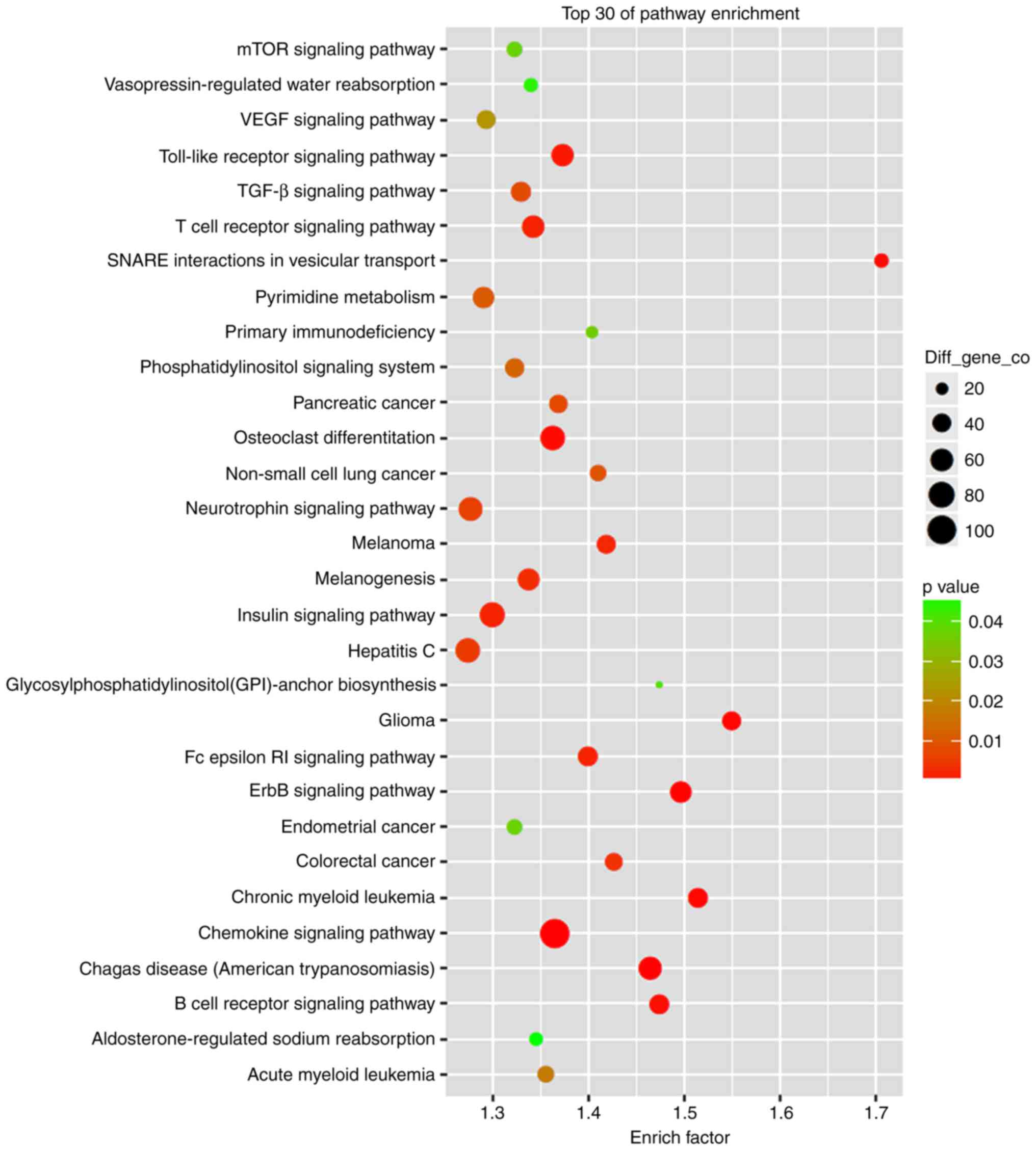
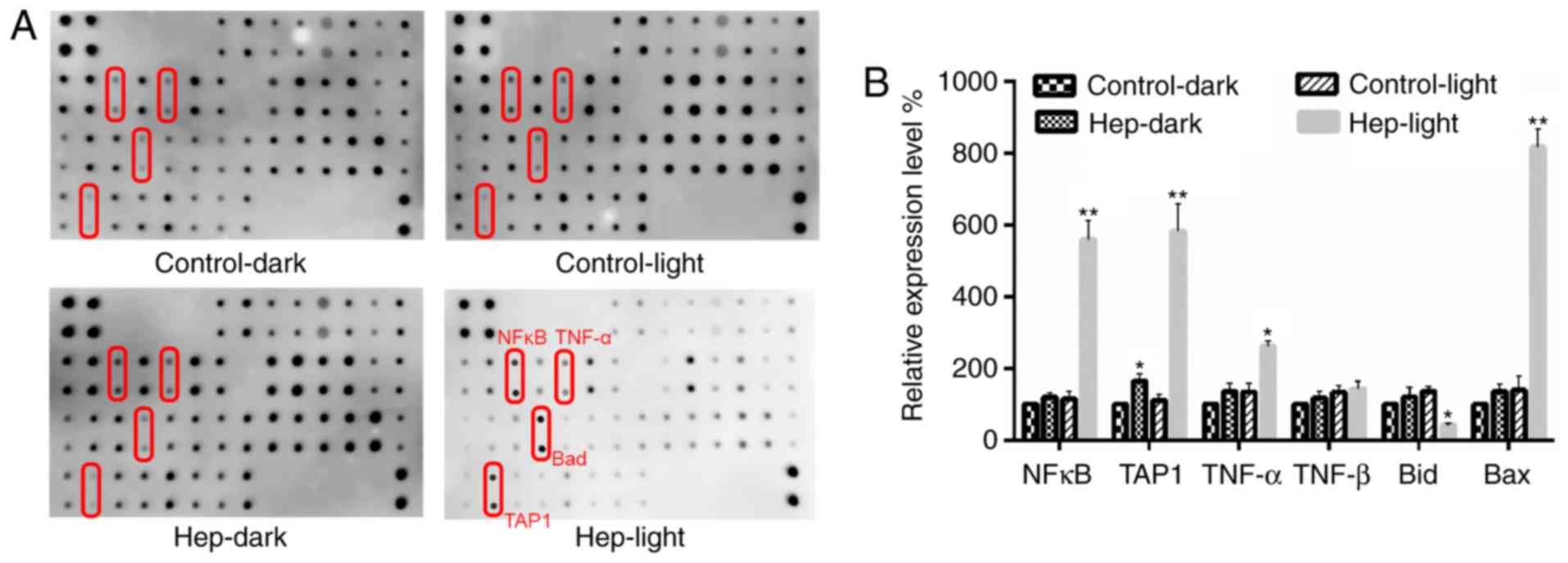
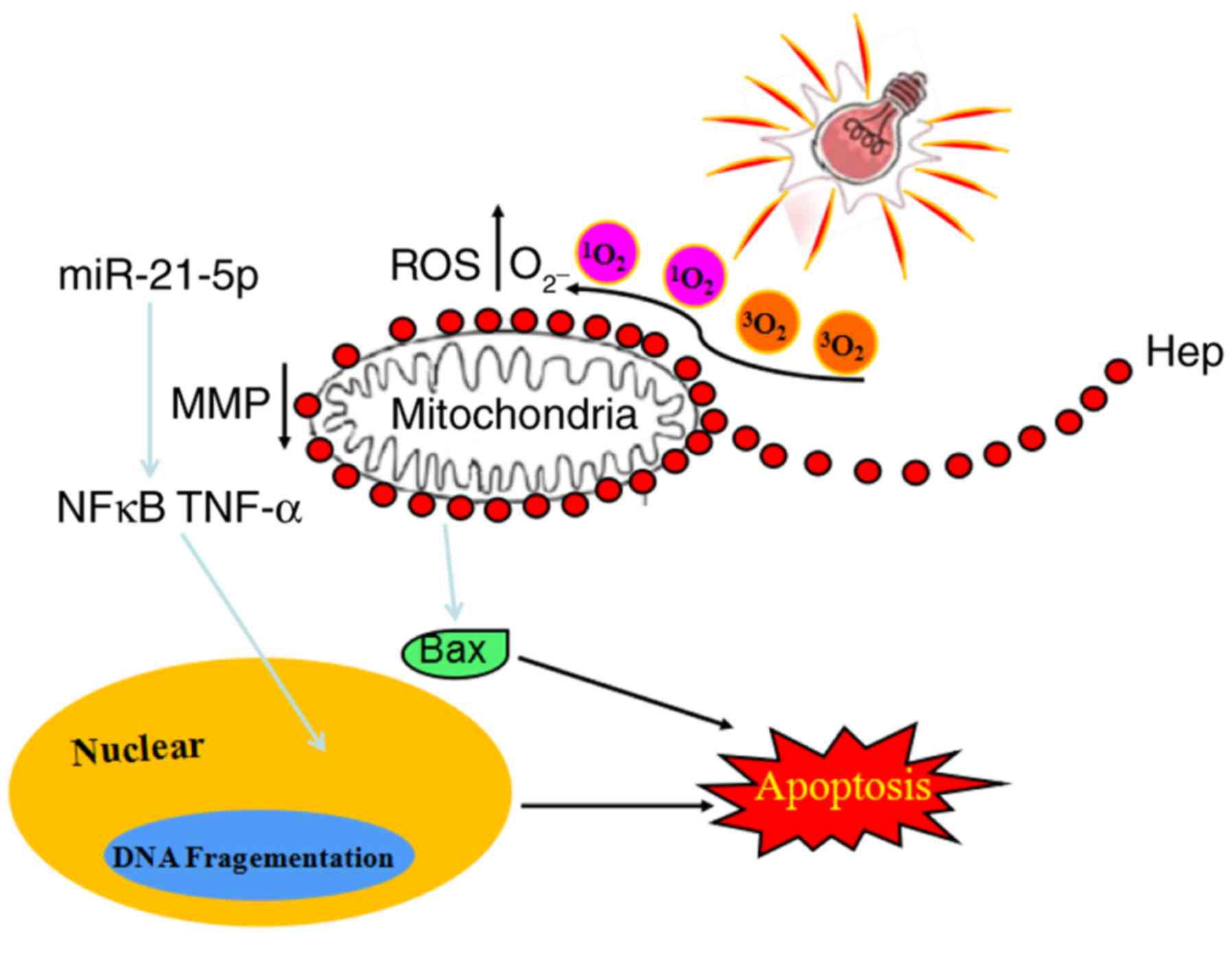
|
1
|
Duan R, Han L, Wang Q, Wei J, Chen L,
Zhang J, Kang C and Wang L: HOXA13 is a potential GBM diagnostic
marker and promotes glioma invasion by activating the Wnt and TGF-β
pathways. Oncotarget. 6:27778–27793. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Watkins S, Robel S, Kimbrough IF, Robert
SM, Ellisdavies G and Sontheimer H: Disruption of
astrocyte-vascular coupling and the blood-brain barrier by invading
glioma cells. Nature Communications. 5:41962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li W and Graeber MB: The molecular profile
of microglia under the influence of glioma. Neuro Oncol.
14:958–978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saito T, Muragaki Y, Maruyama T, Tamura M,
Nitta M and Okada Y: Intraoperative functional mapping and
monitoring during glioma surgery. Neurol Med Chir. 55(Suppl 1):
S1–S13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shi M, Fortin D, Sanche L and Paquette B:
Convection-enhancement delivery of platinum-based drugs and
Lipoplatin™ to optimize the concomitant effect with radiotherapy in
F98 glioma rat model. Invest New Drugs. 33:555–563. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tobias A, Ahmed A, Moon KS and Lesniak MS:
The art of gene therapy for glioma: A review of the challenging
road to the bedside. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 84:213–222.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Charest G, Sanche L, Fortin D, Mathieu D
and Paquette B: Optimization of the route of platinum drugs
administration to optimize the concomitant treatment with
radiotherapy for glio-blastoma implanted in the Fischer rat brain.
J Neurooncol. 115:365–373. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rudà R, Bello L, Duffau H and Soffietti R:
Seizures in low-grade gliomas: Natural history, pathogenesis, and
outcome after treatments. Neuro Oncol. 14(Suppl 4): iv55–iv64.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ethirajan M, Chen Y, Joshi P and Pandey
RK: The role of porphyrin chemistry in tumor imaging and
photodynamic therapy. Chem Soc Rev. 40:340–362. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dougherty TJ, Gomer CJ, Henderson BW, Jori
G, Kessel D, Korbelik M, Moan J and Peng Q: Photodynamic therapy. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 90:889–905. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krosl G, Korbelik M and Dougherty GJ:
Induction of immune cell infiltration into murine SCCVII tumour by
photofrin-based photodynamic therapy. Br J Cancer. 71:549–555.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kessel D, Luo Y, Deng Y and Chang CK: The
role of subcellular localization in initiation of apoptosis by
photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol. 65:422–426. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dougherty TJ and Levy JG: Biomedical
photonics handbook. CRC Press; New York: 2003
|
|
14
|
Tian YY, Wang LL and Wang W: Progress in
photodynamic therapy on tumors. Laser Physics. 18:1119–1123. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sutedja T, Baas P, Stewart F and van
Zandwijk N: A pilot study of photodynamic therapy in patients with
inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 28A:1370–1373.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pandey RK, Goswami LN, Chen Y, Gryshuk A,
Missert JR, Oseroff A and Dougherty TJ: Nature: A rich source for
developing multifunctional agents. Tumor-imaging and photodynamic
therapy. Lasers Surg Med. 38:445–467. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Whelpton R, Michael-Titus AT, Basra SS and
Grahn M: Distribution of temoporfin, a new photosensitizer for the
photo-dynamic therapy of cancer, in a murine tumor model. Photochem
Photobiol. 61:397–401. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ji J, Fan Z, Zhou F and Wang X, Shi L,
Zhang H, Wang P, Yang D, Zhang L, Chen WR and Wang X: Improvement
of DC vaccine with ALA-PDT induced immunogenic apoptotic cells for
skin squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:17135–17146. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wen CC, Li JL, Zhang SY, Xu XK, Ouyang LP,
Yu J and Li FC: Photodynamic therapy mediated with 5-aminolevulinic
acid enhances the expression of proteasomes in glioma cell line
U251 cells. Chin J Clin Neurosurg. 17:154–157. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Le-ping O, Shan-yi Z, Jun-liang L, Xin-ke
X, Yin-lun W, Meiguang Z, Sheng-wen W and Fang-cheng L:
Overexpression of TAP1 up-regulates HLA-I in human glioma U251
cells. In: Chin J Pathophysiol. 29. pp. 425–429. 2013
|
|
21
|
Yuan SX, Li FC, Zhou HJ, Sun X and Yin HJ:
Antitumor efficacy of photodynamic therapy-generated glioma vaccine
from dendritic cells. Tumor. 27:962–967. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Zhang SY, Li JL, Xu XK, Zheng MG, Wen CC
and Li FC: Effect of hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether-based
photodynamic treatment on gene expression of transporter associated
with antigen processing 1 in human U87-MG glioma. Chin J Exp Surg.
27:914–916. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Wen JY, Lv BB, Li X, Ying X, Wang
YJ, Zhang HT, Wang H, Liu HY and Chnag CK: Photocytotoxicity and
G-quadruplex DNA interaction of water-soluble gallium(III)
tris(N-methyl-4-pyridyl)corrole complex. Appl Organometal Chem.
30:132–139. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu JX, Yan ZP, Zhang YY, Wu J, Liu XH and
Zeng Y: Hemodynamic shear stress regulates the transcriptional
expression of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in human umbilical vein
endothelial cell. Cell Mol Biol. 62:28–34. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeng Y, Liu JX, Yan ZP, Yao XH and Liu XH:
Potential microRNA biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Int J Mol
Med. 36:1639–1647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moserova I and Kralova J: Role of ER
stress response in photodynamic therapy: ROS generated in different
subcellular compartments trigger diverse cell death pathways. PLoS
One. 7:e329722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Broekgaarden M, Weijer R, van Gulik TM,
Hamblin MR and Heger M: Tumor cell survival pathways activated by
photody-namic therapy: A molecular basis for pharmacological
inhibition strategies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 34:643–690. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang ZH, Liu HY, Zhou R, Zhang Z, Ali A,
Han BJ, Liu YJ and Xiao XY: DNA-binding, photocleavage, and
photodynamic anti-cancer activities of pyridyl corroles. J Membr
Biol. 249:419–428. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeng Y: Endothelial glycocalyx as a
critical signalling platform integrating the extracellular
haemodynamic forces and chemical signalling. J Cell Mol Med.
21:1457–1462. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Králová J, Bríza T, Moserová I, Dolenský
B, Vasek P, Poucková P, Kejík Z, Kaplánek R, Martásek P, Dvorák M
and Král V: Glycol porphyrin derivatives as potent photodynamic
inducers of apoptosis in tumor cells. J Med Chem. 51:5964–5973.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Geng Y, Lin D, Shao L, Yan F and Ju H:
Cellular delivery of quantum dot-bound hybridization probe for
detection of intracellular pre-microRNA using
chitosan/poly(γ-glutamic acid) complex as a carrier. PLoS One.
8:e655402013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Guo P, Coban O, Snead NM, Trebley J,
Hoeprich S, Guo S and Shu Y: Engineering RNA for targeted siRNA
delivery and medical application. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 62:650–666.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li SJ, Zhou J, Zhang L, Xiang W, Hu Q, He
YY and Chen LG: The effect of miR-21 on SWOZ2 glioma cells and its
biological mechanism. J BUON. 22:468–473. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Q, Cheng Q, Chen Z, Peng R, Chen R, Ma
Z, Wan X, Liu J, Meng M, Peng Z and Jiang B: MicroRNA-663 inhibits
the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioblastoma cells via
targeting TGF-β1. Oncol Rep. 35:1125–1134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yue X, Lan F, Hu M, Pan Q, Wang Q and Wang
J: Downregulation of serum microRNA-205 as a potential diagnostic
and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. J Neurosurg.
124:122–128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lin Q, Geng Y, Zhao M, Lin S, Zhu Q and
Tian Z: MiR-21 Regulates TNF-α-induced CD40 expression via the
SIRT1-NF-κB pathway in renal inner medullary collecting duct cells.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:124–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Misuth M, Horvath D, Miskovsky P and
Huntosova V: Synergism between PKCδ regulators hypericin and
rottlerin enhances apoptosis in U87 MG glioma cells after light
stimulation. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 18:267–274. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pan L, Lin H, Tian S, Bai D, Kong Y and Yu
L: The sensitivity of glioma cells to pyropheophorbide-αmethyl
ester-mediated photodynamic therapy is enhanced by inhibiting
ABCG2. Lasers Surg Med. 49:719–726. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Christie C, Pomeroy A, Nair R, Berg K and
Hirschberg H: Photodynamic therapy enhances the efficacy of
gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther.
18:140–148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|