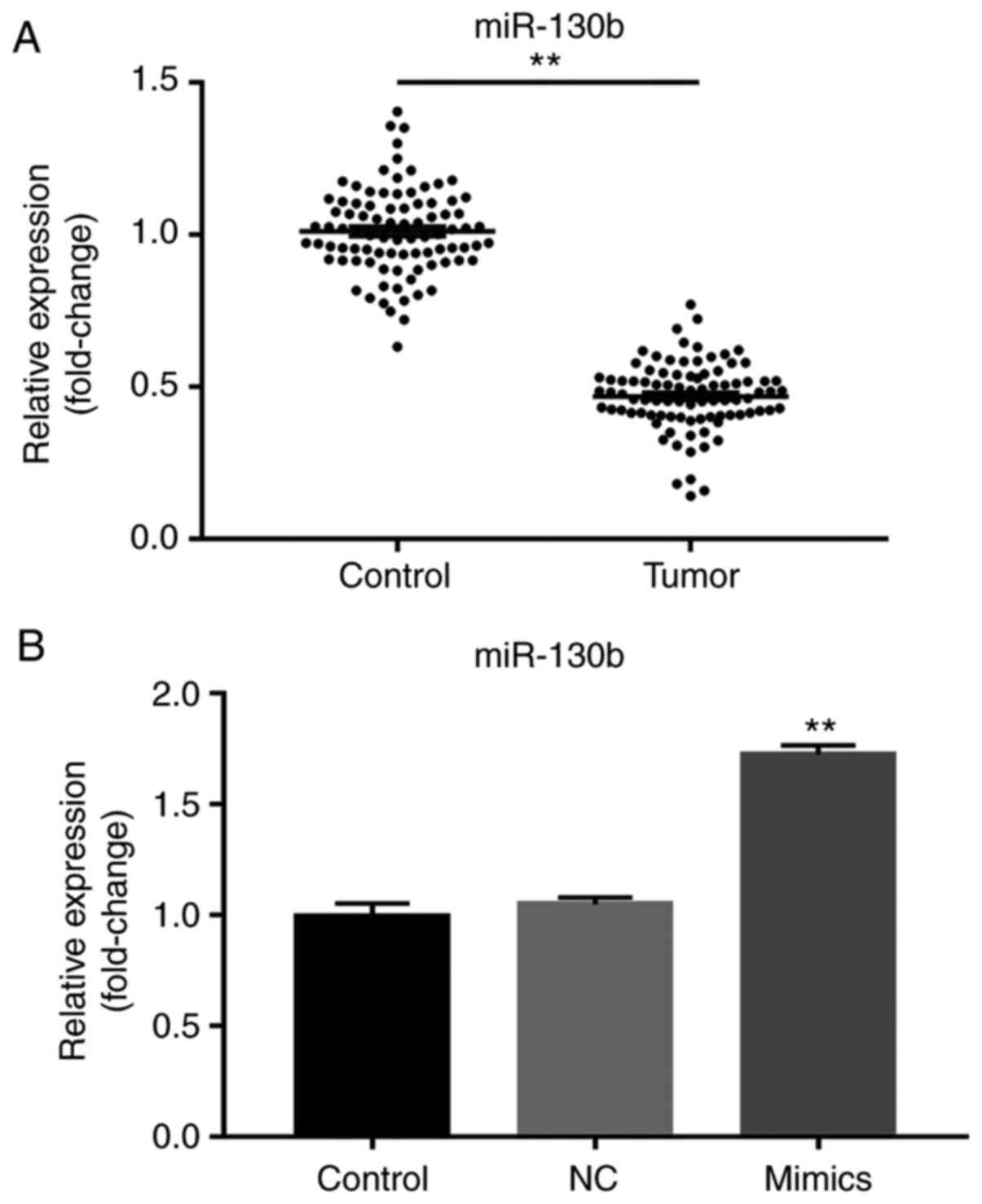
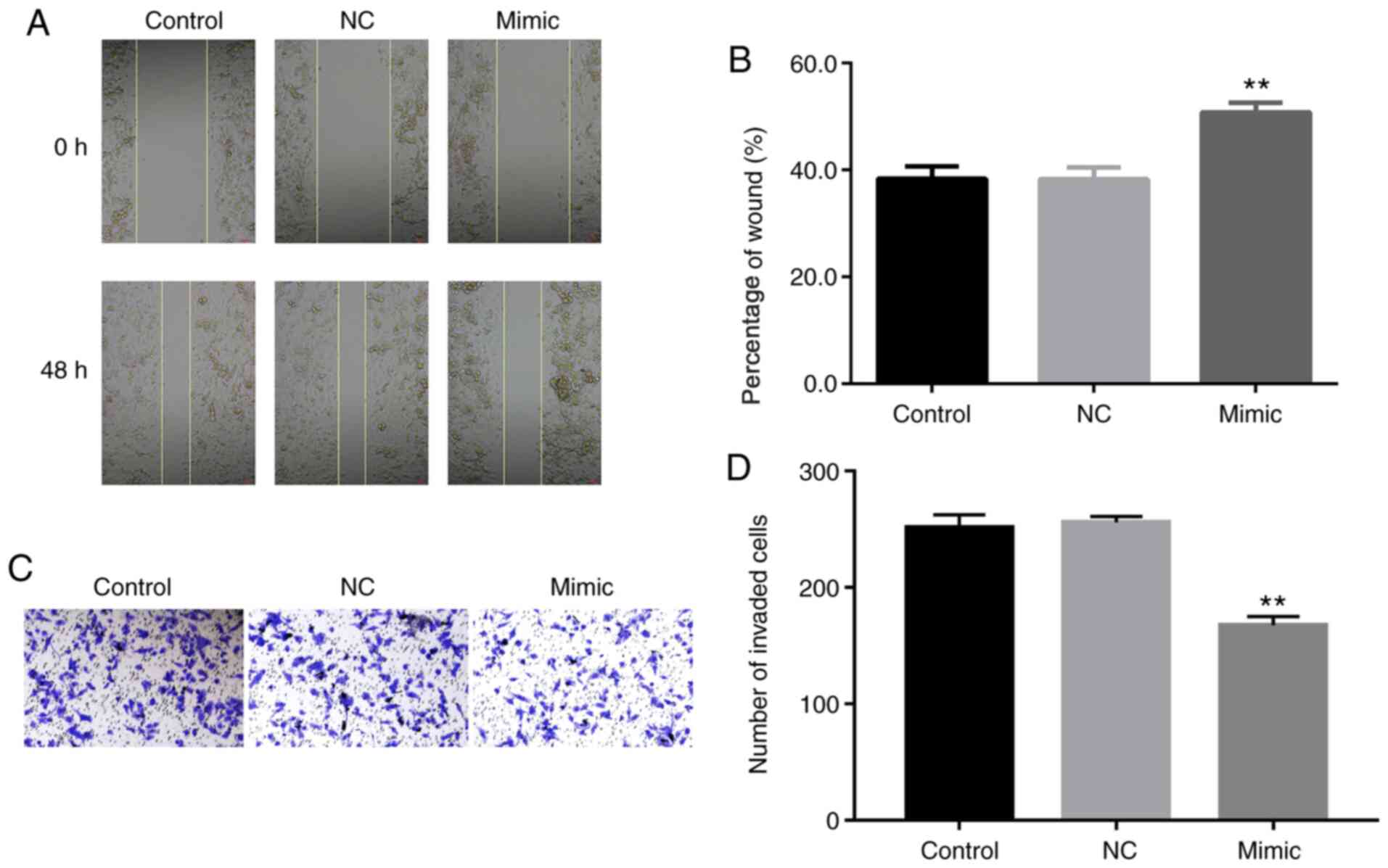
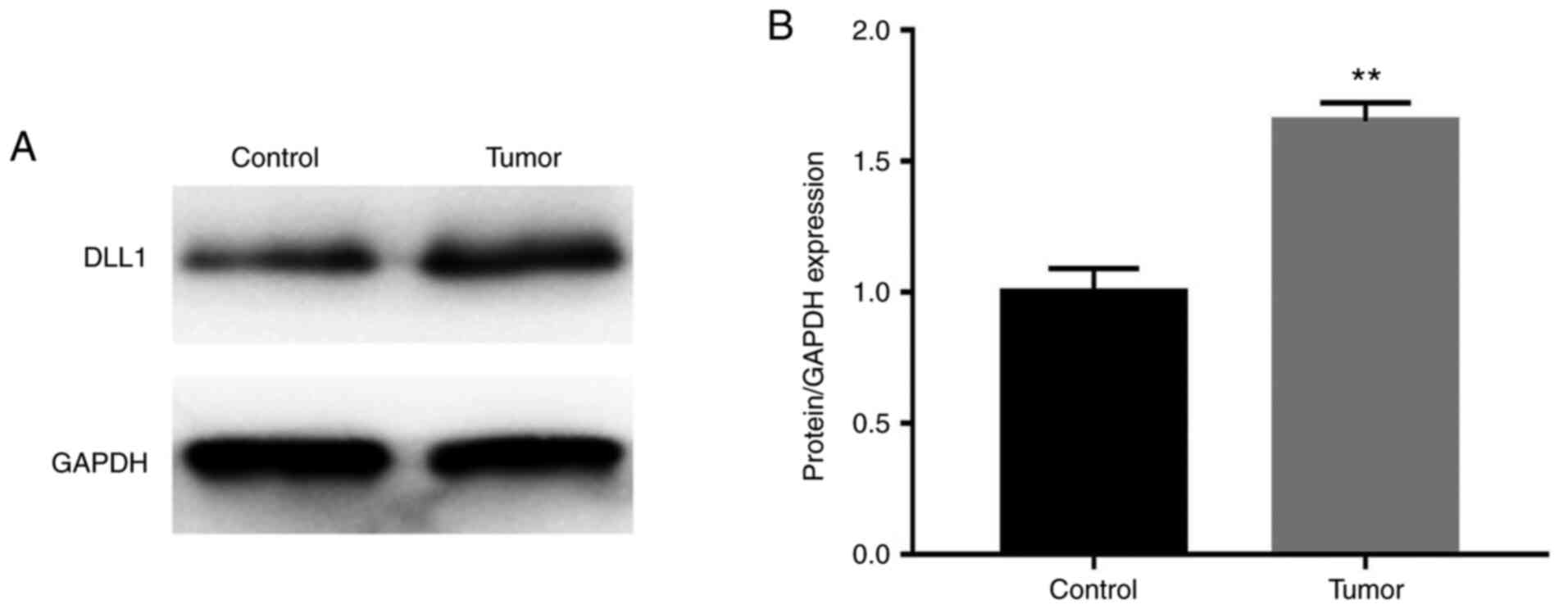
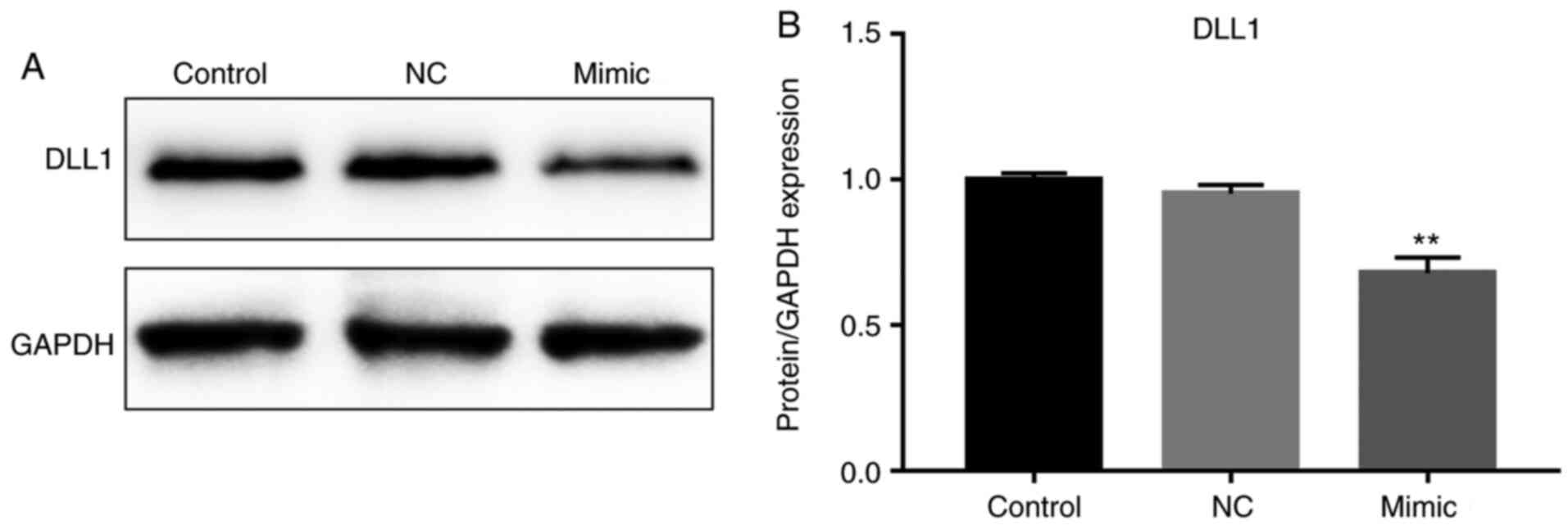
|
1
|
Chen DQ, Yu C, Zhang XF, Liu ZF, Wang R,
Jiang M, Chen H, Yan F, Tao M, Chen LB, et al: HDAC3-mediated
silencing of miR-451 decreases chemosensitivity of patients with
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer by targeting NEDD9.
Ther Adv Med Oncol. 10(1758835918783132)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhu JG, Pan C, Jiang J, Deng M, Gao H, Men
B, McClelland M, Mercola D, Zhong WD and Jia Z: Six stroma-based
RNA markers diagnostic for prostate cancer in European-Americans
validated at the RNA and protein levels in patients in China.
Oncotarget. 6:16757–16765. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Paliouras AR, Monteverde T and Garofalo M:
Oncogene-induced regulation of microrna expression: Implications
for cancer initiation, progression and therapy. Cancer Lett.
421:152–160. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang C, Qian D, Zhao H, Lv N, Yu P and
Sun Z: miR-17 improves insulin sensitivity through inhibiting
expression of ASK1 and anti-inflammation of macrophages. Biomed
Pharmacother. 100:448–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu N, Han Y, Liu H, Jiang M, Chu Y, Cao J,
Lin J, Liu Y, Xu B and Xie X: miR-5590-3p inhibited tumor growth in
gastric cancer by targeting DDX5/AKT/m-TOR pathway. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 503:1491–1497. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sun L, Guo Z, Sun J, Li J, Dong Z, Zhang
Y, Chen J, Kan Q and Yu Z: MiR-133a acts as an anti-oncogene in
Hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting FOSL2 through TGF-β/Smad3
signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:168–176.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kaalund SS, Venø MT, Bak M, Møller RS,
Laursen H, Madsen F, Broholm H, Quistorff B, Uldall P, Tommerup N,
et al: Aberrant expression of mir-218 and mir-204 in human mesial
temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis-convergence on
axonal guidance. Epilepsia. 55:2017–2027. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shen J and Li M: Microrna-744 inhibits
cellular proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer by
directly targeting oncogene notch1. Oncol Res: Feb 22, 2018 (Epub
ahead of print). doi: 10.3727/096504018X15188747585738.
|
|
11
|
Chen Q, Zhao X, Zhang H, Yuan H, Zhu M,
Sun Q, Lai X, Wang Y, Huang J, Yan J and Yu J: miR-130b suppresses
prostate cancer metastasis through down-regulation of MMP2. Mol
Carcinog. 54:1292–1300. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang JP, Li N, Bai WZ, Qiu XC, Ma BA,
Zhou Y, Fan QY and Shan LQ: Notch ligand Delta-like 1 promotes the
metastasis of melanoma by enhancing tumor adhesion. Braz J Med Biol
Res. 47:299–306. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pang RT, Leung CO, Lee CL, Lam KK, Ye TM,
Chiu PC and Yeung WS: MicroRNA-34a is a tumor suppressor in
choriocarcinoma via regulation of Delta-like1. BMC Cancer.
13(25)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yu F, Hao X, Zhao H, Ge C, Yao M, Yang S
and Li J: Delta-like 1 contributes to cell growth by increasing the
interferon-inducible protein 16 expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Liver Int. 30:703–714. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Purow BW, Haque RM, Noel MW, Su Q, Burdick
MJ, Lee J, Sundaresan T, Pastorino S, Park JK, Mikolaenko I, et al:
Expression of notch-1 and its ligands, delta-like-1 and jagged-1,
is critical for glioma cell survival and proliferation. Cancer Res.
65:2353–2363. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Scorey N, Fraser SP, Patel P, Pridgeon C,
Dallman MJ and Djamgoz MB: Notch signalling and voltage-gated Na+
channel activity in human prostate cancer cells: Independent
modulation of in vitro motility. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
9:399–406. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Adimonye A, Stankiewicz E, Kudahetti S,
Trevisan G, Tinwell B, Corbishley C, Lu YJ, Watkin N and Berney D:
Analysis of the pi3k-Akt-mtor pathway in penile cancer: Evaluation
of a therapeutically targetable pathway. Oncotarget. 9:16074–16086.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cretella D, Ravelli A, Fumarola C, La
Monica S, Digiacomo G, Cavazzoni A, Alfieri R, Biondi A, Generali
D, Bonelli M and Petronini PG: The anti-tumor efficacy of cdk4/6
inhibition is enhanced by the combination with pi3k/Akt/mtor
inhibitors through impairment of glucose metabolism in tnbc cells.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37(72)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li H, Xu W, Ma Y, Zhou S and Xiao R: Milk
fat globule membrane protein promotes c2c12 cell proliferation
through the pi3k/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol.
114:1305–1314. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014(150845)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shi X, Yang L, Xie J, Zhao Y, Cong J, Li
Z, Li H, Cheng X and Fan J: UNBS5162 inhibits proliferation of
human melanoma cells by inducing apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:3382–3388. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang XR, Wang SY, Sun W and Wei C:
Isoliquiritigenin inhibits proliferation and metastasis of MKN28
gastric cancer cells by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:3429–3436. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Paplomata E and O'Regan R: The
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in breast cancer: Targets, trials and
biomarkers. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 6:154–166. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang HY, Zhang CY, Xu LT, Zang K, Ning ZY,
Jiang F, Chi HY, Zhu XY and Meng ZQ: Bufalin suppressed
hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis by targeting
HIF-1α via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget. 7:320193–20208.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen Y, Zhao F, Cui D, Jiang R, Chen J,
Huang Q and Shi J: Hoxd-as1/mir-130a sponge regulates glioma
development by targeting e2f8. Int J Cancer. 142:2313–2322.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tang C, Yang Z, Chen D, Xie Q, Peng T, Wu
J and Qi S: Downregulation of mir-130a promotes cell growth and
epithelial to mesenchymal transition by activating hmgb2 in glioma.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 93:25–31. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wei H, Cui R, Bahr J, Zanesi N, Luo Z,
Meng W, Liang G and Croce CM: Mir-130a deregulates pten and
stimulates tumor growth. Cancer Res. 77:6168–6178. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen H, Yang Y, Wang J, Shen D, Zhao J and
Yu Q: miR-130b-5p promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of
gastric cancer cells via targeting RASAL1. Oncol Lett.
15:6361–6367. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Li J and Ji
ZL: The role of mir-130a in cancer. Breast Cancer. 24:521–527.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao G, Zhang JG, Shi Y, Qin Q, Liu Y,
Wang B, Tian K, Deng SC, Li X, Zhu S, et al: miR-130b is a
prognostic marker and inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in
pancreatic cancer through targeting STAT3. PLoS One.
8(e73803)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yu T, Cao R, Li S, Fu M, Ren L, Chen W,
Zhu H, Zhan Q and Shi R: Mir-130b plays an oncogenic role by
repressing PTEN expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
cells. BMC cancer. 15(29)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chang RM, Xu JF, Fang F, Yang H and Yang
LY: Microrna-130b promotes proliferation and emt-induced metastasis
via pten/p-Akt/hif-1alpha signaling. Tumour Biol. 37:10609–10619.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zayzafoon M, Abdulkadir SA and McDonald
JM: Notch signaling and ERK activation are important for the
osteomimetic properties of prostate cancer bone metastatic cell
lines. J Biol Chem. 279:3662–3670. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Carmen M, Ileana G, Stefano B, Oxana B,
Bernard F, Carlo R, Rosario D and Cataldo A: PP242 counteracts
glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, invasiveness and
stemness properties by inhibiting mTORC2/AKT. Front Cell Neurosci.
12(99)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Slattery ML, Herrick JS, Lundgreen A,
Fitzpatrick FA, Curtin K and Wolff RK: Genetic variation in a
metabolic signaling pathway and colon and rectal cancer risk: mTOR,
PTEN, STK11, RPKAA1, PRKAG2, TSC1, TSC2, PI3K and Akt1.
Carcinogenesis. 31:1604–1611. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun DM, Tang BF, Li ZX, Guo HB, Cheng JL,
Song PP and Zhao X: miR-29c reduces the cisplatin resistance of
non-small cell lung cancer cells by negatively regulating the
PI3K/Akt pathway. Sci Rep. 8(8007)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou Y, Gu P, Li J, Li F, Zhu J, Gao P,
Zang Y, Wang Y, Shan Y and Yang D: Suppression of STIM1 inhibits
the migration and invasion of human prostate cancer cells and is
associated with PI3K/Akt signaling inactivation. Oncol Rep.
38:2629–2636. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Xu S, Ge J, Zhang Z and Zhou W: miR-129
inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting ETS1 via
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:634–641. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Dhupkar P, Zhao H, Mujoo K, An Z and Zhang
N: Crk II silencing down-regulates IGF-IR and inhibits migration
and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Rep.
8:382–388. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang W, Hsu P, Zhong B, Guo S and Zhang
C, Wang Y, Luo C, Zhan Y and Zhang C: MiR-34a enhances chondrocyte
apoptosis, senescence and facilitates development of osteoarthritis
by targeting DLL1 and regulating PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 48:1304–1316. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Miao Y, Zheng W, Li N, Su Z, Zhao L, Zhou
H and Jia L: MicroRNA-130b targets PTEN to mediate drug resistance
and proliferation of breast cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Sci Rep. 7(41942)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhou D, Zhang L, Sun W, Guan W, Lin Q, Ren
W, Zhang J and Xu G: Cytidine monophosphate kinase is inhibited by
the TGF-β signalling pathway through the upregulation of
miR-130b-3p in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cell Signal.
35:197–207. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Elizabeth IH, Emma FS and Stack MS: With
great age comes great metastatic ability: Ovarian cancer and the
appeal of the aging peritoneal microenvironment. Cancers (Basel).
10(230)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Shui Y, Yu X, Duan R, Bao Q, Wu J, Yuan H
and Ma C: miR-130b-3p inhibits cell invasion and migration by
targeting the Notch ligand Delta-like 1 in breast carcinoma. Gene.
609:80–87. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Duellman T, Chen X, Wakamiya R and Yang J:
Nucleic acid-induced potentiation of matrix metalloproteinase-9
enzymatic activity. Biochem J. 475:1597–1610. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Murawala H, Patel S, Ranadive I, Desai I
and Balakrishnan S: Variation in expression and activity pattern of
mmp2 and mmp9 on different time scales in the regenerating caudal
fin of poecilia latipinna. J Fish Biol. 92:1604–1619.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sahay AS, Jadhav AT, Sundrani DP, Wagh GN,
Mehendale SS and Joshi SR: Matrix metalloproteinases-2 (mmp-2) and
matrix metalloproteinases-9 (mmp-9) are differentially expressed in
different regions of normal and preeclampsia placentae. J Cell
Biochem. 119:6657–6664. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Weiler J, Mohr M, Zänker KS and Dittmar T:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (mmp9) is involved in the
tnf-alpha-induced fusion of human m13sv1-cre breast epithelial
cells and human mda-mb-435-pfdr1 cancer cells. Cell Commun Signal.
16(14)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|