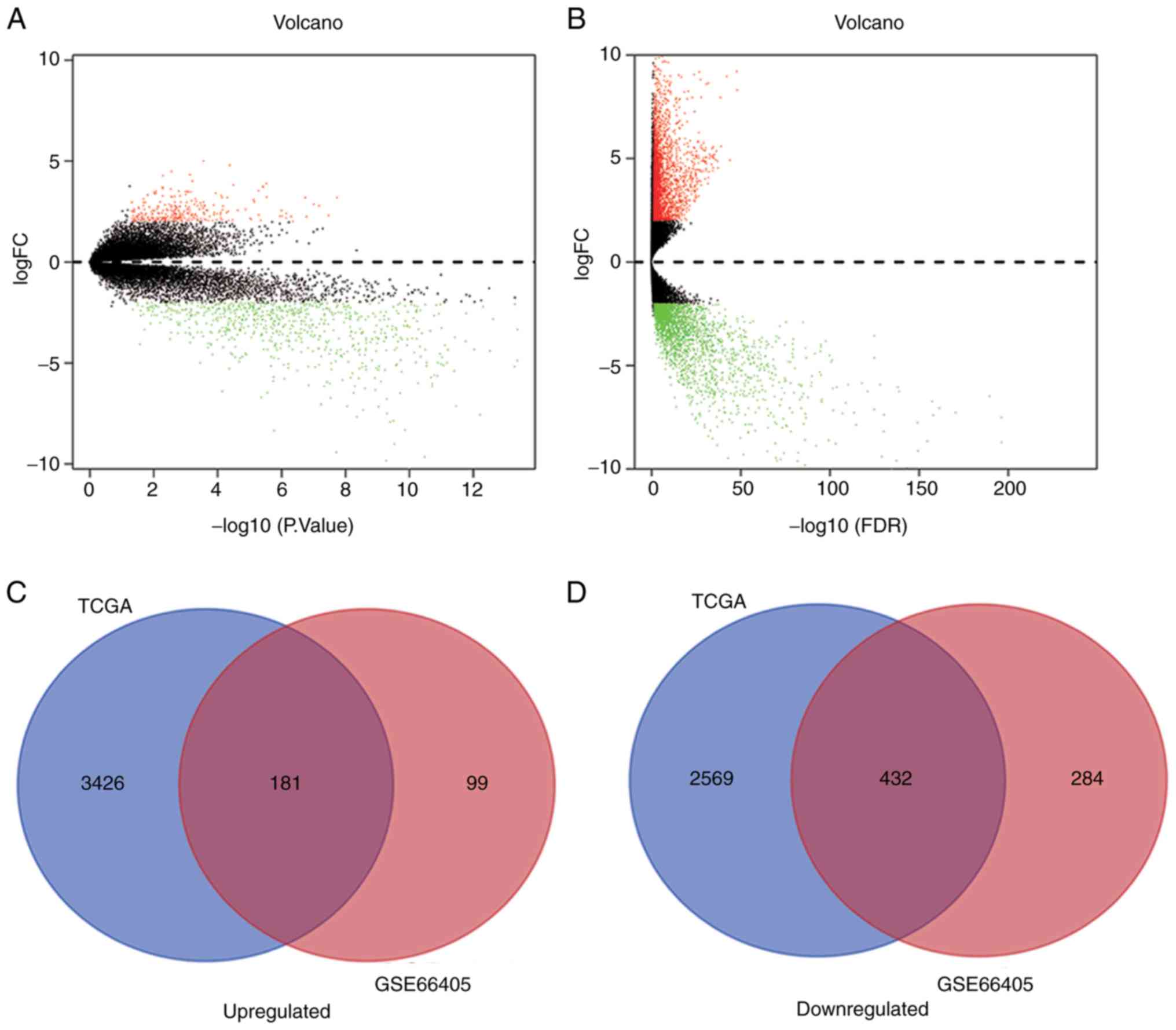
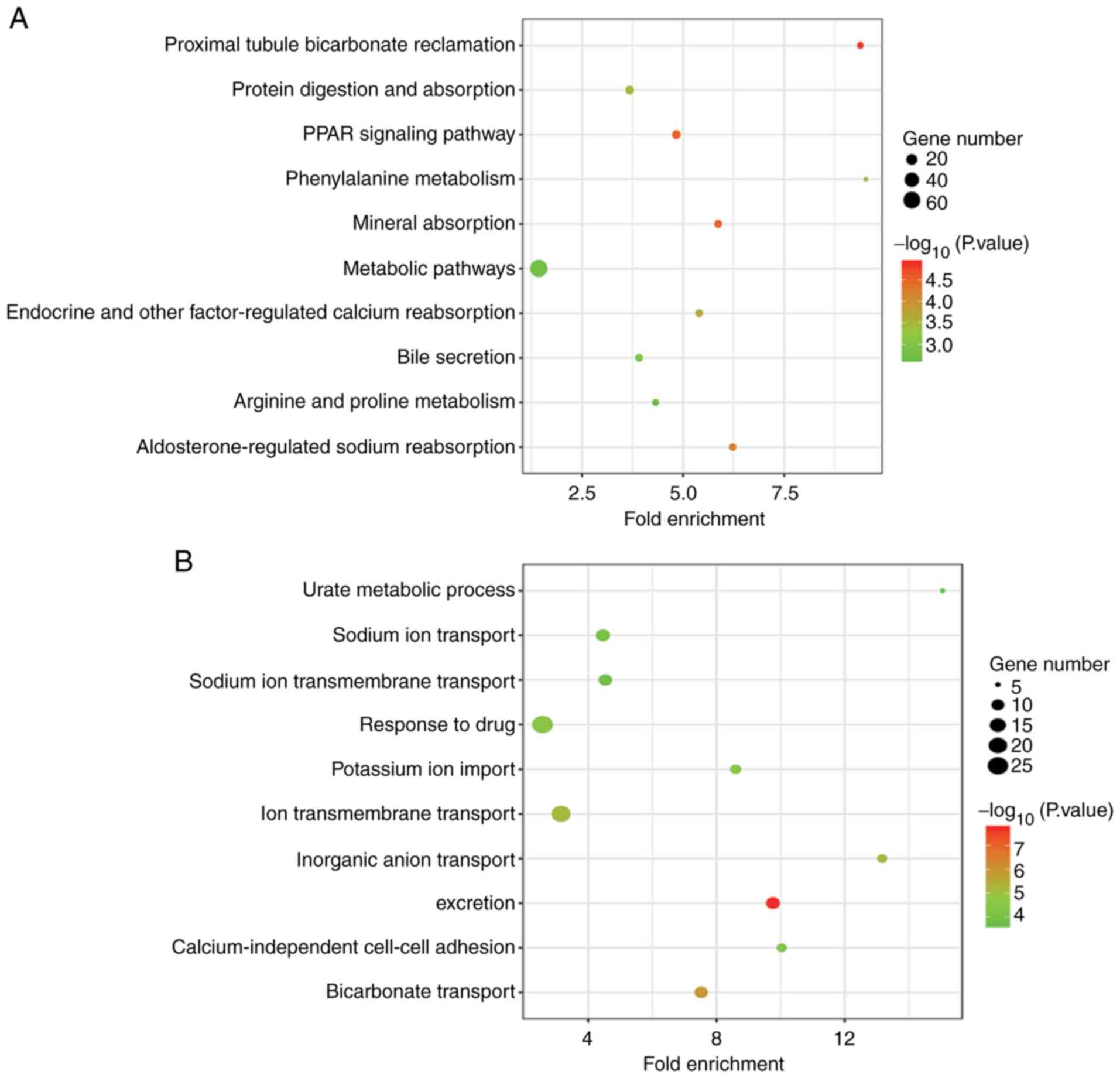
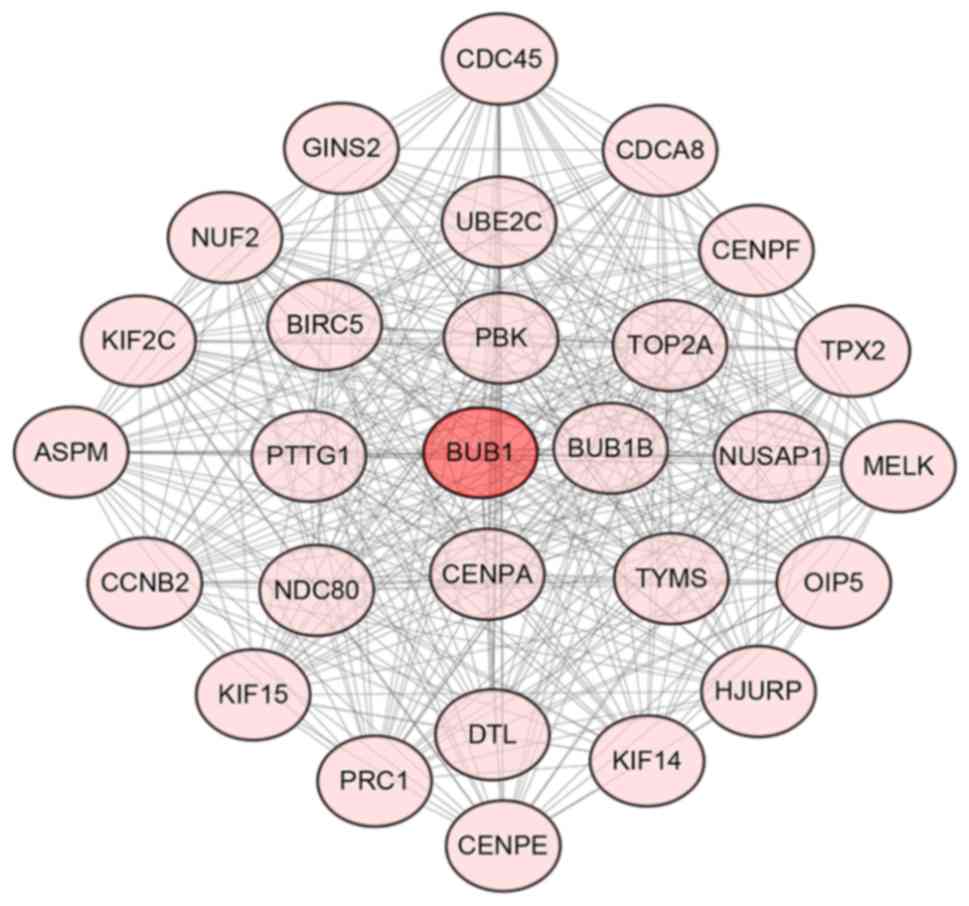
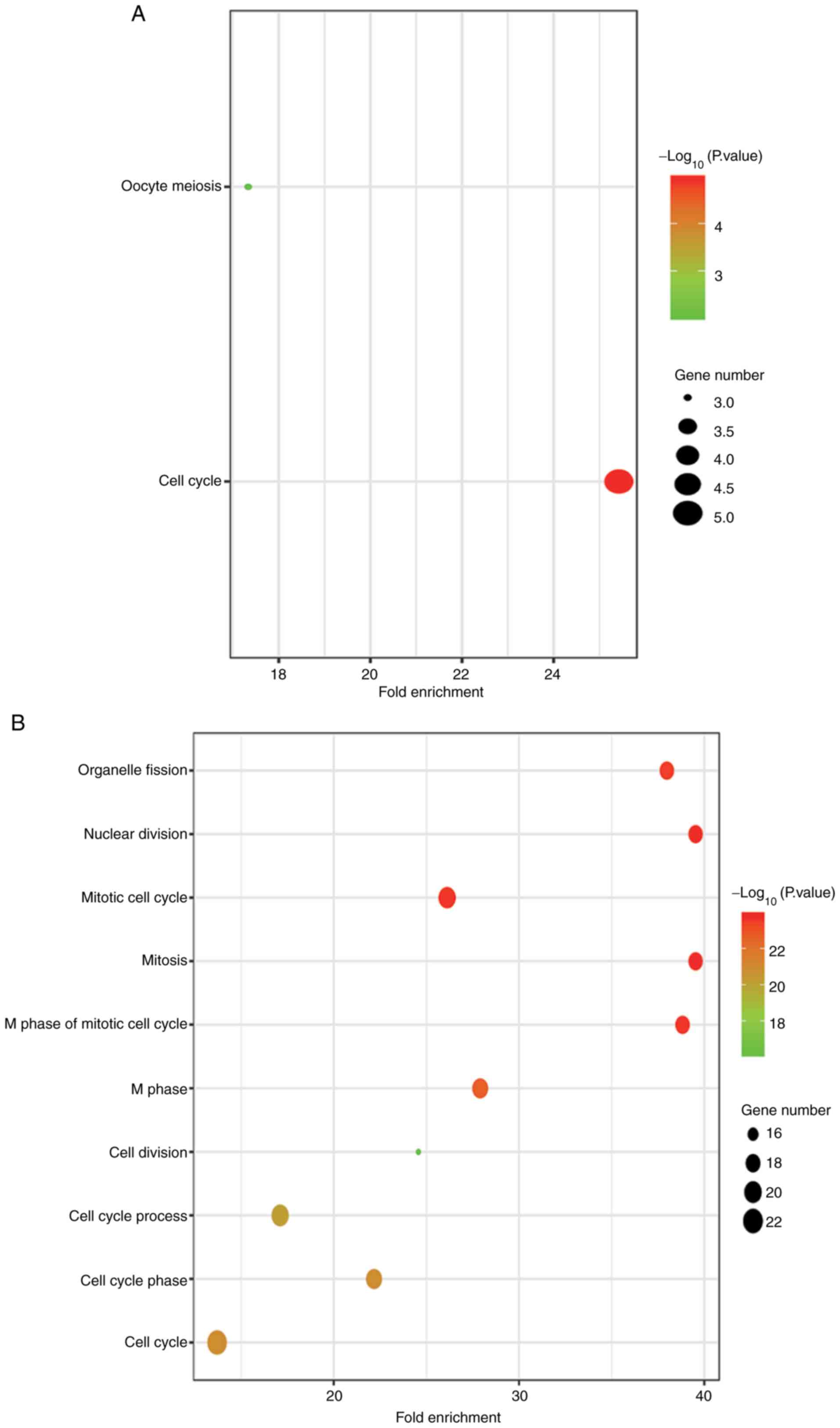
|
1
|
Charlton J, Pavasovic V and
Pritchard-Jones K: Biomarkers to detect Wilms tumors in pediatric
patients: Where are we now? Future Oncol. 11:2221–2234. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Scott RH, Stiller CA, Walker L and Rahman
N: Syndromes and constitutional chromosomal abnormalities
associated with Wilms tumour. J Med Genet. 43:705–715. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hung IJ, Chang WH, Yang CP, Jaing TH,
Liang DC, Lin KH, Lin DT, Hsiao CC, Hsieh YL, Chen JS, et al:
Epidemiology, clinical features and treatment outcome of Wilms'
tumor in Taiwan: A report from Taiwan pediatric oncology group. J
Formos Med Assoc. 103:104–111. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al-Hussain T, Ali A and Akhtar M: Wilms
tumor: An update. Adv Anat Pathol. 21:166–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Segers H, Kersseboom R, Alders M, Pieters
R, Wagner A and van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM: Frequency of WT1 and
11p15 constitutional aberrations and phenotypic correlation in
childhood Wilms tumour patients. Eur J Cancer. 48:3249–3256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fukuzawa R, Holman SK, Chow CW,
Savarirayan R, Reeve AE and Robertson SP: WTX mutations can occur
both early and late in the pathogenesis of Wilms tumour. J Med
Genet. 47:791–794. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li CM, Kim CE, Margolin AA, Guo M, Zhu J,
Mason JM, Hensle TW, Murty VV, Grundy PE, Fearon ER, et al: CTNNB1
mutations and overexpression of Wnt/beta-catenin target genes in
WT1-mutant Wilms' tumors. Am J Pathol. 165:1943–1953. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Haber DA, Buckler AJ, Glaser T, Call KM,
Pelletier J, Sohn RL, Douglass EC and Housman DE: An internal
deletion within an 11p13 zinc finger gene contributes to the
development of Wilms' tumor. Cell. 61:1257–1269. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Scott RH, Murray A, Baskcomb L, Turnbull
C, Loveday C, Al-Saadi R, Williams R, Breatnach F, Gerrard M, Hale
J, et al: Stratification of Wilms tumor by genetic and epigenetic
analysis. Oncotarget. 3:327–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fu W, Zhuo Z, Hua RX, Fu K, Jia W, Zhu J,
Zhang J, Cheng J, Zhou H, Xia H, et al: Association of KRAS and
NRAS gene polymorphisms with Wilms tumor risk: A four-center
case-control study. Aging (Albany NY). 11:1551–1563. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Diets IJ, Hoyer J, Ekici AB, Popp B,
Hoogerbrugge N, van Reijmersdal SV, Bhaskaran R, Hadjihannas M,
Vasileiou G, Thiel CT, et al: TRIM28 haploinsufficiency predisposes
to Wilms tumor. Int J Cancer. 145:941–951. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Polosukhina D, Love HD, Correa H, Su Z,
Dahlman KB, Pao W, Moses HL, Arteaga CL, Lovvorn HN III, Zent R and
Clark PE: Functional KRAS mutations and a potential role for
PI3K/AKT activation in Wilms tumors. Mol Oncol. 11:405–421. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu GL, Yang HJ, Liu B and Liu T: Effects
of microRNA-19b on the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of
Wilms' tumor cells via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Cell
Biochem. 118:3424–3434. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu S, Zhang L, Zhao Z, Fu W, Fu K, Liu G
and Jia W: MicroRNA-92a-3p inhibits the cell proliferation,
migration and invasion of Wilms tumor by targeting NOTCH1. Oncol
Rep. 40:571–578. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu
VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA Jr and Kinzler KW: Cancer genome landscapes.
Science. 339:1546–1558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo Y, Bao Y, Ma M and Yang W:
Identification of key candidate genes and pathways in colorectal
cancer by integrated bioinformatical analysis. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E7222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ludwig N, Werner TV, Backes C, Trampert P,
Gessler M, Keller A, Lenhof HP, Graf N and Meese E: Combining miRNA
and mRNA expression profiles in Wilms tumor subtypes. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:4752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wegert J, Ishaque N, Vardapour R, Geörg C,
Gu Z, Bieg M, Ziegler B, Bausenwein S, Nourkami N, Ludwig N, et al:
Mutations in the SIX1/2 pathway and the DROSHA/DGCR8 miRNA
microprocessor complex underlie high-risk blastemal type Wilms
tumors. Cancer Cell. 27:298–311. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tomczak K, Czerwińska P and Wiznerowicz M:
The cancer genome atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of
knowledge. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19:A68–A77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
EdgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yusenko MV, Kuiper RP, Boethe T, Ljungberg
B, van Kessel AG and Kovacs G: High-resolution DNA copy number and
gene expression analyses distinguish chromophobe renal cell
carcinomas and renal oncocytomas. BMC Cancer. 9:1522009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:050052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chou CH, Chang NW, Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Lin
YL, Lee WH, Yang CD, Hong HC, Wei TY, Tu SJ, et al: miRTarBase
2016: Updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target
interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D239–D247. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D146–D152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pierce J, Murphy AJ, Panzer A, de
Caestecker C, Ayers GD, Neblett D, Saito-Diaz K, de Caestecker M
and Lovvorn HN III: SIX2 effects on wilms tumor biology. Transl
Oncol. 7:800–811. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yap LW, Brok J and Pritchard-Jones K: Role
of CD56 in normal kidney development and Wilms tumorigenesis. Fetal
Pediatr Pathol. 36:62–75. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nordenskjöld A, Friedman E, Sandstedt B,
Söderhäll S and Anvret M: Constitutional and somatic mutations in
the WT1 gene in Wilms' tumor patients. Int J Cancer. 63:516–522.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Alexandrescu S, Akhavanfard S, Harris MH
and Vargas SO: Clinical, pathologic, and genetic features of Wilms
tumors with WTX gene mutation. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 20:105–111.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Deng C, Dai R, Li X and Liu F: Genetic
variation frequencies in Wilms' tumor: A meta-analysis and
systematic review. Cancer Sci. 107:690–699. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ooms AH, Gadd S, Gerhard DS, Smith MA,
Guidry Auvil JM, Meerzaman D, Chen QR, Hsu CH, Yan C, Nguyen C, et
al: Significance of TP53 mutation in Wilms tumors with diffuse
anaplasia: A report from the children's oncology group. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:5582–5591. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dominguez-Brauer C, Thu KL, Mason JM,
Blaser H, Bray MR and Mak TW: Targeting mitosis in cancer: Emerging
strategies. Mol Cell. 60:524–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alimbetov D, Askarova S, Umbayev B, Davis
T and Kipling D: Pharmacological targeting of cell cycle, apoptotic
and cell adhesion signaling pathways implicated in chemoresistance
of cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 19:E16902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Knudsen ES, Pruitt SC, Hershberger PA,
Witkiewicz AK and Goodrich DW: Cell cycle and beyond: Exploiting
new RB1 controlled mechanisms for cancer therapy. Trends Cancer.
5:308–324. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu B, Xu T, Liu H, Min Q, Wang S and Song
Q: miR-490-5p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by
targeting BUB1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Pharmacology.
100:269–282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fu X, Chen G, Cai ZD, Wang C, Liu ZZ, Lin
ZY, Wu YD, Liang YX, Han ZD, Liu JC and Zhong WD: Overexpression of
BUB1B contributes to progression of prostate cancer and predicts
poor outcome in patients with prostate cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
9:2211–2220. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stahl D, Braun M, Gentles AJ, Lingohr P,
Walter A, Kristiansen G and Gütgemann I: Low BUB1 expression is an
adverse prognostic marker in gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:76329–76339. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ocaña A, Pérez-Peña J, Díez-González L,
Sánchez-Corrales V, Templeton A, Seruga B, Amir E and Pandiella A:
Transcriptomic analyses identify association between mitotic
kinases, PDZ-binding kinase and BUB1, and clinical outcome in
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 156:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wei YT, Guo DW, Hou XZ and Jiang DQ:
miRNA-223 suppresses FOXO1 and functions as a potential tumor
marker in breast cancer. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
63:113–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sharma P and Sharma R: miRNA-mRNA
crosstalk in esophageal cancer: From diagnosis to therapy. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 96:449–462. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang D, Zhao L, Shen Q, Lv Q, Jin M, Ma
H, Nie X, Zheng X, Huang S, Zhou P, et al: Down-regulation of
KIAA1199/CEMIP by miR-216a suppresses tumor invasion and metastasis
in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 140:2298–2309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jia AY, Castillo-Martin M, Bonal DM,
Sánchez-Carbayo M, Silva JM and Cordon-Cardo C: MicroRNA-126
inhibits invasion in bladder cancer via regulation of ADAM9. Br J
Cancer. 110:2945–2954. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lv Z, Wei J, You W, Wang R, Shang J, Xiong
Y, Yang H, Yang X and Fu Z: Disruption of the
c-Myc/miR-200b-3p/PRDX2 regulatory loop enhances tumor metastasis
and chemotherapeutic resistance in colorectal cancer. J Transl Med.
15:2572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang Z, Zhu Z, Lin Z, Luo Y, Liang Z,
Zhang C, Chen J and Peng P: miR-429 suppresses cell proliferation,
migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
downregulation of TLN1. Cancer Cell Int. 19:1152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tang CT, Liang Q, Yang L, Lin XL, Wu S,
Chen Y, Zhang XT, Gao YJ and Ge ZZ: RAB31 targeted by miR-30c-2-3p
regulates the GLI1 signaling pathway, affecting gastric cancer cell
proliferation and apoptosis. Front Oncol. 8:5542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jin H, Xie Q, Guo X, Xu J, Wang A, Li J,
Zhu J, Wu XR, Huang H and Huang C: p63α protein up-regulates heat
shock protein 70 expression via E2F1 transcription factor 1,
promoting Wasf3/Wave3/MMP9 signaling and bladder cancer invasion. J
Biol Chem. 292:15952–15963. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kim BR, Dong SM, Seo SH, Lee JH, Lee JM,
Lee SH and Rho SB: Lysyl oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2) controls
tumor-associated cell proliferation through the interaction with
MARCKSL1. Cell Signal. 26:1765–1773. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|