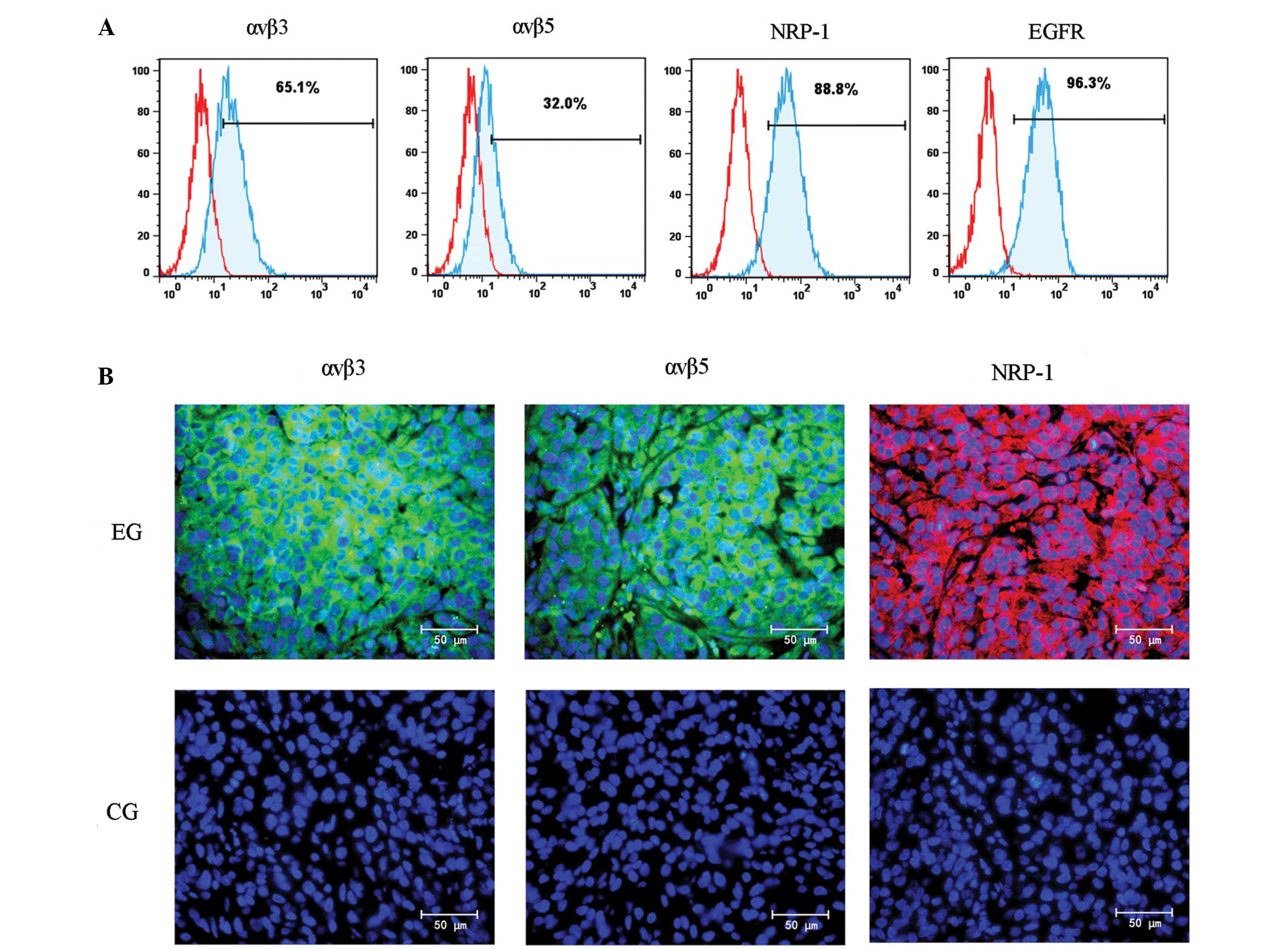
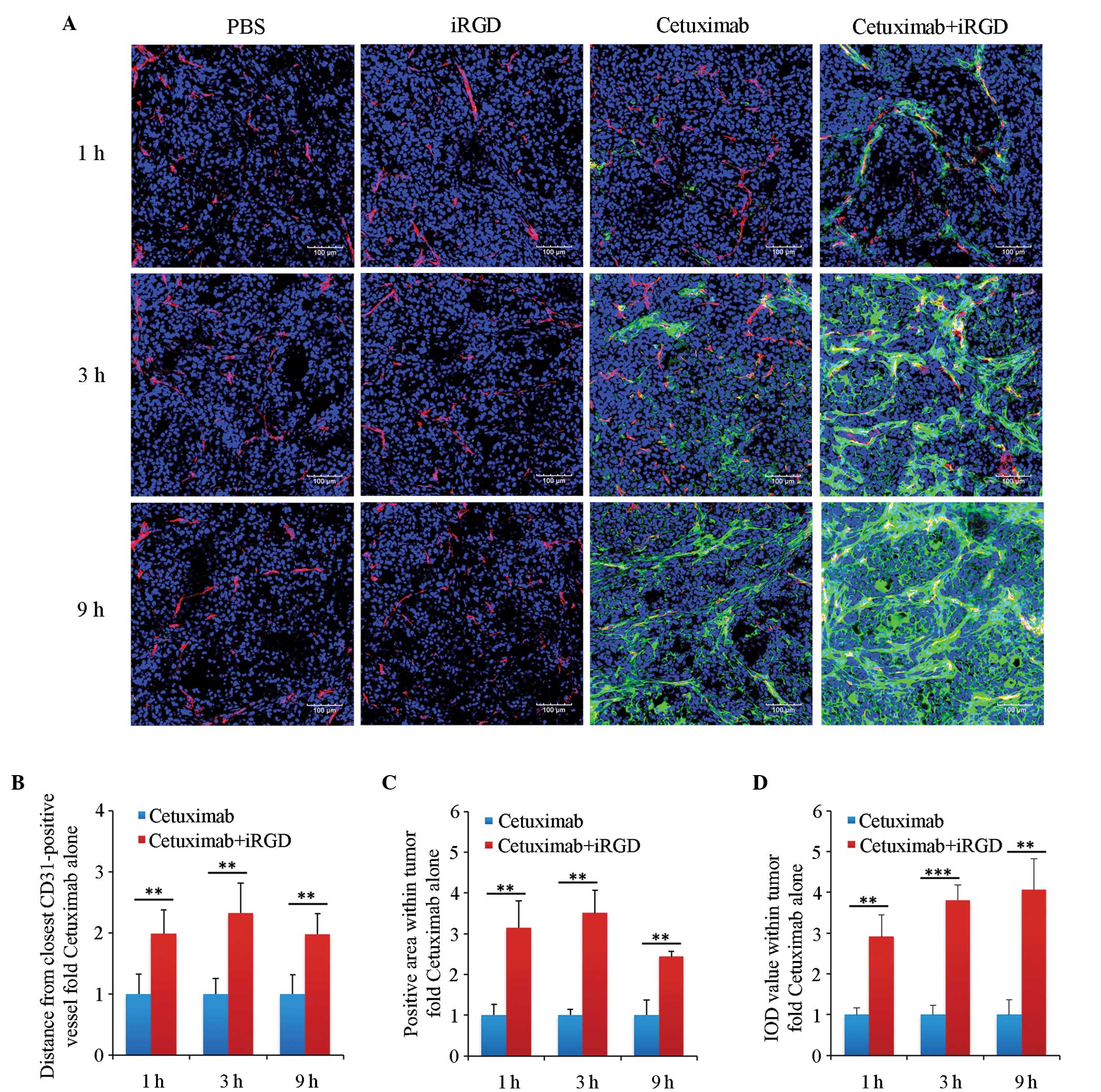
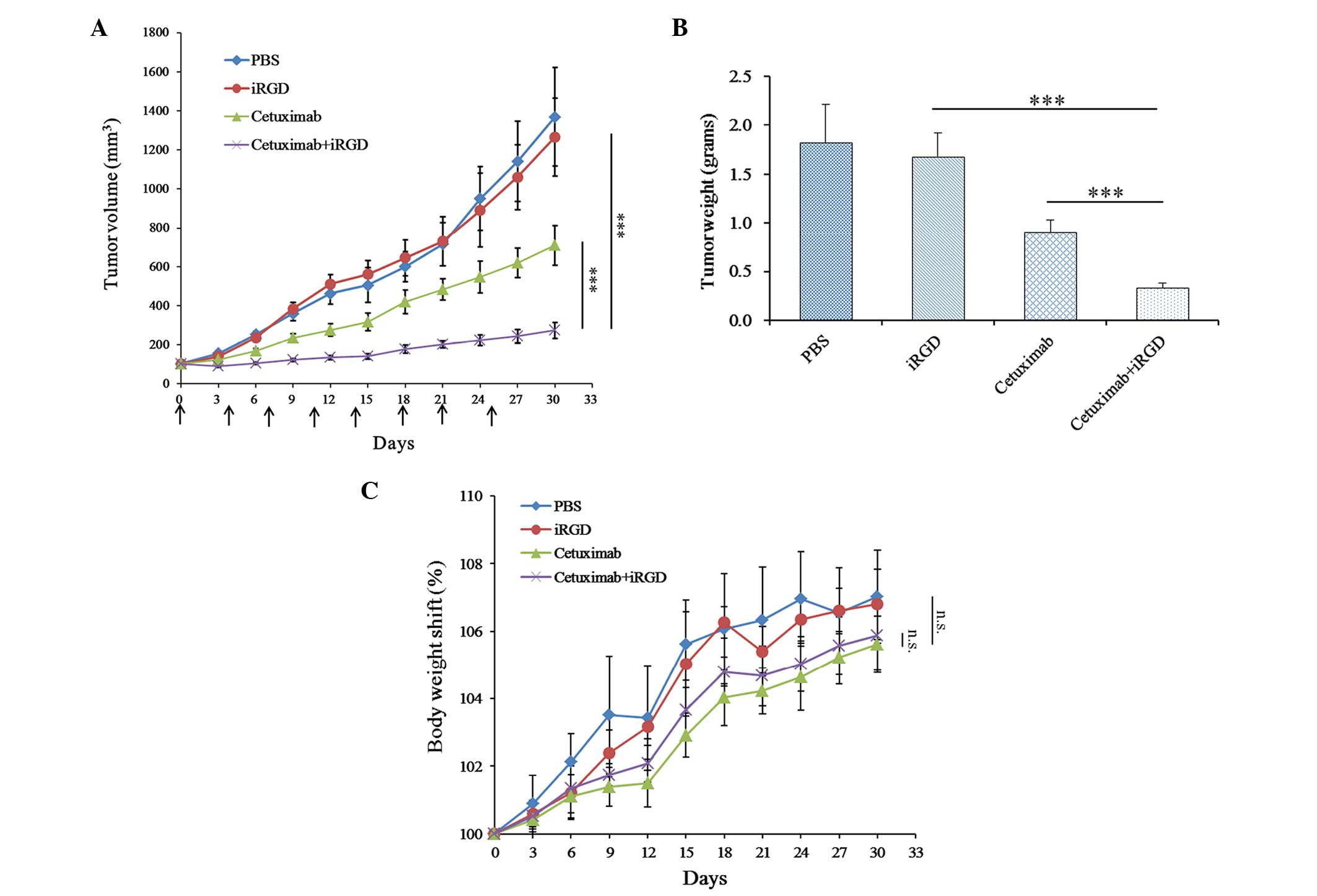
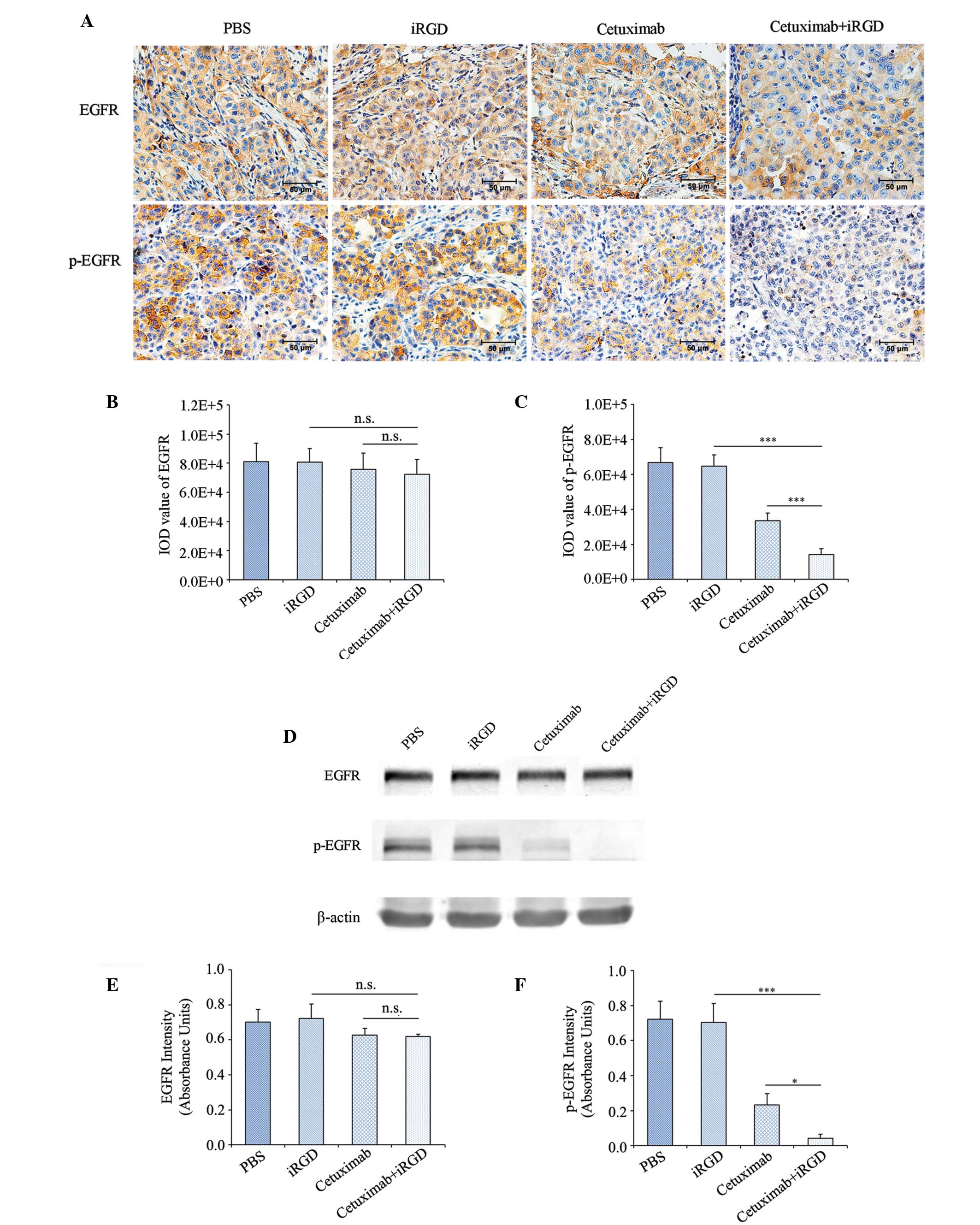
|
1
|
Privitera G, Luca T, Musso N, Vancheri C,
Crimi N, Barresi V, Condorelli D and Castorina S: In vitro
antiproliferative effect of trastuzumab (Herceptin®)
combined with cetuximab (Erbitux®) in a model of human
non-small cell lung cancer expressing EGFR and HER2. Clin Exp Med.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patil N, Abba M and Allgayer H: Cetuximab
and biomarkers in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Biologics.
6:221–231. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pujol JL, Pirker R, Lynch TJ, Butts CA,
Rosell R, Shepherd FA, Vansteenkiste J, O'Byrne KJ, de Blas B,
Heighway J, et al: Meta-analysis of individual patient data from
randomized trials of chemotherapy plus cetuximab as first-line
treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
83:211–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim SM, Kim JS, Kim JH, Yun CO, Kim EM,
Kim HK, Solca F, Choi SY and Cho BC: Acquired resistance to
cetuximab is mediated by increased PTEN instability and leads
cross-resistance to gefitinib in HCC827 NSCLC cells. Cancer Lett.
296:150–159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pirker R, Pereira JR, von Pawel J,
Krzakowski M, Ramlau R, Park K, de Marinis F, Eberhardt WE,
Paz-Ares L, Störkel S, et al: EGFR expression as a predictor of
survival for first-line chemotherapy plus cetuximab in patients
with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Analysis of data from the
phase 3 FLEX study. Lancet Oncol. 13:33–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Douillard JY, Pirker R, O'Byrne KJ, Kerr
KM, Störkel S, von Heydebreck A, Grote HJ, Celik I and Shepherd FA:
Relationship between EGFR expression, EGFR mutation status and the
efficacy of chemotherapy plus cetuximab in FLEX study patients with
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 9:717–724.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
van den Heuvel MM, Uyterlinde W, Vincent
AD, de Jong J, Aerts J, Koppe F, Knegjens J, Codrington H, Kunst
PW, Dieleman E, et al: Additional weekly Cetuximab to concurrent
chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung
carcinoma: Efficacy and safety outcomes of a randomized,
multi-center phase II study investigating. Radiother Oncol.
110:126–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dubey S and Schiller JH: Three emerging
new drugs for NSCLC: Pemetrexed, bortezomib and cetuximab.
Oncologist. 10:282–291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wild R, Fager K, Flefleh C, Kan D, Inigo
I, Castaneda S, Luo FR, Camuso A, McGlinchey K and Rose WC:
Cetuximab preclinical antitumor activity (monotherapy and
combination based) is not predicted by relative total or activated
epidermal growth factor receptor tumor expression levels. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:104–113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu T, Wang Z, Liu K, Wu Y, Fan J, Chen J,
Li C, Zhu G and Li L: High interstitial fluid pressure promotes
tumor progression through inducing lymphatic metastasis-related
protein expressions in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Transl
Oncol. 16:539–547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Milosevic MF, Pintilie M, Hedley DW,
Bristow RG, Wouters BG, Oza AM, Laframboise S, Hill RP and Fyles
AW: High tumor interstitial fluid pressure identifies cervical
cancer patients with improved survival from radiotherapy plus
cisplatin versus radiotherapy alone. Int J Cancer. 135:1692–1699.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Trédan O, Galmarini CM, Patel K and
Tannock IF: Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1441–1454. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song W, Li M, Tang Z, Li Q, Yang Y, Liu H,
Duan T, Hong H and Chen X: Methoxypoly (ethylene glycol)-block-poly
(L-glutamic acid)-loaded cisplatin and a combination with iRGD for
the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancers. Macromol Biosci.
12:1514–1523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sugahara KN, Teesalu T, Karmali PP,
Kotamraju VR, Agemy L, Girard OM, Hanahan D, Mattrey RF and
Ruoslahti E: Tissue-penetrating delivery of compounds and
nanoparticles into tumors. Cancer Cell. 16:510–520. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Su S, Wang H, Liu X, Wu Y and Nie G:
iRGD-coupled responsive fluorescent nanogel for targeted drug
delivery. Biomaterials. 34:3523–3533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alberici L, Roth L, Sugahara KN, Agemy L,
Kotamraju VR, Teesalu T, Bordignon C, Traversari C, Rizzardi GP and
Ruoslahti E: De novo design of a tumor-penetrating peptide. Cancer
Res. 73:804–812. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roth L, Agemy L, Kotamraju VR, Braun G,
Teesalu T, Sugahara KN, Hamzah J and Ruoslahti E: Transtumoral
targeting enabled by a novel neuropilin-binding peptide. Oncogene.
31:3754–3763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sugahara KN, Teesalu T, Karmali PP,
Kotamraju VR, Agemy L, Greenwald DR and Ruoslahti E:
Coadministration of a tumor-penetrating peptide enhances the
efficacy of cancer drugs. Science. 328:1031–1035. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Q, Liu X, Xu S, Li C, Zhang Y, Yang
J and Zheng J: Factor VII light chain-targeted lidamycin shows
intensified therapeutic efficacy for liver cancer. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 27:384–391. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aizawa K, Liu C, Veeramachaneni S, Hu KQ,
Smith DE and Wang XD: Development of ferret as a human lung cancer
model by injecting
4-(Nmethyl-N-nitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK). Lung
Cancer. 82:390–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ning L, Li X, Ding X, Yin Y and Li G: An
iRGD based strategy to study electrochemically the species inside a
cell. Int J Mol Sci. 13:10424–10431. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steiner P, Joynes C, Bassi R, Wang S,
Tonra JR, Hadari YR and Hicklin DJ: Tumor growth inhibition with
cetuximab and chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer xenografts
expressing wild-type and mutated epidermal growth factor receptor.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:1540–1551. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu F, Tian Y, Huang Y, Zhang LL, Guo ZZ,
Huang JJ and Lin TY: EGFR inhibitors sensitize non-small cell lung
cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Chin J Cancer. 30:701–711.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akashi Y, Oda T, Ohara Y, Miyamoto R,
Kurokawa T, Hashimoto S, Enomoto T, Yamada K, Satake M and Ohkohchi
N: Anticancer effects of gemcitabine are enhanced by
co-administered iRGD peptide in murine pancreatic cancer models
that overexpressed neuropilin-1. Br J Cancer. 110:1481–1487. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Villanueva MT: Lung cancer: Cetuximab,
you're fired. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 11:32014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rasul KI and Kerr DJ: Targeted therapies:
Cetuximab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 6:499–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sanchez AJ, Vincent MJ, Erickson BR and
Nichol ST: Crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoprotein
precursor is cleaved by Furin-like and SKI-1 proteases to generate
a novel 38-kilodalton glycoprotein. J Virol. 80:514–525. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wool-Lewis RJ and Bates P: Endoproteolytic
processing of the ebola virus envelope glycoprotein: Cleavage is
not required for function. J Virol. 73:1419–1426. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sjöberg M, Wallin M, Lindqvist B and
Garoff H: Furin cleavage potentiates the membrane
fusion-controlling intersubunit disulfide bond isomerization
activity of leukemia virus Env. J Virol. 80:5540–5551. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|