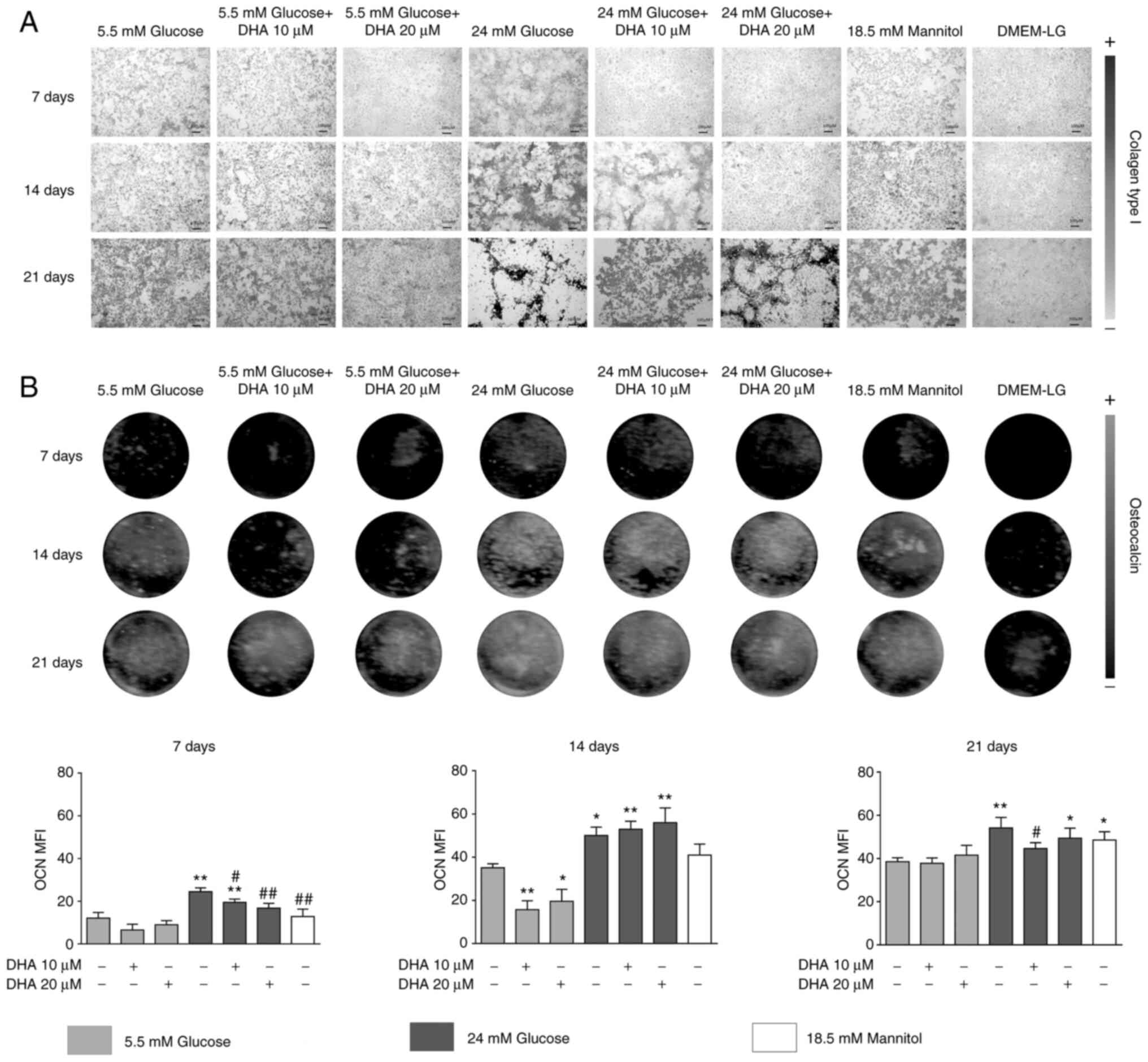
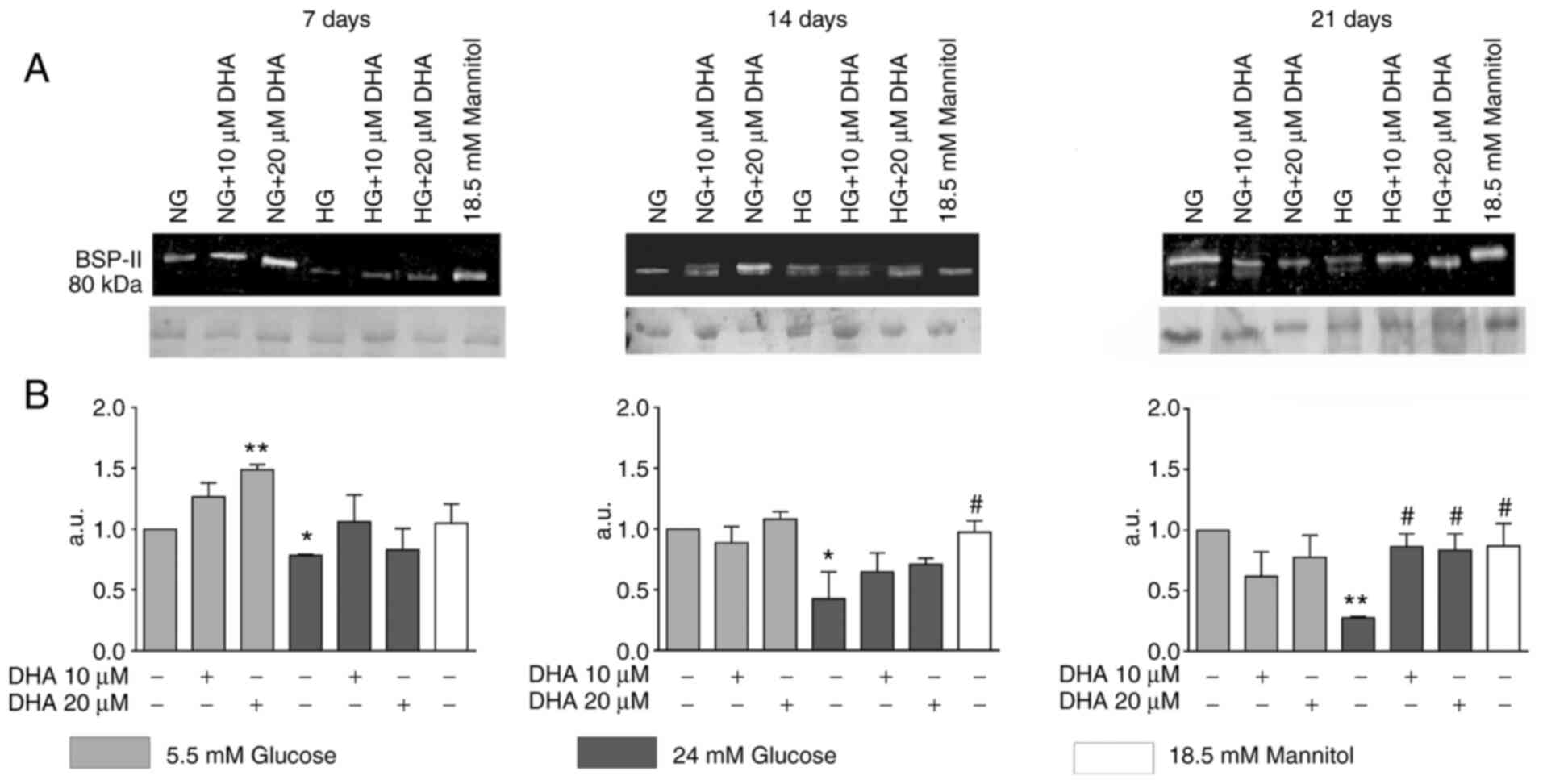
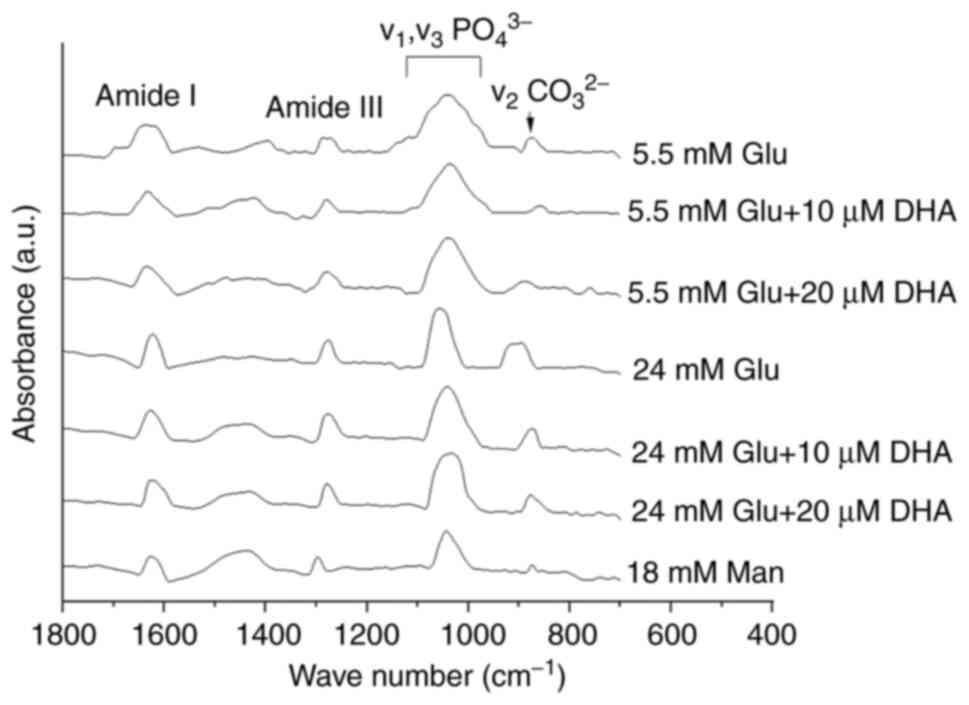
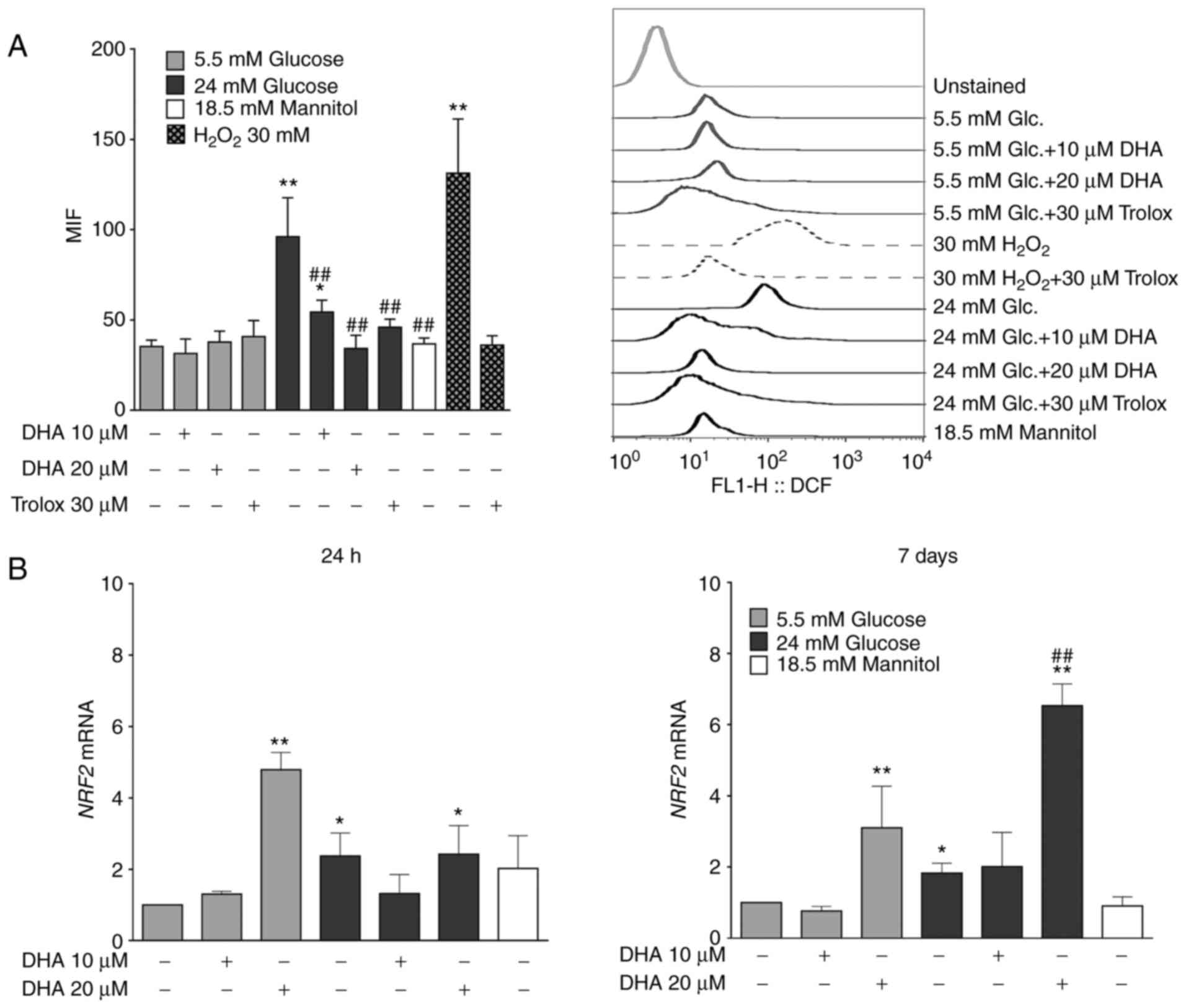
|
1
|
Kerner W and Brückel J: German Diabetes
Association. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes
mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 122:384–386.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
International Diabetes Federation: IDF
diabetes atlas eighth edition, 2017.
|
|
3
|
Farr JN and Khosla S: Determinants of bone
strength and quality in diabetes mellitus in humans. Bone.
82:28–34. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Carnevale V, Romagnoli E, D'Erasmo L and
D'Erasmo E: Bone damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab
Cardiovasc Dis. 24:1151–1157. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hofbauer LC, Brueck CC, Singh SK and
Dobnig H: Osteoporosis in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Bone
Miner Res. 22:1317–1328. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hamann C, Kirschner S, Günther KP and
Hofbauer LC: Bone, sweet bone-osteoporotic fractures in diabetes
mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 8:297–305. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bonds DE, Larson JC, Schwartz AV,
Strotmeyer ES, Robbins J, Rodriguez BL, Johnson KC and Margolis KL:
Risk of fracture in women with type 2 diabetes: The women's health
initiative observational study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
91:3404–1310. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
García-Hernández A, Arzate H,
Gil-Chavarría I, Rojo R and Moreno-Fierros L: High glucose
concentrations alter the biomineralization process in human
osteoblastic cells. Bone. 50:276–288. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y and Yang JH: Activation of the
PI3K/Akt pathway by oxidative stress mediates high glucose-induced
increase of adipogenic differentiation in primary rat osteoblasts.
J Cell Biochem. 114:2595–2602. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Arai M, Shibata Y, Pugdee K, Abiko Y and
Ogata Y: Effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on antioxidant
system and osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells. IUBMB
Life. 59:27–33. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bai XC, Lu D, Bai J, Zheng H, Ke ZY, Li XM
and Luo SQ: Oxidative stress inhibits osteoblastic differentiation
of bone cells by ERK and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
314:197–207. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Richard D, Kefi K, Barbe U, Bausero P and
Visioli F: Polyunsaturated fatty acids as antioxidants. Pharmacol
Res. 57:451–455. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rotstein NP, Politi LE, German OL and
Girotti R: Protective effect of docosahexaenoic acid on oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis of retina photoreceptors. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:2252–2259. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang YC, Lii CK, Wei YL, Li CC, Lu CY, Liu
KL and Chen HW: Docosahexaenoic acid inhibition of inflammation is
partially via cross-talk between Nrf2/heme oxygenase 1 and
IKK/NF-κB pathways. J Nutr Biochem. 24:204–212. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Darlington LG and Stone TW: Antioxidants
and fatty acids in the amelioration of rheumatoid arthritis and
related disorders. Br J Nutr. 85:251–269. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Högström M, Nordström P and Nordström A:
n-3 Fatty acids are positively associated with peak bone mineral
density and bone accrual in healthy men: The NO2 study. Am J Clin
Nutr. 85:803–807. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fallon EM, Nazarian A, Nehra D, Pan AH,
O'Loughlin AA, Nose V and Puder M: The effect of docosahexaenoic
acid on bone microstructure in young mice and bone fracture in
neonates. J Surg Res. 191:148–155. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Farahnak Z, Freundorfer MT, Lavery P and
Weiler HA: Dietary docosahexaenoic acid contributes to increased
bone mineral accretion and strength in young female sprague-dawley
rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 144:32–39.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Atkinson TG, Barker HJ and Meckling-Gill
KA: Incorporation of long-chain n-3 fatty acids in tissues and
enhanced bone marrow cellularity with docosahexaenoic acid feeding
in post-weanling fischer 344 rats. Lipids. 32:293–302.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Watkins BA, Li Y, Lippman HE and Feng S:
Modulatory effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on
osteoblast function and bone metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 68:387–398. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kim HJ, Ohk B, Yoon HJ, Kang WY, Seong SJ,
Kim SY and Yoon YR: Docosahexaenoic acid signaling attenuates the
proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow-derived osteoclast
precursors and promotes apoptosis in mature osteoclasts. Cell
Signal. 29:226–232. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Coetzee M, Haag M and Kruger MC: Effects
of arachidonic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on differentiation and
mineralization of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells. Cell Biochem
Funct. 27:3–11. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Moskot M, Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka J, Kloska
A, Piotrowska E, Narajczyk M and Gabig-Cimińska M: The role of
dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in gene expression modulation and
glycosaminoglycan metabolism in lysosomal storage disorders on an
example of mucopolysaccharidosis. Int J Mol Sci.
20(304)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Maurin AC, Chavassieux PM, Vericel E and
Meunier PJ: Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the inhibitory
effect of human adipocytes on osteoblastic proliferation. Bone.
31:260–266. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Peister A and Prockop
DJ: An Alizarin red-based assay of mineralization by adherent cells
in culture: Comparison with cetylpyridinium chloride extraction.
Anal Biochem. 329:77–84. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tullberg-Reinert H and Jundt G: In situ
measurement of collagen synthesis by human bone cells with a sirius
red-based colorimetric microassay: Effects of transforming growth
factor beta2 and ascorbic acid 2-phosphate. Histochem Cell Biol.
112:271–276. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Romero-Calvo I, Ocón B, Martínez-Moya P,
Suárez MD, Zarzuelo A, Martínez-Augustin O and de Medina FS:
Reversible ponceau staining as a loading control alternative to
actin in western blots. Anal Biochem. 401:318–320. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wrobel E, Leszczynska J and Brzoska E: The
characteristics of human bone-derived cells (HBDCS) during
osteogenesis in vitro. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 21(26)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bourrat C, Radisson J, Chavassieux P,
Azzar G, Roux B and Meunier PJ: Activity increase after extraction
of alkaline phosphatase from human osteoblastic membranes by
nonionic detergents: Influence of age and sex. Calcif Tissue Int.
66:22–28. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Buell MV, Lowry OH, Roberts NR, Chang ML
and Kapphahn JI: The quantitative histochemistry of the brain. V.
Enzymes of glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 232:979–993.
1958.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Figueiredo MM, Gamelas JAF and Martins AG:
Characterization of bone and bone-based graft materials using FTIR
spectroscopy. In: Infrared Spectroscopy-Life and Biomedical
Sciences, Theophile T (ed). IntechOpen, 2012.
|
|
33
|
Rio DC, Ares M Jr, Hannon GJ and Nilsen
TW: Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring
Harb Protoc. 2010(pdb.prot5439)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Manolagas SC: From estrogen-centric to
aging and oxidative stress: A revised perspective of the
pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 31:266–300.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
He F, Ru X and Wen T: NRF2, a
transcription factor for stress response and beyond. Int J Mol Sci.
21(4777)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Casado-Díaz A, Santiago-Mora R, Dorado G
and Quesada-Gómez JM: The omega-6 arachidonic fatty acid, but not
the omega-3 fatty acids, inhibits osteoblastogenesis and induces
adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells: Potential implication
in osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 24:1647–1661. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cunha JS, Ferreira VM, Maquigussa E, Naves
MA and Boim MA: Effects of high glucose and high insulin
concentrations on osteoblast function in vitro. Cell Tissue Res.
358:249–256. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shi P, Liu H, Deng X, Jin Y, Wang Q, Liu
H, Chen M and Han X: Label-free nonenzymatic glycation monitoring
of collagen scaffolds in type 2 diabetic mice by confocal Raman
microspectroscopy. J Biomed Opt. 20(27002)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Vestergaard P: Discrepancies in bone
mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and 2
diabetes-a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 18:427–444.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yamamoto M: Insights into bone fragility
in diabetes: The crucial role of bone quality on skeletal strength.
Endocr J. 62:299–308. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wauquier F, Leotoing L, Coxam V, Guicheux
J and Wittrant Y: Oxidative stress in bone remodelling and disease.
Trends Mol Med. 15:468–477. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sharma T, Sharma A, Maheshwari R, Pachori
G, Kumari P and Mandal CC: Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) inhibits bone
morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) elevated osteoblast potential of
metastatic breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cells in mammary
microcalcification. Nutr Cancer. 72:873–883. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Mao L, Wang M, Li Y, Liu Y, Wang J and Xue
C: Eicosapentaenoic acid-containing phosphatidylcholine promotes
osteogenesis: Mechanism of up-regulating Runx2 and ERK-mediated
phosphorylation of PPARγ at serine 112. J Funct Foods. 52:73–80.
2019.
|
|
45
|
Massaro M, Habib A, Lubrano L, Del Turco
S, Lazzerini G, Bourcier T, Weksler BB and De Caterina R: The
omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoate attenuates endothelial
cyclooxygenase-2 induction through both NADP(H) oxidase and PKC
epsilon inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:15184–15189.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Rahman MM, Bhattacharya A and Fernandes G:
Docosahexaenoic acid is more potent inhibitor of osteoclast
differentiation in RAW 264.7 cells than eicosapentaenoic acid. J
Cell Physiol. 214:201–209. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Poulsen RC, Wolber FM, Moughan PJ and
Kruger MC: Long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids alter
membrane-bound RANK-L expression and osteoprotegerin secretion by
MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
85:42–48. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|