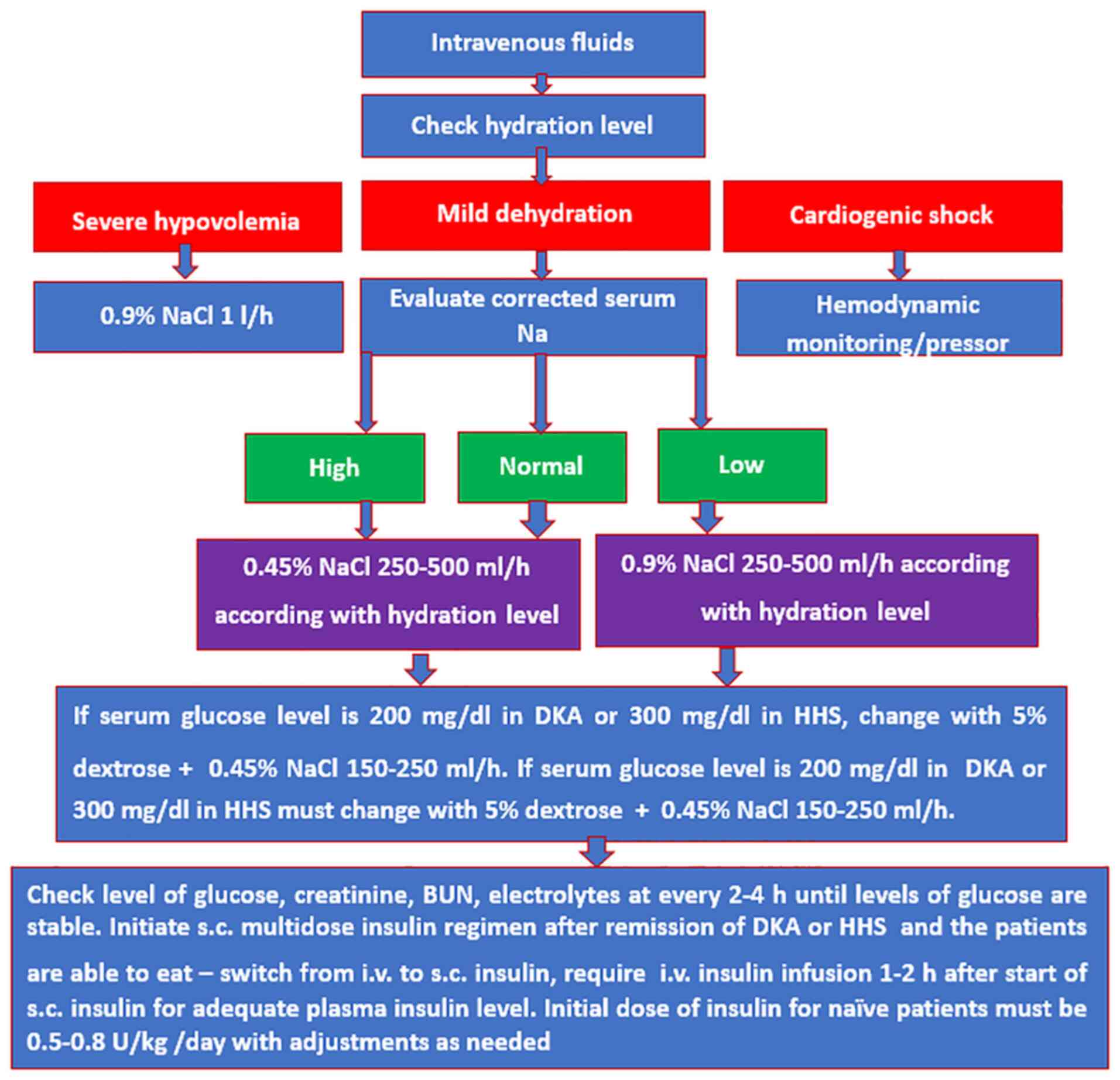
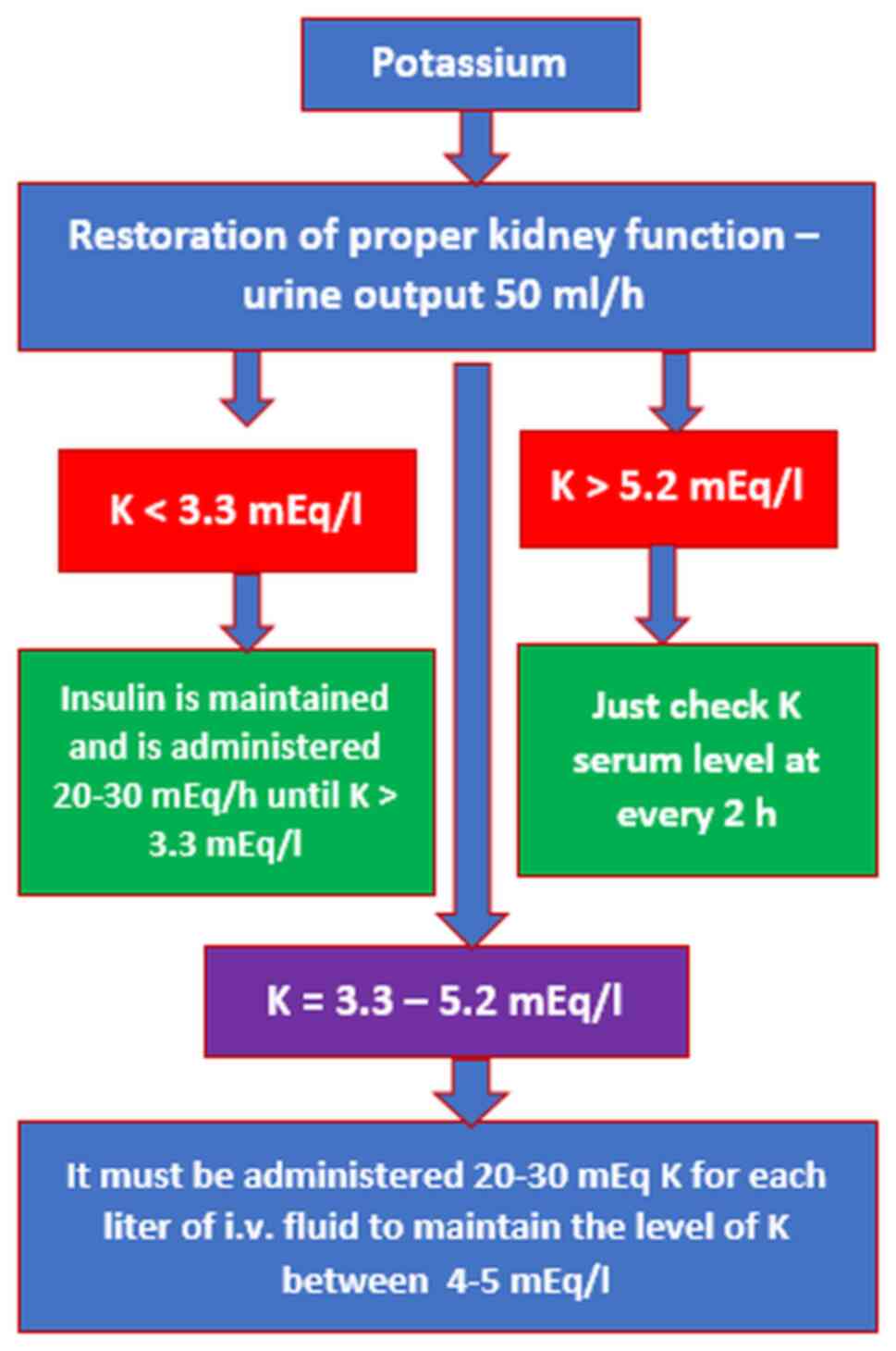
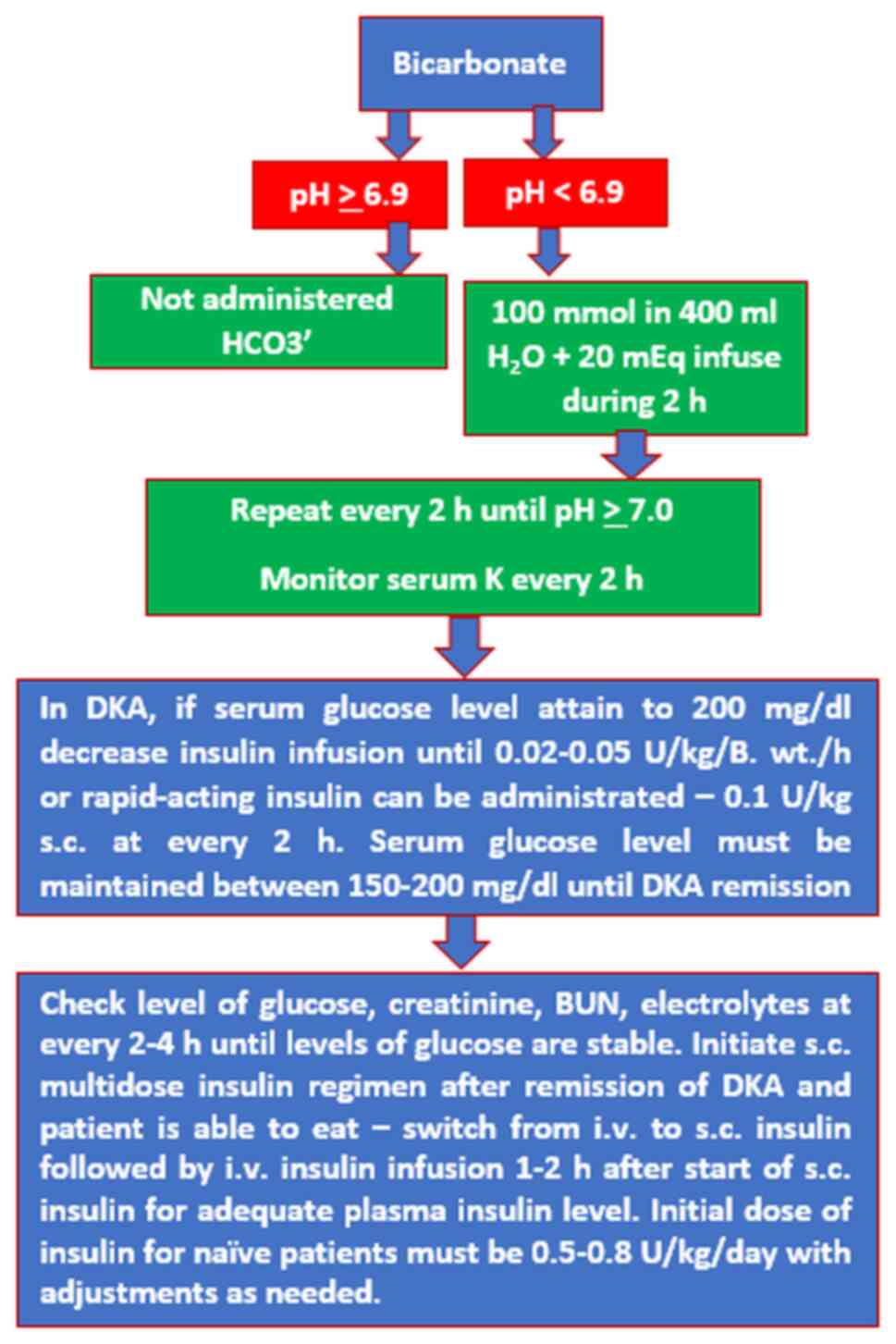
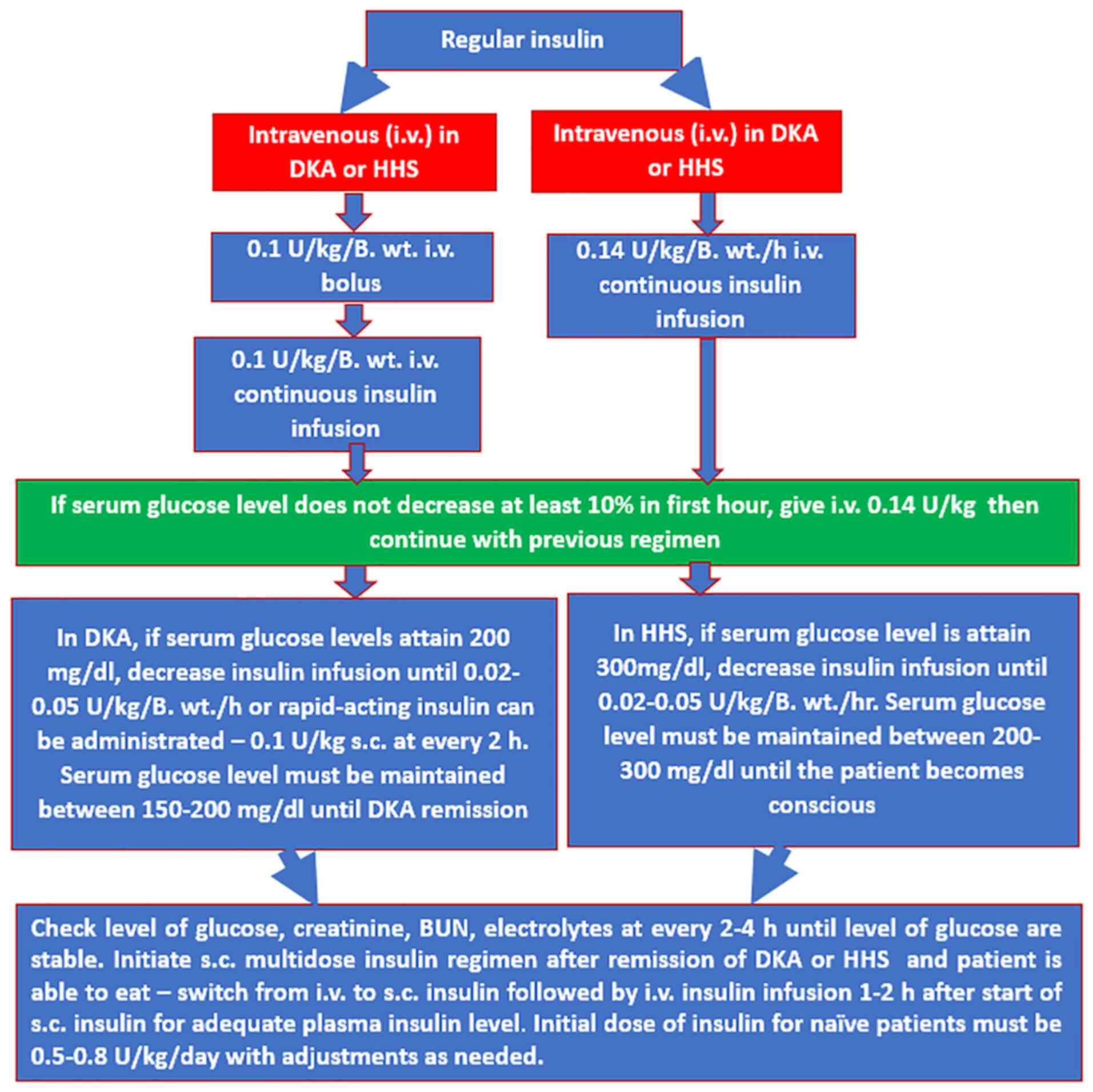
|
1
|
Singh RK, Perros P and Frier BM: Hospital
management of diabetic ketoacidosis: Are clinical guidelines
implemented effectively? Diabet Med. 14:482–486. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hardern RD and Quinn ND: Emergency
management of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults. Emerg Med J.
20:210–213. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Basu A, Close CF, Jenkins D, Krentz AJ,
Nattrass M and Wright AD: Persisting mortality in diabetic
ketoacidosis. Diabet Med. 10:282–284. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kitabchi AE and Wall BM: Diabetic
ketoacidosis. Med Clin North Am. 79:9–37. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
American Diabetes Association (ADA):
Hyperglycemic Crises Consensus Guidelines, 2009. https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/32/Supplement_1/S13.
Access date: September 1, 2021.
|
|
6
|
Dhatariya K, Savage M, Claydon A, Dyer P,
Evans P, Khan A, et al: Joint British Diabetes Societies (JBDS).
Inpatient Care Group: The management of diabetic ketoacidosis in
adults, Second edition, 2013. http://www.diabetologists-abcd.org.uk/JBDS/JBDS_IP_DKA_Adults_Revised.pdf.
Access date: September 1, 2021.
|
|
7
|
Westerberg DP: Diabetic ketoacidosis:
Evaluation and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 87:337–346.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Umpierrez G and Korytkowski M: Diabetic
emergencies-ketoacidosis, hyperglycaemic hyperosmolar state and
hypoglycaemia. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 12:222–232. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yared Z and Chiasson JL: Ketoacidosis and
the hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state in adult diabetic patients.
Diagnosis and treatment. Minerva Med. 94:409–418. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kitabchi AE and Nyenwe EA: Hyperglycemic
crises in diabetes mellitus: Diabetic ketoacidosis and
hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
35:725–751. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM and
Fisher JN: Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes.
Diabetes Care. 32:1335–1343. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Palmer BF and Clegg DJ: Electrolyte and
acid-base disturbances in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J
Med. 373:548–559. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Grigorescu ED, Lăcătușu CM, Crețu I,
Floria M, Onofriescu A, Ceasovschih A, Mihai BM and Șorodoc L:
Self-reported satisfaction to treatment, quality of life and
general health of type 2 diabetes patients with inadequate glycemic
control from North-Eastern Romania. Int J Environ Res Public
Health. 18(3249)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kamel KS and Halperin ML: Acid-base
problems in diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med. 372:1969–1970.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Magder S and Emami A: Practical approach
to physical-chemical acid-base management. Stewart at the bedside.
Ann Am Thorac Soc. 12:111–117. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Seifter JL: Integration of acid-base and
electrolyte disorders. N Engl J Med. 371:1821–1831. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Story DA and Kellum JA: New aspects of
acid-base balance in intensive care. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol.
17:119–123. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schiraldi F and Guiotto G: Base excess,
strong ion difference, and expected compensations: As simple as it
is. Eur J Emerg Med. 21:403–408. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fisher JN and Kitabchi AE: A randomized
study of phosphate therapy in the treatment of diabetic
ketoacidosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 57:177–180. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wilson HK, Keuer SP, Lea AS, Boyd AE III
and Eknoyan G: Phosphate therapy in diabetic ketoacidosis. Arch
Intern Med. 142:517–520. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fayfman M, Pasquel FJ and Umpierrez GE:
Management of hyperglycemic crises: Diabetic ketoacidosis and
hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Med Clin North Am. 101:587–606.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
American Diabetes Association. Hospital
admission guidelines for diabetes (Position Statement). Diabetes
Care. 27 (Suppl 1)(S103)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tomky D: Detection, prevention, and
treatment of hypoglycemia in the hospital. Diabetes Spectrum.
18:39–44. 2005.
|
|
24
|
Greenhalgh T: Oxford Τextbook of Μedicine.
4th edition. Warrell DA, Cox TM, Firth JD and Benz Jr EJ (eds).
Family Practice 20, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2003.
|
|
25
|
Walden E, Stanisstreet D, Graveling A, et
al: Joint British Diabetes Societies: The hospital management of
hypoglycaemia in adults with diabetes mellitus. Third edition.
Diabetes UK, 2013. https://www.diabetes.org.uk/professionals/position-statements-reports/specialist-care-for-children-and-adults-and-complications/the-hospital-management-of-hypoglycaemia-in-adults-with-diabetes-mellitus.
Access date: September 1, 2021.
|
|
26
|
Achoki R, Opiyo N and English M:
Mini-review: Management of hypoglycaemia in children aged 0-59
months. J Trop Pediatr. 56:227–234. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Frier BM: How hypoglycaemia can affect the
life of a person with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 24:87–92.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pearson T: Glucagon as a treatment of
severe hypoglycemia: Safe and efficacious but underutilized.
Diabetes Educ. 34:128–134. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
International Diabetes Federation: IDF
Diabetes Atlas. 9th edition. International Diabetes Federation,
Belgium, 2019. https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/ninth-edition/. Access
date: September 1, 2021.
|
|
30
|
Chen YT, Tan YZ, Cheen M and Wee HL:
Patient-reported outcome measures in registry-based studies of type
2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Curr Diabetes Rep.
19(135)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Grigorescu E, Sorodoc V, Floria M, Anisie
E, Popa AD, Onofriescu A, Ceasovschih A and Sorodoc L: The
inflammatory marker HSCRP as a predictor of increased insulin
resistance in type 2 diabetics without atherosclerotic
manifestations. Rev Chim (Bucharest). 70:1791–1794. 2019.
|
|
32
|
Trikkalinou A, Papazafiropoulou AK and
Melidonis A: Type 2 diabetes and quality of life. World J Diabetes.
8:120–129. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Palamenghi L, Carlucci MM and Graffigna G:
Measuring the quality of life in diabetic patients: A scoping
review. J Diabetes Res. 2020(5419298)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Speight J, Holmes-Truscott E, Hendrieckx
C, Skovlund S and Cooke D: Assessing the impact of diabetes on
quality of life: What have the past 25 years taught us? Diabet Med.
37:483–492. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|