|
1
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157(107843)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thomas CC and Philipson LH: Update on
diabetes classification. Med Clin North Am. 99:1–16.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Müller G: Microvesicles/exosomes as
potential novel biomarkers of metabolic diseases. Diabetes Metab
Syndr Obes. 5:247–282. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Dong Y,
Birmingham A, Seo JB, Ofrecio JM, Wollam J, Hernandez-Carretero A,
Fu W, et al: Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miRNAs can
modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell.
171:372–384.e12. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lin J, Li J, Huang B, Liu J, Chen X, Chen
XM, Xu YM, Huang LF and Wang XZ: Exosomes: Novel biomarkers for
clinical diagnosis. ScientificWorldJournal.
2015(657086)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kalluri R and LeBleu VS: The biology,
function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science.
367(eaau6977)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Théry C, Zitvogel L and Amigorena S:
Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol.
2:569–579. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Doyle LM and Wang MZ: Overview of
extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and
methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells.
8(727)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pegtel DM and Gould SJ: Exosomes. Annu Rev
Biochem. 88:487–514. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J
and Mi S: Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and
function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 13:17–24.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lebovitz HE: Etiology and pathogenesis of
diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Clin North Am. 31:521–530.
1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kaul K, Tarr JM, Ahmad SI, Kohner EM and
Chibber R: Introduction to diabetes mellitus. Adv Exp Med Biol.
771:1–11. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Forbes JM and Cooper ME: Mechanisms of
diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 93:137–188. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jin J, Shi Y, Gong J, Zhao L, Li Y, He Q
and Huang H: Exosome secreted from adipose-derived stem cells
attenuates diabetic nephropathy by promoting autophagy flux and
inhibiting apoptosis in podocyte. Stem Cell Res Ther.
10(95)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chang W and Wang J: Exosomes and their
noncoding RNA cargo are emerging as new modulators for diabetes
mellitus. Cells. 8(853)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Castaño C, Novials A and Párrizas M:
Exosomes and diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
35(e3107)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kakleas K, Soldatou A, Karachaliou F and
Karavanaki K: Associated autoimmune diseases in children and
adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Autoimmun Rev.
14:781–797. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cianciaruso C, Phelps EA, Pasquier M,
Hamelin R, Demurtas D, Alibashe Ahmed M, Piemonti L, Hirosue S,
Swartz MA, De Palma M, et al: Primary human and rat β-cells release
the intracellular autoantigens GAD65, IA-2, and proinsulin in
exosomes together with cytokine-induced enhancers of immunity.
Diabetes. 66:460–473. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rahman MJ, Regn D, Bashratyan R and Dai
YD: Exosomes released by islet-derived mesenchymal stem cells
trigger autoimmune responses in NOD mice. Diabetes. 63:1008–1020.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Garcia-Contreras M, Brooks RW, Boccuzzi L,
Robbins PD and Ricordi C: Exosomes as biomarkers and therapeutic
tools for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:2940–2956. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsukita S, Yamada T, Takahashi K, Munakata
Y, Hosaka S, Takahashi H, Gao J, Shirai Y, Kodama S, Asai Y, et al:
MicroRNAs 106b and 222 improve hyperglycemia in a mouse model of
insulin-deficient diabetes via pancreatic β-cell proliferation.
EBioMedicine. 15:163–172. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Malone JI and Hansen BC: Does obesity
cause type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)? Or is it the opposite?
Pediatr Diabetes. 20:5–9. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Heydemann A: An overview of murine high
fat diet as a model for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res.
2016(2902351)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z, Bai Y, Li Z, Zhang
H, Zhang Q, Guo C, Zhang L and Wang Q: Exosomes from
adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and
obesity through polarizing m2 macrophages and beiging in white
adipose tissue. Diabetes. 67:235–247. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Castaño C, Kalko S, Novials A and Párrizas
M: Obesity-associated exosomal miRNAs modulate glucose and lipid
metabolism in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:12158–12163.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Brown AE and Walker M: Genetics of insulin
resistance and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Cardiol Rep.
18(75)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sun Y, Shi H, Yin S, Ji C, Zhang X, Zhang
B, Wu P, Shi Y, Mao F, Yan Y, et al: Human mesenchymal stem cell
derived exosomes alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus by reversing
peripheral insulin resistance and relieving β-cell destruction. ACS
Nano. 12:7613–7628. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cole JB and Florez JC: Genetics of
diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat Rev Nephrol.
16:377–390. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Barrett EJ, Liu Z, Khamaisi M, King GL,
Klein R, Klein BEK, Hughes TM, Craft S, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, et
al: Diabetic microvascular disease: An endocrine society scientific
statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 102:4343–4410. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shen B, Liu J, Zhang F, Wang Y, Qin Y,
Zhou Z, Qiu J and Fan Y: CCR2 positive exosome released by
mesenchymal stem cells suppresses macrophage functions and
alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury. Stem Cells
Int. 2016(1240301)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liang X, Zhang L, Wang S, Han Q and Zhao
RC: Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial
cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci.
129:2182–2189. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chimenti MS, Ballanti E, Triggianese P and
Perricone R: Vasculitides and the complement system: A
comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 49:333–346.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang C, Fisher KP, Hammer SS, Navitskaya
S, Blanchard GJ and Busik JV: Plasma exosomes contribute to
microvascular damage in diabetic retinopathy by activating the
classical complement pathway. Diabetes. 67:1639–1649.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Martínez-Castelao A, Navarro-González JF,
Górriz JL and de Alvaro F: The concept and the epidemiology of
diabetic nephropathy have changed in recent years. J Clin Med.
4:1207–1216. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang L, Li R, Shi W, Liang X, Liu S, Ye
Z, Yu C, Chen Y, Zhang B, Wang W, et al: NFAT2 inhibitor
ameliorates diabetic nephropathy and podocyte injury in db/db mice.
Br J Pharmacol. 170:426–439. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ioannou K: Diabetic nephropathy: Is it
always there? Assumptions, weaknesses and pitfalls in the
diagnosis. Hormones (Athens). 16:351–361. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sakurai A, Ono H, Ochi A, Matsuura M,
Yoshimoto S, Kishi S, Murakami T, Tominaga T, Nagai K, Abe H and
Doi T: Involvement of Elf3 on Smad3 activation-dependent injuries
in podocytes and excretion of urinary exosome in diabetic
nephropathy. PLoS One. 14(e0216788)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Abe H, Sakurai A, Ono H, Hayashi S,
Yoshimoto S, Ochi A, Ueda S, Nishimura K, Shibata E, Tamaki M, et
al: Urinary exosomal mRNA of WT1 as diagnostic and prognostic
biomarker for diabetic nephropathy. J Med Invest. 65:208–215.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kim H, Bae YU, Jeon JS, Noh H, Park HK,
Byun DW, Han DC, Ryu S and Kwon SH: The circulating exosomal
microRNAs related to albuminuria in patients with diabetic
nephropathy. J Transl Med. 17(236)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Calle P and Hotter G: Macrophage phenotype
and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci.
21(2806)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
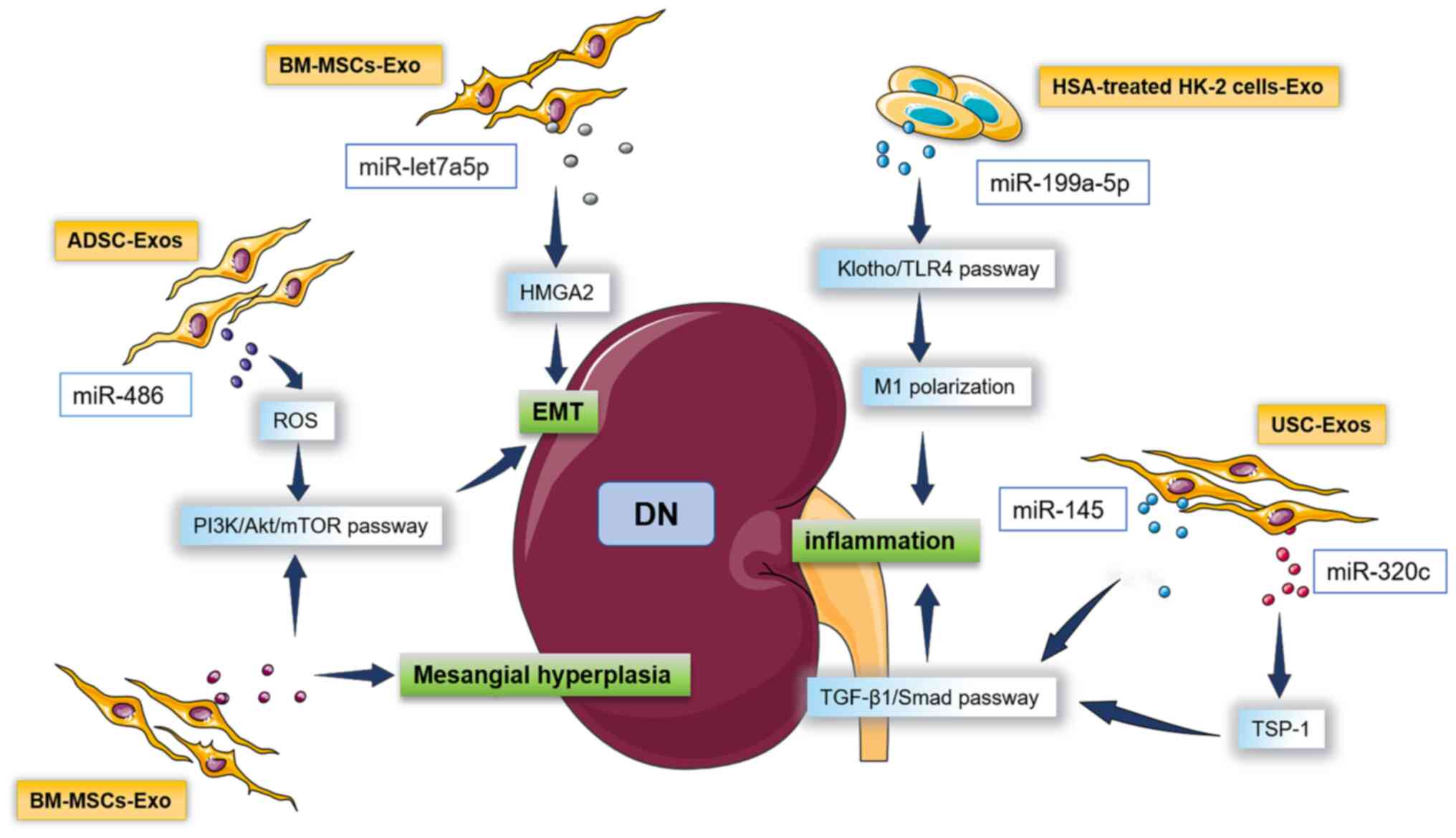
Wang T, Zhu H, Yang S and Fei X: Let-7a-5p
may participate in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy through
targeting HMGA2. Mol Med Rep. 19:4229–4237. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ding Y and Choi ME: Regulation of
autophagy by TGF-β: Emerging role in kidney fibrosis. Semin
Nephrol. 34:62–71. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tervaert TW, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen
AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Haas M, de Heer
E, et al: Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 21:556–563. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Jia Y, Zheng Z, Xue M, Zhang S, Hu F, Li
Y, Yang Y, Zou M, Li S, Wang L, et al: Extracellular vesicles from
albumin-induced tubular epithelial cells promote the M1 macrophage
phenotype by targeting klotho. Mol Ther. 27:1452–1466.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ding Y and Choi ME: Autophagy in diabetic
nephropathy. J Endocrinol. 224:R15–R30. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lu Q, Wang WW, Zhang MZ, Ma ZX, Qiu XR,
Shen M and Yin XX: ROS induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
via the TGF-β1/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Exp
Ther Med. 17:835–846. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Antonetti DA, Klein R and Gardner TW:
Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 366:1227–1239. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Mazzeo A, Beltramo E, Lopatina T, Gai C,
Trento M and Porta M: Molecular and functional characterization of
circulating extracellular vesicles from diabetic patients with and
without retinopathy and healthy subjects. Exp Eye Res. 176:69–77.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Heng LZ, Comyn O, Peto T, Tadros C, Ng E,
Sivaprasad S and Hykin PG: Diabetic retinopathy: Pathogenesis,
clinical grading, management and future developments. Diabet Med.
30:640–650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Shosha E, Xu Z, Narayanan SP, Lemtalsi T,
Fouda AY, Rojas M, Xing J, Fulton D, Caldwell RW and Caldwell RB:
Mechanisms of diabetes-induced endothelial cell senescence: Role of
arginase 1. Int J Mol Sci. 19(1215)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
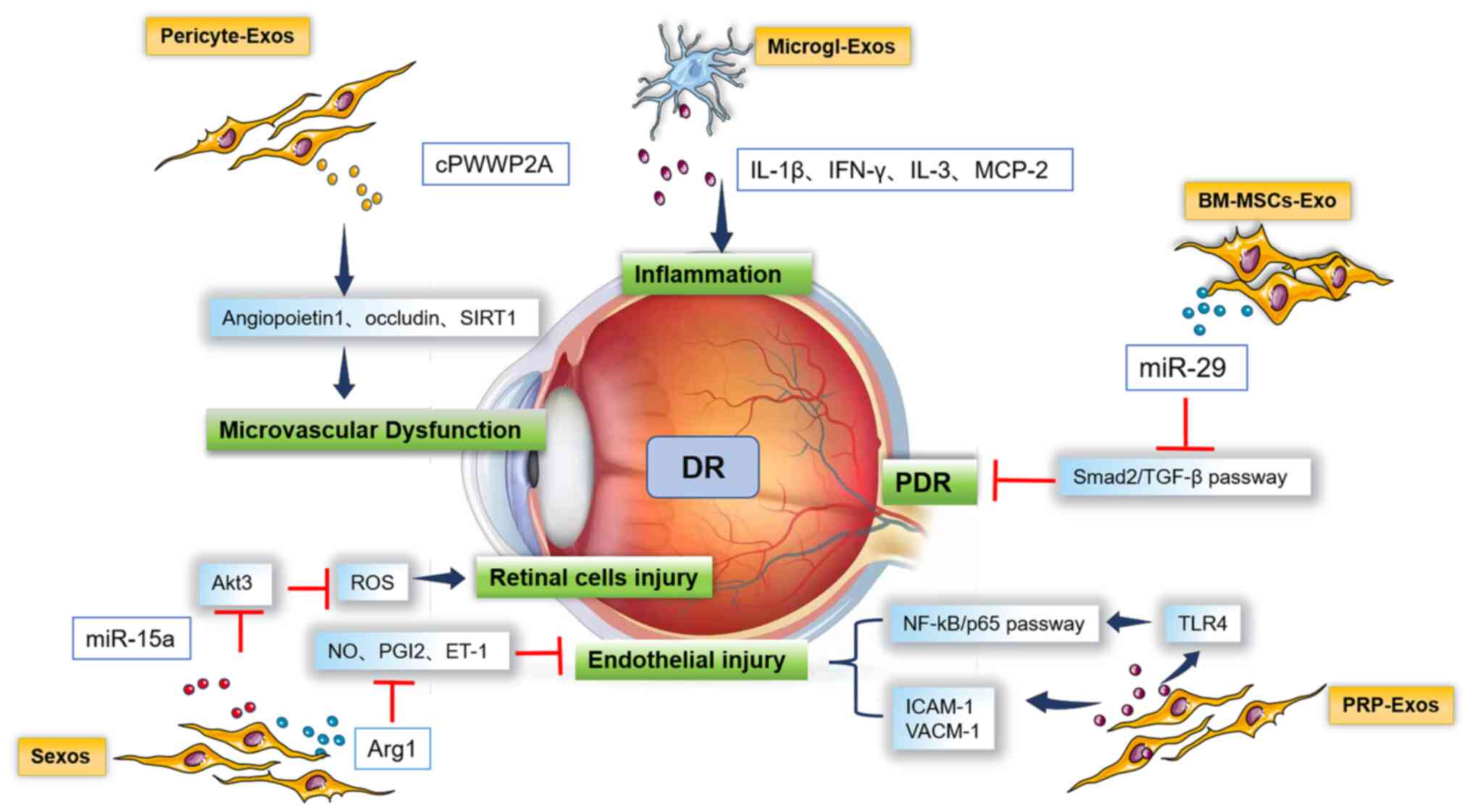
Naruse R, Suetsugu M, Terasawa T, Ito K,
Hara K, Takebayashi K, Morita K, Aso Y and Inukai T: Oxidative
stress and antioxidative potency are closely associated with
diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with type 2
diabetes. Saudi Med J. 34:135–141. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang W, Dong X, Wang T and Kong Y:
Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma mediate
hyperglycemia-induced retinal endothelial injury via targeting the
TLR4 signaling pathway. Exp Eye Res. 189(107813)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Shao L, Zhang Y, Lan B, Wang J, Zhang Z,
Zhang L, Xiao P, Meng Q, Geng YJ, Yu XY and Li Y: MiRNA-sequence
indicates that mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes have similar
mechanism to enhance cardiac repair. Biomed Res Int.
2017(4150705)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Vujosevic S, Micera A, Bini S, Berton M,
Esposito G and Midena E: Proteome analysis of retinal glia
cells-related inflammatory cytokines in the aqueous humour of
diabetic patients. Acta Ophthalmol. 94:56–64. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Liu C, Ge HM, Liu BH, Dong R, Shan K, Chen
X, Yao MD, Li XM, Yao J, Zhou RM, et al: Targeting
pericyte-endothelial cell crosstalk by circular RNA-cPWWP2A
inhibition aggravates diabetes-induced microvascular dysfunction.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:7455–7464. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Dillmann WH: Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Circ
Res. 124:1160–1162. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Bugger H and Abel ED: Molecular mechanisms
of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. 57:660–671.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Jia G, Demarco VG and Sowers JR: Insulin
resistance and hyperinsulinaemia in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 12:144–153. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
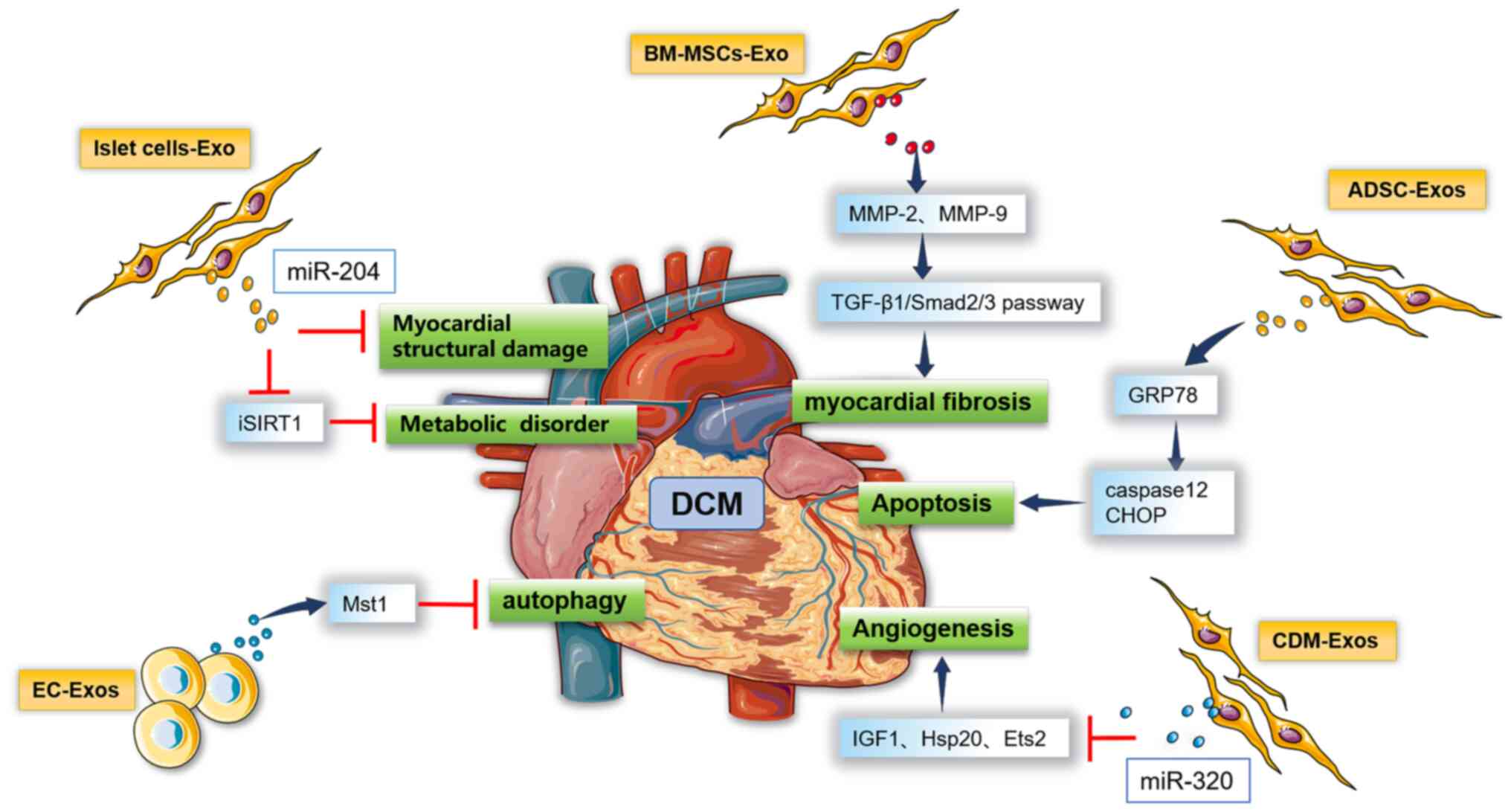
Liu X, Song X, Lu J, Chen X, Liang E, Liu
X, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Du Z and Zhao Y: Neferine inhibits
proliferation and collagen synthesis induced by high glucose in
cardiac fibroblasts and reduces cardiac fibrosis in diabetic mice.
Oncotarget. 7:61703–61715. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Schenk S, McCurdy CE, Philp A, Chen MZ,
Holliday MJ, Bandyopadhyay GK, Osborn O, Baar K and Olefsky JM:
Sirt1 enhances skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in mice during
caloric restriction. J Clin Invest. 121:4281–4288. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Tao S, Chen L, Song J, Zhu N, Song X, Shi
R, Ge G and Zhang Y: Tanshinone IIA ameliorates diabetic
cardiomyopathy by inhibiting Grp78 and CHOP expression in
STZ-induced diabetes rats. Exp Ther Med. 18:729–734.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Wang X, Huang W, Liu G, Cai W, Millard RW,
Wang Y, Chang J, Peng T and Fan GC: Cardiomyocytes mediate
anti-angiogenesis in type 2 diabetic rats through the exosomal
transfer of miR-320 into endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
74:139–150. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Hu J, Wang S, Xiong Z, Cheng Z, Yang Z,
Lin J, Wang T, Feng X, Gao E, Wang H and Sun D: Exosomal Mst1
transfer from cardiac microvascular endothelial cells to
cardiomyocytes deteriorates diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1864:3639–3649. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Quinaglia T, Oliveira DC, Matos-Souza JR
and Sposito AC: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Factual or factoid? Rev
Assoc Med Bras (1992). 65:61–69. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Feldman EL, Callaghan BC, Pop-Busui R,
Zochodne DW, Wright DE, Bennett DL, Bril V, Russell JW and
Viswanathan V: Diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
5(41)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ma J, Yu H, Liu J, Chen Y, Wang Q and
Xiang L: Metformin attenuates hyperalgesia and allodynia in rats
with painful diabetic neuropathy induced by streptozotocin. Eur J
Pharmacol. 764:599–606. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
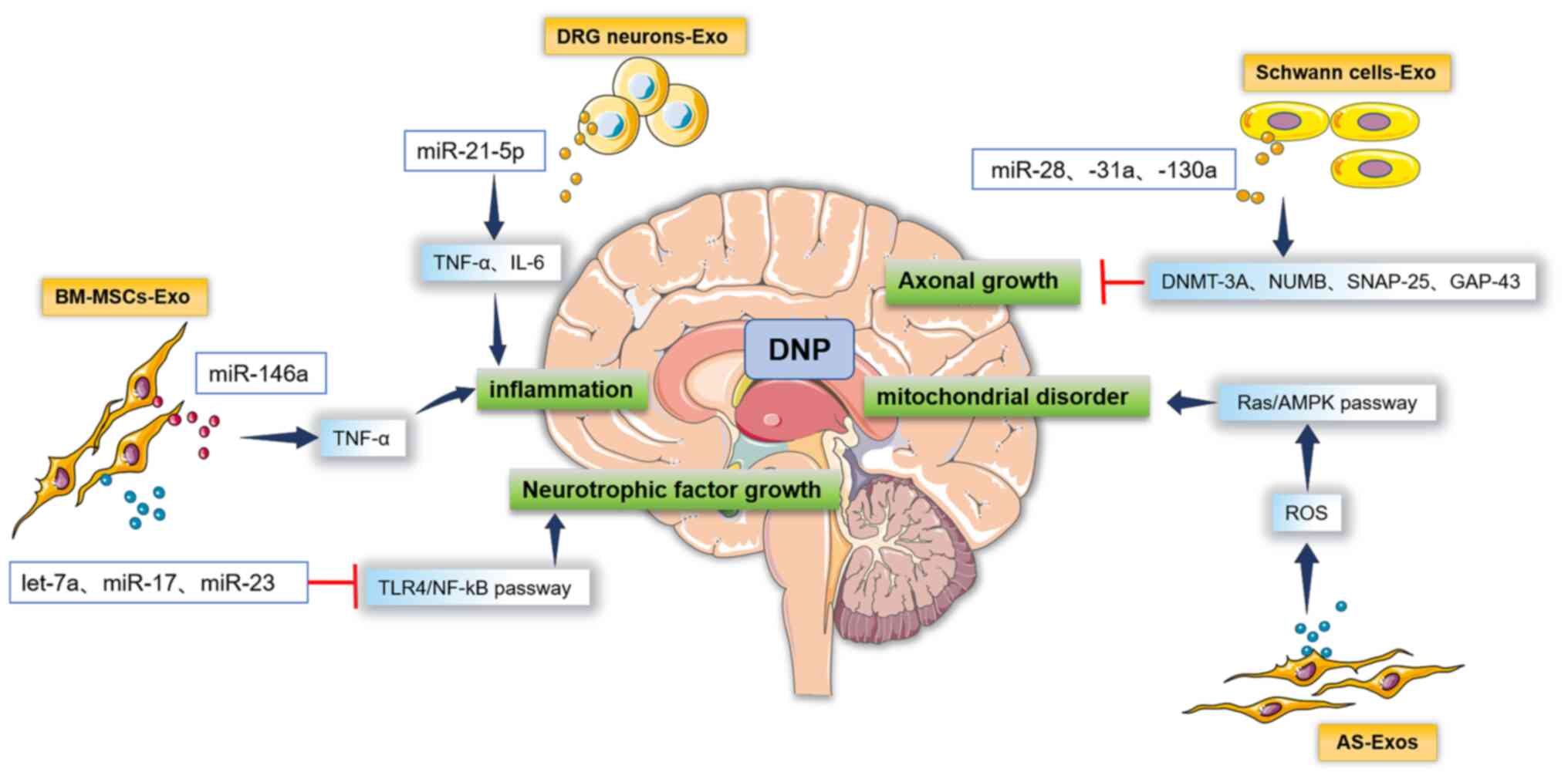
Yin Z, Han Z, Hu T, Zhang S, Ge X, Huang
S, Wang L, Yu J, Li W, Wang Y, et al: Neuron-derived exosomes with
high miR-21-5p expression promoted polarization of M1 microglia in
culture. Brain Behav Immun. 83:270–282. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Feng Y, Chen L, Luo Q, Wu M, Chen Y and
Shi X: Involvement of microRNA-146a in diabetic peripheral
neuropathy through the regulation of inflammation. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 12:171–177. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Jia L, Chopp M, Wang L, Lu X, Szalad A and
Zhang ZG: Exosomes derived from high-glucose-stimulated Schwann
cells promote development of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. FASEB
J. 32(fj201800597R)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Alomar SY, Gheit R, Enan ET, El-Bayoumi
KS, Shoaeir MZ, Elkazaz AY, Al Thagfan SS, Zaitone SA and El-Sayed
RM: Novel mechanism for memantine in attenuating diabetic
neuropathic pain in mice via downregulating the spinal
HMGB1/TRL4/NF-kB inflammatory axis. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
14(307)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Chen Q, Zhang D, Wang L, Zhang Y, Chen H,
Chen F and He Z: Effect of intermittent high glucose on
oxygen-glucose deprivation/refurnish neuronal survival. Zhonghua
Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 31:61–66. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
72
|
Bonomelli B, Martegani E and Colombo S:
Lack of SNF1 induces localization of active Ras in mitochondria and
triggers apoptosis in the yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 523:130–134. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Boulton AJ: Diabetic neuropathy and foot
complications. Handb Clin Neurol. 126:97–107. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Noor S, Zubair M and Ahmad J: Diabetic
foot ulcer-a review on pathophysiology, classification and
microbial etiology. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 9:192–199.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Li X, Xie X, Lian W, Shi R, Han S, Zhang
H, Lu L and Li M: Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells
overexpressing Nrf2 accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting
vascularization in a diabetic foot ulcer rat model. Exp Mol Med.
50:1–14. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Zhu B, Zhang L, Liang C, Liu B, Pan X,
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xie W, Yan B, et al: Stem cell-derived
exosomes prevent aging-induced cardiac dysfunction through a novel
exosome/lncRNA MALAT1/NF-κB/TNF-α signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2019(9739258)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Harrell CR, Jovicic N, Djonov V,
Arsenijevic N and Volarevic V: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived
exosomes and other extracellular vesicles as new remedies in the
therapy of inflammatory diseases. Cells. 8(1605)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Li M, Wang T, Tian H, Wei G, Zhao L and
Shi Y: Macrophage-derived exosomes accelerate wound healing through
their anti-inflammation effects in a diabetic rat model. Artif
Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:3793–3803. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Chen O, Donnelly CR and Ji RR: Regulation
of pain by neuro-immune interactions between macrophages and
nociceptor sensory neurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 62:17–25.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar :
Qing L, Chen H,
Tang J and Jia X: Exosomes and their MicroRNA cargo: New players in
peripheral nerve regeneration. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 32,
765-776, 2018.
|
|
80
|
Qing L, Chen H, Tang J and Jia X: Exosomes
and Their MicroRNA Cargo: New Players in Peripheral Nerve
Regeneration. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 32:765–776.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Dalirfardouei R, Jamialahmadi K, Jafarian
AH and Mahdipour E: Promising effects of exosomes isolated from
menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing
process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.
13:555–568. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, Henry
RR, Herman WH, Holst JJ, Hu FB, Kahn CR, Raz I, Shulman GI, et al:
Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
1(15019)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Cho JA, Yeo DJ, Son HY, Kim HW, Jung DS,
Ko JK, Koh JS, Kim YN and Kim CW: Exosomes: A new delivery system
for tumor antigens in cancer immunotherapy. Int J Cancer.
114:613–622. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Rani S, Ryan AE, Griffin MD and Ritter T:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Toward
cell-free therapeutic applications. Mol Ther. 23:812–823.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Zhang Y, Bi J, Huang J, Tang Y, Du S and
Li P: Exosome: A review of its classification, isolation
techniques, storage, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications.
Int J Nanomedicine. 15:6917–6934. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|