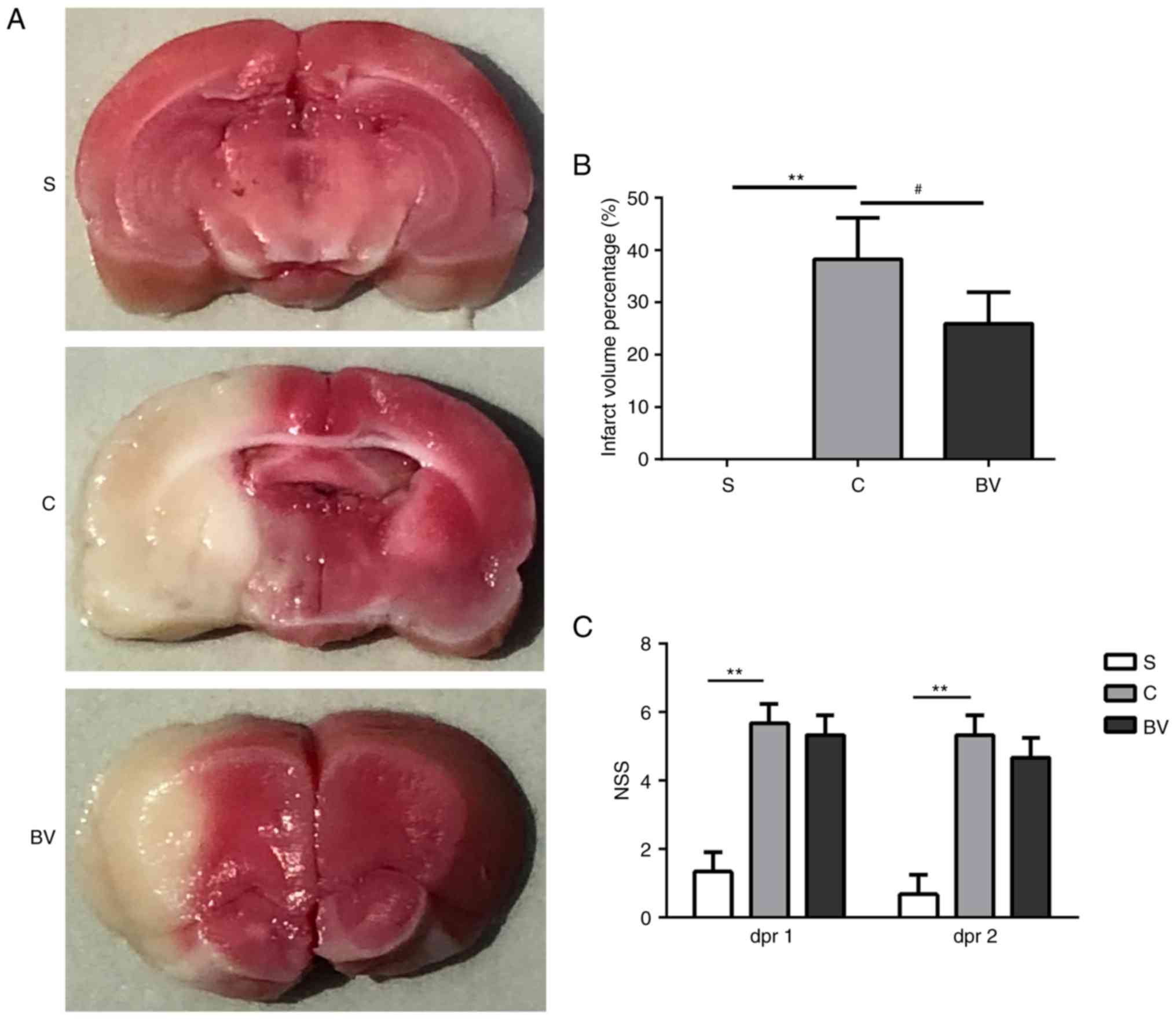
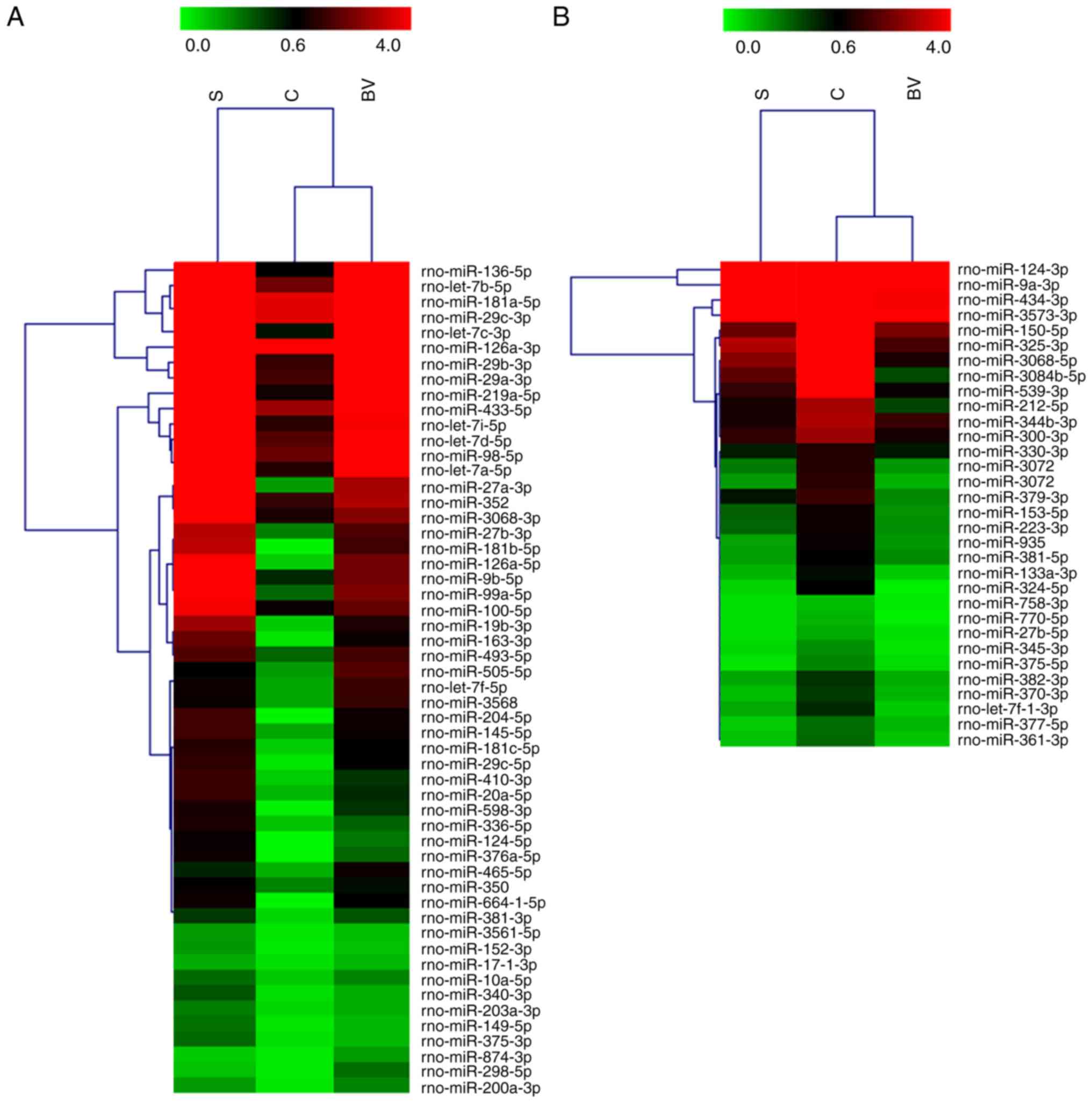
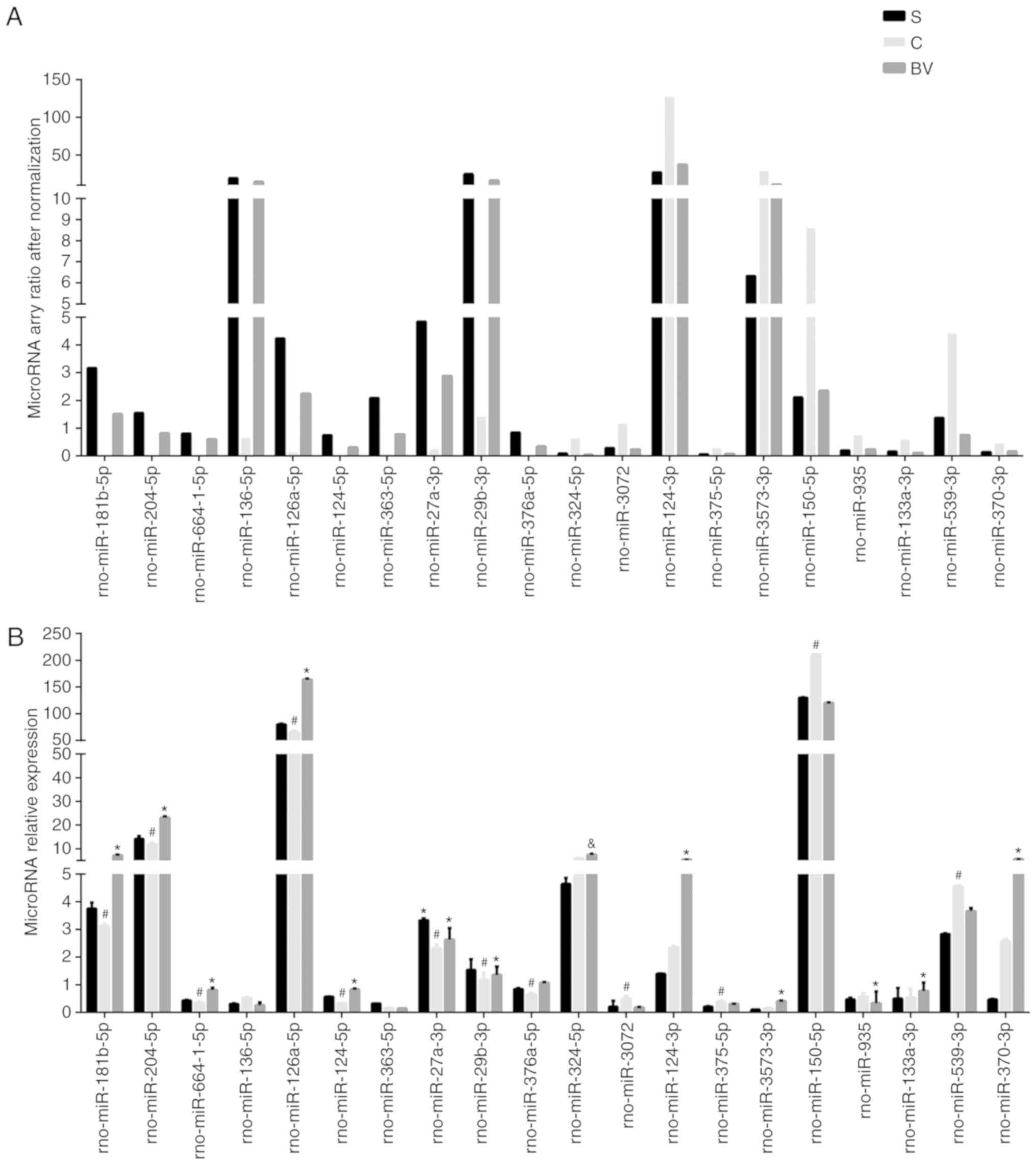
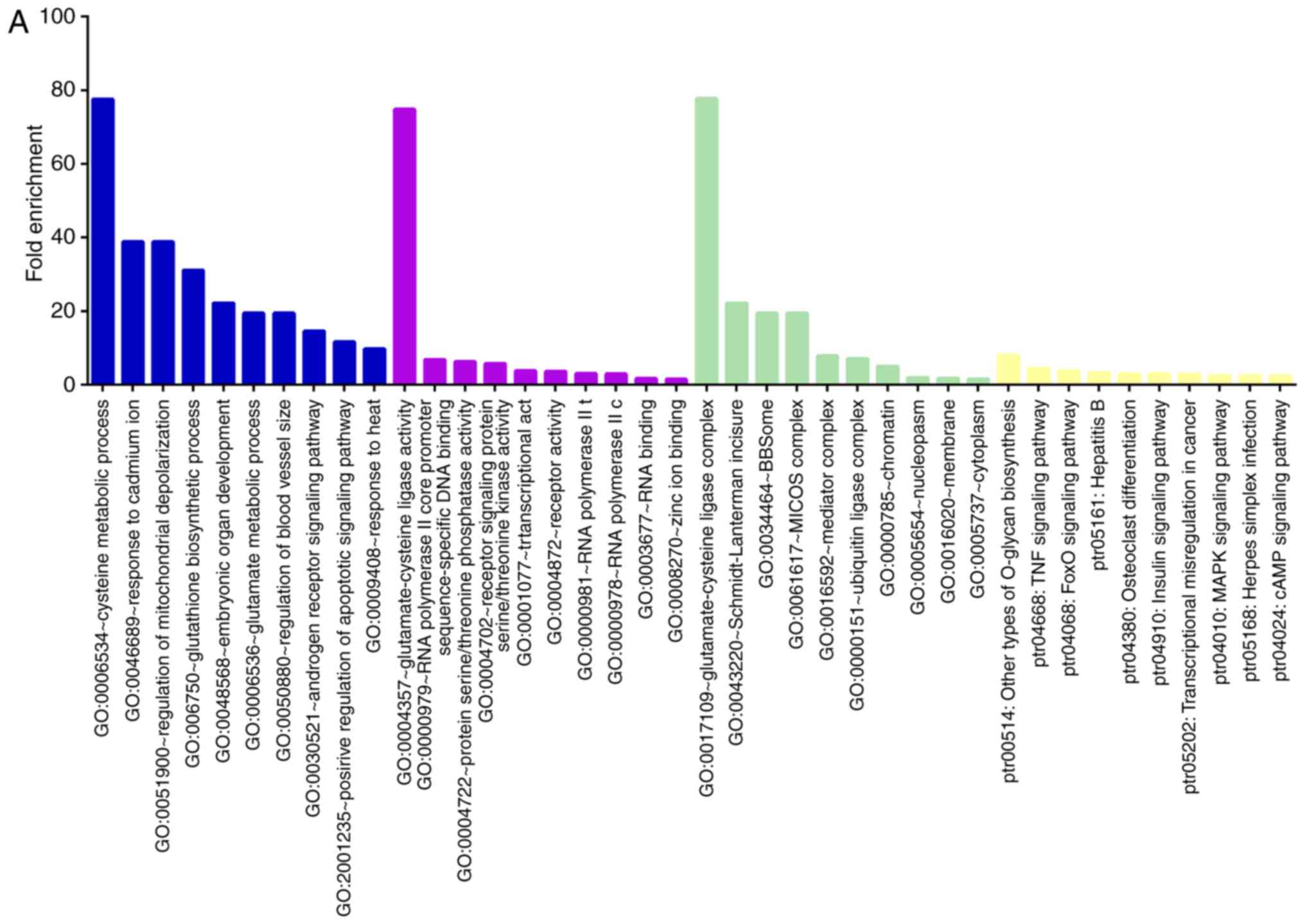
|
1
|
Sarady-Andrews JK, Liu F, Gallo D, Nakao
A, Overhaus M, Ollinger R, Choi AM and Otterbein LE: Biliverdin
administration protects against endotoxin-induced acute lung injury
in rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 289:L1131–L1137. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou XQ, Zeng XN, Kong H and Sun XL:
Neuroprotective effects of berberine on stroke models in vitro and
in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 447:31–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen GY and Nuñez G: Sterile inflammation:
Sensing and reacting to damage. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:826–837. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Deng H, Zuo X, Zhang J, Liu X, Liu L, Xu
Q, Wu Z and Ji A: Alphalipoic acid protects against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Mol Med Rep.
11:3659–3665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamasaki Y, Matsuura N, Shozuhara H,
Onodera H, Itoyama Y and Kogure K: Interleukin-1 as a pathogenetic
mediator of ischemic brain damage in rats. Stroke. 26:676–681.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lavine SD, Hofman FM and Zlokovic BV:
Circulating antibody against tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects
rat brain from reperfusion injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
18:52–58. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fondevila C, Shen XD, Tsuchiyashi S,
Yamashita K, Csizmadia E, Lassman C, Busuttil RW, Kupiec-Weglinski
JW and Bach FH: Biliverdin therapy protects rat livers from
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Hepatology. 40:1333–1341. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kosaka J, Morimatsu H, Takahashi T,
Shimizu H, Kawanishi S, Omori E, Endo Y, Tamaki N, Morita M and
Morita K: Effects of biliverdin administration on acute lung injury
induced by hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation in rats. PLoS One.
8:e636062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakao A, Kaczorowski DJ, Sugimoto R,
Billiar TR and McCurry KR: Application of heme oxygenase-1, carbon
monoxide and biliverdin for the prevention of intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 42:78–88. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wegiel B, Gallo D, Csizmadia E, Roger T,
Kaczmarek E, Harris C, Zuckerbraun BS and Otterbein LE: Biliverdin
inhibits Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) expression through nitric
oxide-dependent nuclear translocation of biliverdin reductase. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:18849–18854. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Holst B, Raby AC, Hall JE and Labéta MO:
Complement takes its Toll: An inflammatory crosstalk between
Toll-like receptors and the receptors for the complement
anaphylatoxin C5a. Anaesthesia. 67:60–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu J, Liu F, Yin P, Zhu X, Cheng G, Wang
N, Lu A, Luan W, Zhang N, Li J, et al: 2.2 Integrating miRNA and
mRNA expression profiles in response to heat stress-induced injury
in rat small intestine. Funct Integr Genomics. 11:203–213. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nassar FJ, El Eit R and Nasr R: An
integrative analysis of microRNA and mRNA profiling in CML stem
cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1465:219–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen JH, He HC, Jiang FN, Militar J, Ran
PY, Qin GQ, Cai C, Chen XB, Zhao J, Mo ZY, et al: Analysis of the
specific pathways and networks of prostate cancer for gene
expression profiles in the Chinese population. Med Oncol.
29:1972–1984. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chiang T, Messing RO and Chou WH: Mouse
model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Vis Exp.
2761:2011.
|
|
17
|
Li JJ, Zou ZY, Liu J, Xiong LL, Jiang HY,
Wang TH and Shao JL: Biliverdin administration ameliorates cerebral
ischemia reperfusion injury in rats and is associated with
proinflammatory factor downregulation. Exp Ther Med. 14:671–679.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kam KY, Yu SJ, Jeong N, Hong JH, Jalin AM,
Lee S, Choi YW, Lee CK and Kang SG: p-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol
prevents brain injury and behavioral impairment by activating Nrf2,
PDI, and neurotrophic factor genes in a rat model of brain
ischemia. Mol Cells. 31:209–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Andria B, Bracco A, Attanasio C, Castaldo
S, Cerrito MG, Cozzolino S, Di Napoli D, Giovannoni R, Mancini A,
Musumeci A, et al: Biliverdin protects against liver ischemia
reperfusion injury in swine. PLoS One. 8:e699722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Yang Z, Tsuji T, Gong J, Xie J,
Chen C, Li W, Amar S and Luo Z: LITAF and TNFSF15, two downstream
targets of AMPK, exert inhibitory effects on tumor growth.
Oncogene. 30:1892–1900. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Orvis GD, Hartzell AL, Smith JB, Barraza
LH, Wilson SL, Szulc KU, Turnbull DH and Joyner AL: The engrailed
homeobox genes are required in multiple cell lineages to coordinate
sequential formation of fissures and growth of the cerebellum. Dev
Biol. 367:25–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu BH, Lin X, Yang X, Dong H, Yue X,
Andrade KC, Guo Z, Yang J, Wu L, Zhu X, et al: Downregulation of
RND3/RhoE in glioblastoma patients promotes tumorigenesis through
augmentation of notch transcriptional complex activity. Cancer Med.
4:1404–1416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yue XJ, Lin X, Yang T, Yang X, Yi X, Jiang
X, Li X, Li T, Guo J, Dai Y, et al: Rnd3/RhoE modulates
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α/vascular endothelial growth factor
signaling by stabilizing hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and regulates
responsive cardiac angiogenesis. Hypertension. 67:597–605. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo L, Zhong D, Lau S, Liu X, Dong XY, Sun
X, Yang VW, Vertino PM, Moreno CS, Varma V, et al: Sox7 is an
independent checkpoint for beta-catenin function in prostate and
colon epithelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1421–1430. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Huang SY, Dong W, Li L, Feng Y,
Pan L, Han Z, Wang X, Ren G, Su D, et al: SOX7, down-regulated in
colorectal cancer, induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 277:29–37. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang C, Qin L, Min Z, Zhao Y, Zhu L, Zhu J
and Yu S: SOX7 interferes with β-catenin activity to promote
neuronal apoptosis. Eur J Neurosci. 41:1430–1437. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gustafsson Sheppard N, Jarl L, Mahadessian
D, Strittmatter L, Schmidt A, Madhusudan N, Tegnér J, Lundberg EK,
Asplund A, Jain M and Nilsson R: The folate-coupled enzyme MTHFD2
is a nuclear protein and promotes cell proliferation. Sci Rep.
5:150292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tedeschi PM, Vazquez A, Kerrigan JE and
Bertino JR: Mitochondrial methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase
(MTHFD2) overexpression is associated with tumor cell proliferation
and is a novel target for drug development. Mol Cancer Res.
13:1361–1366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
la Torre A, Muscarella LA, Parrella P,
Balsamo T, Bisceglia M, Valori VM, la Torre A, Barbano R, Perrella
E, Poeta ML, et al: Aberrant genes promoter methylation in neural
crest-derived tumors. Int J Biol Marker. 27:E389–E394. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhou H, Zhang Z, Liu C, Jin C, Zhang J,
Miao X and Jia L: B4GALT1 gene knockdown inhibits the hedgehog
pathway and reverses multidrug resistance in the human leukemia
K562/adriamycin-resistant cell line. IUBMB Life. 64:889–900. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xie H, Zhu Y, An H, Wang H, Zhu Y, Fu H,
Wang Z, Fu Q, Xu J and Ye D: Increased B4GALT1 expression
associates with adverse outcome in patients with non-metastatic
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:32723–32730.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yuan J, Kang JL, Liao H, Wang XX, Nie ML,
Shuai R and Deng C: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
6-fusion protein (MAP2K6-FP) potentiates the anti-tumor effects of
paclitaxel in ovarian cancer. Anticancer Agent Med Chem.
15:1308–1316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nakamura K, Yamashita K, Sawaki H, Waraya
M, Katoh H, Nakayama N, Kawamata H, Nishimiya H, Ema A, Narimatsu H
and Watanabe M: Aberrant methylation of GCNT2 Is tightly related to
lymph node metastasis of primary CRC. Anticancer Res. 35:1411–1421.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang H, Meng F, Wu S, Kreike B, Sethi S,
Chen W, Miller FR and Wu G: Engagement of I-branching {beta}-1,
6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 in breast cancer metastasis and
TGF-{beta} signaling. Cancer Res. 71:4846–4856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mikami J, Tobisawa Y, Yoneyama T,
Hatakeyama S, Mori K, Hashimoto Y, Koie T, Ohyama C and Fukuda M:
I-branching N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase regulates prostate
cancer invasiveness by enhancing α5β1 integrin signaling. Cancer
Sci. 107:359–368. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Rogers LM, Riordan JD, Swick BL, Meyerholz
DK and Dupuy AJ: Ectopic expression of Zmiz1 induces cutaneous
squamous cell malignancies in a mouse model of cancer. J Invest
Dermatol. 133:1863–1869. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feijóo CG, Sarrazin AF, Allende ML and
Glavic A: Cystein-serine-rich nuclear protein 1, Axud1/Csrnp1, is
essential for cephalic neural progenitor proliferation and survival
in zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 238:2034–2043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rekaik H, Blaudin de Thé FX, Prochiantz A,
Fuchs J and Joshi RL: Dissecting the role of Engrailed in adult
dopaminergic neurons-insights into Parkinson disease pathogenesis.
FEBS Lett. 589:3786–3794. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shiomi N, Myokai F, Naruishi K, Oyaizu K,
Senoo K, Yamaguchi T, Amar S and Takashiba S: Cloning and
characterization of lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis
factor alpha factor promoter. Fems Immunol Med Mic. 47:360–368.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bushell KN, Leeman SE, Gillespie E, Gower
AC, Reed KL, Stucchi AF, Becker JM and Amar S: LITAF mediation of
increased TNF-α secretion from inflamed colonic lamina propria
macrophages. PLoS One. 6:e258492011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Tang XR and Amar S: Kavain involvement in
LPS-induced signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 117:2272–2280.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wawro M, Kochan J, Krzanik S, Jura J and
Kasza A: Intact NYN/PIN-like domain is crucial for the degradation
of inflammation-related transcripts by ZC3H12D. J Cell Biochem.
118:487–498. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Minagawa K, Wakahashi K, Kawano H,
Nishikawa S, Fukui C, Kawano Y, Asada N, Sato M, Sada A, Katayama Y
and Matsui T: Posttranscriptional modulation of cytokine production
in T cells for the regulation of excessive inflammation by TFL. J
Immunol. 192:1512–1524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang H, Wang WC, Chen JK, Zhou L, Wang M,
Wang ZD, Yang B, Xia YM, Lei S, Fu EQ and Jiang T: ZC3H12D
attenuated inflammation responses by reducing mRNA stability of
proinflammatory genes. Mol Immunol. 67:206–212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Patel J, McNeill E, Douglas G, Hale AB, de
Bono J, Lee R, Iqbal AJ, Regan-Komito D, Stylianou E, Greaves DR
and Channon KM: RGS1 regulates myeloid cell accumulation in
atherosclerosis and aortic aneurysm rupture through altered
chemokine signalling. Nat Commun. 6:66142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Grigoriu BD, Depontieu F, Scherpereel A,
Gourcerol D, Devos P, Ouatas T, Lafitte JJ, Copin MC, Tonnel AB and
Lassalle P: Endocan expression and relationship with survival in
human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4575–4582.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang C, Basta T and Klymkowsky MW: SOX7
and SOX18 are essential for cardiogenesis in Xenopus. Dev Dyn.
234:878–891. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Herpers R, van de Kamp E, Duckers HJ and
Schulte-Merker S: Redundant roles for sox7 and sox18 in
arteriovenous specification in zebrafish. Circ Res. 102:12–15.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Arderiu G, Peña E and Badimon L:
Angiogenic microvascular endothelial cells release microparticles
rich in tissue factor that promotes postischemic collateral vessel
formation. Arterioscl Throm Vasc Biol. 35:348–357. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Cai L, Leng ZG, Guo YH, Lin SJ, Wu ZR, Su
ZP, Lu JL, Wei LF, Zhuge QC, Jin K and Wu ZB: Dopamine agonist
resistance-related endocan promotes angiogenesis and cells
viability of prolactinomas. Endocrine. 52:641–651. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Bensellam M, Montgomery MK, Luzuriaga J,
Chan JY and Laybutt DR: Inhibitor of differentiation proteins
protect against oxidative stress by regulating the
antioxidant-mitochondrial response in mouse beta cells.
Diabetologia. 58:758–770. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bian C, Xu TD, Zhu H, Pan D, Liu Y, Luo Y,
Wu P and Li D: Luteolin inhibits ischemia/reperfusion-induced
myocardial injury in rats via downregulation of microRNA-208b-3p.
PLoS One. 10:e01448772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang LL, Wang T and Valle D: Reduced PLP2
expression increases ER-stress-induced neuronal apoptosis and risk
for adverse neurological outcomes after hypoxia ischemia injury.
Hum Mol Genet. 24:7221–7226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li AY, Yang Q and Yang K: miR-133a
mediates the hypoxia-induced apoptosis by inhibiting TAGLN2
expression in cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:173–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Han SW, Kim HP, Shin JY, Jeong EG, Lee WC,
Kim KY, Park SY, Lee DW, Won JK, Jeong SY, et al: RNA editing in
RHOQ promotes invasion potential in colorectal cancer. J Exp Med.
211:613–621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sako H, Yada K and Suzuki K: Genome-wide
analysis of acute endurance exercise-induced translational
regulation in mouse skeletal muscle. PLoS One. 11:e01483112016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Karunakaran D, Thrush B, Nguyen MA,
Richards L, Geoffrion M, Singaravelu R, Ramphos E, Shangari P,
Ouimet M, Pezacki JP, et al: Macrophage mitochondrial energy status
regulates cholesterol efflux and is enhanced by anti-miR33 in
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 117:266–278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee D, Sun S, Ho AS, Kiang KM, Zhang XQ,
Xu FF and Leung GK: Hyperoxia resensitizes chemoresistant
glioblastoma cells to temozolomide through unfolded protein
response. Anticancer Res. 34:2957–2966. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Eastman SW, Martin-Serrano J, Chung W,
Zang T and Bieniasz PD: Identification of human VPS37C, a component
of endosomal sorting complex required for transport-I important for
viral budding. J Biol Chem. 280:628–636. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Lanfear DE, Yang JJ, Mishra S and Sabbah
HN: Genome-wide approach to identify novel candidate genes for beta
blocker response in heart failure using an experimental model.
Discov Med. 11:359–366. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lewis AH and Raman IM: Resurgent current
of voltage-gated Na(+) channels. J Physiol. 592:4825–4838. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yeh I, Botton T, Talevich E, Shain AH,
Sparatta AJ, de la Fouchardiere A, Mully TW, North JP, Garrido MC,
Gagnon A, et al: Activating MET kinase rearrangements in melanoma
and Spitz tumours. Nat Commun. 6:71742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ebrahimie E, Nurollah Z, Ebrahimi M,
Hemmatzadeh F and Ignjatovic J: Unique ability of pandemic
influenza to downregulate the genes involved in neuronal disorders.
Mol Biol Rep. 42:1377–1390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chu M, Qin S, Wu R, Zhou X, Tang X, Zhang
S, Zhao Q, Wang H, Liu Y, Han X, et al: Role of MiR-126a-3p in
endothelial injury in endotoxic mice. Criti Care Med. 44:e639–e650.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Huo X, Zhang K, Yi L, Mo Y, Liang Y, Zhao
J, Zhang Z, Xu Y and Zhen G: Decreased epithelial and plasma
miR-181b-5p expression associates with airway eosinophilic
inflammation in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 46:1281–1290. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ding Z, Jian S, Peng X, Liu Y, Wang J,
Zheng L, Ou C, Wang Y, Zeng W and Zhou M: Loss of MiR-664
expression enhances cutaneous malignant melanoma proliferation by
upregulating PLP2. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e13272015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhu H, Miao MH, Ji XQ, Xue J and Shao XJ:
miR-664 negatively regulates PLP2 and promotes cell proliferation
and invasion in T-cell acute lymphoblastic. leukaemia Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 459:340–345. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Chen Q, Lu G, Cai Y, Li Y, Xu R, Ke Y and
Zhang S: MiR-124-5p inhibits the growth of high-grade gliomas
through posttranscriptional regulation of LAMB1. Neuro Oncol.
16:637–651. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yang M, Cui G, Ding M, Yang W, Liu Y, Dai
D and Chen L: miR-935 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation by
targeting SOX7. Biomed Pharmacother. 79:153–158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang L, Zeng D, Chen Y, Li N, Lv Y, Li Y,
Xu X and Xu G: miR-937 contributes to the lung cancer cell
proliferation by targeting INPP4B. Life Sci. 155:110–115. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Keasey MP, Scott HL, Bantounas I, Uney JB
and Kelly S: MiR-132 is upregulated by ischemic preconditioning of
cultured hippocampal neurons and protects them from subsequent OGD
toxicity. J Mol Neurosci. 59:404–410. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Stylli SS, Adamides AA, Koldej RM, Luwor
RB, Ritchie DS, Ziogas J and Kaye AH: miRNA expression profiling of
cerebrospinal fluid in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 126:1131–1139. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Pulliam JV, Xu Z, Ford GD, Liu C, Li Y,
Stovall KC, Cannon VS, Tewolde T, Moreno CS and Ford BD:
Computational identification of conserved transcription factor
binding sites upstream of genes induced in rat brain by transient
focal ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 1495:76–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Plotnik JP, Budka JA, Ferris MW and
Hollenhorst PC: ETS1 is a genome-wide effector of RAS/ERK signaling
in epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:11928–11940. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|