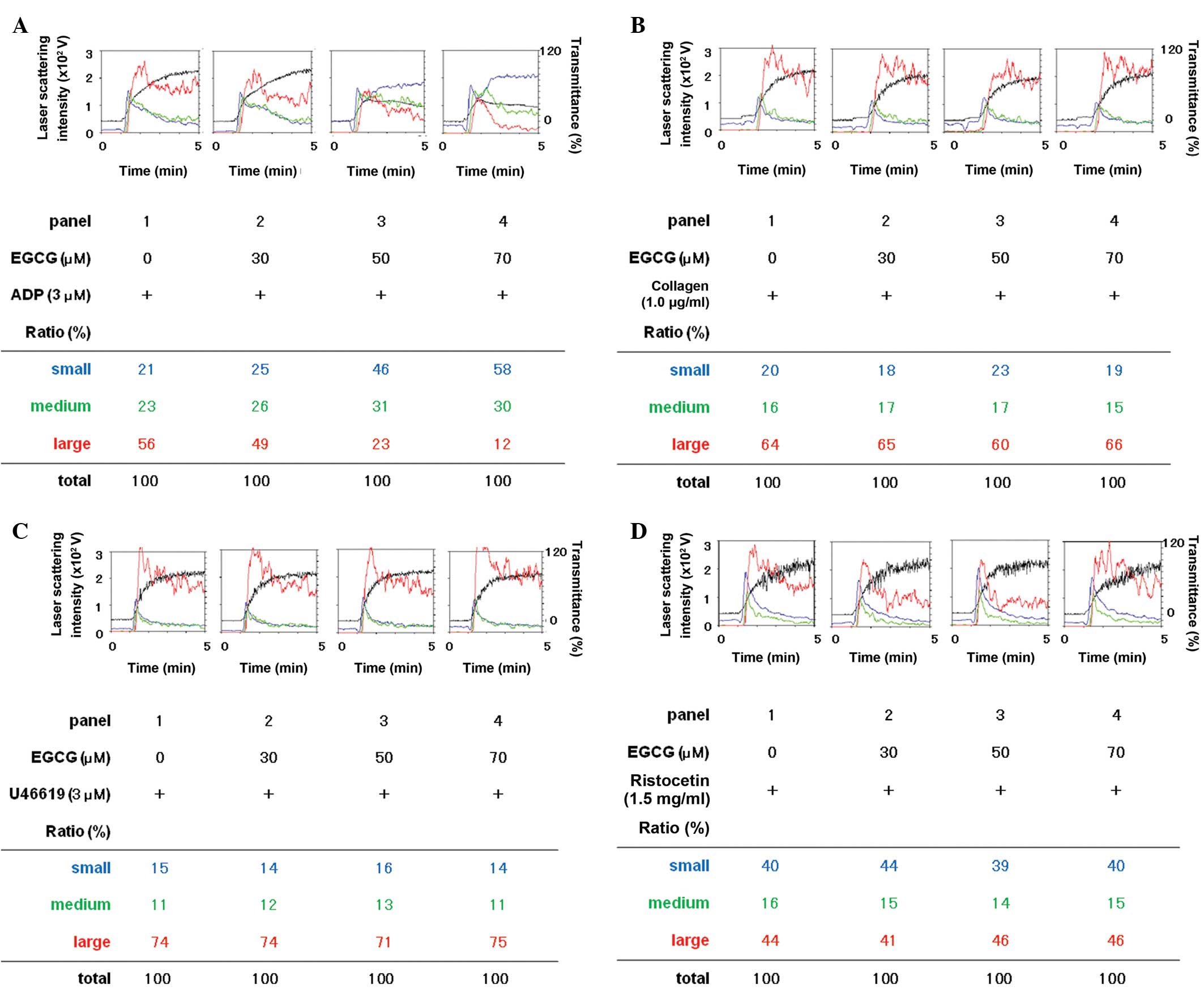
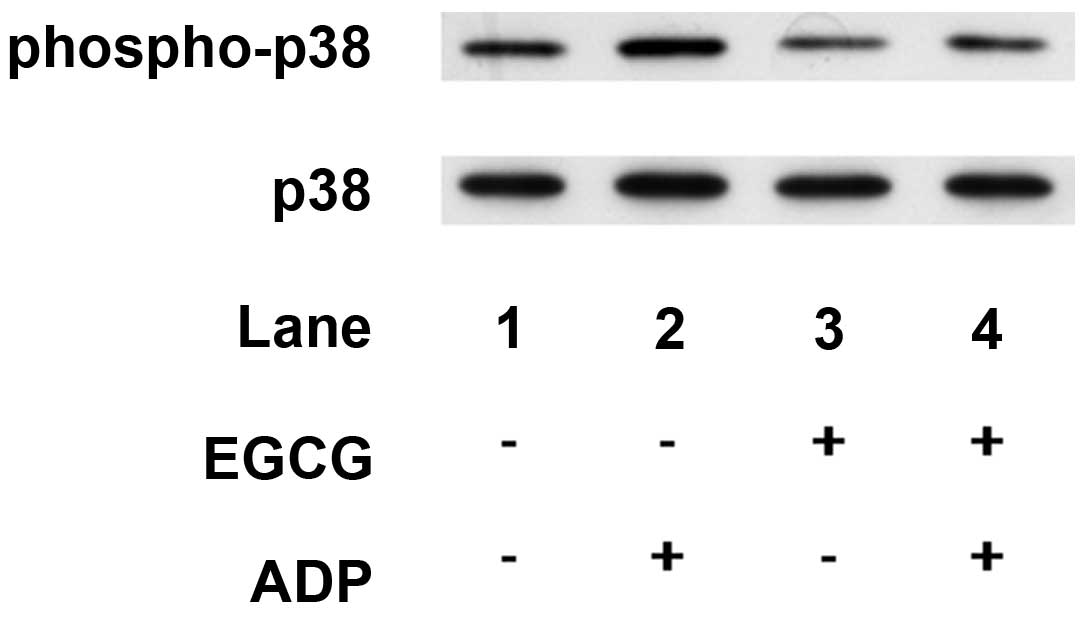
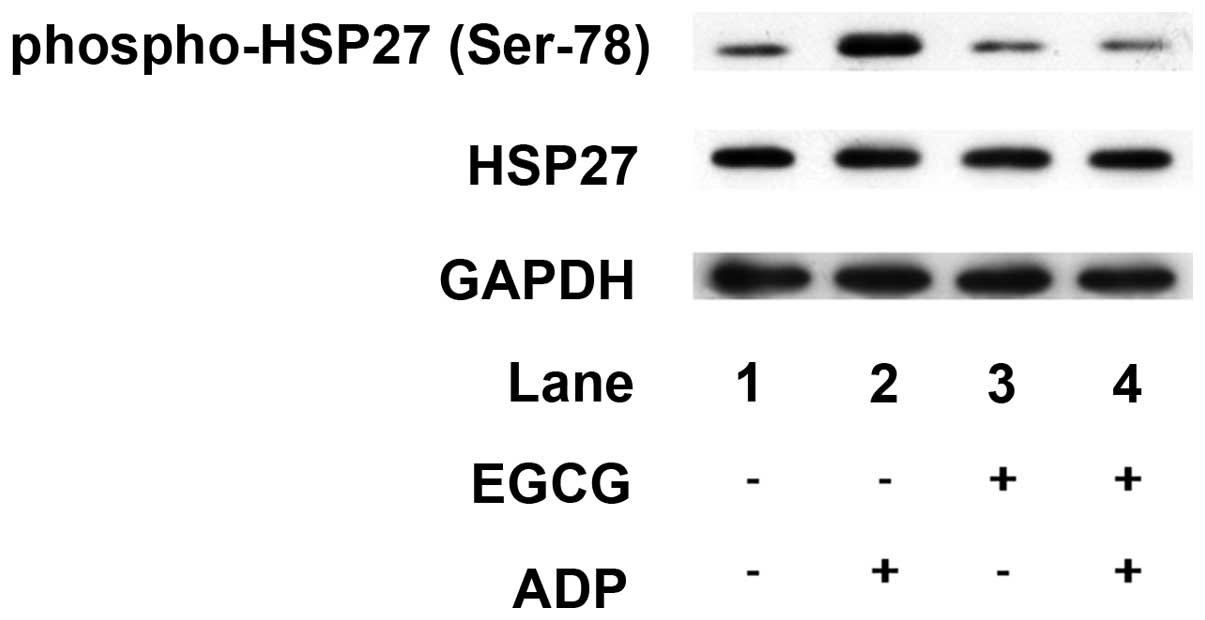
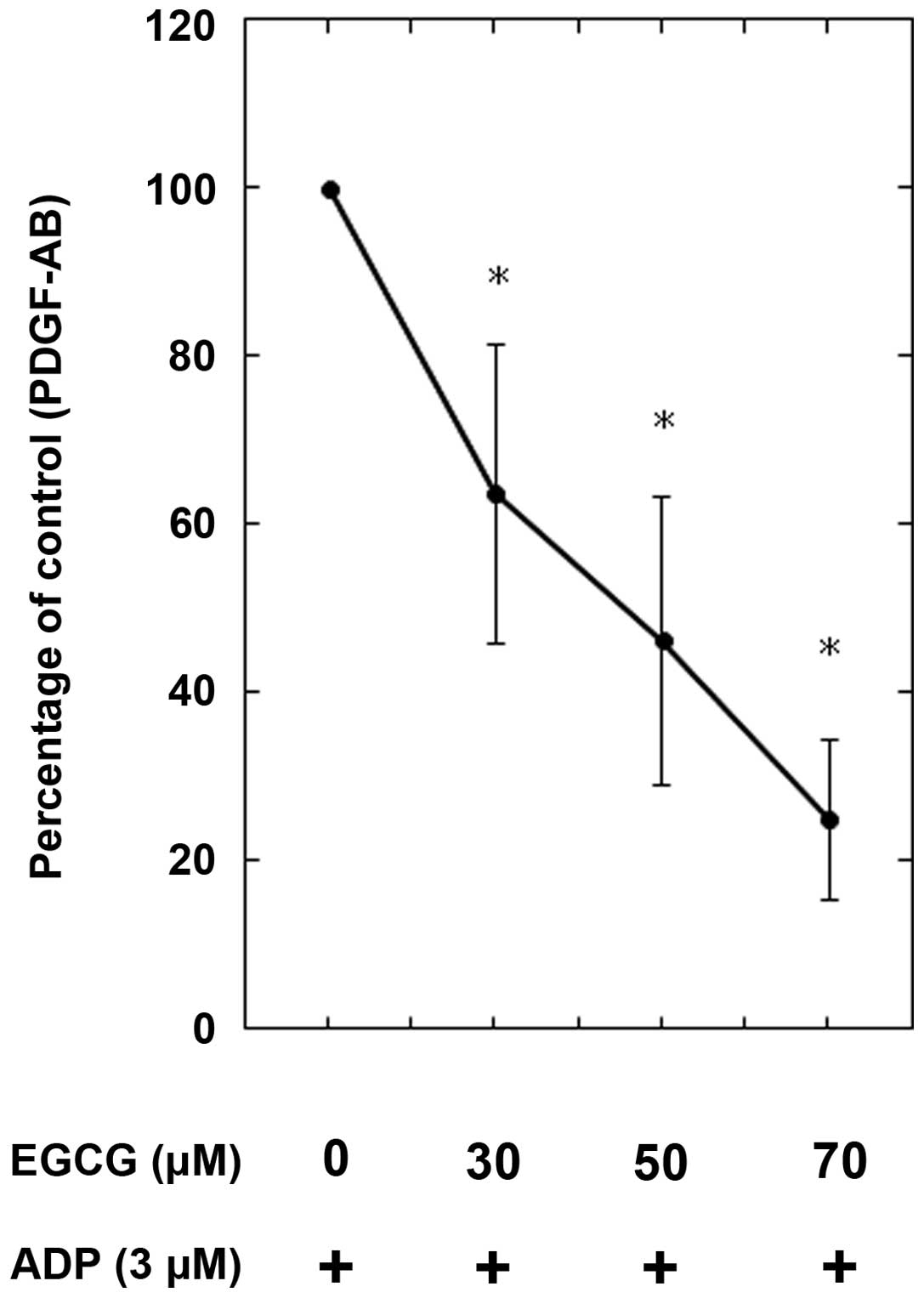
|
1
|
Jankun J, Selman SH, Swiercz R and
Skrzypczak-Jankun E: Why drinking green tea could prevent cancer.
Nature. 387:5611997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kang WS, Lim IH, Yuk DY, et al:
Antithrombotic activities of green tea catechins and
(−)-epigallocatechin gallate. Thromb Res. 96:229–237. 1999.
|
|
3
|
Oyama J, Maeda T, Kouzuma K, et al: Green
tea catechins improve human forearm endothelial dysfunction and
have antiatherosclerotic effects in smokers. Circ J. 74:578–588.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Harborne JB and Williams CA: Advances in
flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry. 55:418–504. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ruggeri ZM: The role of von Willebrand
factor in thrombus formation. Thromb Res. 120:S5–S9. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berndt MC, Shen Y, Dopheide SM, Gardiner
EE and Andrews RK: The vascular biology of the glycoprotein Ib-IX-V
complex. Thromb Haemost. 86:178–188. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garcia A, Quinton TM, Dorsam RT and
Kunapuli SP: Src family kinase-mediated and Erk-mediated
thromboxane A2 generation are essential for VWF/GPIb-induced
fibrinogen receptor activation in human platelets. Blood.
106:3410–3414. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jennings LK: Mechanisms of platelet
activation: need for new strategies to protect against
platelet-mediated atherothrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 102:248–257.
2009.
|
|
9
|
Dong JF, Berndt MC, Schade A, McIntire LV,
Andrews RK and López JA: Ristocetin-dependent, but not
botrocetin-dependent, binding of von Willebrand factor to the
platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex correlates with
shear-dependent interactions. Blood. 97:162–168. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hechler B, Léon C, Vial C, Vigne P, Frelin
C, Cazenave JP and Gachet C: The P2Y1 receptor is necessary for
adenosine 5′-diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation. Blood.
92:152–159. 1998.
|
|
11
|
Daniel JL, Dangelmaier C, et al: Role of
intracellular signaling events in ADP-induced platelet aggregation.
Thromb Haemost. 82:1322–1326. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kato H, Takai S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R,
Adachi S, Minamitani C, Otsuka T, Tokuda H, Akamatsu S, Doi T,
Ogura S and Kozawa O: HSP27 phosphorylation is correlated with
ADP-induced platelet granule secretion. Arch Biochem Biophys.
475:80–86. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Doi T, Adachi S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R,
Kato H, Enomoto Y, Minamitani C, Otsuka T, Tokuda H, Akamatsu S,
Iwama T, Kozawa O and Ogura S: Antithrombin III suppresses
ADP-induced platelet granule secretion: inhibition of HSP27
phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 489:62–67. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Enomoto Y, Adachi S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki
R, Doi T, Niwa M, Akamastu S, Tokuda H, Ogura S, Yoshimura S, Iwama
T and Kozawa O: Thromboxane A(2) promotes soluble CD40 ligand
release from human platelets. Atherosclerosis. 209:415–421. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin YR, Im JH, Park ES, Cho MR, Han XH,
Lee JJ, Lim Y, Kim TJ and Yun YP: Antiplatelet activity of
epigallocatechin gallate is mediated by the inhibition of PLCgamma2
phosphorylation, elevation of PGD2 production, and maintaining
calcium-ATPase activity. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 51:45–54. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fabre JE, Nguyen M, Latour A, Keifer JA,
Audoly LP, Coffman TM and Koller BH: Decreased platelet
aggregation, increased bleeding time and resistance to
thromboembolism in P2Y1-deficient mice. Nat Med. 5:1199–1202. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kato K, Ito H, Hasegawa K, Inaguma Y,
Kozawa O and Asano T: Modulation of the stress-induced synthesis of
hsp27 and αB-crystallin by cyclic AMP in C6 rat glioma cells. J
Neurochem. 66:946–950. 1996.
|
|
18
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature.
227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu J, Pestina TI, Berndt MC, Steward SA,
Jackson CW and Gartner TK: The roles of ADP and TXA2 in
botrocetin/VWF-induced aggregation of washed platelets. J Thromb
Haemost. 2:2213–2222. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakahata N: Thromboxane A2:
physiology/pathophysiology, cellular signal transduction and
pharmacology. Pharmacol Ther. 118:18–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rendu F and Brohard-Bohn B: The platelet
release reaction: granules’ constituents, secretion and functions.
Platelets. 12:261–273. 2001.
|
|
22
|
Heldin CH and Westermark B: Mechanism of
action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol
Rev. 79:1283–1316. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hermann A, Rauch BH, Braun M, Schrör K and
Weber AA: Platelet CD40 ligand (CD40L) - subcellular localization,
regulation of expression, and inhibition by clopidogrel. Platelets.
12:74–82. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
André P, Nannizzi-Alaimo L, Prasad SK and
Phillips DR: Platelet-derived CD40L: the switch-hitting player of
cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 106:896–899. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Henn V, Slupsky JR, Gräfe M,
Anagnostopoulos I, Förster R, Müller-Berghaus G and Kroczek RA:
CD40 ligand on activated platelets triggers an inflammatory
reaction of endothelial cells. Nature. 391:591–594. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heeschen C, Dimmeler S, Hamm CW, van den
Brand MJ, Boersma E, Zeiher AM and Simoons ML; CAPTURE Study
Investigators. Soluble CD40 ligand in acute coronary syndromes. N
Engl J Med. 348:1104–1111. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|