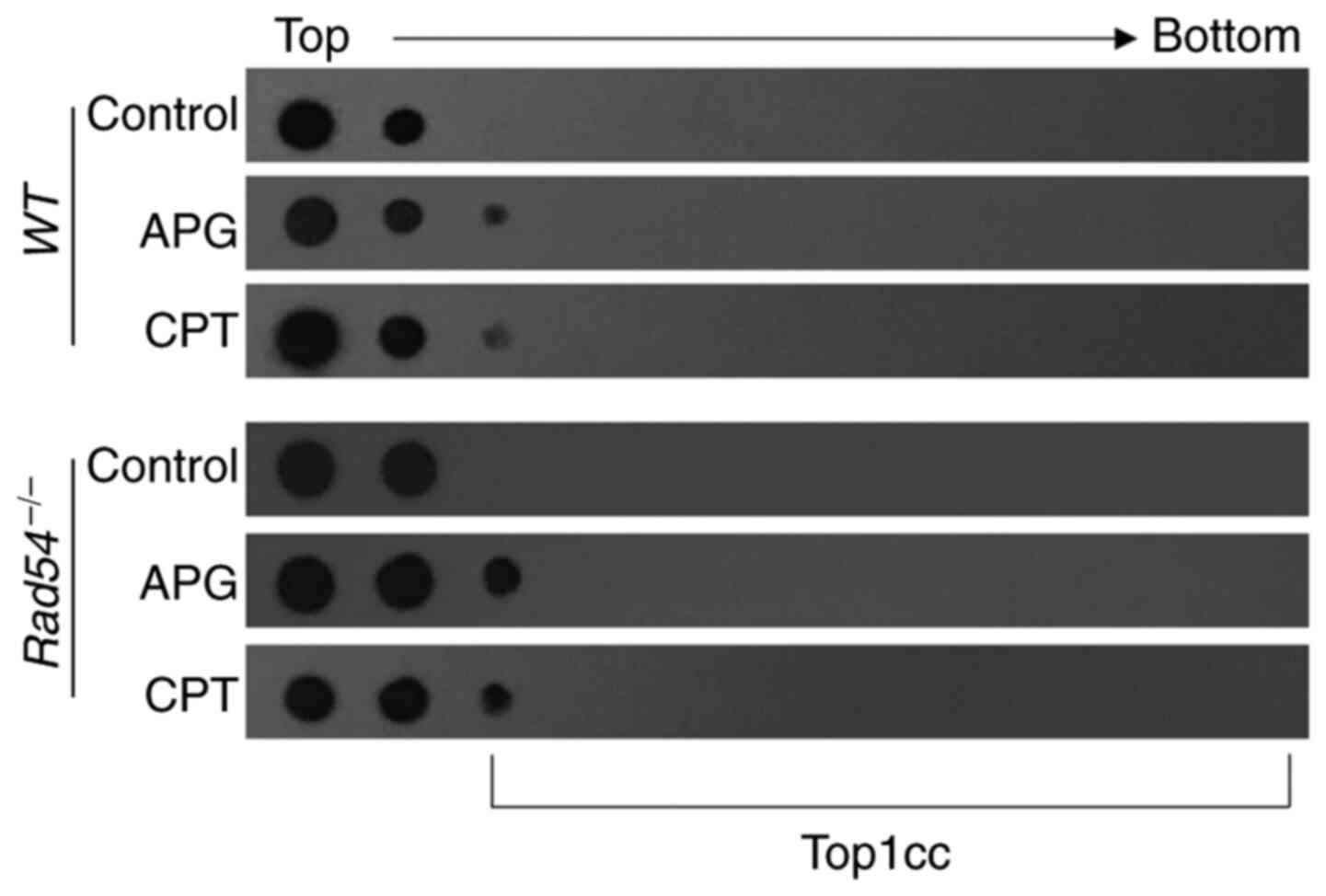
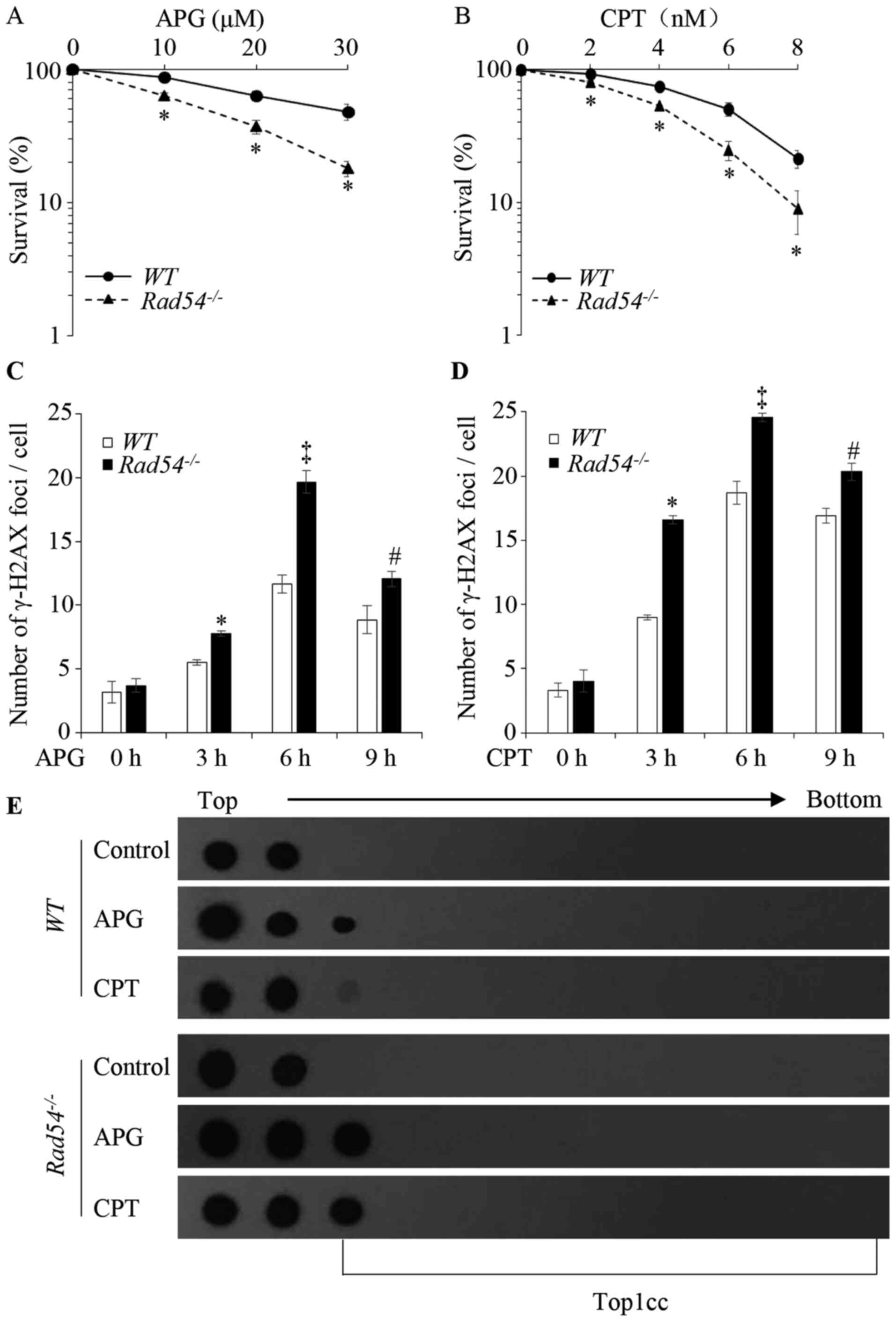
|
1
|
Shukla S, Bhaskaran N, Babcook MA, Fu P,
Maclennan GT and Gupta S: Apigenin inhibits prostate cancer
progression in TRAMP mice via targeting PI3K/Akt/FoxO pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 35:452–460. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tong X and Pelling JC: Targeting the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis by apigenin for cancer prevention. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 13:971–978. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Perrott KM, Wiley CD, Desprez PY and
Campisi J: Apigenin suppresses the senescence-associated secretory
phenotype and paracrine effects on breast cancer cells.
Geroscience. 39:161–173. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shukla S, Kanwal R, Shankar E, Datt M,
Chance MR, Fu P, MacLennan GT and Gupta S: Apigenin blocks IKKα
activation and suppresses prostate cancer progression. Oncotarget.
6:31216–31232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shao H, Jing K, Mahmoud E, Huang H, Fang X
and Yu C: Apigenin sensitizes colon cancer cells to antitumor
activity of ABT-263. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2640–2650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Souza RP, Bonfim-Mendonça PS, Gimenes F,
Ratti BA, Kaplum V, Bruschi ML, Nakamura CV, Silva SO, Maria-Engler
SS and Consolaro ME: Oxidative stress triggered by apigenin induces
apoptosis in a comprehensive panel of human cervical cancer-derived
cell lines. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017(1512745)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yin F, Giuliano AE, Law RE and Van Herle
AJ: Apigenin inhibits growth and induces G2/M arrest by modulating
cyclin-CDK regulators and ERK MAP kinase activation in breast
carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 21:413–420. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang W, Heideman L, Chung CS, Pelling JC,
Koehler KJ and Birt DF: Cell-cycle arrest at G2/M and growth
inhibition by apigenin in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Mol
Carcinog. 28:102–110. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Caltagirone S, Rossi C, Poggi A,
Ranelletti FO, Natali PG, Brunetti M, Aiello FB and Piantelli M:
Flavonoids apigenin and quercetin inhibit melanoma growth and
metastatic potential. Int J Cancer. 87:595–600. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ujiki MB, Ding XZ, Salabat MR, Bentrem DJ,
Golkar L, Milam B, Talamonti MS, Bell RH Jr, Iwamura T and Adrian
TE: Apigenin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation through
G2/M cell cycle arrest. Mol Cancer. 5(76)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen Z, Chen J, Liu H, Dong W, Huang X,
Yang D, Hou J and Zhang X: The SMAC mimetic APG-1387 sensitizes
immune-mediated cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front
Pharmacol. 9(1298)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li BX, Wang HB, Qiu MZ, Luo QY, Yi HJ, Yan
XL, Pan WT, Yuan LP, Zhang YX, Xu JH, et al: Novel smac mimetic
APG-1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing through TNF-alpha,
Ripoptosome and autophagy mediated cell death pathway. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 37(53)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vargo MA, Voss OH, Poustka F, Cardounel
AJ, Grotewold E and Doseff AI: Apigenin-induced-apoptosis is
mediated by the activation of PKCdelta and caspases in leukemia
cells. Biochem Pharmaco. 72:681–692. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin-induced
cell cycle arrest is mediated by modulation of MAPK, PI3K-Akt, and
loss of cyclin D1 associated retinoblastoma dephosphorylation in
human prostate cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 6:1102–1114.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Meng S, Zhu Y, Li JF, Wang X, Liang Z, Li
SQ, Xu X, Chen H, Liu B, Zheng XY, et al: Apigenin inhibits renal
cell carcinoma cell proliferation. Oncotarget. 8:19834–19842.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Farooqi AA, Wu SJ, Chang YT, Tang JY, Li
KT, Ismail M, Liaw CC, Li RN and Chang HW: Activation and
inhibition of ATM by phytochemicals: Awakening and sleeping the
guardian angel naturally. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz).
63:357–366. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Noel S, Kasinathan M and Rath SK:
Evaluation of apigenin using in vitro cytochalasin blocked
micronucleus assay. Toxicol In Vitro. 20:1168–1172. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Papachristou F, Chatzaki E, Petrou A,
Kougioumtzi I, Katsikogiannis N, Papalambros A, Tripsianis G,
Simopoulos C and Tsaroucha AK: Time course changes of anti- and
pro-apoptotic proteins in apigenin-induced genotoxicity. Chin Med.
8(9)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Song J, Parker L, Hormozi L and Tanouye
MA: DNA topoisomerase I inhibitors ameliorate seizure-like
behaviors and paralysis in a Drosophila model of epilepsy.
Neuroscience. 156:722–728. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Boege F, Straub T, Kehr A, Boesenberg C,
Christiansen K, Andersen A, Jakob F and Köhrle J: Selected novel
flavones inhibit the DNA binding or the DNA religation step of
eukaryotic topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 271:2262–2270.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Adachi N, Suzuki H, Iiizumi S and Koyama
H: Hypersensitivity of nonhomologous DNA end-joining mutants to
VP-16 and ICRF-193: Implications for the repair of topoisomerase
II-mediated DNA damage. J Biol Chem. 278:35897–35902.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Plante I, Slaba T, Shavers Z and Hada M: A
bi-exponential repair algorithm for radiation-induced double-strand
breaks: Application to simulation of chromosome aberrations. Genes
(Basel). 10(10)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Morimoto S, Tsuda M, Bunch H, Sasanuma H,
Austin C and Takeda S: Type II DNA topoisomerases cause spontaneous
double-strand breaks in genomic DNA. Genes (Basel).
10(10)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cho JE and Jinks-Robertson S: Deletions
associated with stabilization of the Top1 cleavage complex in yeast
are products of the nonhomologous end-joining pathway. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 116:22683–22691. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li F, Jiang T, Li Q and Ling X:
Camptothecin (CPT) and its derivatives are known to target
topoisomerase I (Top1) as their mechanism of action: Did we miss
something in CPT analogue molecular targets for treating human
disease such as cancer? Am J Cancer Res. 7:2350–2394.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pommier Y: Drugging topoisomerases:
Lessons and challenges. ACS Chem Biol. 8:82–95. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ji Y, Dang X, Nguyen LN, Nguyen LN, Zhao
J, Cao D, Khanal S, Schank M, Wu XY, Morrison ZD, et al:
Topological DNA damage, telomere attrition and T cell senescence
during chronic viral infections. Immun Ageing.
16(12)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Petermann E, Orta ML, Issaeva N, Schultz N
and Helleday T: Hydroxyurea-stalled replication forks become
progressively inactivated and require two different RAD51-mediated
pathways for restart and repair. Mol Cell. 37:492–502.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Borda MA, Palmitelli M, Verón G,
González-Cid M and de Campos Nebel M: Tyrosyl-DNA-phosphodiesterase
I (TDP1) participates in the removal and repair of stabilized-Top2α
cleavage complexes in human cells. Mutat Res. 781:37–48.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cuya SM, Comeaux EQ, Wanzeck K, Yoon KJ
and van Waardenburg RC: Dysregulated human Tyrosyl-DNA
phosphodiesterase I acts as cellular toxin. Oncotarget.
7:86660–86674. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tripathi K, Mani C, Clark DW and Palle K:
Rad18 is required for functional interactions between FANCD2,
BRCA2, and Rad51 to repair DNA topoisomerase 1-poisons induced
lesions and promote fork recovery. Oncotarget. 7:12537–12553.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yonetani Y, Hochegger H, Sonoda E, Shinya
S, Yoshikawa H, Takeda S and Yamazoe M: Differential and
collaborative actions of Rad51 paralog proteins in cellular
response to DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:4544–4552.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vance JR and Wilson TE: Yeast Tdp1 and
Rad1-Rad10 function as redundant pathways for repairing Top1
replicative damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:13669–13674.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Buerstedde JM, Reynaud CA, Humphries EH,
Olson W, Ewert DL and Weill JC: Light chain gene conversion
continues at high rate in an ALV-induced cell line. EMBO J.
9:921–927. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Buerstedde JM and Takeda S: Increased
ratio of targeted to random integration after transfection of
chicken B cell lines. Cell. 67:179–188. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hoa NN, Shimizu T, Zhou ZW, Wang ZQ,
Deshpande RA, Paull TT, Akter S, Tsuda M, Furuta R, Tsutsui K, et
al: Mre11 is essential for the removal of lethal topoisomerase 2
covalent cleavage complexes. Mol Cell. 64:580–592. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sasanuma H, Tsuda M, Morimoto S, Saha LK,
Rahman MM, Kiyooka Y, Fujiike H, Cherniack AD, Itou J, Callen Moreu
E, et al: BRCA1 ensures genome integrity by eliminating
estrogen-induced pathological topoisomerase II-DNA complexes. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E10642–E10651. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zong D, Adam S, Wang Y, Sasanuma H, Callén
E, Murga M, Day A, Kruhlak MJ, Wong N, Munro M, et al: BRCA1
haploinsufficiency is masked by RNF168-mediated chromatin
ubiquitylation. Mol Cell. 73:1267–1281.e7. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Liu H, Wu Y, He F, Cheng Z, Zhao Z, Xiang
C, Feng X, Bai X, Takeda S, Wu X, et al: Brca1 is involved in
tolerance to adefovir dipivoxil induced DNA damage. Int J Mol Med.
43:2491–2498. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Z, Bu X, Chen H, Wang Q and Sha W:
Bmi-1 promotes the invasion and migration of colon cancer stem
cells through the downregulation of E-cadherin. Int J Mol Med.
38:1199–1207. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Thapa M, Bommakanti A, Shamsuzzaman M,
Gregory B, Samsel L, Zengel JM and Lindahl L: Repressed synthesis
of ribosomal proteins generates protein-specific cell cycle and
morphological phenotypes. Mol Biol Cell. 24:3620–3633.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lecomte S, Demay F, Pham TH, Moulis S,
Efstathiou T, Chalmel F and Pakdel F: Deciphering the molecular
mechanisms sustaining the estrogenic activity of the two major
dietary compounds zearalenone and apigenin in ER-positive breast
cancer cell lines. Nutrients. 11(11)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hu X, Wu X, Liu H, Cheng Z, Zhao Z, Xiang
C, Feng X, Takeda S and Qing Y: Genistein-induced DNA damage is
repaired by nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination
in TK6 cells. J Cell Physiol. 234:2683–2692. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Wu X, Hu X, Chen Z, Liu H, Takeda S
and Qing Y: Multiple repair pathways mediate cellular tolerance to
resveratrol-induced DNA damage. Toxicol In Vitro. 42:130–138.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Baba TW, Giroir BP and Humphries EH: Cell
lines derived from avian lymphomas exhibit two distinct phenotypes.
Virology. 144:139–151. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sonoda E, Morrison C, Yamashita YM, Takata
M and Takeda S: Reverse genetic studies of homologous DNA
recombination using the chicken B-lymphocyte line, DT40. Philos
Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 356:111–117. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Dhar PK, Sonoda E, Fujimori A, Yamashita
YM and Takeda S: DNA repair studies: experimental evidence in
support of chicken DT40 cell line as a unique model. J Environ
Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 20:273–283. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Asagoshi K, Tano K, Chastain PD II, Adachi
N, Sonoda E, Kikuchi K, Koyama H, Nagata K, Kaufman DG, Takeda S,
et al: FEN1 functions in long patch base excision repair under
conditions of oxidative stress in vertebrate cells. Mol Cancer Res.
8:204–215. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yoshinaga N, Shindo K, Matsui Y, Takiuchi
Y, Fukuda H, Nagata K, Shirakawa K, Kobayashi M, Takeda S and
Takaori-Kondo A: A screening for DNA damage response molecules that
affect HIV-1 infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 513:93–98.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ooka M, Abe T, Cho K, Koike K, Takeda S
and Hirota K: Chromatin remodeler ALC1 prevents replication-fork
collapse by slowing fork progression. PLoS One.
13(e0192421)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Petukhova G, Stratton S and Sung P:
Catalysis of homologous DNA pairing by yeast Rad51 and Rad54
proteins. Nature. 393:91–94. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Qing Y, Yamazoe M, Hirota K, Dejsuphong D,
Sakai W, Yamamoto KN, Bishop DK, Wu X and Takeda S: The epistatic
relationship between BRCA2 and the other RAD51 mediators in
homologous recombination. PLoS Genet. 7(e1002148)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Takata M, Sasaki MS, Sonoda E, Morrison C,
Hashimoto M, Utsumi H, Yamaguchi-Iwai Y, Shinohara A and Takeda S:
Homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining pathways of
DNA double-strand break repair have overlapping roles in the
maintenance of chromosomal integrity in vertebrate cells. EMBO J.
17:5497–5508. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Al Abo M, Sasanuma H, Liu X, Rajapakse VN,
Huang SY, Kiselev E, Takeda S, Plunkett W and Pommier Y: TDP1 is
critical for the repair of DNA breaks induced by sapacitabine, a
nucleoside also targeting ATM- and BRCA-deficient tumors. Mol
Cancer Ther. 16:2543–2551. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lountos GT, Zhao XZ, Kiselev E, Tropea JE,
Needle D, Pommier Y, Burke TR Jr and Waugh DS: Identification of a
ligand binding hot spot and structural motifs replicating aspects
of tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I (TDP1) phosphoryl recognition by
crystallographic fragment cocktail screening. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:10134–10150. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Sharma H, Kanwal R, Bhaskaran N and Gupta
S: Plant flavone apigenin binds to nucleic acid bases and reduces
oxidative DNA damage in prostate epithelial cells. PLoS One.
9(e91588)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Jayasooriya RG, Kang SH, Kang CH, Choi YH,
Moon DO, Hyun JW, Chang WY and Kim GY: Apigenin decreases cell
viability and telomerase activity in human leukemia cell lines.
Food Chem Toxicol. 50:2605–2611. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Chung CS, Jiang Y, Cheng D and Birt DF:
Impact of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor supressor gene in
human colon cancer cell lines on cell cycle arrest by apigenin. Mol
Carcinog. 46:773–782. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Gupta S, Afaq F and Mukhtar H: Involvement
of nuclear factor-kappa B, Bax and Bcl-2 in induction of cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis by apigenin in human prostate carcinoma cells.
Oncogene. 21:3727–3738. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Subhasitanont P, Chokchaichamnankit D,
Chiablaem K, Keeratichamroen S, Ngiwsara L, Paricharttanakul NM,
Lirdprapamongkol K, Weeraphan C, Svasti J and Srisomsap C: Apigenin
inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma
cells. Oncol Lett. 14:4361–4371. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Sharma NK: Modulation of radiation-induced
and mitomycin C-induced chromosome damage by apigenin in human
lymphocytes in vitro. J Radiat Res (Tokyo). 54:789–797.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Agarwal S, van Cappellen WA, Guénolé A,
Eppink B, Linsen SE, Meijering E, Houtsmuller A, Kanaar R and
Essers J: ATP-dependent and independent functions of Rad54 in
genome maintenance. J Cell Biol. 192:735–750. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Mazin AV, Alexeev AA and Kowalczykowski
SC: A novel function of Rad54 protein. Stabilization of the Rad51
nucleoprotein filament. J Biol Chem. 278:14029–14036.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Mazin AV, Bornarth CJ, Solinger JA, Heyer
WD and Kowalczykowski SC: Rad54 protein is targeted to pairing loci
by the Rad51 nucleoprotein filament. Mol Cell. 6:583–592.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
García-Luis J and Machín F: Fanconi
anaemia-like Mph1 helicase nacks up Rad54 and Rad5 to circumvent
replication stress-driven chromosome bridges. Genes (Basel).
9(9)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Tang S, Liu B, Liu M, Li Z, Liu J, Wang H,
Wang J, Oh YT, Shen L and Wang Y: Ionizing radiation-induced growth
in soft agar is associated with miR-21 upregulation in wild-type
and DNA double strand break repair deficient cells. DNA Repair
(Amst). 78:37–44. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Crickard JB, Kaniecki K, Kwon Y, Sung P,
Lisby M and Greene EC: Regulation of Hed1 and Rad54 binding during
maturation of the meiosis-specific presynaptic complex. EMBO J.
37(37)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhang XP, Janke R, Kingsley J, Luo J,
Fasching C, Ehmsen KT and Heyer WD: A conserved sequence extending
motif III of the motor domain in the Snf2-family DNA translocase
Rad54 is critical for ATPase activity. PLoS One.
8(e82184)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zhang L, Cheng X, Gao Y, Zheng J, Xu Q,
Sun Y, Guan H, Yu H and Sun Z: Apigenin induces autophagic cell
death in human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells. Food Funct.
6:3464–3472. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Fang J, Bao YY, Zhou SH and Fan J:
Apigenin inhibits the proliferation of adenoid cystic carcinoma via
suppression of glucose transporter-1. Mol Med Rep. 12:6461–6466.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Lim W, Park S, Bazer FW and Song G:
Apigenin reduces survival of choriocarcinoma cells by inducing
apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 MAPK pathways. J Cell
Physiol. 231:2690–2699. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Nitiss J and Wang JC: DNA
topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs can be studied in yeast.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:7501–7505. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Chen G and Guo M: Screening for natural
inhibitors of topoisomerases I from Rhamnus davurica by affinity
ultrafiltration and high-performance liquid chromatography-mass
spectrometry. Front Plant Sci. 8(1521)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Champoux JJ: DNA topoisomerases:
Structure, function, and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. 70:369–413.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Interthal H, Pouliot JJ and Champoux JJ:
The tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase Tdp1 is a member of the
phospholipase D superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:12009–12014. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Krawczyk C, Dion V, Schär P and Fritsch O:
Reversible Top1 cleavage complexes are stabilized
strand-specifically at the ribosomal replication fork barrier and
contribute to ribosomal DNA stability. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:4985–4995. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|