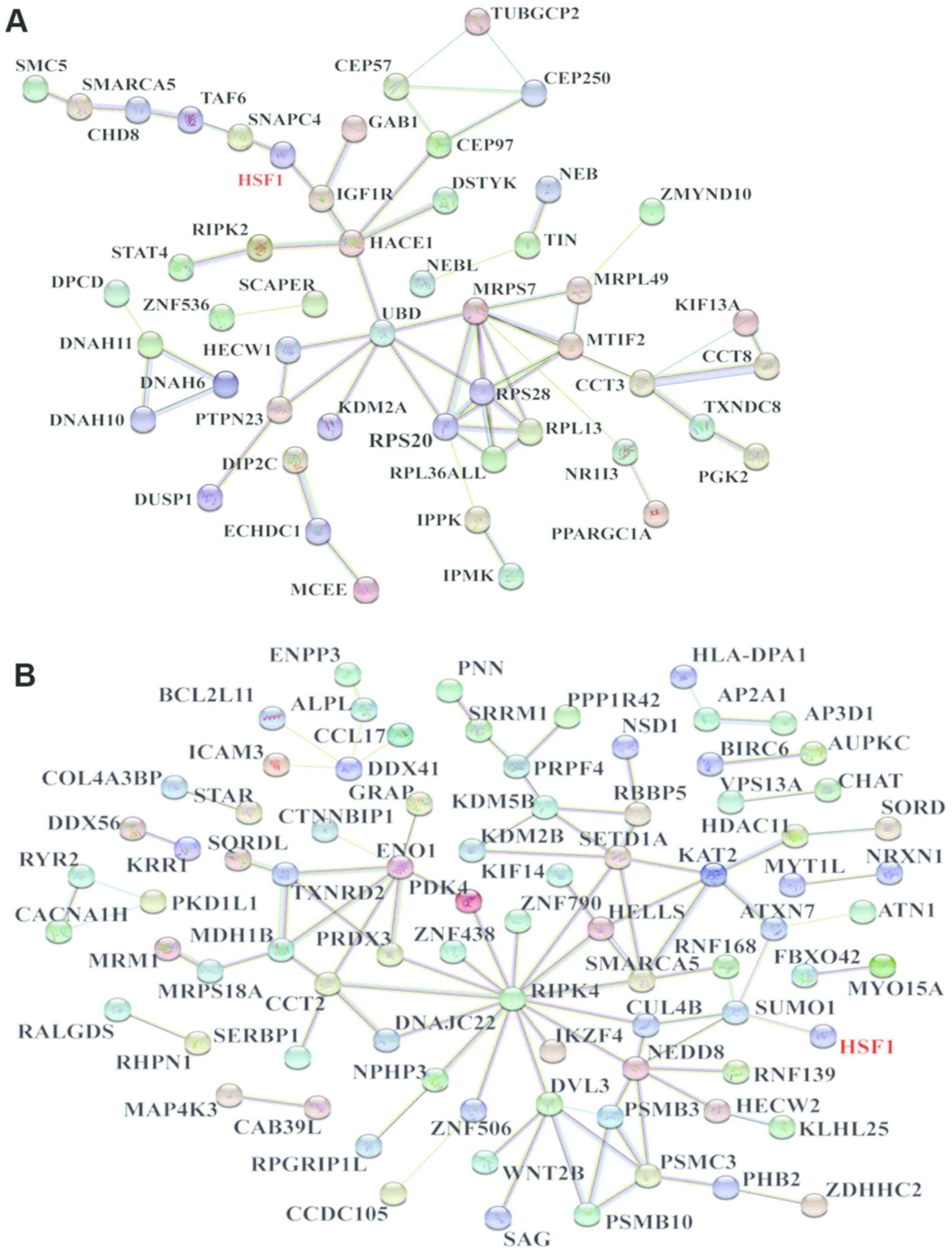
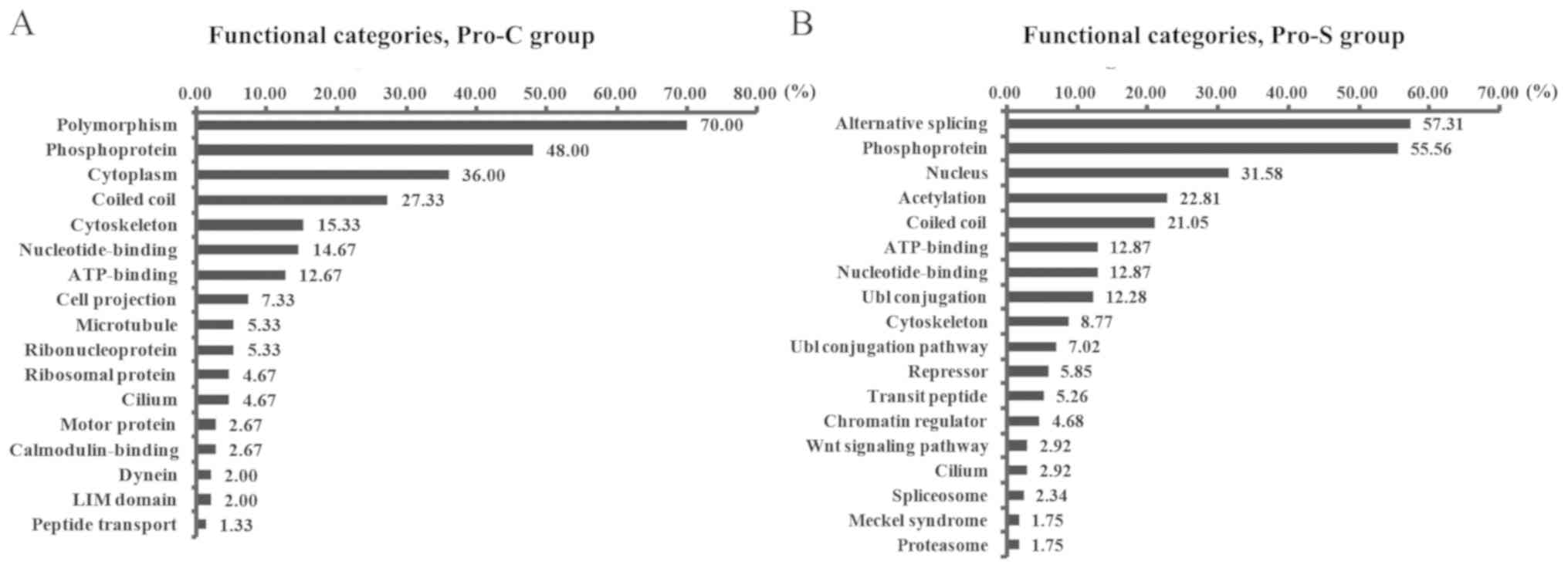
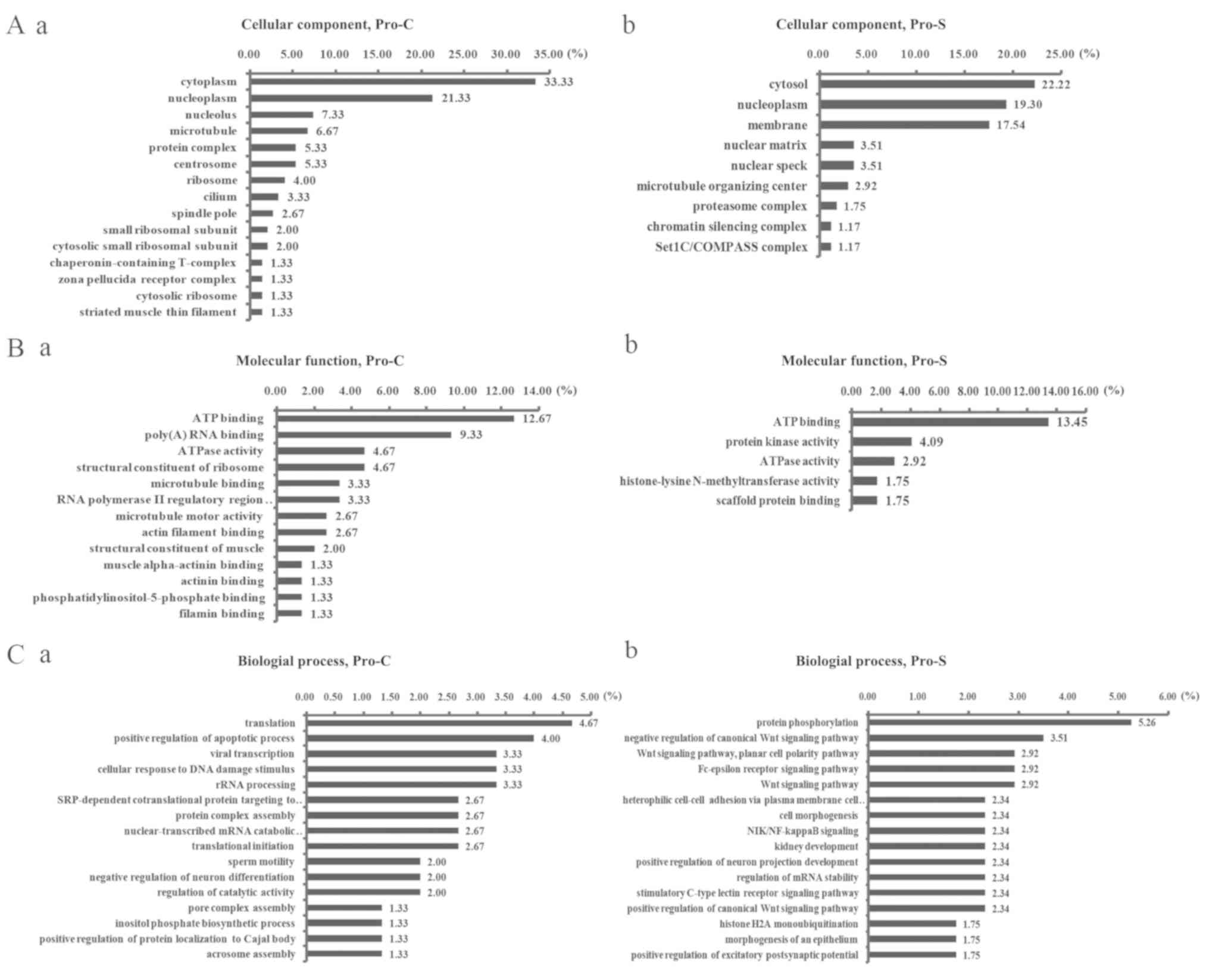
|
1
|
Hsu HC, Li X, Curtin JP, Goldberg JD and
Schiff PB: Surveillance epidemiology and end results analysis
demonstrates improvement in overall survival for cervical cancer
patients treated in the era of concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Front
Oncol. 5:812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ritossa F: A new puffing pattern induced
by temperature shock and DNP in Drosophila. Experientia.
18:571–573. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Baler R, Dahl G and Voellmy R: Activation
of human heat shock genes is accompanied by oligomerization,
modification, and rapid translocation of heat shock transcription
factor HSF1. Mol Cell Biol. 13:2486–2496. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi Y, Mosser DD and Morimoto RI:
Molecular chaperones as HSF1-specific transcriptional repressors.
Genes Dev. 12:654–666. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Santagata S, Hu R, Lin NU, Mendillo ML,
Collins LC, Hankinson SE, Schnitt SJ, Whitesell L, Tamimi RM,
Lindquist S and Ince TA: High levels of nuclear heat-shock factor 1
(HSF1) are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:18378–18383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Powell CD, Paullin TR, Aoisa C, Menzie CJ,
Ubaldini A and Westerheide SD: The heat shock transcription factor
hsf1 induces ovarian cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition in a
3D spheroid growth model. PLoS One. 11:e01683892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu S, Cheng M, Hou L, Zhang W, Liu B and
Linghu H: HSF1 expression in cervical carcinoma and its correlation
with clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis. J Third
Mil Med Univ. 36:560–563. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Calderwood SK: Elevated levels of HSF1
indicate a poor prognosis in breast cancer. Future Oncol.
8:399–401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai C, Whitesell L, Rogers AB and
Lindquist S: Heat shock factor 1 is a powerful multifaceted
modifier of carcinogenesis. Cell. 130:1005–1018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mendillo ML, Santagata S, Koeva M, Bell
GW, Hu R, Tamimi RM, Fraenkel E, Ince TA, Whitesell L and Lindquist
S: HSF1 drives a transcriptional program distinct from heat shock
to support highly malignant human cancers. Cell. 150:549–562. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Scherz-Shouval R, Santagata S, Mendillo
ML, Sholl LM, Ben-Aharon I, Beck AH, Dias-Santagata D, Koeva M,
Stemmer SM, Whitesell L and Lindquist S: The reprogramming of tumor
stroma by HSF1 is a potent enabler of malignancy. Cell.
158:564–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Yang M, Wang Q, Liu M, Liang Q,
Zhang H and Xiao X: HSF1 regulates expression of G-CSF through the
binding element for NF-IL6/CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta. Mol
Cell Biochem. 352:11–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Grammatikakis N, Siganou A,
Stevenson MA and Calderwood SK: Interactions between extracellular
signal-regulated protein kinase 1, 14-3-3epsilon, and heat shock
factor 1 during stress. J Biol Chem. 279:49460–49469. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eroglu B, Min JN, Zhang Y, Szurek E,
Moskophidis D, Eroglu A and Mivechi NF: An essential role for heat
shock transcription factor binding protein 1 (HSBP1) during early
embryonic development. Dev Biol. 386:448–460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luo T, Fu J, Xu A, Su B, Ren Y, Li N, Zhu
J, Zhao X, Dai R, Cao J, et al: PSMD10/gankyrin induces autophagy
to promote tumor progression through cytoplasmic interaction with
ATG7 and nuclear transactivation of ATG7 expression. Autophagy.
12:1355–1371. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ostling P, Björk JK, Roos-Mattjus P,
Mezger V and Sistonen L: Heat shock factor 2 (HSF2) contributes to
inducible expression of hsp genes through interplay with HSF1. J
Biol Chem. 282:7077–7086. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie Y, Chen C, Stevenson MA, Auron PE and
Calderwood SK: Heat shock factor 1 represses transcription of the
IL-1beta gene through physical interaction with the nuclear factor
of interleukin 6. J Biol Chem. 277:11802–11810. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I,
Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP and Burge CB: Alternative
isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature.
456:470–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rong C, Feng Y and Ye Z: Notch is a
critical regulator in cervical cancer by regulating Numb splicing.
Oncol Lett. 13:2465–2470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gaytan-Cervantes J, Gonzalez-Torres C,
Maldonado V, Zampedri C, Ceballos-Cancino G and Melendez-Zajgla J:
Protein Sam68 regulates the alternative splicing of survivin DEx3.
J Biol Chem. 292:13745–13757. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nikoshkov A, Broliden K, Attarha S,
Sviatoha V, Hellström AC, Mints M and Andersson S: Expression
pattern of the PRDX2, RAB1A, RAB1B, RAB5A and RAB25 genes in normal
and cancer cervical tissues. Int J Oncol. 46:107–112. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bradley T, Cook ME and Blanchette M: SR
proteins control a complex network of RNA-processing events. RNA.
21:75–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xia W, Guo Y, Vilaboa N, Zuo J and Voellmy
R: Transcriptional activation of heat shock factor HSF1 probed by
phosphopeptide analysis of factor 32P-labeled in vivo. J Biol Chem.
273:8749–8755. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Holmberg CI, Hietakangas V, Mikhailov A,
Rantanen JO, Kallio M, Meinander A, Hellman J, Morrice N,
MacKintosh C, Morimoto RI, et al: Phosphorylation of serine 230
promotes inducible transcriptional activity of heat shock factor 1.
EMBO J. 20:3800–3810. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chu B, Soncin F, Price BD, Stevenson MA
and Calderwood SK: Sequential phosphorylation by mitogen-activated
protein kinase and glycogen synthase kinase 3 represses
transcriptional activation by heat shock factor-1. J Biol Chem.
271:30847–30857. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cotto JJ, Kline M and Morimoto RI:
Activation of heat shock factor 1 DNA binding precedes
stress-induced serine phosphorylation. Evidence for a multistep
pathway of regulation. J Biol Chem. 271:3355–3358. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin J, Jiang XY, Qi W, Ji CG, Xie XL,
Zhang DX, Cui ZJ, Wang CK, Bai Y, Wang J and Jiang HQ: piR-823
contributes to colorectal tumorigenesis by enhancing the
transcriptional activity of HSF1. Cancer Sci. 108:1746–1756. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Azizmohammadi S, Azizmohammadi S, Safari
A, Kaghazian M, Sadrkhanlo M, Behnod V and Seifoleslami M:
High-Level Expression of RIPK4 and EZH2 contributes to lymph node
metastasis and predicts favorable prognosis in patients with
cervical cancer. Oncol Res. 25:495–501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang X, McGann JC, Liu BY, Hannoush RN,
Lill JR, Pham V, Newton K, Kakunda M, Liu J, Yu C, et al:
Phosphorylation of Dishevelled by protein kinase RIPK4 regulates
Wnt signaling. Science. 339:1441–1445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dayalan Naidu S, Sutherland C, Zhang Y,
Risco A, de la Vega L, Caunt CJ, Hastie CJ, Lamont DJ, Torrente L,
Chowdhry S, et al: Heat shock factor 1 Is a substrate for p38
mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 36:2403–2417.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hietakangas V, Ahlskog JK, Jakobsson AM,
Hellesuo M, Sahlberg NM, Holmberg CI, Mikhailov A, Palvimo JJ,
Pirkkala L and Sistonen L: Phosphorylation of serine 303 is a
prerequisite for the stress-inducible SUMO modification of heat
shock factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 23:2953–2968. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Banks GT, Haas MA, Line S, Shepherd HL,
Alqatari M, Stewart S, Rishal I, Philpott A, Kalmar B, Kuta A, et
al: Behavioral and other phenotypes in a cytoplasmic Dynein light
intermediate chain 1 mutant mouse. J Neurosci. 31:5483–5494. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Szeliga M, Obara-Michlewska M, Matyja E,
Łazarczyk M, Lobo C, Hilgier W, Alonso FJ, Márquez J and Albrecht
J: Transfection with liver-type glutaminase cDNA alters gene
expression and reduces survival, migration and proliferation of
T98G glioma cells. Glia. 57:1014–1023. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Antonietti P, Linder B, Hehlgans S,
Mildenberger IC, Burger MC, Fulda S, Steinbach JP, Gessler F, Rödel
F, Mittelbronn M and Kögel D: Interference with the HSF1/HSP70/bag3
pathway primes glioma cells to matrix detachment and BH3
mimetic-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:156–168. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Beyer S, Zhu J, Mayr D, Kuhn C, Schulze S,
Hofmann S, Dannecker C, Jeschke U and Kost BP: Histone H3 acetyl K9
and histone H3 tri methyl K4 as prognostic markers for patients
with cervical cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E4772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Col E, Hoghoughi N, Dufour S, Penin J,
Koskas S, Faure V, Ouzounova M, Hernandez-Vargash H, Reynoird N,
Daujat S, et al: Bromodomain factors of BET family are new
essential actors of pericentric heterochromatin transcriptional
activation in response to heat shock. Sci Rep. 7:54182017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu J, Zheng Q, Deng Y, Cheng CS,
Kallenbach NR and Lu M: A seven-helix coiled coil. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:15457–15462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shinada K, Tsukiyama T, Sho T, Okumura F,
Asaka M and Hatakeyama S: RNF43 interacts with NEDL1 and regulates
p53-mediated transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
404:143–147. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Choi KS, Choi HJ, Lee JK, Im S, Zhang H,
Jeong Y, Park JA, Lee IK, Kim YM and Kwon YG: The endothelial E3
ligase HECW2 promotes endothelial cell junctions by increasing
AMOTL1 protein stability via K63-linked ubiquitination. Cell
Signal. 28:1642–1651. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bahrami A, Hasanzadeh M, ShahidSales S,
Yousefi Z, Kadkhodayan S, Farazestanian M, Joudi Mashhad M, Gharib
M, Mahdi Hassanian S and Avan A: Clinical significance and
prognosis value of Wnt signaling pathway in cervical cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 118:3028–3033. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang R, Lu H, Lyu YY, Yang XM, Zhu LY,
Yang GD, Jiang PC, Re Y, Song WW, Wang JH, et al:
E6/E7-P53-POU2F1-CTHRC1 axis promotes cervical cancer metastasis
and activates Wnt/PCP pathway. Sci Rep. 7:447442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li G, Song Y, Zhang Y, Wang H and Xie J:
miR-34b Targets HSF1 to suppress cell survival in acute myeloid
leukemia. Oncol Res. 24:109–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|