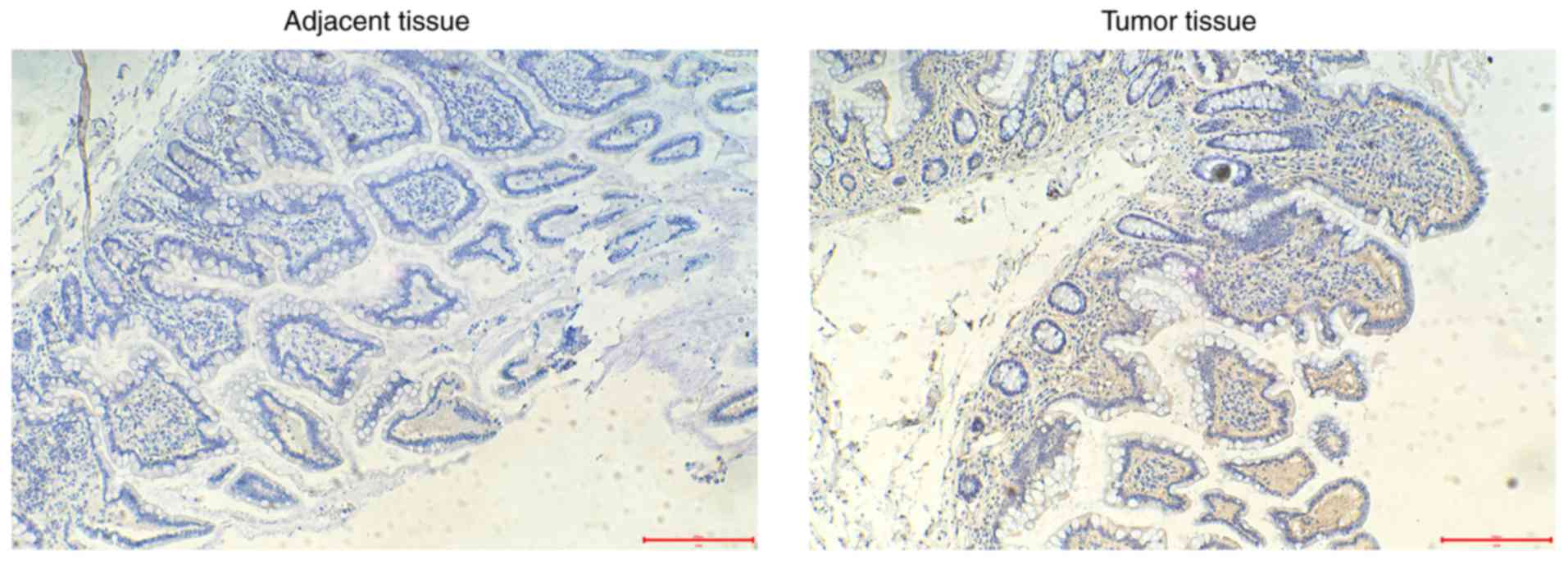
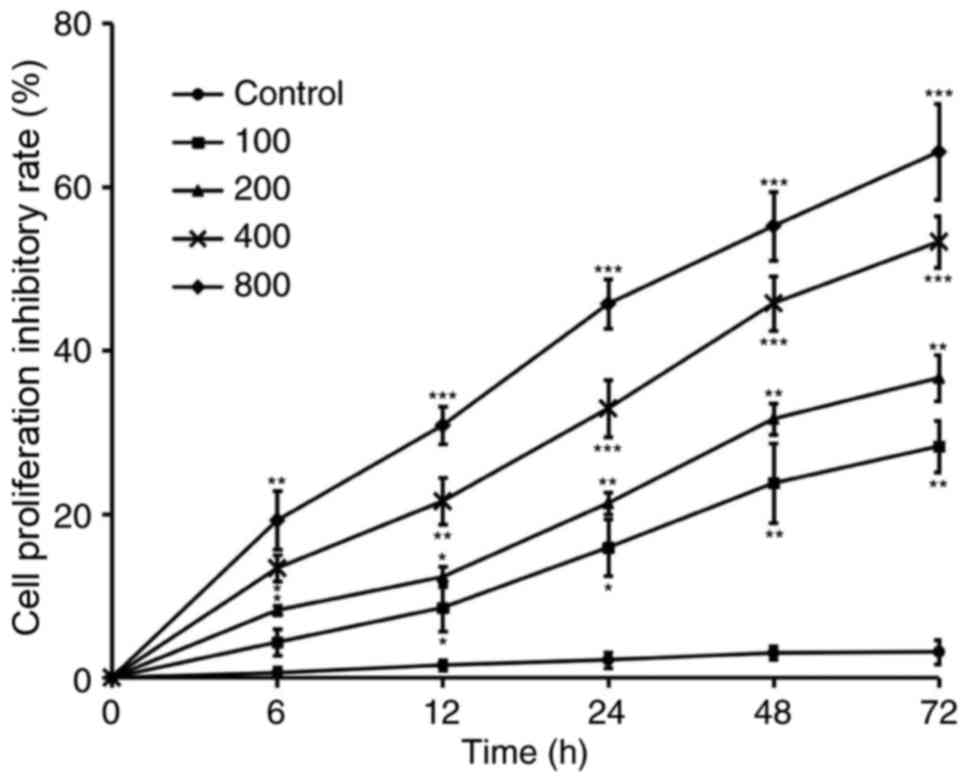
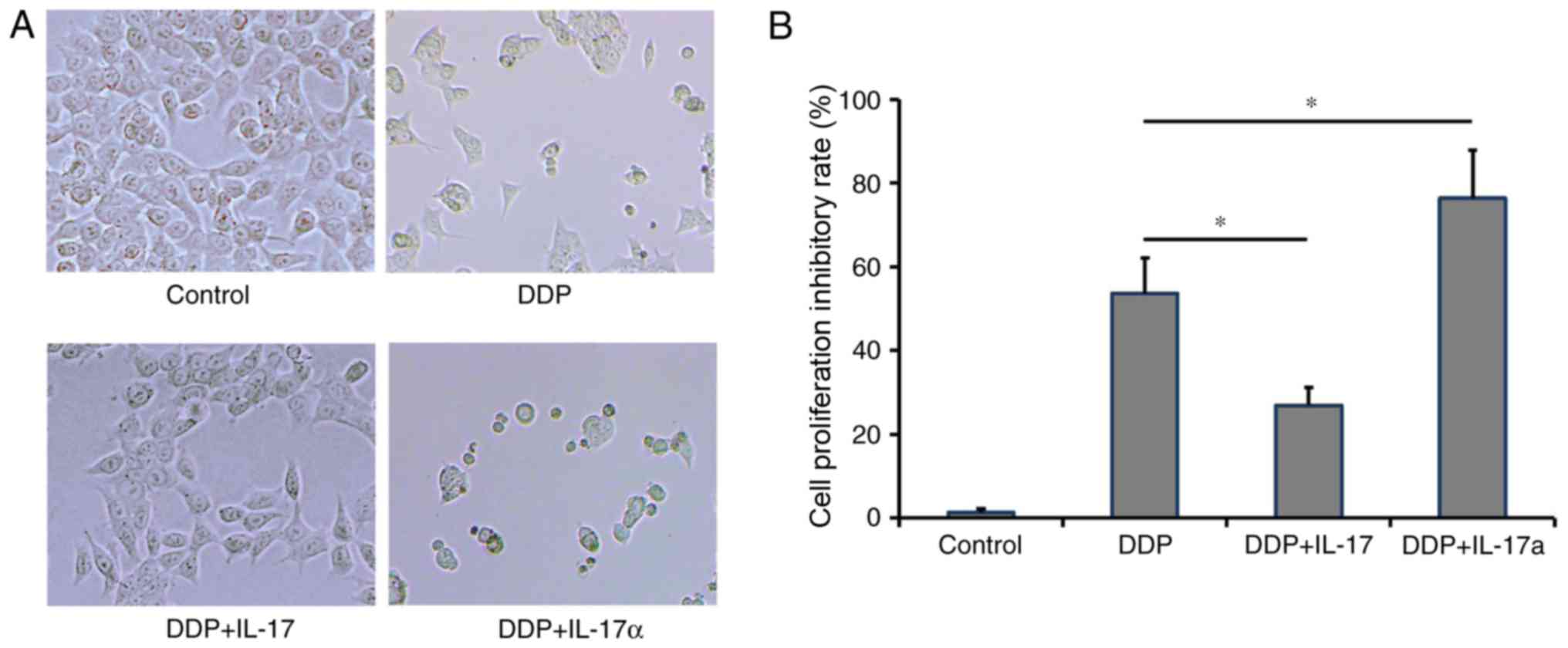
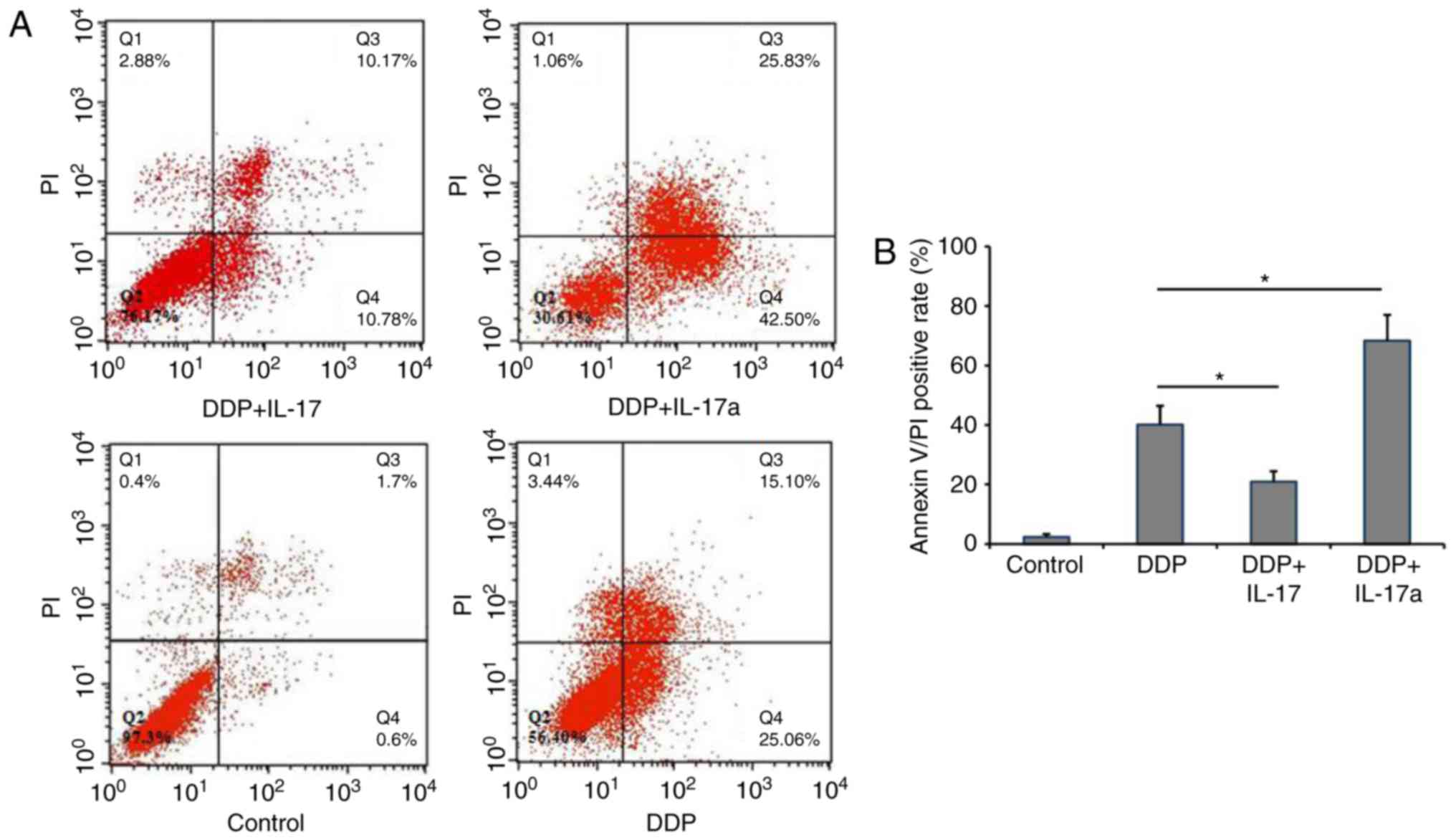
|
1
|
McQuade RM, Stojanovska V, Bornstein JC
and Nurgali K: Colorectal cancer chemotherapy: The evolution of
treatment and new approaches. Curr Med Chem. 24:1537–1557. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Michels J, Brenner
C, Szabadkai G, Harel-Bellan A, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Systems
biology of cisplatin resistance: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dise. 5:e12572014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Valsecchi ME: Combined nivolumab and
ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Eng J Med.
373:12702015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, Feng J, Lu S, Huang
Y, Li W, Hou M, Shi JH, Lee KY, et al: Afatinib versus cisplatin
plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations
(LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 15:213–222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Landskron G, De la Fuente M, Thuwajit P,
Thuwajit C and Hermoso MA: Chronic inflammation and cytokines in
the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res. 2014:1491852014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujino S, Andoh A, Bamba S, Ogawa A, Hata
K, Araki Y, Bamba T and Fujiyama Y: Increased expression of
interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 52:65–70. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chabaud M, Garnero P, Dayer JM, Guerne PA,
Fossiez F and Miossec P: Contribution of interleukin 17 to synovium
matrix destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. 12:1092–1099.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Akbay EA, Koyama S, Liu Y, Dries R, Bufe
LE, Silkes M, Alam MM, Magee DM, Jones R, Jinushi M, et al:
Interleukin-17A Promotes lung tumor progression through neutrophil
attraction to tumor sites and mediating resistance to PD-1
blockade. J Thorac Oncol. 12:1268–1279. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carvalho DFG, Zanetti BR, Miranda L,
Hassumi-Fukasawa MK, Miranda-Camargo F, Crispim JCO and Soares EG:
High IL-17 expression is associated with an unfavorable prognosis
in thyroid cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:1925–1931. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wilke CM, Kryczek I, Wei S, Zhao E, Wu K,
Wang G and Zou W: Th17 cells in cancer: Help or hindrance?
Carcinogenesis. 32:643–649. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu J, Ye H, Zhang D, Liu W, Li M, Mao Y
and Lu Y: U87MG glioma cells overexpressing IL-17 acclerate
early-stage growth in vivo and cause a higher level of CD31 mRNA
expression in tumor tissues. Oncol Lett. 6:993–999. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ernst M and Putoczki T: IL-17 cuts to the
chase in colon cancer. Immunity. 41:880–882. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang K, Kim MK, Di Caro G, Wong J,
Shalapour S, Wan J, Zhang W, Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E, Wu LW, et
al: Interleukin-17 receptor a signaling in transformed enterocytes
promotes early colorectal tumorigenesis. Immunity. 41:1052–1063.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang Y, Al-Alwan L, Risse PA, Halayko AJ,
Martin JG, Baglole CJ, Eidelman DH and Hamid Q: Th17-associated
cytokines promote human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation.
FASEB J. 26:5152–5160. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang B, Kang H, Fung A, Zhao H, Wang T and
Ma D: The role of interleukin 17 in tumour proliferation,
angiogenesis, and metastasis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:6237592014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cochaud S, Giustiniani J, Thomas C,
Laprevotte E, Garbar C, Savoye AM, Curé H, Mascaux C, Alberici G,
Bonnefoy N, et al: IL-17A is produced by breast cancer TILs and
promotes chemoresistance and proliferation through ERK1/2. Sci Rep.
3:34562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Boulikas T and Vougiouka M: Cisplatin and
platinum drugs at the molecular level. (Review). Oncol Rep.
10:1663–1682. 2003.
|
|
18
|
Zhang HB, Lu P, Guo QY, Zhang ZH and Meng
XY: Baicalein induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells through modulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncol
Lett. 5:722–728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Al-Fatlawi AA, Al-Fatlawi AA, Irshad M,
Zafaryab M, Rizvi MM and Ahmad A: Rice bran phytic acid induced
apoptosis through regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and p53 genes in HepG2
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:3731–3736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji Y and Zhang W: Th17 cells: Positive or
negative role in tumor? Cancer Immunol Immunother. 59:979–987.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lereclus E, Tout M, Girault A, Baroukh N,
Caulet M, Borg C, Bouché O, Ternant D, Paintaud G, Lecomte T and
Raoul W: A possible association of baseline serum IL-17A
concentrations with progression-free survival of metastatic
colorectal cancer patients treated with a bevacizumab-based
regimen. BMC Cancer. 17:2202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Al-Samadi A, Moossavi S, Salem A, Sotoudeh
M, Tuovinen SM, Konttinen YT, Salo T and Bishehsari F: Distinctive
expression pattern of interleukin-17 cytokine family members in
colorectal cancer. Tumor Bio. 37:1609–1615. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|