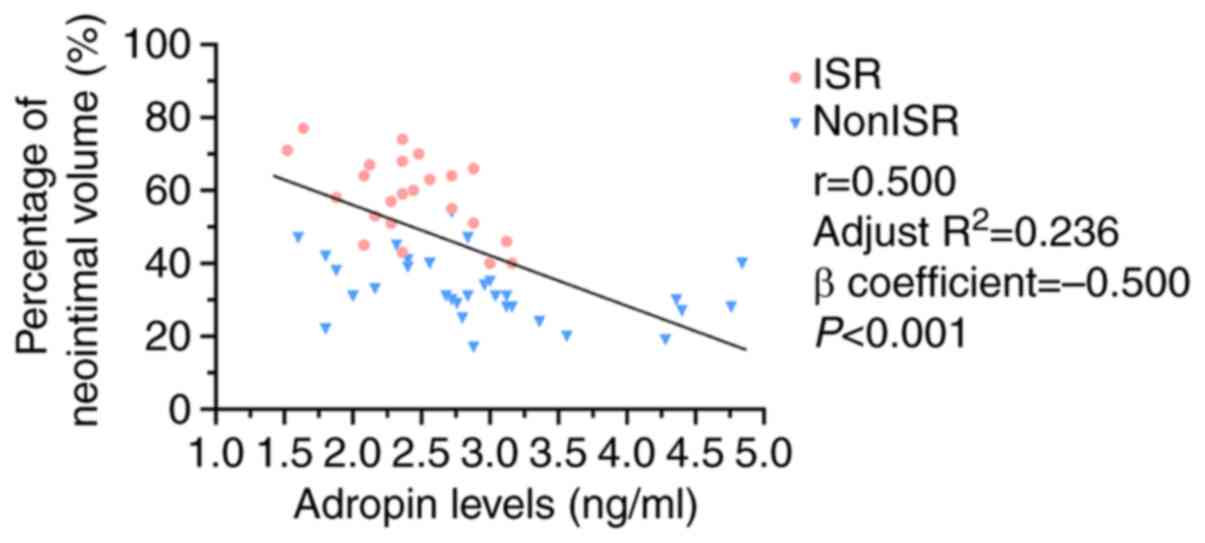
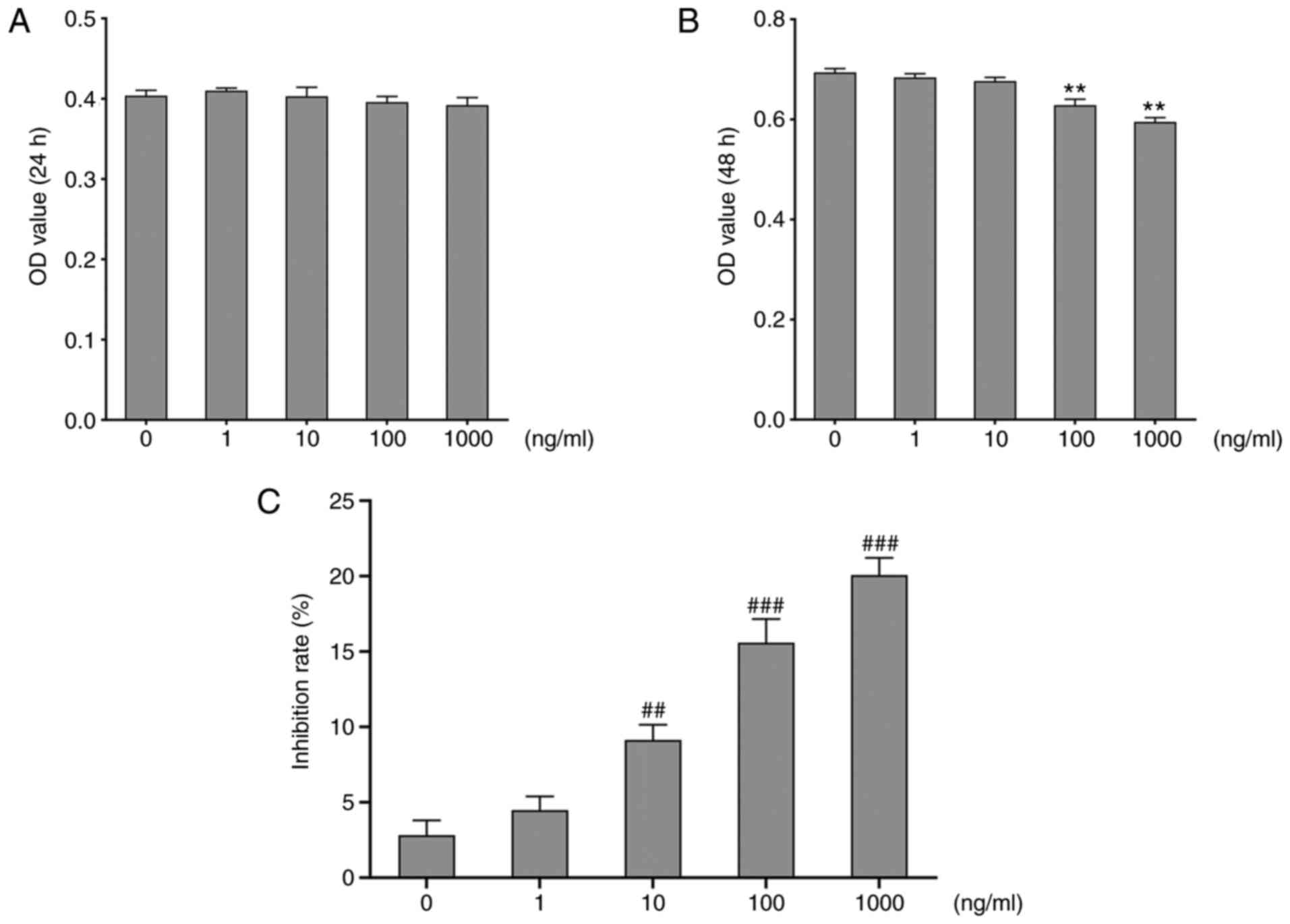
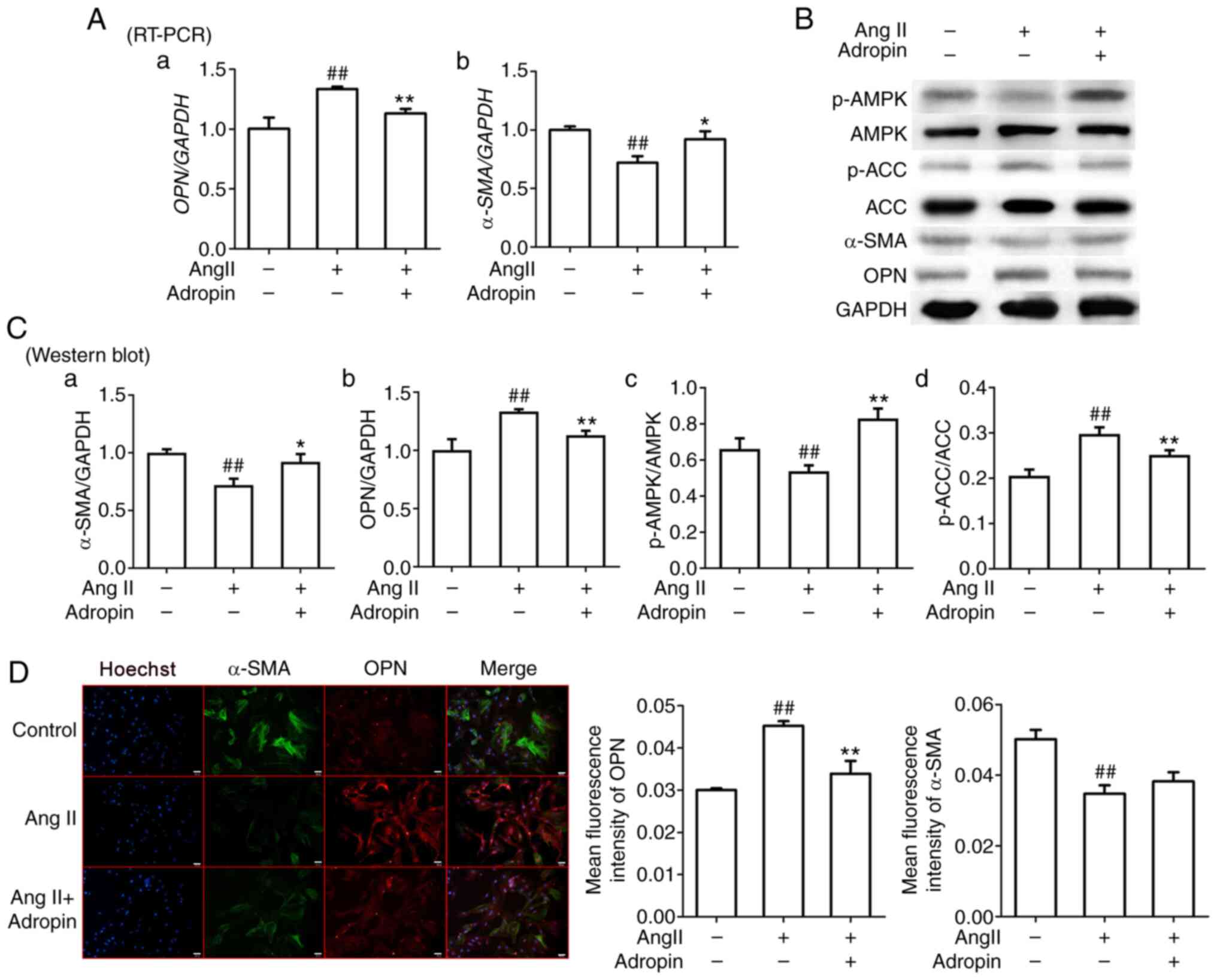
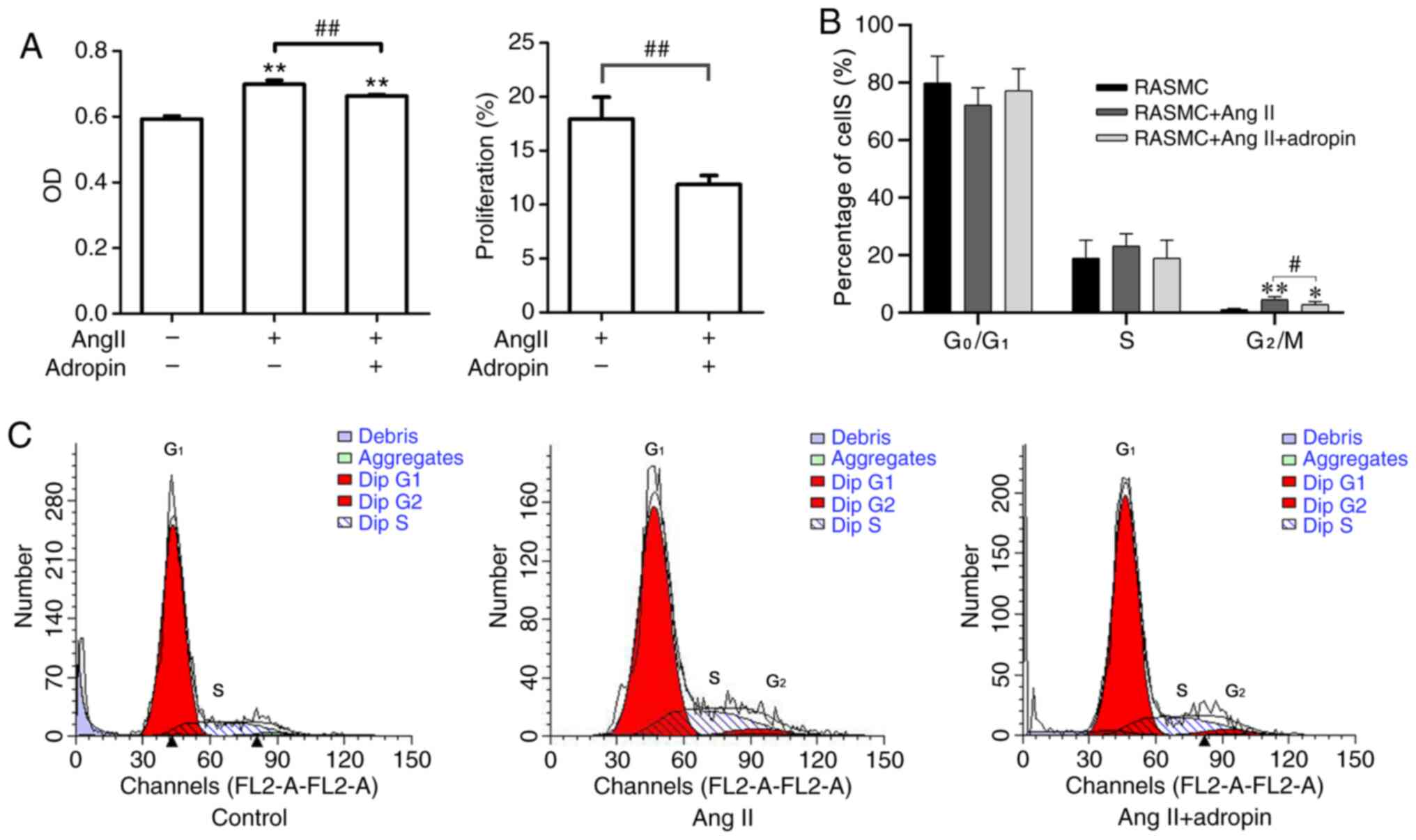
|
1
|
Dangas GD, Claessen BE, Caixeta A, Sanidas
EA, Mintz GS and Mehran R: In-stent restenosis in the drug-eluting
stent era. J Am Coll Cardiol. 56:1897–1907. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Babapulle MN, Joseph L, Bélisle P, Brophy
JM and Eisenberg MJ: A hierarchical bayesian meta-analysis of
randomised clinical trials of drug-eluting stents. Lancet.
364:583–591. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Solinas E, Dangas G, Kirtane AJ, Lansky
AJ, Franklin-Bond T, Boland P, Syros G, Kim YH, Gupta A, Mintz G,
et al: Angiographic patterns of drug-eluting stent restenosis and
one-year outcomes after treatment with repeated percutaneous
coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 102:311–315. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lu WD, Huang CW, Li YH and Chen JY:
Multiple mechanisms in 1 in-stent restenosis assessed by optical
coherence tomography. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 10:2340–2341.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kim WJ, Yoon SE, Kang SM, Jo U, Park HW,
Cho YR, Park GM, Lee JY, Park DW, Kang SJ, et al: Long term
prognosis of in-stent restenosis after drug-eluting stent
implantation and predictors of recurrent restenosis: Data from the
ASAN DES-ISR registry. Am J Cardiol. 111 (7 Suppl)(27B)2013.
|
|
6
|
Farb A, Sangiorgi G, Carter AJ, Walley VM,
Edwards WD, Schwartz RS and Virmani R: Pathology of acute and
chronic coronary stenting in humans. Circulation. 99:44–52.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shlofmitz E, Iantorno M and Waksman R:
Restenosis of drug-eluting stents: A new classification system
based on disease mechanism to guide treatment and state-of-the-art
review. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 12(e007023)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis-an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Isoda K, Nishikawa K, Kamezawa Y, Yoshida
M, Kusuhara M, Moroi M, Tada N and Ohsuzu F: Osteopontin plays an
important role in the development of medial thickening and
neointimal formation. Circ Res. 91:77–82. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kurdi A, De Meyer GR and Martinet W:
Potential therapeutic effects of mTORinhibition in atherosclerosis.
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 82:1267–1279. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Liu Y, Jing Z, Peng L, Jin P, Lin
Y, Zhou Y, Yang L, Ren J, Xie Q and Jin X: N-oleoylethanolamide
suppresses intimal hyperplasia after balloon injury in rats through
AMPK/PPARα pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 496:415–421.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Peng L, Huang X, Jin X, Jing Z, Yang L,
Zhou Y, Ren J and Zhao Y: Wedelolactone, a plant coumarin, prevents
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and injury-induced
neointimal hyperplasia through Akt and AMPK signaling. Exp
Gerontol. 96:73–81. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim MK, Kim SH, Yu HS, Park HG, Kang UG,
Ahn YM and Kim YS: The effect of clozapine on the AMPK-ACC-CPT1
pathway in the rat frontal cortex. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol.
15:907–917. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kumar KG, Trevaskis JL, Lam DD, Sutton GM,
Koza RA, Chouljenko VN, Kousoulas KG, Rogers PM, Kesterson RA,
Thearle M, et al: Identification of adropin as a secreted factor
linking dietary macronutrient intake with energy homeostasis and
lipid metabolism. Cell Metab. 8:468–481. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu L, Fang J, Yuan X, Xiong C and Chen L:
Adropin reduces hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced myocardial injury via
the reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway. Exp Ther Med.
18:3307–3314. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Altamimi TR, Gao S, Karwi QG, Fukushima A,
Rawat S, Wagg CS, Zhang L and Lopaschuk GD: Adropin regulates
cardiac energy metabolism and improves cardiac function and
efficiency. Metabolism. 98:37–48. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Thapa D, Xie B, Zhang M, Stoner MW,
Manning JR, Huckestein BR, Edmunds LR, Mullett SJ, McTiernan CF,
Wendell SG, et al: Adropin treatment restores cardiac glucose
oxidation in pre-diabetic obese mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
129:174–178. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yosaee S, Soltani S, Sekhavati E and
Jazayeri S: Adropin-a novel biomarker of heart disease: A
systematic review article. Iran J Public Health. 45:1568–1576.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao LP, You T, Chan SP, Chen JC and Xu
WT: Adropin is associated with hyperhomocysteine and coronary
atherosclerosis. Exp Ther Med. 11:1065–1070. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sato K, Yamashita T, Shirai R, Shibata K,
Okano T, Yamaguchi M, Mori Y, Hirano T and Watanabe T: Adropin
contributes to anti-atherosclerosis by suppressing
monocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and smooth muscle cell
proliferation. Int J Mol Sci. 19:1293–1309. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mehran R, Dangas G, Abizaid AS, Mintz GS,
Lansky AJ, Satler LF, Pichard AD, Kent KM, Stone GW and Leon MB:
Angiographic patterns of in-stent restenosis: Classification and
implications for long-term outcome. Circulation. 100:1872–1878.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mintz GS, Nissen SE, Anderson WD, Bailey
SR, Erbel R, Fitzgerald PJ, Pinto FJ, Rosenfield K, Siegel RJ,
Tuzcu EM and Yock PG: American college of cardiology clinical
expert consensus document on standards for acquisition, measurement
and reporting of intravascular ultrasound studies (IVUS). A report
of the American college of cardiology task force on clinical expert
consensus documents. J Am Coll Cardiol. 37:1478–1492.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ray JL, Leach R, Herbert JM and Benson M:
Isolation of vascular smooth muscle cells from a single murine
aorta. Methods Cell Sci. 23:185–188. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liao N, Shi Y, Zhang C, Zheng Y, Wang Y,
Zhao B, Zeng Y, Liu X and Liu J: Antioxidants inhibit cell
senescence and preserve stemness of adipose tissue-derived stem
cells by reducing ROS generation during long-term in vitro
expansion. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10(306)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jojima T, Uchida K, Akimoto K, Tomotsune
T, Yanagi K, Iijima T, Suzuki K, Kasai K and Aso Y: Liraglutide, a
GLP-1 receptor agonist, inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation by enhancing AMP-activated protein kinase and cell
cycle regulation, and delays atherosclerosis in ApoE deficient
mice. Atherosclerosis. 261:44–51. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th
edition. National Academic Press (US), Washington, DC, 2011.
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ghoshal S, Stevens JR, Billon C, Girardet
C, Sitaula S, Leon AS, Rao DC, Skinner JS, Rankinen T, Bouchard C,
et al: Adropin: An endocrine link between the biological clock and
cholesterol homeostasis. Mol Metab. 8:51–64. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Stevens JR, Kearney ML, St-Onge MP,
Stanhope KL, Havel PJ, Kanaley JA, Thyfault JP, Weiss EP and Butler
AA: Inverse association between carbohydrate consumption and plasma
adropin concentrations in humans. Obesity (Silver Spring).
24:1731–1740. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhu LH, Huang L, Zhang X, Zhang P, Zhang
SM, Guan H, Zhang Y, Zhu XY, Tian S, Deng K and Li H: Mindin
regulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype and prevents
neointima formation. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:129–145. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ding Y, Zhang M, Zhang W, Lu Q, Cai Z,
Song P, Okon IS, Xiao L and Zou MH: AMP-activated protein kinase
alpha 2 deletion induces VSMC phenotypic switching and reduces
features of atherosclerotic plaque stability. Circ Res.
119:718–730. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao Y, Shang F, Shi W, Zhang J, Zhang J,
Liu X, Li B, Hu X and Wang L: Angiotensin II receptor type 1
antagonists modulate vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration via AMPK/mTOR. Cardiology. 143:1–10. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cuculi F, Bossard M, Zasada W, Moccetti F,
Voskuil M, Wolfrum M, Malinowski KP, Toggweiler S and Kobza R:
Performing percutaneous coronary interventions with predilatation
using non-compliant balloons at high-pressure versus conventional
semi-compliant balloons: Insights from two randomised studies using
optical coherence tomography. Open heart. 7(e001204)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cassese S, De Luca G, Ribichini F,
Cernigliaro C, Sansa M, Versaci F, Proietti I, Stankovic G,
Stojkovic S, Fernandez-Pereira C, et al: ORAl iMmunosuppressive
therapy to prevent in-stent rEstenosiS (RAMSES) cooperation: A
patient-level meta-analysis of randomized trials. Atherosclerosis.
237:410–417. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xie H, Yang J, Han Y, Zhu X and Fang Q:
Inhibition of intimal hyperplasia via local delivery of vascular
endothelial growth factor cDNA nanoparticles in a rabbit model of
restenosis induced by abdominal aorta balloon injury. Exp Ther Med.
10:55–61. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Theodoropoulos K, Mennuni MG, Dangas GD,
Meelu OA, Bansilal S, Baber U, Sartori S, Kovacic JC, Moreno PR,
Sharma SK, et al: Resistant in-stent restenosis in the drug eluting
stent era. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 88:777–785. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jensen LO, Vikman S, Antonsen L, Kosonen
P, Niemelä M, Christiansen EH, Kervinen K, Erglis A, Harnek J,
Kumsars I, et al: Intravascular ultrasound assessment of minimum
lumen area and intimal hyperplasia in in-stent restenosis after
drug-eluting or bare-metal stent implantation. The nordic
intravascular ultrasound study (NIVUS). Cardiovasc Revasc Med.
18:577–582. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Nakamura D, Yasumura K, Nakamura H,
Matsuhiro Y, Yasumoto K, Tanaka A, Matsunaga-Lee Y, Yano M, Yamato
M, Egami Y, et al: Different neoatherosclerosis patterns in
drug-eluting- and bare-metal stent restenosis-optical coherence
tomography study. Circ J. 83:313–319. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ando H, Amano T, Takashima H, Harada K,
Kitagawa K, Suzuki A, Kunimura A, Shimbo Y, Harada K, Yoshida T, et
al: Differences in tissue characterization of restenotic neointima
between sirolimus-eluting stent and bare-metal stent: integrated
backscatter intravascular ultrasound analysis for in-stent
restenosis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 14:996–1001.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhao SG, Xu JJ, Tao ZH, Jin L, Liu Q,
Zheng WY, Jiang LQ and Wang NF: CHA2DS2-Vasc
score and CHA2DS2-Vasc-HS score are poor
predictors of in-stent restenosis among patients with coronary
drug-eluting stents. J Int Med Res. 47:2533–2544. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Umeda H, Kawai T, Misumida N, Ota T,
Hayashi K, Iwase M, Izawa H, Sugino S, Shimizu T, Takeichi Y, et
al: Impact of sirolimus-eluting stent fracture on 4-year clinical
outcomes. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 4:349–354. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kubo S, Kadota K, Ozaki M, Ichinohe T,
Eguchi H, Miyake K, Hyodo Y, Saito N, Otsuji H, Otsuru S, et al:
Difference in clinical and angiographic characteristics of very
late stent thrombosis between drug-eluting and bare-metal stent
implantations. Circ J. 77:1453–1460. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Conway C, Desany GJ, Bailey LR, Keating
JH, Baker BL and Edelman ER: Fracture in drug-eluting stents
increases focal intimal hyperplasia in the atherosclerosed rabbit
iliac artery. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 93:278–285.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bochaton-Piallat ML and Gabbiani G:
Modulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration: Role
of smooth muscle cell heterogeneity. Atherosclerosis: Diet and
Drugs. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp645-663, 2005.
|
|
45
|
Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Singh KK, Shukla
PC, Gupta M, Al-Omran M, Teoh H and Verma S: Adropin is a novel
regulator of endothelial function. Circulation. 122 (Suppl
11):S185–S192. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Herzig S and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Guardian of
metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
19:121–135. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Stone JD, Narine A, Shaver PR, Fox JC,
Vuncannon JR and Tulis DA: AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration and
vascular remodeling following injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 304:H369–H381. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Osman I and Segar L: Pioglitazone, a PPARγ
agonist, attenuates PDGF-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation through AMPK-dependent and AMPK-independent
inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K and ERK signaling. Biochem Pharmacol.
101:54–70. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Nagata D, Takeda R, Sata M, Satonaka H,
Suzuki E, Nagano T and Hirata Y: AMP-activated protein kinase
inhibits angiotensin II-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation. Circulation. 110:444–451. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Igata M, Motoshima H, Tsuruzoe K, Kojima
K, Matsumura T, Kondo T, Taguchi T, Nakamaru K, Yano M, Kukidome D,
et al: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase suppresses
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through the inhibition of
cell cycle progression. Circ Res. 97:837–844. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Peyton KJ, Yu Y, Yates B, Shebib AR, Liu
XM, Wang H and Durante W: Compound C inhibits vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation and migration in an AMP-activated protein
kinase-independent fashion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 338:476–484.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Song P, Wang S, He C, Wang S, Liang B,
Viollet B and Zou MH: AMPKalpha2 deletion exacerbates neointima
formation by upregulating Skp2 in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Circ Res. 109:1230–1239. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kim SY, Jeoung NH, Oh CJ, Choi YK, Lee HJ,
Kim HJ, Kim JY, Hwang JH, Tadi S, Yim YH, et al: Activation of
NAD(P)H:Quinone oxidoreductase 1 prevents arterial restenosis by
suppressing vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circ Res.
104:842–850. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Smith BK and Steinberg GR: AMP-activated
protein kinase, fatty acid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity.
Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 20:248–253. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Bonnefont JP, Djouadi F, Prip-Buus C,
Gobin S, Munnich A and Bastin J: Carnitine palmitoyltransferases 1
and 2: Biochemical, molecular and medical aspects. Mol Aspects Med.
25:495–520. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Ferdinandusse S, Denis S, Van Roermund CW,
Wanders RJ and Dacremont G: Identification of the peroxisomal
beta-oxidation enzymes involved in the degradation of long-chain
dicarboxylic acids. J Lipid Res. 45:1104–1111. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Lochner M, Berod L and Sparwasser T: Fatty
acid metabolism in the regulation of T cell function. Trends
Immunol. 36:81–91. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Gao S, McMillan RP, Jacas J, Zhu Q, Li X,
Kumar GK, Casals N, Hegardt FG, Robbins PD, Lopaschuk GD, et al:
Regulation of substrate oxidation preferences in muscle by the
peptide hormone adropin. Diabetes. 63:3242–3252. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Thapa D, Stoner MW, Zhang M, Xie B,
Manning JR, Guimaraes D, Shiva S, Jurczak MJ and Scott I: Adropin
regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase in cardiac cells via a novel
GPCR-MAPK-PDK4 signaling pathway. Redox Biol. 18:25–32.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Gobin S, Thuillier L, Jogl G, Faye A, Tong
L, Chi M, Bonnefont JP, Girard J and Prip-Buus C: Functional and
structural basis of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A deficiency. J
Biol Chem. 278:50428–50434. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Oaxaca-Castillo D, Andreoletti P, Vluggens
A, Yu S, Van Veldhoven PP, Reddy JK and Cherkaoui-Malki M:
Biochemical characterization of two functional human liver acyl-CoA
oxidase isoforms 1a and 1b encoded by a single gene. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 360:314–319. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Wu L, Fang J, Chen L, Zhao Z, Luo Y, Lin C
and Fan L: Low serum adropin is associated with coronary
atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Clin
Chem Lab Med. 52:751–758. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|