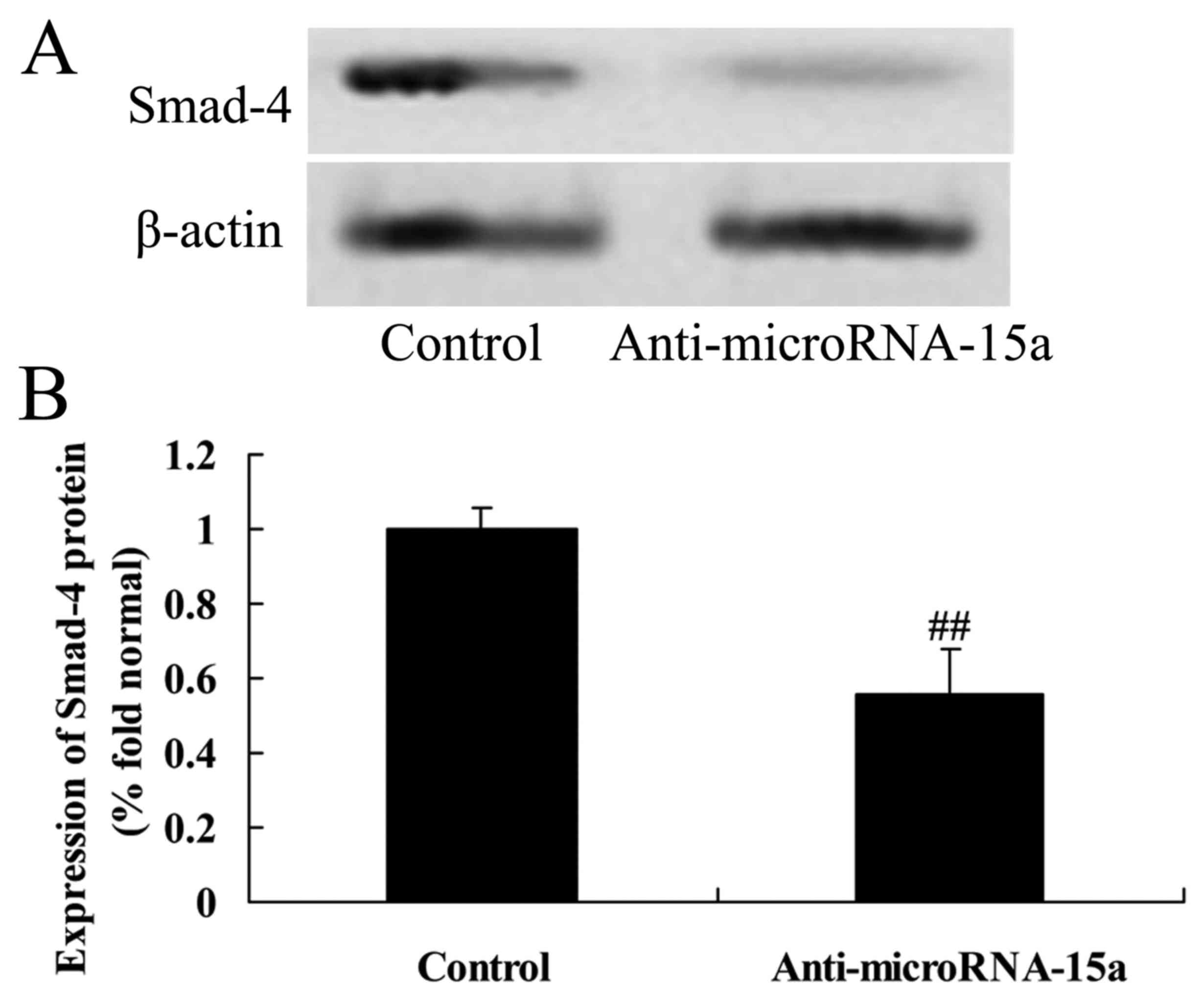
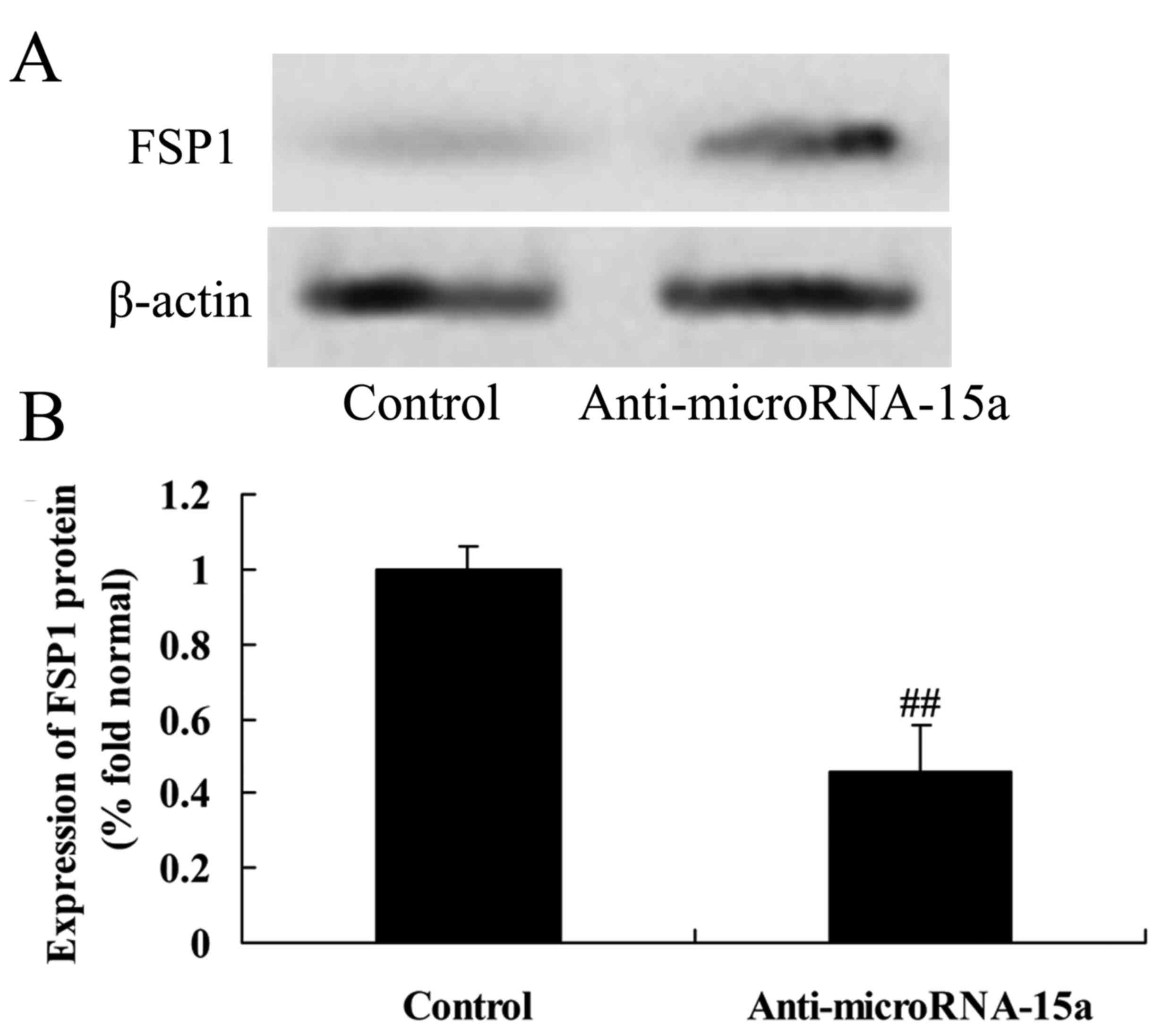
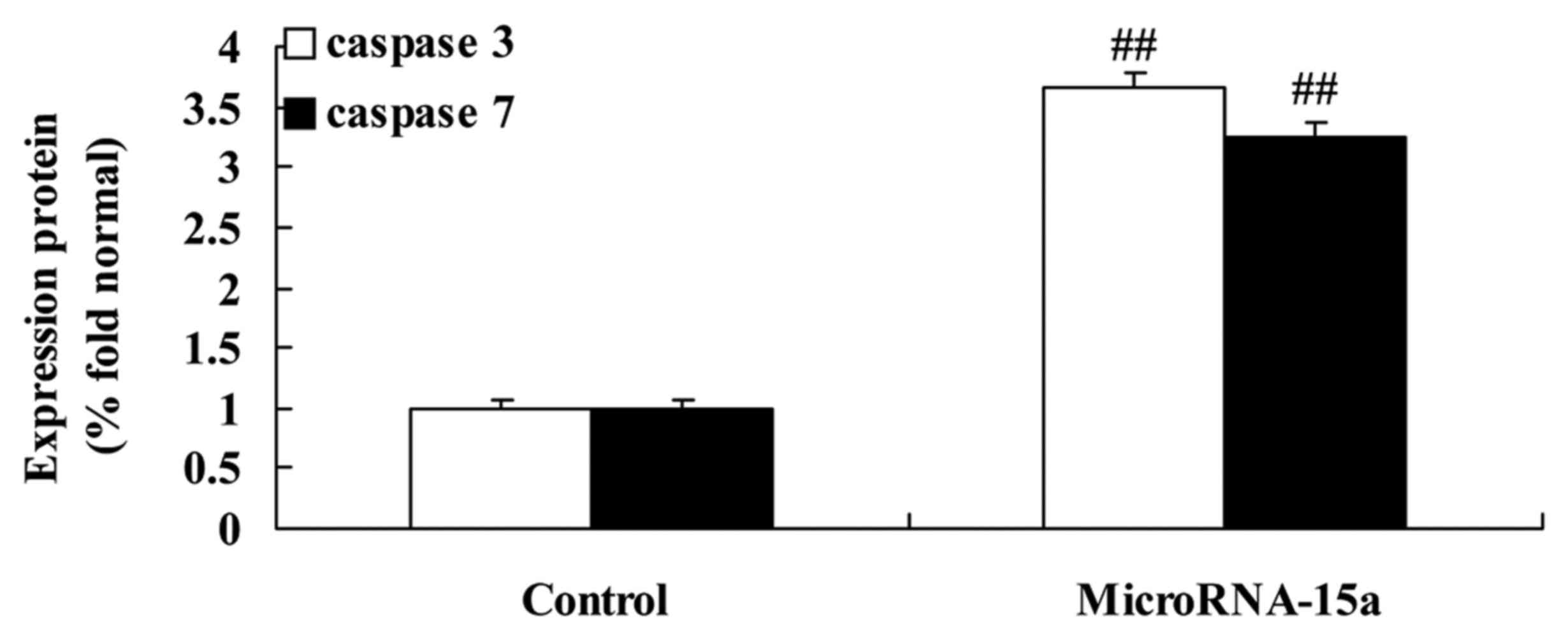
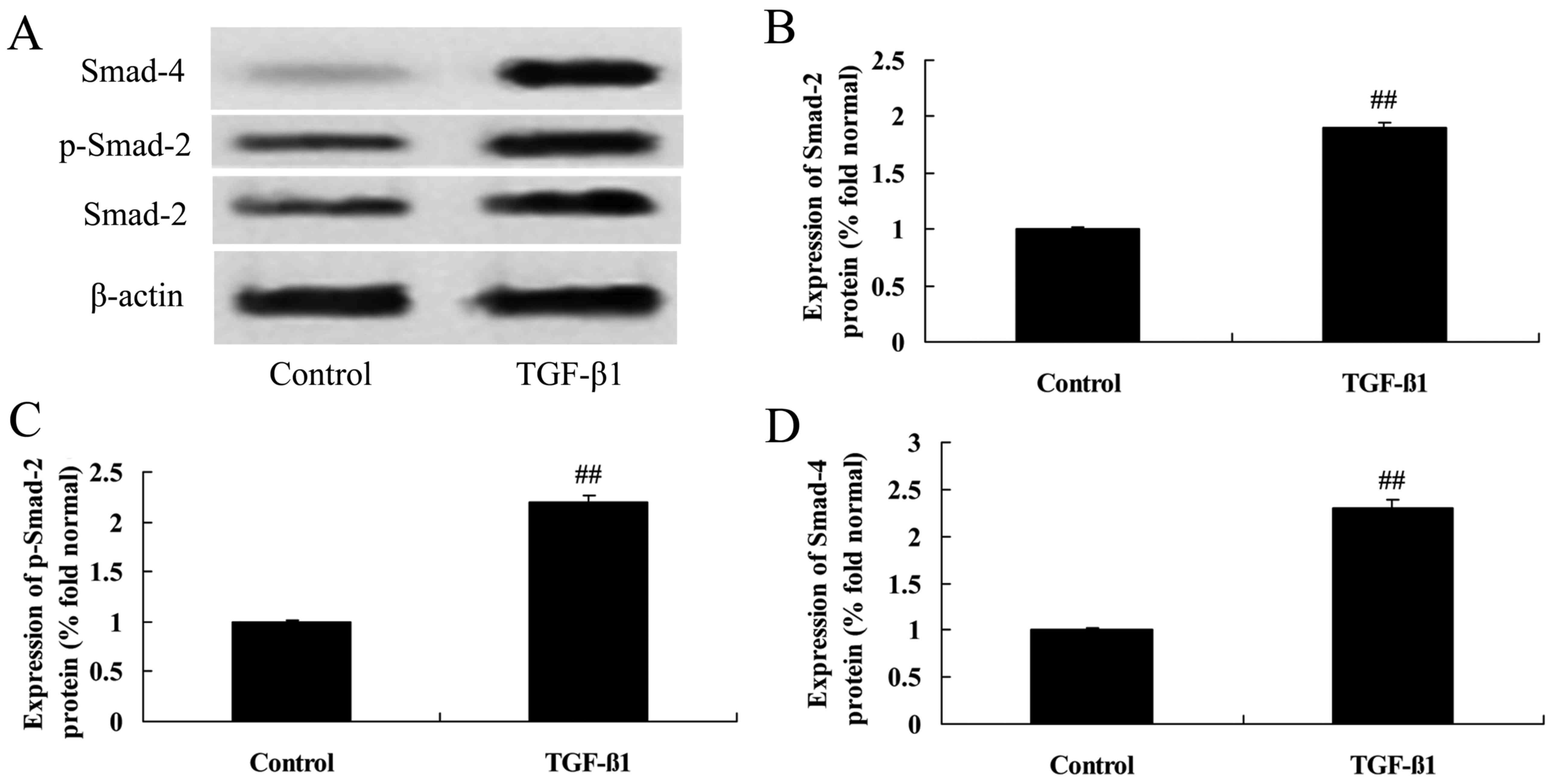
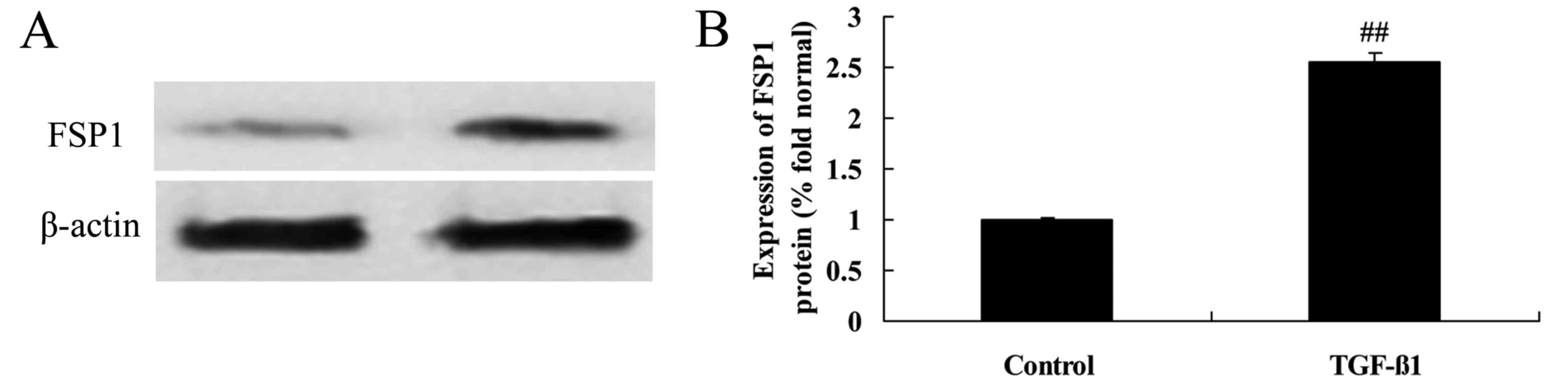
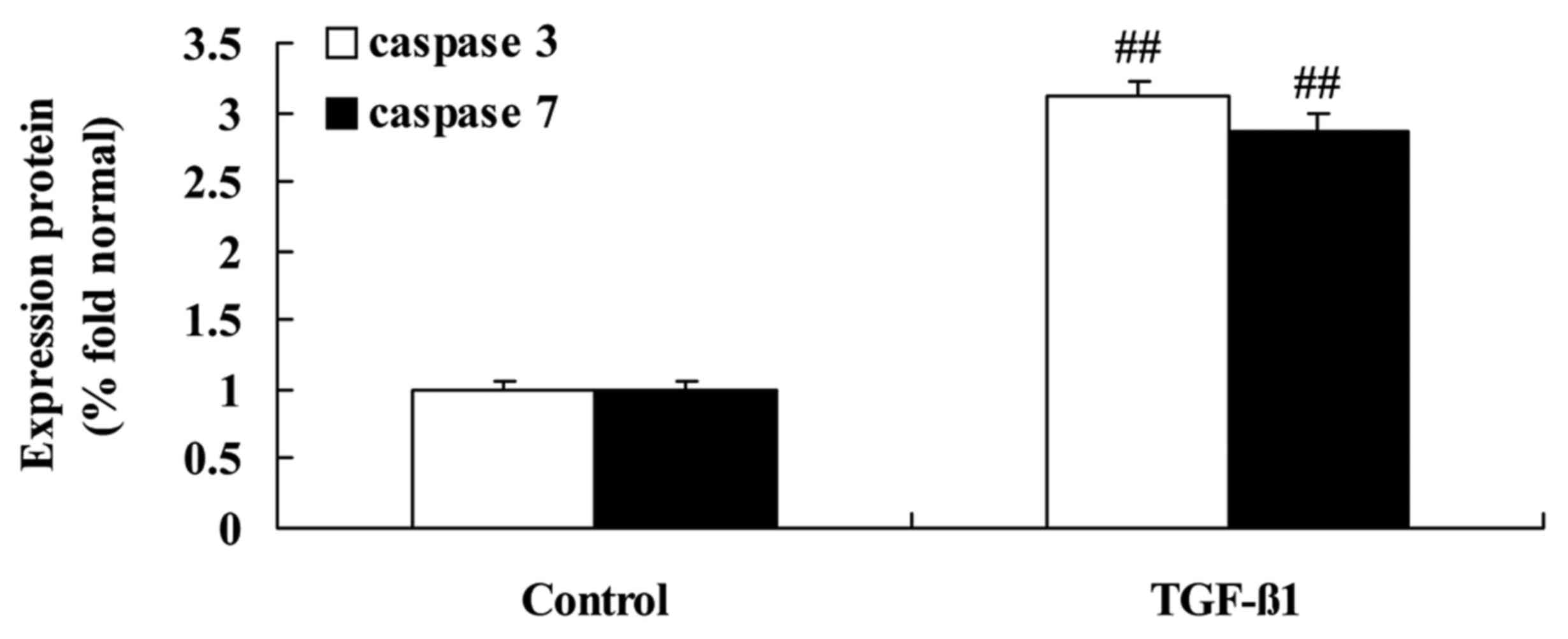
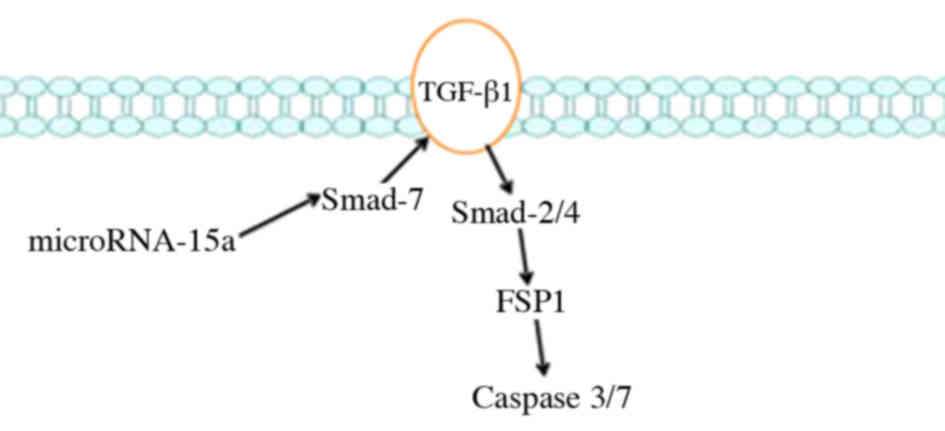
|
1
|
Andreotti M, Pirillo MF, Liotta G, Jere H,
Maulidi M, Sagno JB, Luhanga R, Amici R, Mancini MG, Gennaro E, et
al: The impact of HBV or HCV infection in a cohort of HIV-infected
pregnant women receiving a nevirapine-based antiretroviral regimen
in Malawi. BMC Infect Dis. 14:1802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Celen MK, Mert D, Ay M, Dal T, Kaya S,
Yildirim N, Gulsun S, Barcin T, Kalkanli S, Dal MS, et al: Efficacy
and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in pregnancy for the
prevention of vertical transmission of HBV infection. World J.
19:9377–9382. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Ive P, MacLeod W, Mkumla N, Orrell C,
Jentsch U, Wallis CL, Stevens W, Wood R, Sanne I and Bhattacharya
D: Low prevalence of liver disease but regional differences in HBV
treatment characteristics mark HIV/HBV co-infection in a South
African HIV clinical trial. PLoS One. 8:e749002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Amaddeo G, Cao Q, Ladeiro Y, Imbeaud S,
Nault JC, Jaoui D, Mathe Y Gaston, Laurent C, Laurent A,
Bioulac-Sage P, et al: Integration of tumour and viral genomic
characterizations in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut.
64:820–829. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
El-Serag H, McGlynn KA, Graham GN, So S,
Howell CD, Fang T, Anderson JT and Thiel TK: Achieving health
equity to eliminate racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic disparities
in HBV- and HCV-associated liver disease. J Fam Pract. 59 Suppl
4:S37–S42. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Piao CY, Fujioka S, Iwasaki Y, Fujio K,
Kaneyoshi T, Araki Y, Hashimoto K, Senoh T, Terada R, Nishida T, et
al: Lamivudine treatment in patients with HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma - using an untreated, matched control
cohort. Acta Med Okayama. 59:217–224. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng J, Zeng Z, Zhang D, Yu Y, Wang F and
Pan CQ: Prevalence and significance of hepatitis B reverse
transcriptase mutants in different disease stages of untreated
patients. Liver Int. 32:1535–1542. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qu C, Chen T, Fan C, Zhan Q, Wang Y, Lu J,
Lu LL, Ni Z, Huang F, Yao H, et al: Efficacy of neonatal HBV
vaccination on liver cancer and other liver diseases over 30-year
follow-up of the Qidong hepatitis B intervention study: A cluster
randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 11:e10017742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu Q, Qin H, Zhao Q and He XX: Emerging
role of transcription factor-microRNA-target gene feed-forward
loops in cancer. Biomed Rep. 3:611–616. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gu L, Li H, Chen L, Ma X, Gao Y, Li X,
Zhang Y, Fan Y and Zhang X: MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular
signatures in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 6:32545–32560. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang YK and Yu JC: Circulating microRNAs
and long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer diagnosis: An update and
review. World J Gastroenterol. 21:9863–9886. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anwar SL and Lehmann U: MicroRNAs:
Emerging novel clinical biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinomas. J
Clin Med. 4:1631–1650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Macias MJ, Martin-Malpartida P and
Massagué J: Structural determinants of Smad function in TGF-β
signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 40:296–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu L, Tian D and Zheng Y: Pleiotropic
roles of TGFβ/Smad signaling in the progression of chronic liver
disease. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 23:237–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heldin CH, Landström M and Moustakas A:
Mechanism of TGF-beta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:166–176.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gordon SC, Lamerato LE, Rupp LB, Li J,
Holmberg SD, Moorman AC, Spradling PR, Teshale EH, Vijayadeva V,
Boscarino JA, et al: CHeCS Investigators: Antiviral therapy for
chronic hepatitis B virus infection and development of
hepatocellular carcinoma in a US population. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 12:885–893. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giannini EG, Savarino V, Risso D, Di Nolfo
MA, Del Poggio P, Benvegnù L, Farinati F, Zoli M, Borzio F,
Caturelli E, et al: Italian Liver Cancer (ITA.LI.CA.) group:
Relative decrease in the role played by hepatitis B virus infection
in the aetiology of hepatocellular carcinoma during a 20-year
period: A multicentre Italian study. Liver Int. 31:192–196. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shuqun C, Mengchao W, Han C, Feng S, Jiahe
Y, Wenming C, Zhengfeng Y, Yuxiang Z and Peijun W: Antiviral
therapy using lamivudine and thymosin alpha1 for hepatocellular
carcinoma coexisting with chronic hepatitis B infection.
Hepatogastroenterology. 53:249–252. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chung YH, Di Bisceglie AM, McMahon BJ,
Lanier AP, Harpster A, Alter MJ, Parkinson AJ and Zanis C:
Hepatocellular carcinoma not related to hepatitis B virus infection
among Alaska natives. Int J Circumpolar Health. 58:208–213.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greene CM, Varley RB and Lawless MW:
MicroRNAs and liver cancer associated with iron overload:
Therapeutic targets unravelled. World J Gastroenterol.
19:5212–5226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cohen MM Jr: TGF beta/Smad signaling
system and its pathologic correlates. Am J Med Genet A. 116A:1–10.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang Y: Pro-metastasis function of TGFbeta
mediated by the Smad pathway. J Cell Biochem. 98:1380–1390. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang WB, Ling GH, Sun L and Liu FY: Smad
anchor for receptor activation (SARA) in TGF-beta signaling. Front
Biosci. 2:857–860. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Conidi A, van den Berghe V and Huylebroeck
D: Aptamers and their potential to selectively target aspects of
EGF, Wnt/β-catenin and TGFβ-smad family signaling. Int J Mol Sci.
14:6690–6719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsuzaki K, Date M, Furukawa F, Tahashi
Y, Matsushita M, Sugano Y, Yamashiki N, Nakagawa T, Seki T,
Nishizawa M, et al: Regulatory mechanisms for transforming growth
factor beta as an autocrine inhibitor in human hepatocellular
carcinoma: Implications for roles of smads in its growth.
Hepatology. 32:218–227. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang Y, Wang C, Li YY, et al: Mistletoe
alkaloid fractions alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver
fibrosis through inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation via
TGF-beta/Smad interference. J Ethnopharmacol. 158(Pt A): 230–238.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu N, Jiao T, Huang Y, Liu W, Li Z and Ye
X: Hepatitis B virus regulates apoptosis and tumorigenesis through
the microRNA-15a-Smad-7-transforming growth factor beta pathway. J
Virol. 89:2739–2749. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|