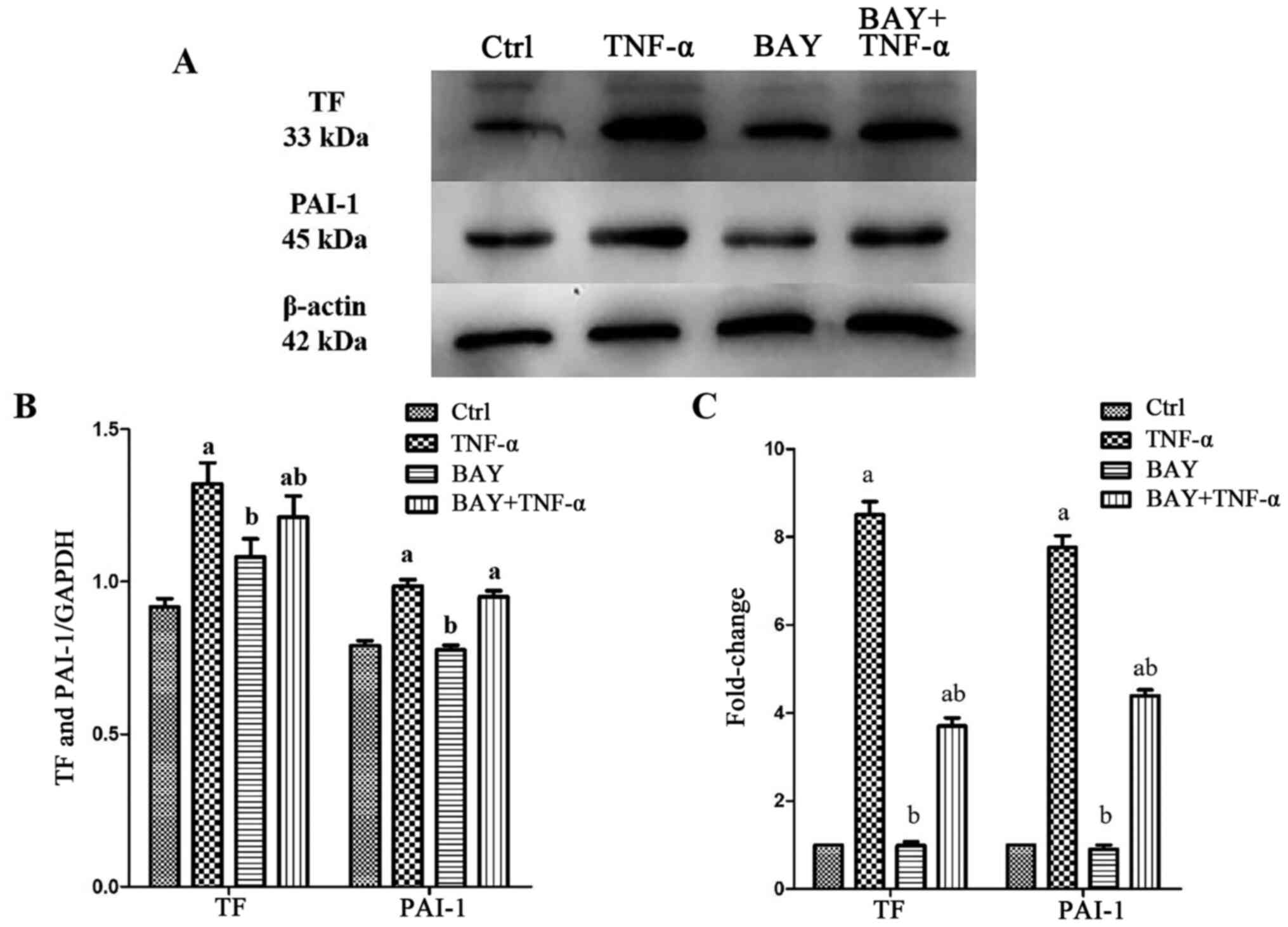
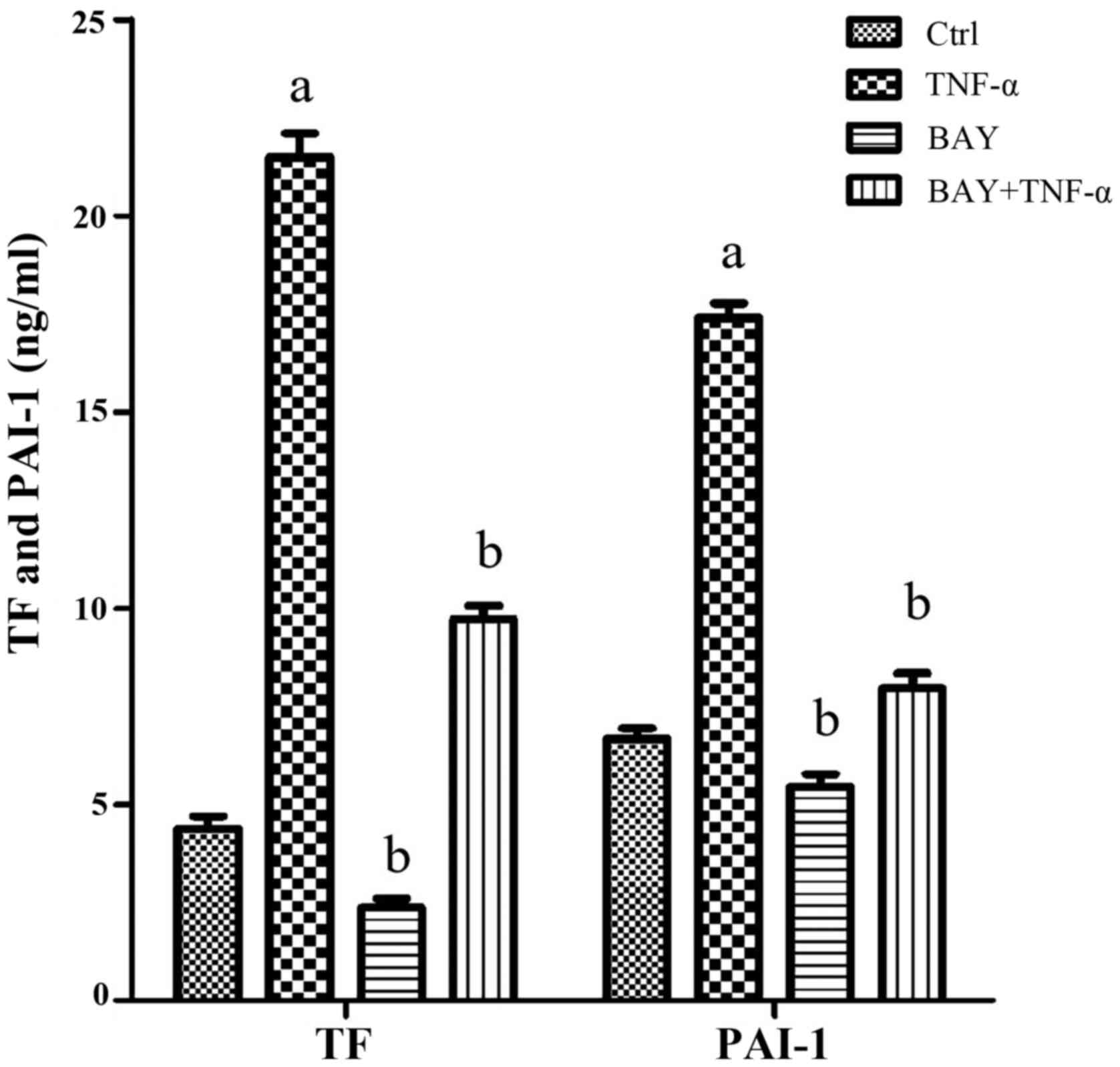
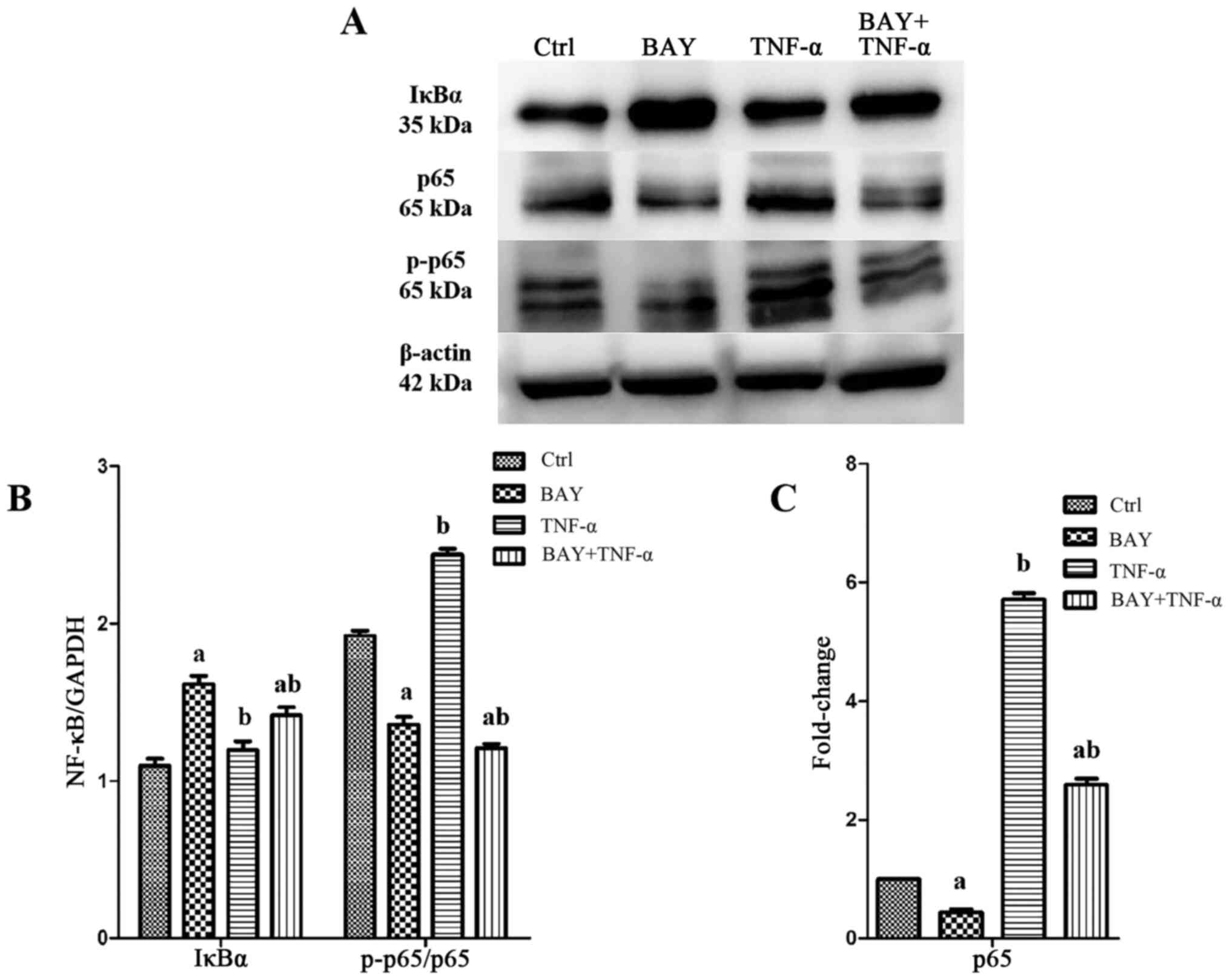
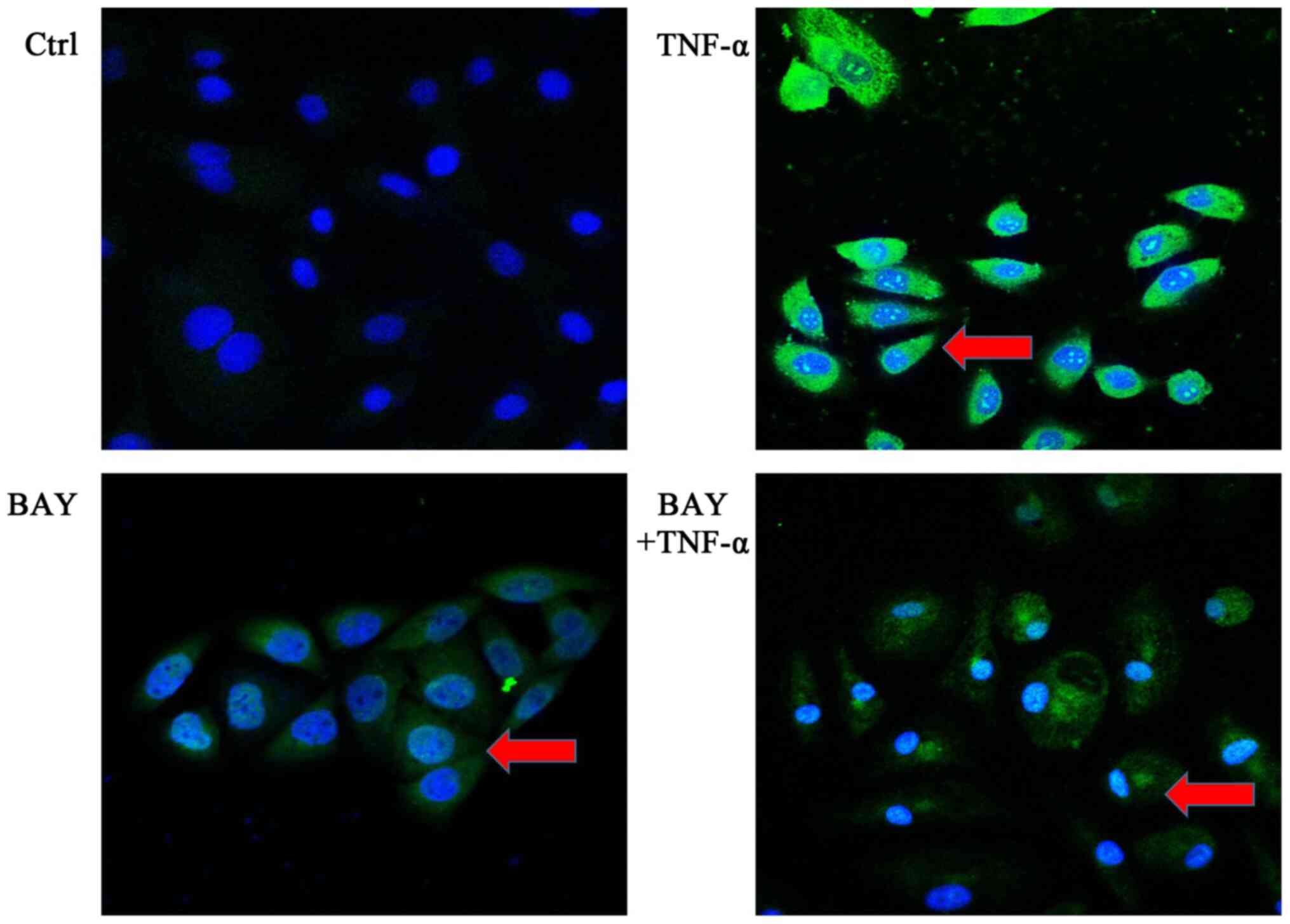
|
1
|
Frantzeskaki F, Armaganidis A and Orfanos
SE: Immunothrombosis in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Cross
talks between inflammation and coagulation. Respiration.
93:212–225. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tuinman PR, Dixon B, Levi M, Juffermans NP
and Schultz MJ: Nebulized anticoagulants for acute lung injury-a
systematic review of preclinical and clinical investigations. Crit
Care. 16(R70)2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ozolina A, Sarkele M, Sabelnikovs O,
Skesters A, Jaunalksne I, Serova J, Ievins T, Bjertnaes LJ and
Vanags I: Activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute
respiratory distress syndrome: A prospective pilot study. Front Med
(Lausanne). 3(64)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bastarache JA, Sebag SC, Clune JK, Grove
BS, Lawson WE, Janz DR, Roberts LJ II, Dworski R, Mackman N and
Ware LB: Low levels of tissue factor lead to alveolar haemorrhage,
potentiating murine acute lung injury and oxidative stress. Thorax.
67:1032–1039. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Zhang L, Duan W, Liu B, Gong P,
Ding Y and Wu X: Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide by
inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway in LPS-induced acute lung
injury in a murine model. Mol Med Rep. 10:447–452. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sebag SC, Bastarache JA and Ware LB:
Therapeutic modulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute
lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 12:1481–1496. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Christiaans SC, Wagener BM, Esmon CT and
Pittet JF: Protein C and acute inflammation: A clinical and
biological perspective. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
305:L455–L466. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bonizzi G and Karin M: The two NF-kappaB
activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity.
Trends Immunol. 25:280–288. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gao MY, Chen L, Yang L, Yu X, Kou JP and
Yu BY: Berberine inhibits LPS-induced TF procoagulant activity and
expression through NF-κB/p65, Akt and MAPK pathway in THP-1 cells.
Pharmacol Rep. 66:480–484. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jeffers A, Owens S, Koenig K, Quaid B,
Pendurthi UR, Rao VM, Idell S and Tucker TA: Thrombin
down-regulates tissue factor pathway inhibitor expression in a
PI3K/nuclear factor-κB-dependent manner in human pleural
mesothelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 52:674–682.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
El Kebir D, Damlaj A, Makhezer N and Filep
JG: Toll-like receptor 9 signaling regulates tissue factor and
tissue factor pathway inhibitor expression in human endothelial
cells and coagulation in mice. Crit Care Med. 43:e179–e189.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Deng X, Jin K, Li Y, Gu W, Liu M and Zhou
L: Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor β1
regulate ARDS-associated lung fibrosis through distinct signaling
pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:937–946. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bastarache JA, Wang L, Geiser T, Wang Z,
Albertine KH, Matthay MA and Ware LB: The alveolar epithelium can
initiate the extrinsic coagulation cascade through expression of
tissue factor. Thorax. 62:608–616. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu B, Wu Y, Wang Y, Cheng Y, Yao L, Liu
Y, Qian H, Yang H and Shen F: NF-κB p65 Knock-down inhibits TF,
PAI-1 and promotes activated protein C production in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated alveolar epithelial cells type II.
Exp Lung Res. 44:241–251. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu B, Wang Y, Wu Y, Cheng Y, Qian H, Yang
H and Shen F: IKKβ regulates the expression of coagulation and
fibrinolysis factors through the NF-κB canonical pathway in
LPS-stimulated alveolar epithelial cells type II. Exp Ther Med.
18:2859–2866. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mori N, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, Yamasaki Y,
Tsukasaki K, Tanaka Y, Tomonaga M, Yamamoto N and Fujii M: Bay
11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces
apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines andprimary adult T-cell
leukemia cells. Blood. 100:1828–1834. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gonzales JN, Lucas R and Verin AD: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome: Mechanisms and perspective
therapeutic approaches. Austin J Vasc Med. 2(1009)2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Camprubí-Rimblas M, Tantinyà N, Bringué J,
Guillamat-Prats R and Artigas A: Anticoagulant therapy in acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Ann Transl Med. 6(36)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Glas GJ, Van Der Sluijs KF, Schultz MJ,
Hofstra JJ, Van Der Poll T and Levi M: Bronchoalveolar hemostasis
in lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Thromb
Haemost. 11:17–25. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kasthuri RS, Glover SL, Boles J and
Mackman N: Tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor as key
regulators of global hemostasis: Measurement of their levels in
coagulation assays. Semin Thromb Hemost. 36:764–771.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu RM: Oxidative stress, plasminogen
activator inhibitor 1, and lung fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
10:303–319. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Song M, Fang F, Dai X, Yu L, Fang M and Xu
Y: MKL1 is an epigenetic mediator of TNF-α-induced proinflammatory
transcription in macrophages by interacting with ASH2. FEBS Lett.
591:934–945. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
He Z, Du L, Ke Y, Wen C and Zhang Y:
PP2ACα of alveolar macrophages is a novel protective factor for
LPS-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflammation.
42:1004–1014. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Qi D, Wand D, Zhang C, Tang X, He J, Zhao
Y, Deng W and Deng X: Vaspin protects against LPS-induced ARDS by
inhibiting inflammation, apoptosis and reactive oxygen species
generation in pulmonary endothelial cells via the Akt/GSK-3β
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 40:1803–1817. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim YS, Kim JS, Kwon JS, Jeong MH, Cho JG,
Park JC, Kang JC and Ahn Y: BAY 11-7082, a nuclear factor-κB
inhibitor, reduces inflammation and apoptosis in a rat cardiac
ischemia-reperfusion injury model. Int Heart J. 51:348–353.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lampiasi N, Azzolina A, D'Alessandro N,
Umezawa K, McCubrey JA, Montalto G and Cervello M: Antitumor
effects of dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a novel nuclear
factor-kappaB inhibitor, in human liver cancer cells are mediated
through a reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanism. Mol
Pharmacol. 76:290–300. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang A, Wang K, Ding L, Bao X, Wang X,
Qiu X and Liu J: Bay11-7082 attenuates neuropathic pain via
inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B and nucleotide-binding
domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation in dorsal
root ganglions in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation. J Pain
Res. 10:375–382. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gamble C, McIntosh K, Scott R, Ho KH,
Plevin R and Paul A: Inhibitory kappa B Kinases as targets for
pharmacological regulation. Br J Pharmacol. 165:802–819.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zheng C, Yin Q and Wu H: Structural
studies of NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:183–195. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|