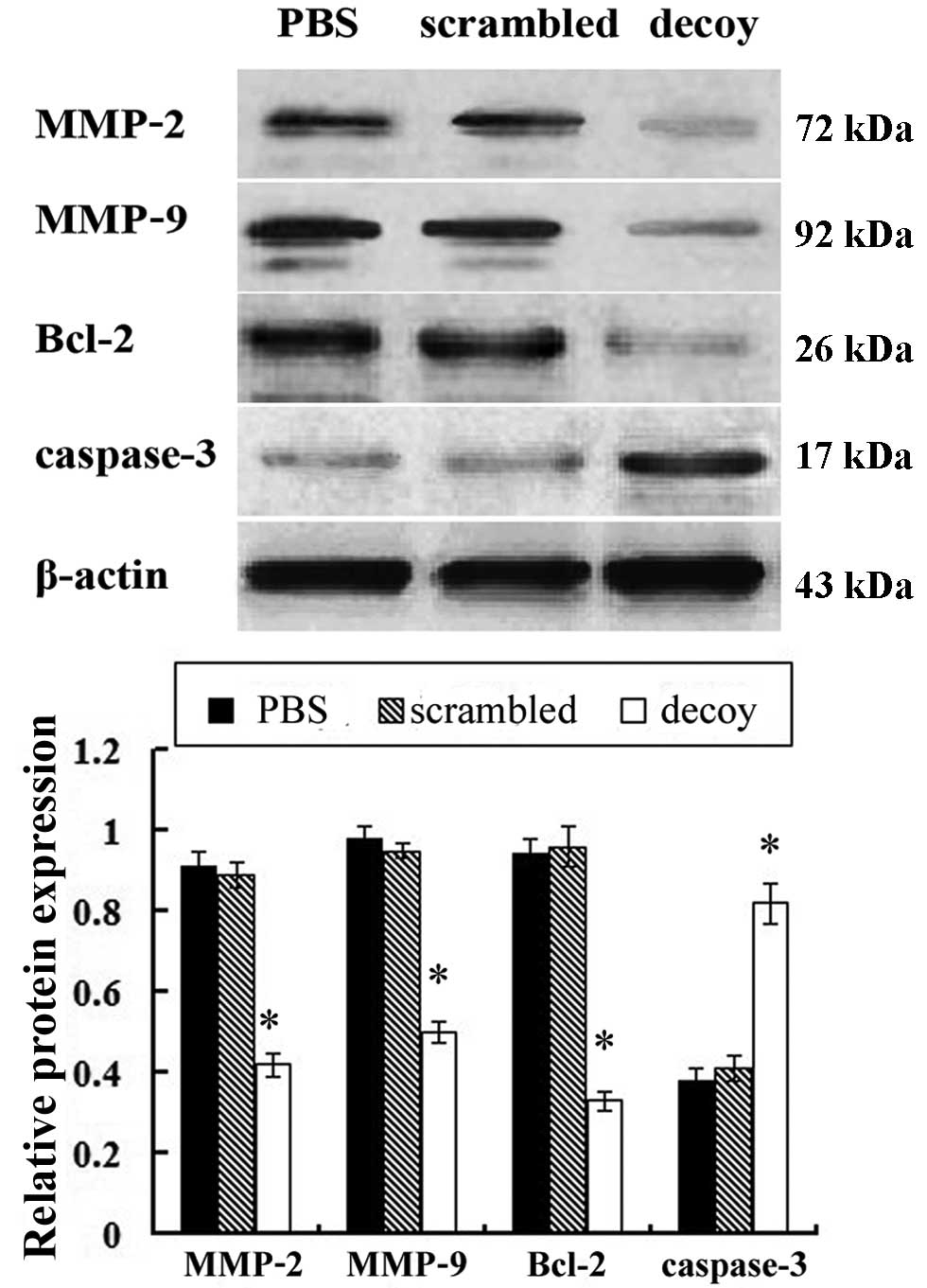
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J,
Smigal C and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
56:106–130. 2006.
|
|
2
|
Edwards BK, Brown ML, Wingo PA, Howe HL,
Ward E, Ries LA, et al: Annual report to the nation on the status
of cancer, 1975–2002, featuring population-based trends in cancer
treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 97:1407–1427. 2005.
|
|
3
|
Bromberg JF: Activation of STAT proteins
and growth control. Bioessays. 23:161–169. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buettner R, Mora LB and Jove R: Activated
STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for
therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 8:945–954.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro
MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L,
Fernandez-Luna JL, Nunez G, Dalton WS and Jove R: Constitutive
activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in
human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity. 10:105–115. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao B, Shen X, Kunos G, Meng Q, Goldberg
ID, Rosen EM and Fan S: Constitutive activation of JAK-STAT3
signaling by BRCA1 in human prostate cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
488:179–184. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Al Zaid Siddiquee K and Turkson J: STAT3
as a target for inducing apoptosis in solid and hematological
tumors. Cell Res. 18:254–267. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Ali-Seyed M, Gunduz M, Xia
W, Wei Y, Bartholomeusz G, Shih JY and Hung MC: Nuclear interaction
of EGFR and STAT3 in the activation of the iNOS/NO pathway. Cancer
Cell. 7:575–589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park OK, Schaefer TS and Nathans D: In
vitro activation of Stat3 by epidermal growth factor receptor
kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:13704–13708. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Turkson J and Jove R: STAT proteins: novel
molecular targets for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene.
19:6613–6626. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bromberg J and Darnell JE Jr: The role of
STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular
function. Oncogene. 19:2648–2673. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Landen CN Jr, Lin YG, Armaiz Pena GN, et
al: Neuroendocrine modulation of signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 67:10389–10396.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duan Z, Foster R, Bell DA, Mahoney J,
Wolak K, Vaidya A, Hampel C, Lee H and Seiden MV: Signal
transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathway activation in
drug-resistant ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5055–5063. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nefedova Y and Gabrilovich DI: Targeting
of Jak/STAT pathway in antigen presenting cells in cancer. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 7:71–77. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schlessinger K and Levy DE: Malignant
transformation but not normal cell growth depends on signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res.
65:5828–5834. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cai L, Zhang G, Tong X, You Q, An Y, Wang
Y, Guo L, Wang T, Zhu D and Zheng J: Growth inhibition of human
ovarian cancer cells by blocking STAT3 activation with small
interfering RNA. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 148:73–80. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Ma X, Xiao L, Tang M, Weng X, Sun
L and Cao Y: Uniquely modified RNA oligonucleotides targeting STAT3
suppress melanoma growth both in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol
Ther. 8:2065–2072. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu J, Li G, Sun T, Su Y, Zhang X, Shen J,
Tian Z and Zhang J: Blockage of the STAT3 signaling pathway with a
decoy oligonucleotide suppresses growth of human malignant glioma
cells. J Neurooncol. 89:9–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Souissi I, Najjar I, Ah-Koon L, et al: A
STAT3-decoy oligonucleotide induces cell death in a human
colorectal carcinoma cell line by blocking nuclear transfer of
STAT3 and STAT3-bound NF-κB. BMC Cell Biology. 12:142011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Liu P, Zhang B, Wang A and Yang
M: Role of STAT3 decoy oligodeoxynucleotides on cell invasion and
chemosensitivity in human epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Cancer
Genet Cytogenet. 197:46–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leong PL, Andrews GA, Johnson DE, Dyer KF,
Xi S, Mai JC, Robbins PD, Gadiparthi S, Burke NA, Watkins SF and
Grandis JR: Targeted inhibition of Stat3 with a decoy
oligonucleotide abrogates head and neck cancer cell growth. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:4138–4143. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Zhang L, Wang L, Wei H and Tian
Z: Therapeutic effects of STAT3-decoy oligodeoxynucleotide on human
lung cancer in xenograft mice. BMC Cancer. 7:1492007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Devalapally H, Duan Z, Seiden MV and Amiji
MM: Modulation of drug resistance in ovarian adenocarcinoma by
enhancing intracellular ceramide using tamoxifen-loaded
biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Clin Cancer Res.
14:3193–3203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mao HL, Liu PS, Zheng JF, Zhang PH, Zhou
LG, Xin G and Liu C: Transfection of Smac/DIABLO sensitizes
drug-resistant tumor cells to TRAIL or paclitaxel-induced apoptosis
in vitro. Pharmacol Res. 56:483–492. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bromberg J: Stat proteins and oncogenesis.
J Clin Invest. 109:1139–1142. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fletcher S, Turkson J and Gunning PT:
Molecular approaches towards the inhibition of the signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) protein.
ChemMedChem. 3:1159–1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leeman RJ, Lui VW and Grandis JR: STAT3 as
a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer. Expert Opin Biol
Ther. 6:231–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Colomiere M, Findlay J, Ackland L and
Ahmed N: Epidermal growth factor-induced ovarian carcinoma cell
migration is associated with JAK2/STAT3 signals and changes in the
abundance and localization of alpha6beta1 integrin. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 41:1034–1045. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jing N and Tweardy DJ: Targeting Stat3 in
cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs. 16:601–607. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen J, Li R and Li G: Inhibitory effects
of decoy-ODN targeting activated STAT3 on human glioma growth in
vivo. In Vivo. 23:237–243. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liotta LA and Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tumor
invasion and metastasis: an imbalance of positive and negative
regulation. Cancer Res. 51(Suppl 18): 5054S–5059S. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Belotti D, Paganoni P, Manenti L, Garofalo
A, Marchini S, Taraboletti G and Giavazzi R: Matrix
metalloproteinases (MMP9 and MMP2) induce the release of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by ovarian carcinoma cells:
implications for ascites formation. Cancer Res. 63:5224–5229.
2003.
|
|
33
|
dos Santos LG, Lopes-Costa PV, dos Santos
AR, Facina G and da Silva BB: Bcl-2 oncogene expression in estrogen
receptor-positive and negative breast carcinoma. Eur J Gynaecol
Oncol. 29:459–461. 2008.
|
|
34
|
Alas S and Bonavida B: Inhibition of
constitutive STAT3 activity sensitizes resistant non-Hodgkin's
lymphoma and multiple myeloma to chemotherapeutic drug-mediated
apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 9:316–326. 2003.
|
|
35
|
Selvendiran K, Koga H, Ueno T, et al:
Luteolin promotes degradation in signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 in human hepatoma cells: an implication for the
antitumor potential of flavonoids. Cancer Res. 66:4826–4834. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Enari M, Sakahira H, Yokoyama H, Okawa K,
Iwamatsu A and Nagata S: A caspase-activated DNase that degrades
DNA during apoptosis and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature. 391:43–50.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kamada S, Kikkawa U, Tsujimoto Y and
Hunter T: Nuclear translocation of caspase-3 is dependent on its
proteolytic activation and recognition of a substrate-like
protein(s). J Biol Chem. 280:857–860. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|