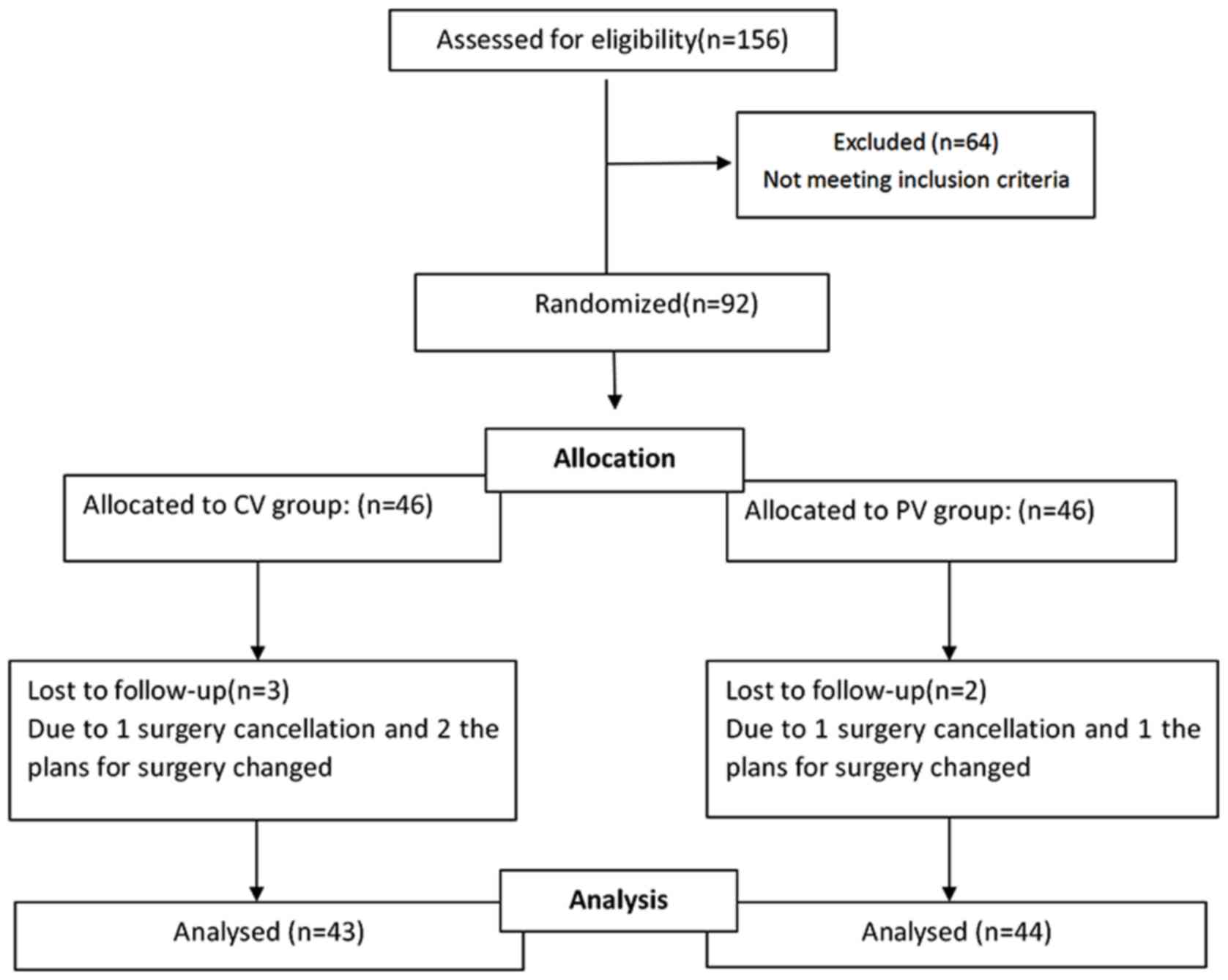
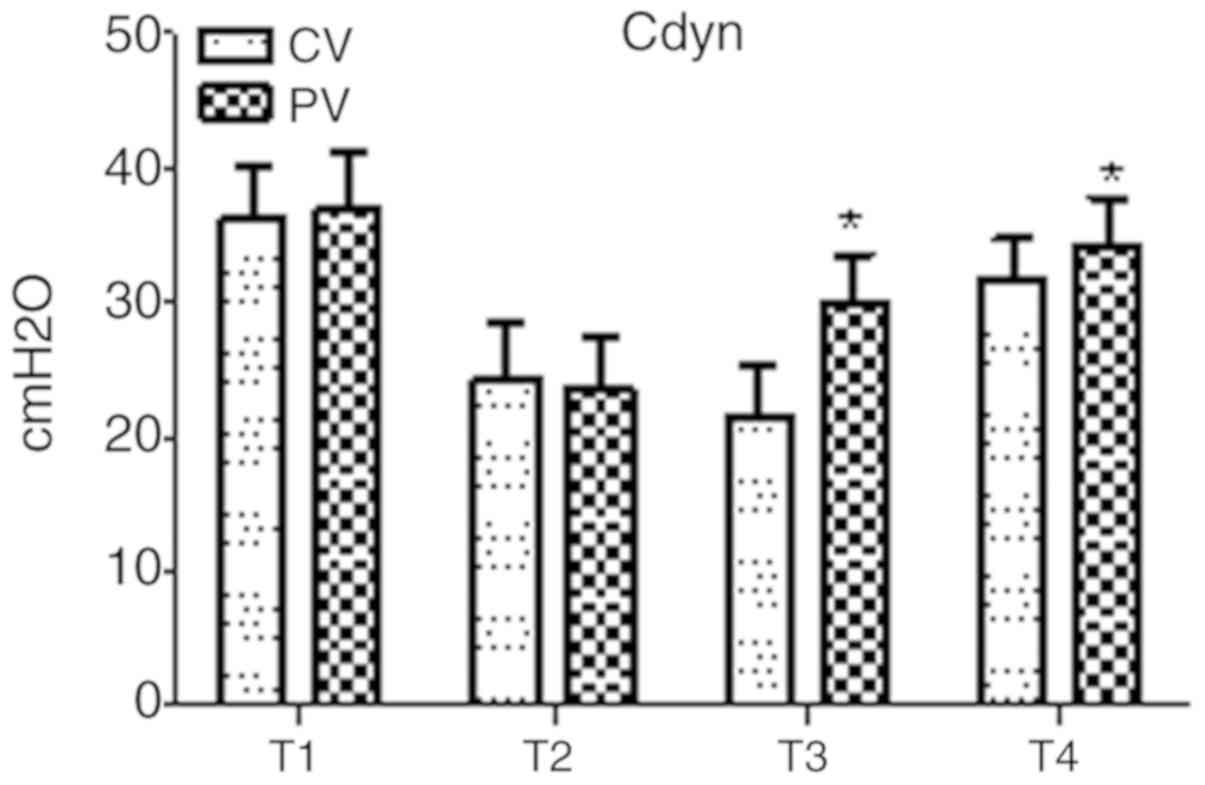
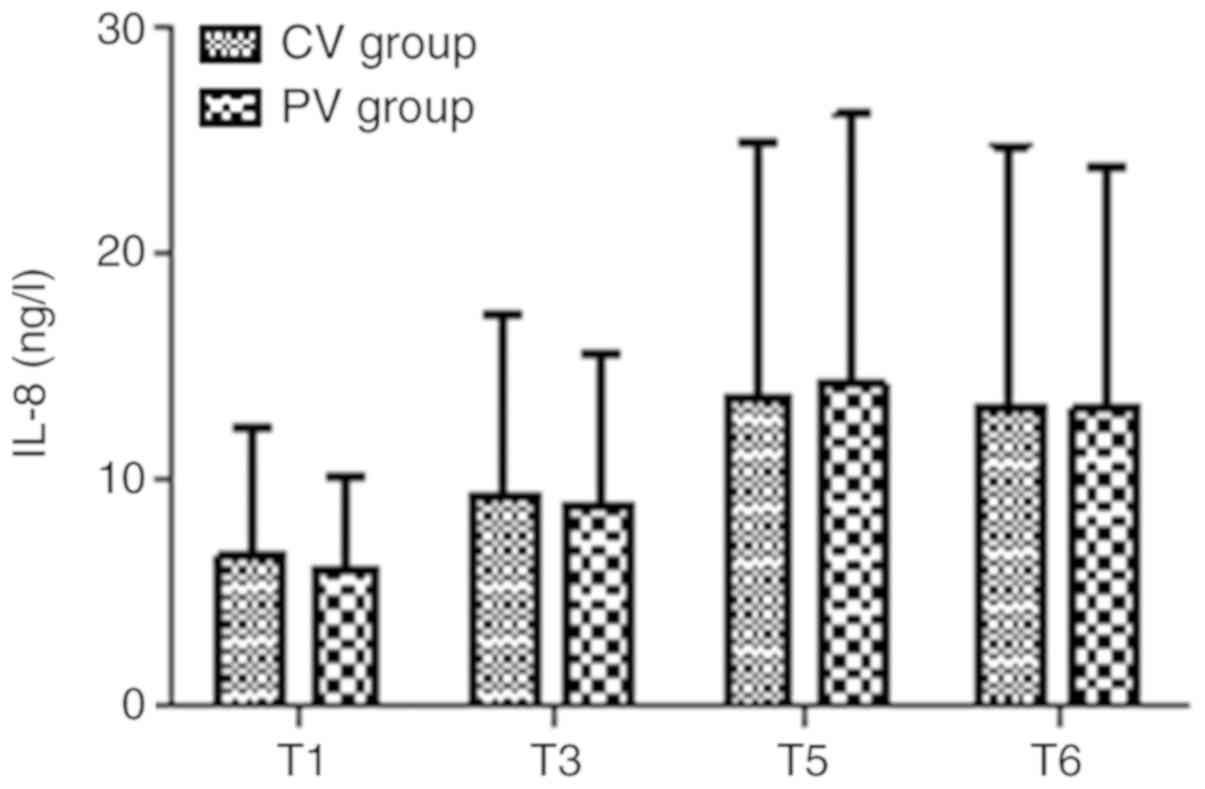
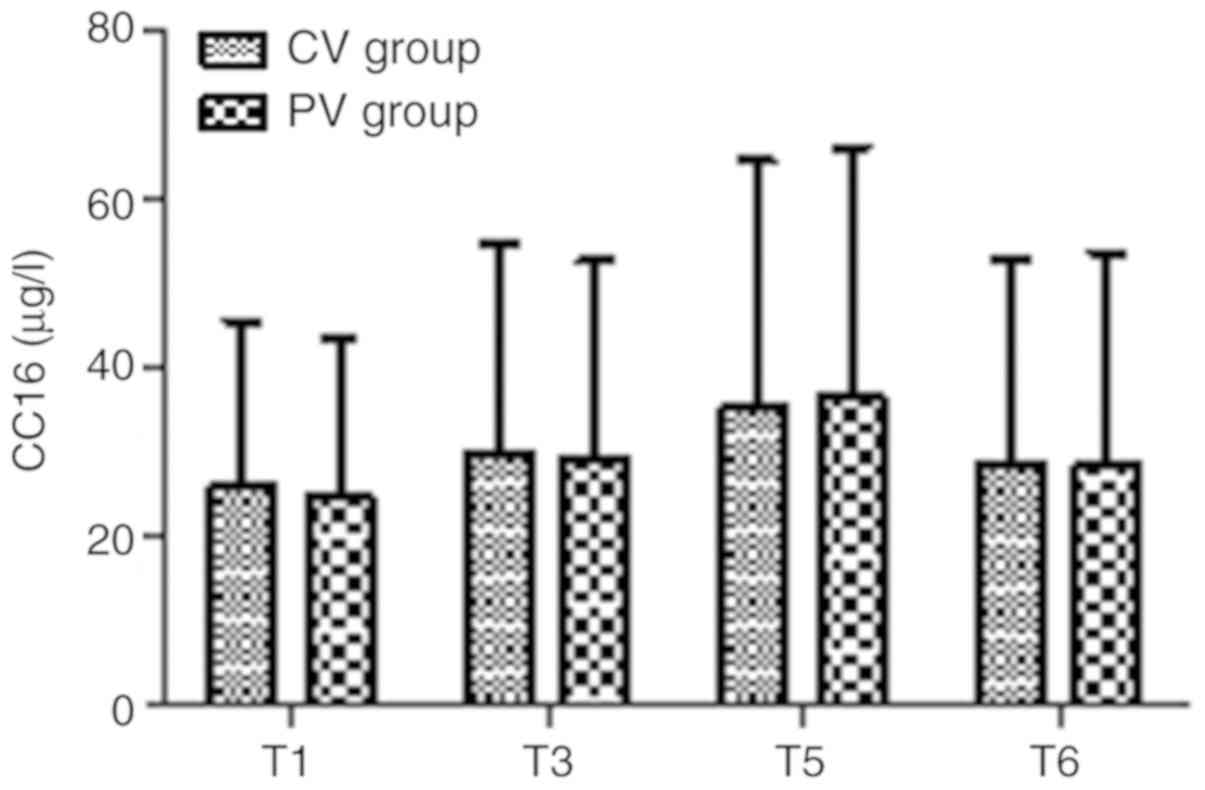
|
1
|
Slutsky AS and Ranieri VM:
Ventilator-induced lung injury. N Engl J Med. 369:2126–2136.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ricard JD, Dreyfuss D and Saumon G:
Ventilator-induced lung injury. Eur Respir J. Suppl 42(2s-9s)2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ware LB, Koyama T, Zhao Z, Janz DR,
Wickersham N, Bernard GR, May AK, Calfee CS and Matthay MA:
Biomarkers of lung epithelial injury and inflammation distinguish
severe sepsis patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Crit Care. 17(R253)2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Famous KR, Delucchi K, Ware LB, Kangelaris
KN, Liu KD, Thompson BT and Calfee CS: ARDS Network: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome subphenotypes respond differently to
randomized fluid management strategy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
195:331–338. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bos LD, Schouten LR, van Vught LA, Wiewel
MA, Ong DSY, Cremer O, Artigas A, Martin-Loeches I, Hoogendijk AJ,
van der Poll T, et al: Identification and validation of distinct
biological phenotypes in patients with acute respiratory distress
syndrome by cluster analysis. Thorax. 72:876–883. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Broeckaert F and Bernard A: Clara cell
secretory protein (CC16): Characteristics and perspectives as lung
peripheral biomarker. Clin Exp Allergy. 30:469–475. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fernandez-Bustamante A, Klawitter J,
Repine JE, Agazio A, Janocha AJ, Shah C, Moss M, Douglas IS, Tran
ZV, Erzurum SC, et al: Early effect of tidal volume on lung injury
biomarkers in surgical patients with healthy lungs. Anesthesiology.
121:469–481. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wutzler S, Lehnea T, Laurer H, Lehnert M,
Becker M, Henrich D, Vogl T and Marzi I: Circulating levels of
clara cell protein 16 but not surfactant protein D identify and
quantify lung damage in patients with multiple injuries. J Tranma.
71(E31-E36)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Futier E, Constantin JM, Paugam-Burtz C,
Pascal J, Eurin M, Neuschwander A, Marret E, Beaussier M, Gutton C,
Lefrant JY, et al: A trial of intraoperative low-tidal-volume
ventilation in abdominal surgery. N Engl J Med. 369:428–437.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
PROVE Network Investigators for the
Clinical Trial Network of the European Society of Anaesthesiology
, Hemmes SN, Gama de Abreu M, Pelosi P and Schultz MJ: High
versus low positive end-expiratory pressure during general
anaesthesia for open abdominal surgery (PROVHILO trial): A
multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 384:495–503.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Brower RG, Lanken PN, MacIntyre N, Matthay
MA, Morris A, Ancukiewicz M, Schoenfeld D and Thompson BT: National
Heart Lung and Blood Institute ARDS Clinical Trials Network: Higher
versus lower positive end-expiratory pressures in patients with the
acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 351:327–336.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jaber S, Coisel Y, Chanques G, Futier E,
Constantin J, Michelet P, Beaussier M, Lefrant JY, Allaouchiche B,
Capdevila X and Marret E: A multicentre observational study of
intra-operative ventilatory management during general anaesthesia:
Tidal volumes and relation to body weight. Anaesthesia.
67:999–1008. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Haliloglu M, Bilgili B, Ozdemir M,
Umuroglu T and Bakan N: Low tidal volume positive end-expiratory
pressure versus high tidal volume zero-positive end-expiratory
pressure and postoperative pulmonary functions in robot-assisted
laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Med Princ Pract. 26:573–578.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hansen JK, Anthony DG, Li L, Wheeler D,
Sessler DI and Bashour CA: Comparison of positive end-expiratory
pressure of 8 versus 5 cm H2O on outcome after cardiac
operations. J Intensive Care Med. 6:338–343. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Reis Miranda D, Gommers D, Struijs A,
Dekker R, Mekel J, Feelders R, Lachmann B and Bogers AJ:
Ventilation according to the open lung concept attenuates pulmonary
inflammatory response in cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
28:889–895. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
García-Delgado M, Navarrete-Sánchez I and
Colmenero M: Preventing and managing perioperative pulmonary
complications following cardiac surgery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol.
27:146–152. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Serpa Neto A, Hemmes SN, Barbas CS,
Beiderlinden M, Biehl M, Binnekade JM, Canet J,
Fernandez-Bustamante A, Futier E, Gajic O, et al: Protective versus
conventional ventilation for surgery. A systematic review and
individual patient data meta-analysis. Anesthesiology. 123:66–78.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang Z, Hu X, Zhang X, Zhu X, Chen L, Zhu
L, Hu C and Du B: China Critical Care Clinical Trials Group
(CCCCTG): Lung protective ventilation in patients undergoing major
surgery: A systematic review incorporating a Bayesian approach. BMJ
Open. 5(e007473)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang D, Grant MC, Stone A, Wu CL and Wick
EC: A meta-analysis of intraoperative ventilation strategies to
prevent pulmonary complications: Is tidal volume alone sufficient
to protect healthy lungs? Ann Surg. 263:881–887. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Villar J, Blanco J and Kacmarek RM:
Current incidence and outcome of the acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care. 22:1–6. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Levin MA, McCormick PJ, Lin HM, Hosseinian
L and Fischer GW: Low intraoperative tidal volume ventilation with
minimal PEEP is associated with increased mortality. Br J Anaesth.
113:97–108. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Vargas M, Sutherasan Y, Gregoretti C and
Pelosi P: PEEP role in ICU and operating room: From pathophysiology
to clinical practice. ScientificWorldJournal.
2014(852356)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Menendez C, Martinez-Caro L, Moreno L, Nin
N, Moral-Sanz J, Morales D, Cogolludo A, Esteban A, Lorente JA and
Perez-Vizcaino F: Pulmonary vascular dysfunction induced by high
tidal volume mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med.
41(e149-e155)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nieman GF, Satalin J, Andrews P, Aiash H,
Habashi NM and Gatto LA: Personalizing mechanical ventilation
according to physiologic parameters to stabilize alveoli and
minimize ventilator induced lung injury (VILI). Intensive Care Med
Exp. 5(8)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kishida M, Yamada Y, Inayama E, Kitamura
M, Nishino T, Ota K, Shintani A and Ikenoue T: Effectiveness of
music therapy for alleviating pain during haemodialysis access
cannulation for patients undergoing haemodialysis: A
multi-facility, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Trials.
20(631)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lawrence VA, Cornell JE and Smetana GW:
American College of Physicians: Strategies to reduce postoperative
pulmonary complications after noncardiothoracic surgery: Systematic
review for the American college of physicians. Ann Intern Med.
144:596–608. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Güldner A, Kiss T, Serpa Neto A, Hemmes
SN, Canet J, Spieth PM, Rocco PR, Schultz MJ, Pelosi P and Gama de
Abreu M: Intraoperative protective mechanical ventilation for
prevention of postoperative pulmonary complications: A
comprehensive review of the role of tidal volume, positive
end-expiratory pressure, and lung recruitment maneuvers.
Anesthesiology. 123:692–713. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ruszkai Z, Kiss E, László I, Gyura F,
Surány E, Bartha PT, Bokrétás GP, Rácz E, Buzogány I, Bajory Z, et
al: Effects of intraoperative PEEP optimization on postoperative
pulmonary complications and the inflammatory response: Study
protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials.
18(375)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Marret E, Cinotti R, Berard L, Piriou V,
Jobard J, Barrucand B, Radu D, Jaber S, Bonnet F and the PPV study
group : Protective ventilation during anaesthesia reduces
major postoperative complications after lung cancer surgery: A
double-blind randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol.
35:727–735. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Okada S, Ito K, Shimada J, Kato D,
Shimomura M, Tsunezuka H, Miyata N, Ishihara S, Furuya T and Inoue
M: Clinical application of postoperative non-invasive positive
pressure ventilation after lung cancer surgery. Gen Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 66:565–572. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jammer I, Wickboldt N, Sander M, Smith A,
Schultz MJ, Pelosi P, Leva B, Rhodes A, Hoeft A, Walder B, et al:
Standards for definitions and use of outcome measures for clinical
effectiveness research in perioperative medicine: European
perioperative clinical outcome (EPCO) definitions: A statement from
the ESA-ESICM joint taskforce on perioperative outcome measures.
Eur J Anaesthesiol. 32:88–105. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gallart L and Canet J: Post-operative
pulmonary complications: Understanding definitions and risk
assessment. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 29:315–330.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Arslantas MK, Kara HV, Tuncer BB,
Yildizeli B, Yuksel M, Bostanci K, Bekiroglu N, Kararmaz A, Cinel I
and Batirel HF: Effect of the amount of intraoperative fluid
administration on postoperative pulmonary complications following
anatomic lung resections. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 149314–320.
(321.e1)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mommers EHH, Wegdam JA, van der Wolk S,
Nienhuijs SW and de Vries Reilingh TS: Impact of hernia volume on
pulmonary complications following complex hernia repair. J Surg
Res. 211:8–13. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A and Lang
AG: Statistical power analyses using G* Power 3.1: Tests
for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods.
41:1149–1160. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Smetana GW, Lawrence VA and Cornell JE:
American College of Physicians: Preoperative pulmonary risk
stratification for noncardiothoracic surgery: Systematic review for
the American college of physicians. Ann Intern Med. 144:581–595.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Futier E and Jaber S: Lung-protective
ventilation in abdominal surgery. Curr Opin Crit Care. 20:426–430.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sutherasan Y, Vargas M and Pelosi P:
Protective mechanical ventilation in the non-injured lung: Review
and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 18(211)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Pelosi P, Gama de Abreu M and Rocco PR:
New and conventional strategies for lung recruitment in acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care. 14(210)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Severgnini P, Selmo G, Lanza C, Chiesa A,
Frigerio A, Bacuzzi A, Dionigi G, Novario R, Gregoretti C, de Abreu
MG, et al: Protective mechanical ventilation during general
anesthesia for open abdominal surgery improves postoperative
pulmonary function. Anesthesiology. 118:1307–1321. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Serpa Neto A, Cardoso SO, Manetta JA,
Pereira VG, Espósito DC, Pasqualucci Mde O, Damasceno MC and
Schultz MJ: Association between use of lung-protective ventilation
with lower tidal volumes and clinical outcomes among patients
without acute respiratory distress syndrome: A meta-analysis. JAMA.
308:1651–1659. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lee JH, Bae JI, Jang YE, Kim EH, Kim HS
and Kim JT: Lung protective ventilation during pulmonary resection
in children: A prospective, single-centre, randomised controlled
trial. Br J Anaesth. 122:692–701. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kokulu S, Günay E, Baki ED, Ulasli SS,
Yilmazer M, Koca B, Arıöz DT, Ela Y and Sivaci RG: Impact of a
lung-protective ventilatory strategy on systemic and pulmonary
inflammatory responses during laparoscopic surgery: Is it really
helpful? Inflammation. 38:361–367. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Memtsoudis SG, Bombardieri AM, Ma Y and
Girardi FP: The effect of low versus high tidal volume ventilation
on inflammatory markers in healthy individuals undergoing posterior
spine fusion in the prone position: A randomized controlled trial.
J Clin Anesth. 24:263–269. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|