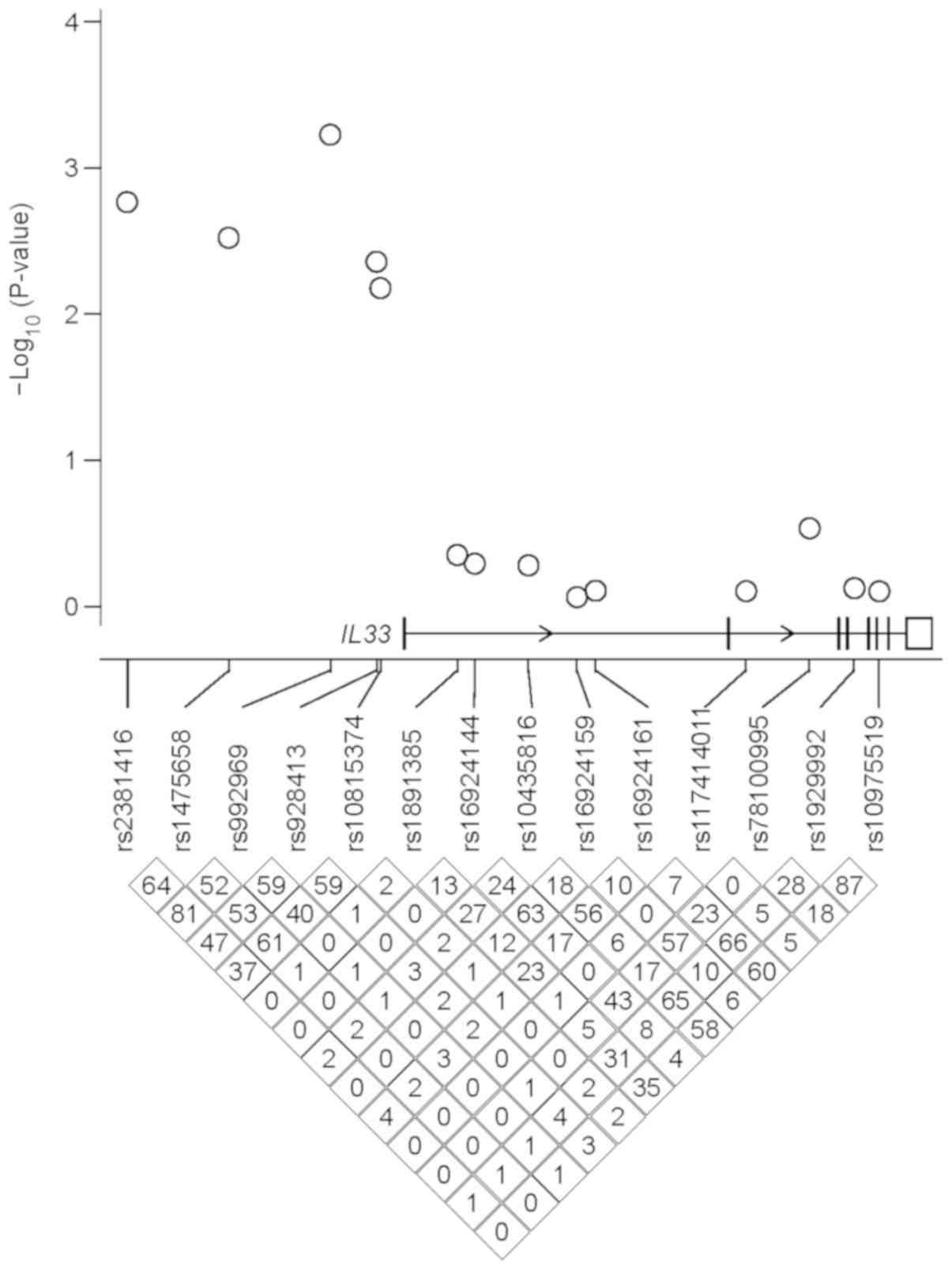
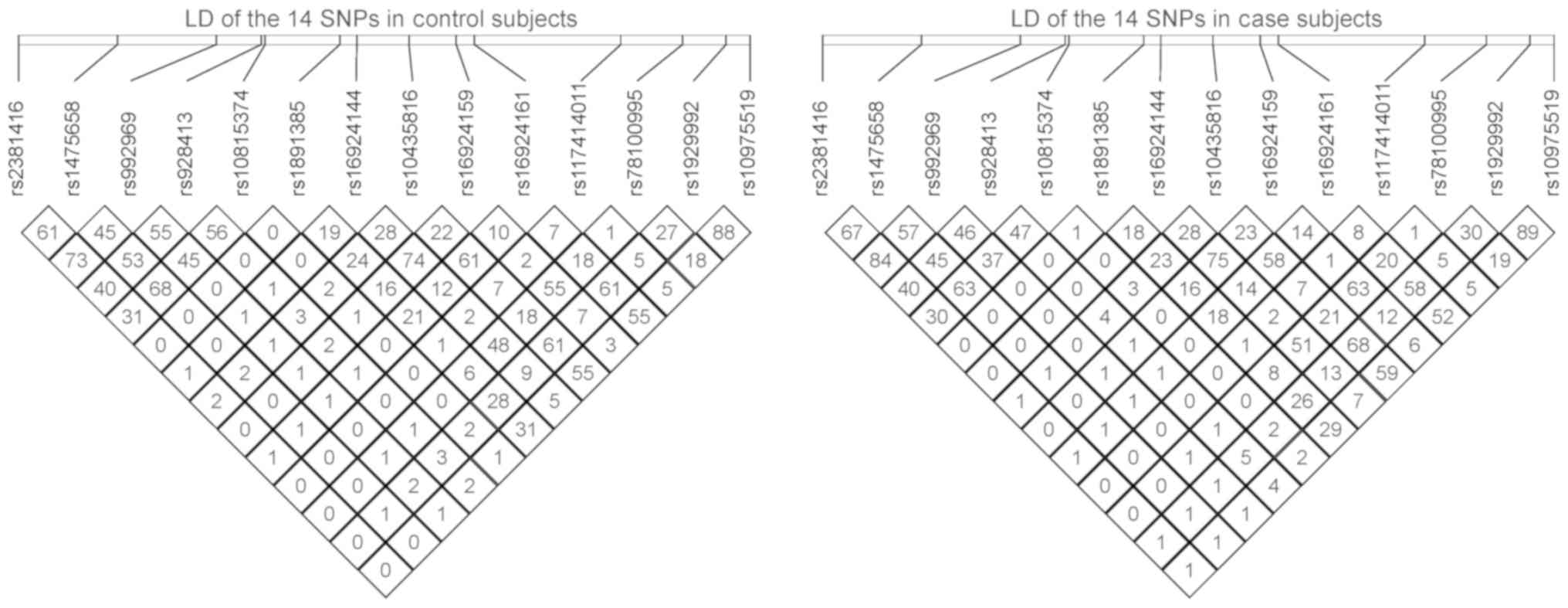
|
1
|
Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg
J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, Zuberbier T, Baena-Cagnani CE, Canonica
GW, van Weel C, et al: Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma
(ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the world health
organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 63 (Suppl
86):S8–S160. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Leynaert B, Neukirch F, Demoly P and
Bousquet J: Epidemiologic evidence for asthma and rhinitis
comorbidity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 106 (5 Suppl):S201–S205.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bousquet J, Van Cauwenberge P and Khaltaev
N: Aria Workshop Group; World Health Organization. Allergic
rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 108 (5
Suppl):S147–S334. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Falade AG, Ige OM, Yusuf BO, Onadeko MO
and Onadeko BO: Trends in the prevalence and severity of symptoms
of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema. J Natl
Med Assoc. 101:414–418. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nathan RA: The burden of allergic
rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 28:3–9. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Worldwide variation in prevalence of
symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, atopic eczema.
ISAAC. The international study of asthma and allergies in childhood
(ISAAC) steering committee. Lancet. 351:1225–1232. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Haahtela T, Holgate S, Pawankar R, Akdis
CA, Benjaponpitak S, Caraballo L, Demain J, Portnoy J and von
Hertzen L: WAO Special Committee on Climate Change and
Biodiversity. The biodiversity hypothesis and allergic disease:
World allergy organization position statement. World Allergy Organ
J. 6(3)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang XD, Zheng M, Lou HF, Wang CS, Zhang
Y, Bo MY, Ge SQ, Zhang N, Zhang L and Bachert C: An increased
prevalence of self-reported allergic rhinitis in major Chinese
cities from 2005 to 2011. Allergy. 71:1170–1180. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Thompson AK, Juniper E and Meltzer EO:
Quality of life in patients with allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy
Asthma Immunol. 85:338–347; quiz 347-8. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dunlop J, Matsui E and Sharma HP: Allergic
rhinitis: Environmental determinants. Immunol Allergy Clin North
Am. 36:367–377. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Greiner AN, Hellings PW, Rotiroti G and
Scadding GK: Allergic rhinitis. Lancet. 378:2112–2122.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Portelli MA, Hodge E and Sayers I: Genetic
risk factors for the development of allergic disease identified by
genome-wide association. Clin Exp Allergy. 45:21–31.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Willemsen G, van Beijsterveldt TC, van
Baal CG, Postma D and Boomsma DI: Heritability of self-reported
asthma and allergy: A study in adult Dutch twins, siblings and
parents. Twin Res Hum Genet. 11:132–142. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fagnani C, Annesi-Maesano I, Brescianini
S, D'Ippolito C, Medda E, Nisticò L, Patriarca V, Rotondi D,
Toccaceli V and Stazi MA: Heritability and shared genetic effects
of asthma and hay fever: An Italian study of young twins. Twin Res
Hum Genet. 11:121–131. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bunyavanich S, Schadt EE, Himes BE,
Lasky-Su J, Qiu W, Lazarus R, Ziniti JP, Cohain A, Linderman M,
Torgerson DG, et al: Integrated genome-wide association,
coexpression network, and expression single nucleotide polymorphism
analysis identifies novel pathway in allergic rhinitis. BMC Med
Genomics. 7(48)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Andiappan AK, Wang de Y, Anantharaman R,
Parate PN, Suri BK, Low HQ, Li Y, Zhao W, Castagnoli P, Liu J and
Chew FT: Genome-wide association study for atopy and allergic
rhinitis in a Singapore Chinese population. PLoS One.
6(e19719)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fujii R, Hishida A, Wu MC, Kondo T,
Hattori Y, Naito M, Endoh K, Nakatochi M, Hamajima N, Kubo M, et
al: Genome-wide association study for pollinosis identified two
novel loci in interleukin (IL)-1B in a Japanese population. Nagoya
J Med Sci. 80:109–120. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shen Y, Liu Y, Wang XQ, Ke X, Kang HY and
Hong SL: Association between TNFSF4 and BLK gene polymorphisms and
susceptibility to allergic rhinitis. Mol Med Rep. 16:3224–3232.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Lin X, Desrosiers M, Zhang W,
Meng N, Zhao L, Han D and Zhang L: Association pattern of
interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 gene polymorphisms with
allergic rhinitis in a Han Chinese population. PLoS One.
6(e21769)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ke X, Song S, Wang X, Shen Y, Kang H and
Hong S: Associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms of PTPN22
and Ctla4 genes with the risk of allergic rhinitis in a Chinese Han
population. Hum Immunol. 78:227–231. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kanazawa J, Masuko H, Yatagai Y, Sakamoto
T, Yamada H, Kitazawa H, Iijima H, Naito T, Saito T, Noguchi E, et
al: Association analyses of eQTLs of the TYRO3 gene and allergic
diseases in Japanese populations. Allergol Int. 68:77–81.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ke X, Yang Y, Shen Y, Wang X and Hong S:
Association between TNFAIP3 gene polymorphisms and risk of allergic
rhinitis in a Chinese Han population. Iran J Allergy Asthma
Immunol. 15:46–52. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nilsson D, Andiappan AK, Hallden C, Tim
CF, Säll T, Wang de Y and Cardell LO: Poor reproducibility of
allergic rhinitis SNP associations. PLoS One.
8(e53975)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Waage J, Standl M, Curtin JA, Jessen LE,
Thorsen J, Tian C and Schoettler N: 23andMe Research Team; AAGC
collaborators, Flores C, et al. Genome-wide association and
HLA fine-mapping studies identify risk loci and genetic pathways
underlying allergic rhinitis. Nat Genet. 50:1072–1080.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li J, Zhang Y and Zhang L: Discovering
susceptibility genes for allergic rhinitis and allergy using a
genome-wide association study strategy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin
Immunol. 15:33–40. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Romagnani S: The increased prevalence of
allergy and the hygiene hypothesis: Missing immune deviation,
reduced immune suppression, or both? Immunology. 112:352–363.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Romagnani S: Lymphokine production by
human T cells in disease states. Annu Rev Immunol. 12:227–257.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Abbas AK, Murphy KM and Sher A: Functional
diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 383:787–793.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li L, Xia Y, Nguyen A, Lai YH, Feng L,
Mosmann TR and Lo D: Effects of Th2 cytokines on chemokine
expression in the lung: IL-13 potently induces eotaxin expression
by airway epithelial cells. J Immunol. 162:2477–2487.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Durham SR, Ying S, Varney VA, Jacobson MR,
Sudderick RM, Mackay IS, Kay AB and Hamid QA: Cytokine messenger
RNA expression for IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, and
granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor in the nasal
mucosa after local allergen provocation: Relationship to tissue
eosinophilia. J Immunol. 148:2390–2394. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bischoff SC, Sellge G, Lorentz A, Sebald
W, Raab R and Manns MP: IL-4 enhances proliferation and mediator
release in mature human mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:8080–8085. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hardman CS, Panova V and McKenzie AN:
IL-33 citrine reporter mice reveal the temporal and spatial
expression of IL-33 during allergic lung inflammation. Eur J
Immunol. 43:488–498. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bystrom J, Patel SY, Amin K and
Bishop-Bailey D: Dissecting the role of eosinophil cationic protein
in upper airway disease. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 12:18–23.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Prefontaine D, Nadigel J, Chouiali F,
Audusseau S, Semlali A, Chakir J, Martin JG and Hamid Q: Increased
IL-33 expression by epithelial cells in bronchial asthma. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 125:752–754. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lloyd CM: IL-33 family members and
asthma-bridging innate and adaptive immune responses. Curr Opin
Immunol. 22:800–806. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shimizu M, Matsuda A, Yanagisawa K, Hirota
T, Akahoshi M, Inomata N, Ebe K, Tanaka K, Sugiura H, Nakashima K,
et al: Functional SNPs in the distal promoter of the ST2 gene are
associated with atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol Genet. 14:2919–2927.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Grotenboer NS, Ketelaar ME, Koppelman GH
and Nawijn MC: Decoding asthma: Translating genetic variation in
IL-33 and IL1RL1 into disease pathophysiology. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 131:856–865. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Watanabe M, Nakamoto K, Inui T, Sada M,
Honda K, Tamura M, Ogawa Y, Yokoyama T, Saraya T, Kurai D, et al:
Serum sST2 levels predict severe exacerbation of asthma. Respir
Res. 19(169)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li R, Yang G, Yang R, Peng X and Li J:
Interleukin-33 and receptor ST2 as indicators in patients with
asthma: A meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:14935–14943.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y,
Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et
al: IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1
receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated
cytokines. Immunity. 23:479–490. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Oshikawa K, Yanagisawa K, Tominaga S and
Sugiyama Y: Expression and function of the ST2 gene in a murine
model of allergic airway inflammation. Clin Exp Allergy.
32:1520–1526. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lohning M, Stroehmann A, Coyle AJ, Grogan
JL, Lin S, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Levinson D, Radbruch A and Kamradt
T: T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells,
independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10,
and important for Th2 effector function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:6930–6935. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Coyle AJ, Lloyd C, Tian J, Nguyen T,
Erikkson C, Wang L, Ottoson P, Persson P, Delaney T, Lehar S, et
al: Crucial role of the interleukin 1 receptor family member T1/ST2
in T helper cell type 2-mediated lung mucosal immune responses. J
Exp Med. 190:895–902. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xu D, Chan WL, Leung BP, Huang FP, Wheeler
R, Piedrafita D, Robinson JH and Liew FY: Selective expression of a
stable cell surface molecule on type 2 but not type 1 helper T
cells. J Exp Med. 187:787–794. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lecart S, Lecointe N, Subramaniam A, Alkan
S, Ni D, Chen R, Boulay V, Pène J, Kuroiwa K, Tominaga S and Yssel
H: Activated, but not resting human Th2 cells, in contrast to Th1
and T regulatory cells, produce soluble ST2 and express low levels
of ST2L at the cell surface. Eur J Immunol. 32:2979–2987.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Trajkovic V, Sweet MJ and Xu D: T1/ST2-an
IL-1 receptor-like modulator of immune responses. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 15:87–95. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ding W, Zou GL, Zhang W, Lai XN, Chen HW
and Xiong LX: Interleukin-33: Its emerging role in allergic
diseases. Molecules. 23(1665)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Haenuki Y, Matsushita K,
Futatsugi-Yumikura S, Ishii KJ, Kawagoe T, Imoto Y, Fujieda S,
Yasuda M, Hisa Y, Akira S, et al: A critical role of IL-33 in
experimental allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 130:184–194
e11. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gluck J, Rymarczyk B and Rogala B: Serum
IL-33 but not ST2 level is elevated in intermittent allergic
rhinitis and is a marker of the disease severity. Inflamm Res.
61:547–550. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sakashita M, Yoshimoto T, Hirota T, Harada
M, Okubo K, Osawa Y, Fujieda S, Nakamura Y, Yasuda K, Nakanishi K
and Tamari M: Association of serum interleukin-33 level and the
interleukin-33 genetic variant with Japanese cedar pollinosis. Clin
Exp Allergy. 38:1875–1881. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Du Y, Luo Y, Yang C, Liu J, Wan J and Wang
K: Discussion IL-33 and its receptor ST2 associated with the
pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou
Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 29:811–814. 2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
52
|
Guo-Zhu H, Xi-Ling Z, Zhu W, Li-Hua W, Dan
H, Xiao-Mu W, Wen-Yun Z and Wei-Xu H: Therapeutic potential of
combined anti-IL-1β IgY and anti-TNF-α IgY in guinea pigs with
allergic rhinitis induced by ovalbumin. Int Immunopharmacol.
25:155–161. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Asaka D, Yoshikawa M, Nakayama T,
Yoshimura T, Moriyama H and Otori N: Elevated levels of
interleukin-33 in the nasal secretions of patients with allergic
rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 158 (Suppl 1):S47–S50.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Kim YH, Yang TY, Park CS, Ahn SH, Son BK,
Kim JH, Lim DH and Jang TY: Anti-IL-33 antibody has a therapeutic
effect in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 67:183–190.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kamekura R, Kojima T, Takano K, Go M,
Sawada N and Himi T: The role of IL-33 and its receptor ST2 in
human nasal epithelium with allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy.
42:218–228. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Shaw JL, Fakhri S, Citardi MJ, Porter PC,
Corry DB, Kheradmand F, Liu YJ and Luong A: IL-33-responsive innate
lymphoid cells are an important source of IL-13 in chronic
rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
188:432–439. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Soyka MB, Holzmann D, Basinski TM,
Wawrzyniak M, Bannert C, Bürgler S, Akkoc T, Treis A, Rückert B,
Akdis M, et al: The induction of IL-33 in the sinus epithelium and
its influence on T-helper cell responses. PLoS One.
10(e0123163)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Baumann R, Rabaszowski M, Stenin I,
Tilgner L, Gaertner-Akerboom M, Scheckenbach K, Wiltfang J, Chaker
A, Schipper J and Wagenmann M: Nasal levels of soluble IL-33R ST2
and IL-16 in allergic rhinitis: Inverse correlation trends with
disease severity. Clin Exp Allergy. 43:1134–1143. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Position paper: Allergen standardization
and skin tests The European academy of allergology and clinical
immunology. Allergy. 48:48–82. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
1000 Genomes Project Consortium. Auton A,
Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, Korbel JO, Marchini JL,
McCarthy S, McVean GA and Abecasis GR. A global reference for human
genetic variation. Nature. 526:68–74. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Torgerson DG, Ampleford EJ, Chiu GY,
Gauderman WJ, Gignoux CR, Graves PE, Himes BE, Levin AM, Mathias
RA, Hancock DB, et al: Meta-analysis of genome-wide association
studies of asthma in ethnically diverse North American populations.
Nat Genet. 43:887–892. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Demenais F, Margaritte-Jeannin P, Barnes
KC, Cookson WOC, Altmüller J, Ang W, Barr RG, Beaty TH, Becker AB,
Beilby J, et al: Multiancestry association study identifies new
asthma risk loci that colocalize with immune-cell enhancer marks.
Nat Genet. 50:42–53. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhu Z, Lee PH, Chaffin MD, Chung W, Loh
PR, Lu Q, Christiani DC and Liang L: A genome-wide cross-trait
analysis from UK Biobank highlights the shared genetic architecture
of asthma and allergic diseases. Nat Genet. 50:857–864.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Bonnelykke K, Sleiman P, Nielsen K,
Kreiner-Møller E, Mercader JM, Belgrave D, den Dekker HT, Husby A,
Sevelsted A, Faura-Tellez G, et al: A genome-wide association study
identifies CDHR3 as a susceptibility locus for early childhood
asthma with severe exacerbations. Nat Genet. 46:51–55.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J and Daly MJ:
Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps.
Bioinformatics. 21:263–265. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Shi YY and He L: SHEsis, a powerful
software platform for analyses of linkage disequilibrium, haplotype
construction, and genetic association at polymorphism loci. Cell
Res. 15:97–98. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Li Z, Zhang Z, He Z, Tang W, Li T, Zeng Z,
He L and Shi Y: A partition-ligation-combination-subdivision EM
algorithm for haplotype inference with multiallelic markers: Update
of the SHEsis. (http://analysis.bio-x.cn).
Cell Res. 19:519–523. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lemonnier N, Melen E, Jiang Y, Joly S,
Ménard C, Aguilar D, Acosta-Perez E, Bergström A, Boutaoui N,
Bustamante M, et al: A novel whole blood gene expression signature
for asthma, dermatitis, and rhinitis multimorbidity in children and
adolescents. Allergy 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
69
|
Rogala B and Gluck J: The role of
interleukin-33 in rhinitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 13:196–202.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Tomita K, Sakashita M, Hirota T, Tanaka S,
Masuyama K, Yamada T, Fujieda S, Miyatake A, Hizawa N, Kubo M, et
al: Variants in the 17q21 asthma susceptibility locus are
associated with allergic rhinitis in the Japanese population.
Allergy. 68:92–100. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Li Y, Chen J, Rui X, Li N, Jiang F and
Shen J: The association between sixteen genome-wide association
studies-related allergic diseases loci and childhood allergic
rhinitis in a Chinese Han population. Cytokine. 111:162–170.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Yoon D, Ban HJ, Kim YJ, Kim EJ, Kim HC,
Han BG, Park JW, Hong SJ, Cho SH, Park K and Lee JS: Replication of
genome-wide association studies on asthma and allergic diseases in
Korean adult population. BMB Rep. 45:305–310. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Amarin JZ, Naffa RG, Suradi HH, Alsaket
YM, Obeidat NM, Mahafza TM and Zihlif MA: An intronic
single-nucleotide polymorphism (rs13217795) in FOXO3 is associated
with asthma and allergic rhinitis: A case-case-control study. BMC
Med Genet. 18(132)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Li X, Hastie AT, Hawkins GA, Moore WC,
Ampleford EJ, Milosevic J, Li H, Busse WW, Erzurum SC, Kaminski N,
et al: eQTL of bronchial epithelial cells and bronchial alveolar
lavage deciphers GWAS-identified asthma genes. Allergy.
70:1309–1318. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Ketelaar ME, Portelli MA, Dijk FN, Shrine
N, Faiz A, Vermeulen CJ, Xu CJ, Hankinson J, Bhaker S, Henry AP, et
al: Phenotypic and functional translation of IL-33 genetics in
asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
76
|
Gorbacheva AM, Korneev KV, Kuprash DV and
Mitkin NA: The risk G allele of the single-nucleotide polymorphism
rs928413 creates a CREB1-Binding site that activates IL-33 promoter
in lung epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 19(2911)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Paller AS, Spergel JM, Mina-Osorio P and
Irvine AD: The atopic march and atopic multimorbidity: Many
trajectories, many pathways. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 143:46–55.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Akdis CA, Arkwright PD, Bruggen MC, Busse
W, Gadina M, Guttman-Yassky E, Kabashima K, Mitamura Y, Vian L, Wu
J and Palomares O: Type 2 immunity in the skin and lungs. Allergy.
75:1582–1605. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
D'Amato G, Ortega OPM, Annesi-Maesano I
and D'Amato M: Prevention of allergic asthma with allergen
avoidance measures and the role of exposome. Curr Allergy Asthma
Rep. 20(8)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Liccardi G, Cazzola M, Walter Canonica G,
Passalacqua G and D'Amato G: New insights in allergen avoidance
measures for mite and pet sensitized patients. A critical
appraisal. Respir Med. 99:1363–1376. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Halken S: Prevention of allergic disease
in childhood: Clinical and epidemiological aspects of primary and
secondary allergy prevention. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 15 (Suppl
16):4–5, 9-32. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Cook J and Saglani S: Pathogenesis and
prevention strategies of severe asthma exacerbations in children.
Curr Opin Pulm Med. 22:25–31. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Chen WY, Tsai TH, Yang JL and Li LC:
Therapeutic strategies for targeting IL-33/ST2 signalling for the
treatment of inflammatory diseases. Cell Physiol Biochem.
49:349–358. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Takatori H, Makita S, Ito T, Matsuki A and
Nakajima H: Regulatory mechanisms of IL-33-ST2-Mediated allergic
inflammation. Front Immunol. 9(2004)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|