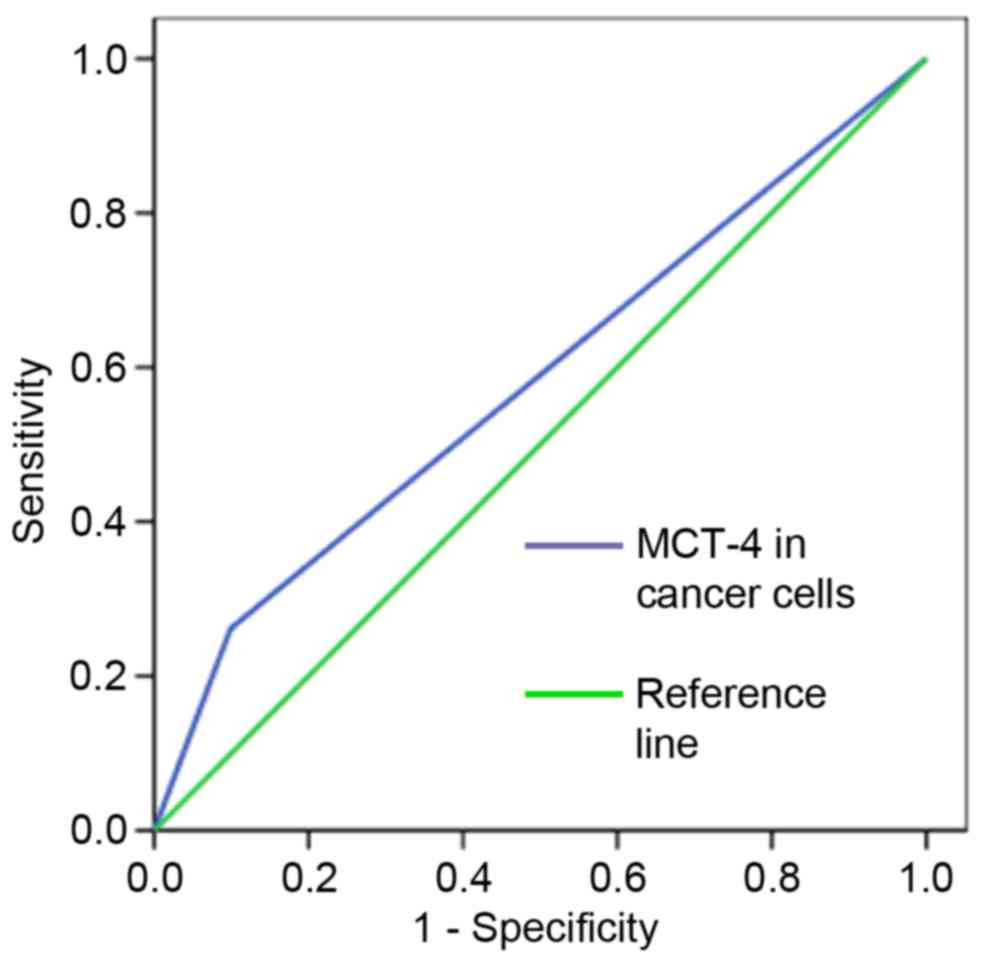
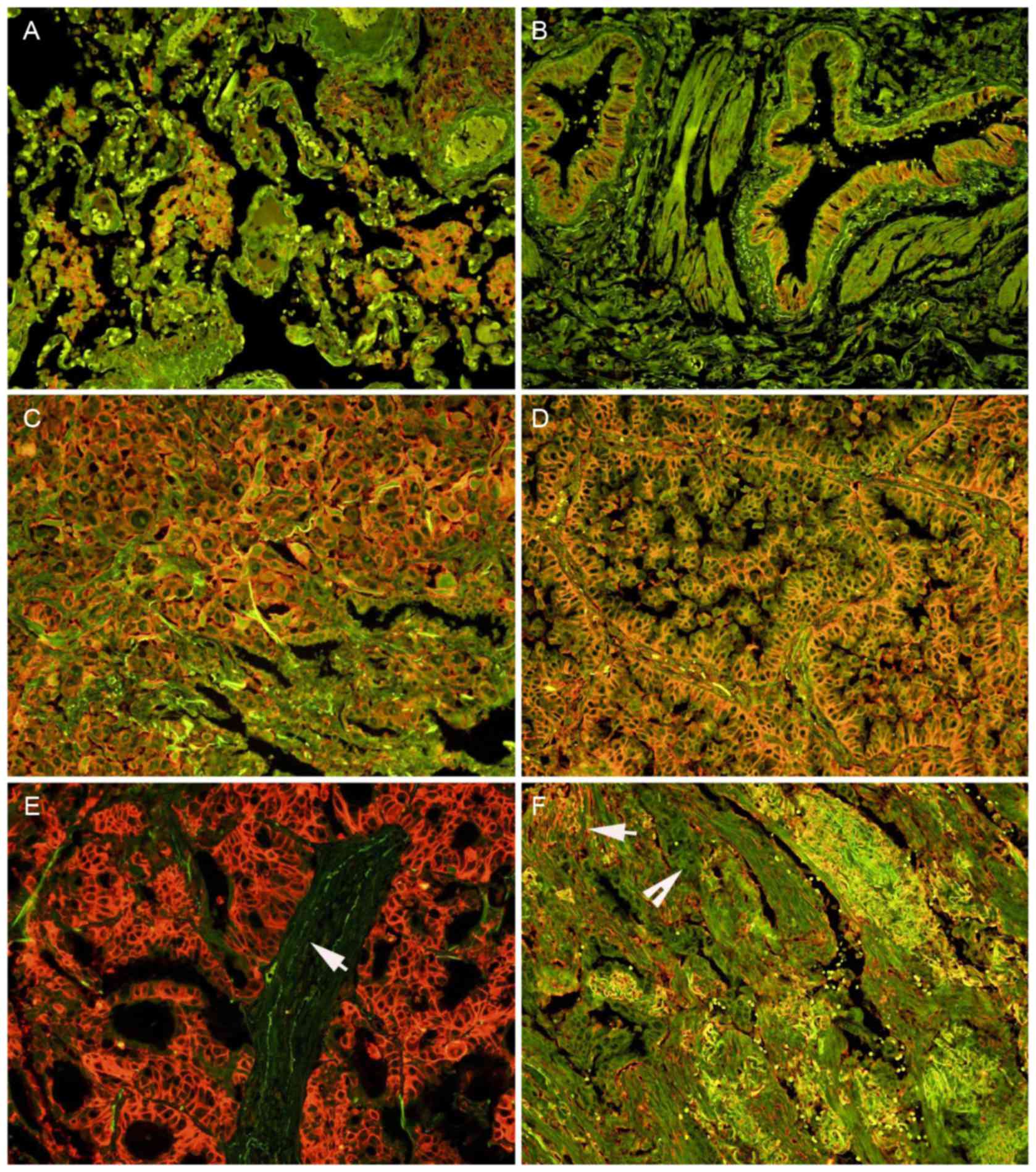
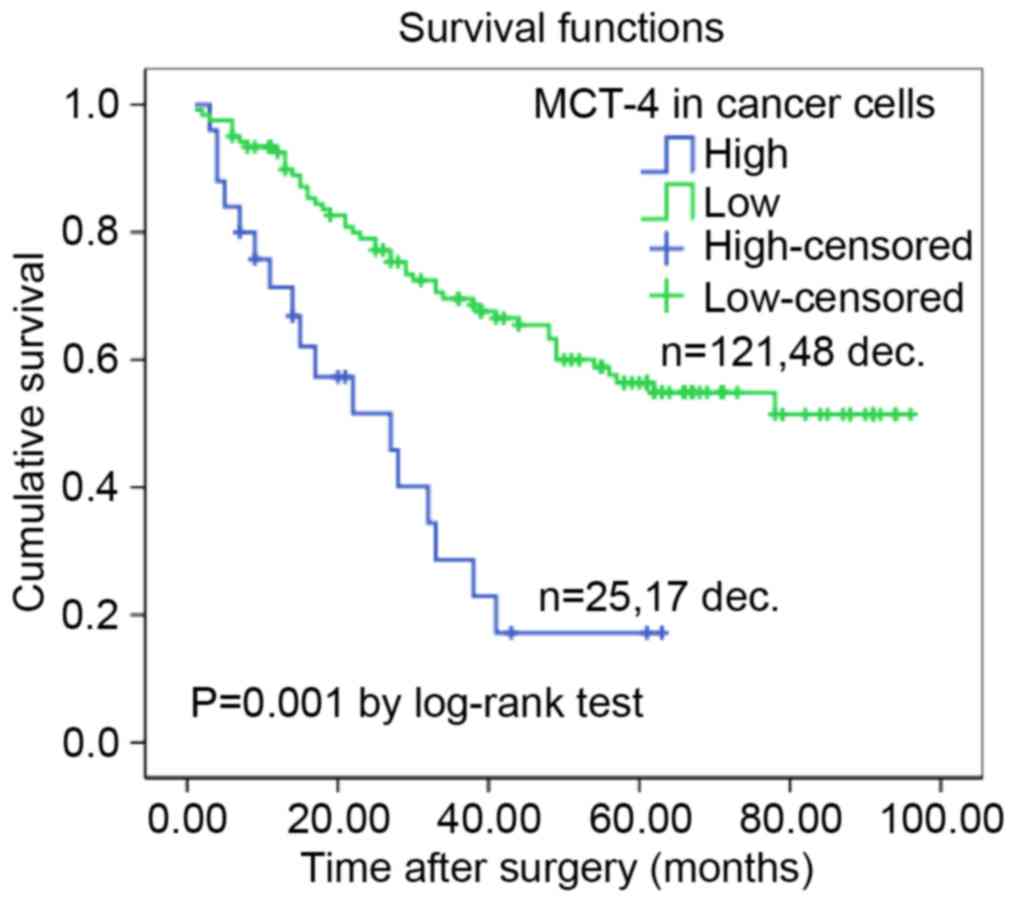
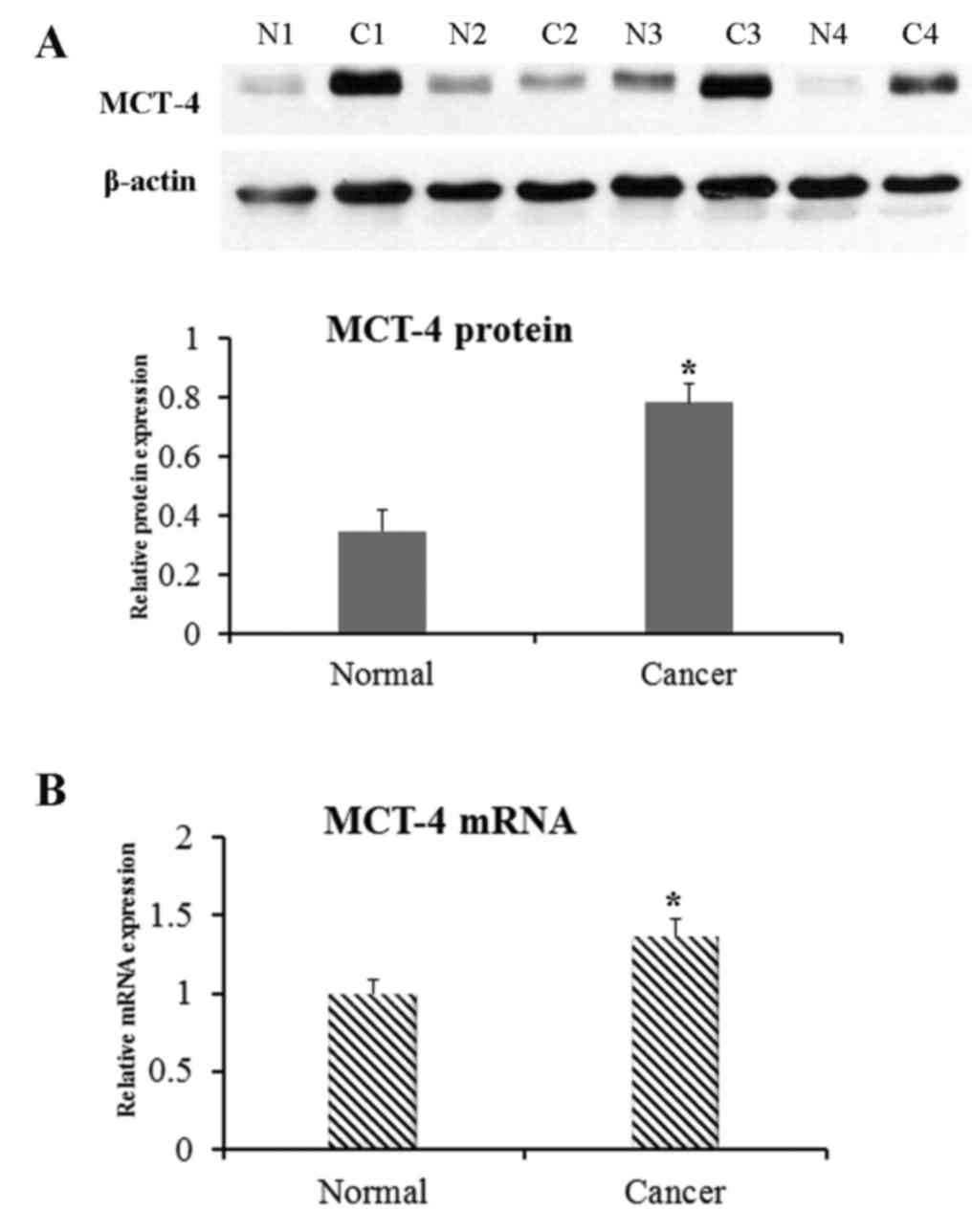
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA A Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thomas A, Liu SV, Subramaniam DS and
Giaccone G: Refining the treatment of NSCLC according to
histological and molecular subtypes. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
12:511–526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sica G, Yoshizawa A, Sima CS, Azzoli CG,
Downey RJ, Rusch VW, Travis WD and Moreira A: A grading system of
lung adenocarcinomas based on histologic pattern is predictive of
disease recurrence in stage I tumors. Am J Surg Patho.
34:1155–1162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Alberg AJ, Ford JG and Samet JM: American
College of Chest Physicians: Epidemiology of lung cancer: ACCP
evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 132:29S–55S.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M,
Nicholson AG, Geisinger K, Yatabe Y, Powell CA, Beer D, Riely G,
Garg K, et al: International Association for the Study of Lung
Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society:
International multidisciplinary classification of lung
adenocarcinoma: executive summary. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 8:381–385.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sterlacci W, Savic S, Schmid T, Oberaigner
W, Auberger J, Fiegl M and Tzankov A: Tissue-sparing application of
the newly proposed IASLC/ATS/ERS classification of adenocarcinoma
of the lung shows practical diagnostic and prognostic impact. Am J
Clin Pathol. 137:946–956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bissell MJ and Radisky D: Putting tumours
in context. Nat Rev Cancer. 1:46–54. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mueller MM and Fusenig NE: Friends or
foes-bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:839–849. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dvorak HF, Weaver VM, Tlsty TD and Bergers
G: Tumor microenvironment and progression. J Surg Oncol.
103:468–474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vaupel P, Kallinowski F and Okunieff P:
Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply and metabolic
microenvironment of human tumors: A review. Cancer Res.
49:6449–6465. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Izumi H, Torigoe T, Ishiguchi H, Uramoto
H, Yoshida Y, Tanabe M, Ise T, Murakami T, Yoshida T, Nomoto M and
Kohno K: Cellular pH regulators: Potentially promising molecular
targets for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 29:541–549.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pinheiro C, Longatto-Filho A,
Azevedo-Silva J, Casal M, Schmitt FC and Baltazar F: Role of
monocarboxylate transporters in human cancers: State of the art. J
Bioenerg Biomembr. 44:127–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Halestrap AP and Price NT: The
proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) family: Structure,
function and regulation. Biochem J. 343:281–299. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Broer S, Bröer A, Schneider H, Stegen C,
Halestrap A and Deitmer J: Characterization of the high-affinity
monocarboxylate transporter MCT2 in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biochem
J. 341:529–535. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grollman EF, Philp NJ, McPhie P, Ward RD
and Sauer B: Determination of transport kinetics of chick MCT3
monocarboxylate transporter from retinal pigment epithelium by
expression in genetically modified yeast. Biochemistry.
39:9351–9357. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dimmer KS, Friedrich B, Lang F, Deitmer JW
and Bröer S: The low-affinity monocarboxylate transporter MCT4 is
adapted to the export of lactate in highly glycolytic cells.
Biochem J. 350:219–227. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fox JEM, Meredith D and Halestrap AP:
Characterisation of human monocarboxylate transporter 4
substantiates its role in lactic acid efflux from skeletal muscle.
J Physiol. 529:285–293. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Harris
AL and Sivridis E: Comparison of metabolic pathways between cancer
cells and stromal cells in colorectal carcinomas: A metabolic
survival role for tumor-associated stroma. Cancer Res. 66:632–637.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin RY, Vera JC, Chaganti RS and Golde DW:
Human monocarboxylate transporter 2 (MCT2) is a high affinity
pyruvate transporter. J Biol Chem. 273:28959–28965. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lambert DW, Wood IS, Ellis A and
Shirazi-Beechey S: Molecular changes in the expression of human
colonic nutrient transporters during the transition from normality
to malignancy. Br J Cancer. 86:1262–1269. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pinheiro C, Longatto-Filho A, Scapulatempo
C, Ferreira L, Martins S, Pellerin L, Rodrigues M, Alves VA,
Schmitt F and Baltazar F: Increased expression of monocarboxylate
transporters 1, 2 and 4 in colorectal carcinomas. Virchows Archiv.
452:139–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Juel C and Halestrap AP: Lactate transport
in skeletal muscle-role and regulation of the monocarboxylate
transporter. J Physiol. 517:633–642. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pinheiro C, Reis RM, Ricardo S,
Longatto-Filho A, Schmitt F and Baltazar F: Expression of
monocarboxylate transporters 1, 2 and 4 in human tumours and their
association with CD147 and CD44. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:4276942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakayama Y, Torigoe T, Inoue Y, Minagawa
N, Izumi H, Kohno K and Yamaguchi K: Prognostic significance of
monocarboxylate transporter 4 expression in patients with
colorectal cancer. Exp Ther Med. 3:25–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim MJ, Kim DH, Jung WH and Koo JS:
Expression of metabolism-related proteins in triple-negative breast
cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:301–312. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu J, Wu YN, Zhang W, Zhang XM, Ding X,
Li HQ, Geng M, Xie ZQ and Wu HM: Monocarboxylate transporter 4
facilitates cell proliferation and migration and is associated with
poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. PLoS One.
9:e879042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pértega-Gomes N, Vizcaíno JR,
Miranda-Gonçalves V, Pinheiro C, Silva J, Pereira H, Monteiro P,
Henrique RM, Reis RM, Lopes C and Baltazar F: Monocarboxylate
transporter 4 (MCT4) and CD147 overexpression is associated with
poor prognosis in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer. 11:3122011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: International Union against CancerTNM classification of
malignant tumours. 7th. Chichester, Hoboken NJ: Wiley-Blackwell;
2010
|
|
29
|
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallionimeni A,
Bärlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S, Torhorst J, Mihatsch MJ, Sauter G
and Kallioniemi OP: Tissue microarrays for high-throughput
molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med. 4:844–847. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li M, Chen H, Diao L, Zhang Y, Xia C and
Yang F: Caveolin-1 and VEGF-C promote lymph node metastasis in the
absence of intratumoral lymphangiogenesis in non-small cell lung
cancer. Tumori. 96:7342010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen H, Xue J, Zhang Y, Zhu X, Gao J and
Yu B: Comparison of quantum dots immunofluorescence histochemistry
and conventional immunohistochemistry for the detection of
caveolin-1 and PCNA in the lung cancer tissue microarray. J Mol
Histol. 40:261–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao X, He Y, Gao J, Fan L, Li Z, Yang G
and Chen H: Caveolin-1 expression level in cancer associated
fibroblasts predicts outcome in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
8:e591022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meijer TW, Schuurbiers OC, Kaanders JH,
Looijen-Salamon MG, de Geus-Oei LF, Verhagen AF, Lok J, van der
Heijden HF, Rademakers SE, Span PN and Bussink J: Differences in
metabolism between adeno-and squamous cell non-small cell lung
carcinomas: Spatial distribution and prognostic value of GLUT1 and
MCT4. Lung Cancer. 76:316–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mathupala SP, Parajuli P and Sloan AE:
Silencing of monocarboxylate transporters via small interfering
ribonucleic acid inhibits glycolysis and induces cell death in
malignant glioma: An in vitro study. Neurosurgery. 55:1410–1419.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sonveaux P, Végran F, Schroeder T, Wergin
MC, Verrax J, Rabbani ZN, De Saedeleer CJ, Kennedy KM, Diepart C,
Jordan BF, et al: Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively
kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:3930–3942.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eilertsen M, Andersen S, Al-Saad S,
Kiselev Y, Donnem T, Stenvold H, Pettersen I, Al-Shibli K,
Richardsen E, Busund LT and Bremnes RM: Monocarboxylate
transporters 1–4 in NSCLC: MCT1 is an independent prognostic marker
for survival. PLoS One. 9:e1050382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Garcia CK, Goldstein JL, Pathak RK,
Anderson RG and Brown MS: Molecular characterization of a membrane
transporter for lactate, pyruvate and other monocarboxylates:
Implications for the Cori cycle. Cell. 76:865–873. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Izumi H, Takahashi M, Uramoto H, Nakayama
Y, Oyama T, Wang KY, Sasaguri Y, Nishizawa S and Kohno K:
Monocarboxylate transporters 1 and 4 are involved in the invasion
activity of human lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 102:1007–1013.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lorusso G and Rüegg C: The tumor
microenvironment and its contribution to tumor evolution toward
metastasis. Histochem Cell Biol. 130:1091–1103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao Z, Han F, He Y, Yang S, Hua L, Wu J
and Zhan W: Stromal-epithelial metabolic coupling in gastric
cancer: Stromal MCT4 and mitochondrial TOMM20 as poor prognostic
factors. Eur J Surg Oncol. 40:1361–1368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Andersen S, Solstad Ø, Moi L, Donnem T,
Eilertsen M, Nordby Y, Ness N, Richardsen E, Busund LT and Bremnes
RM: Organized metabolic crime in prostate cancer: The coexpression
of MCT1 in tumor and MCT4 in stroma is an independent
prognosticator for biochemical failure. Urol Oncol. 33:338.e9–17.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sanità P, Capulli M, Teti A, Galatioto GP,
Vicentini C, Chiarugi P, Bologna M and Angelucci A: Tumor-stroma
metabolic relationship based on lactate shuttle can sustain
prostate cancer progression. BMC Cancer. 14:154–167. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
San-Millán I and Brooks GA: Reexamining
cancer metabolism: Lactate production for carcinogenesis could be
the purpose and explanation of the Warburg Effect. Carcinogenesis.
38:119–133. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|