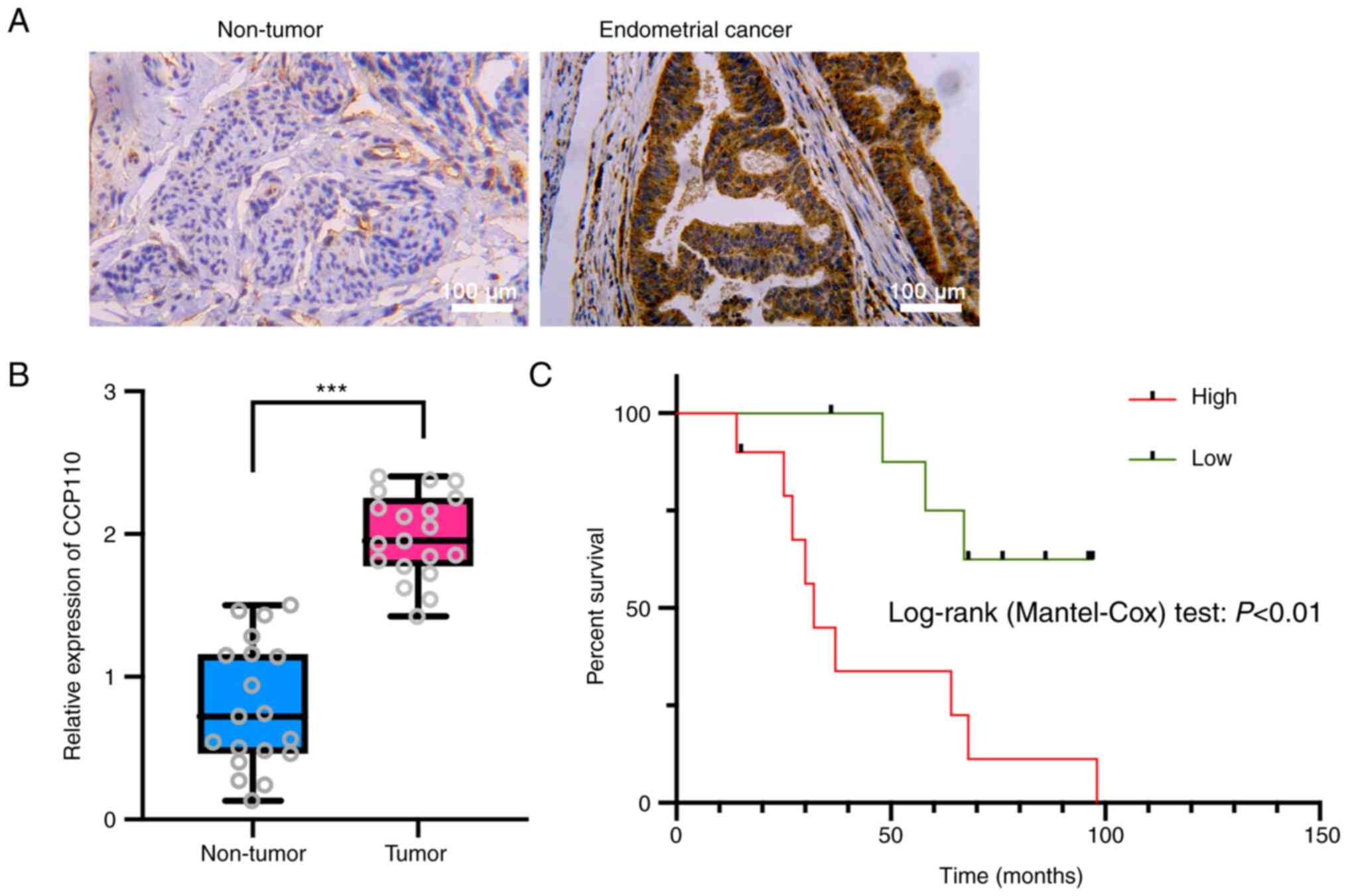
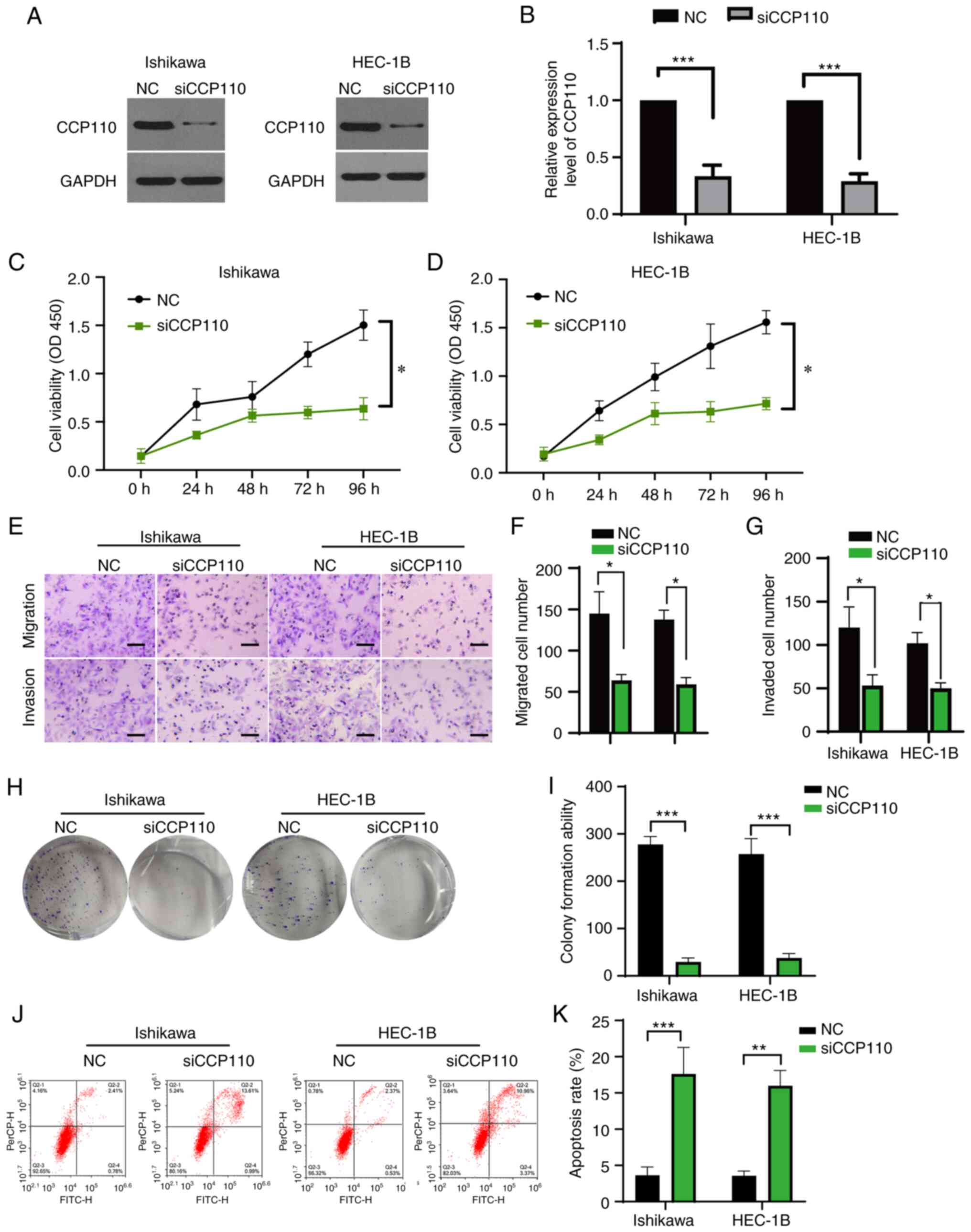
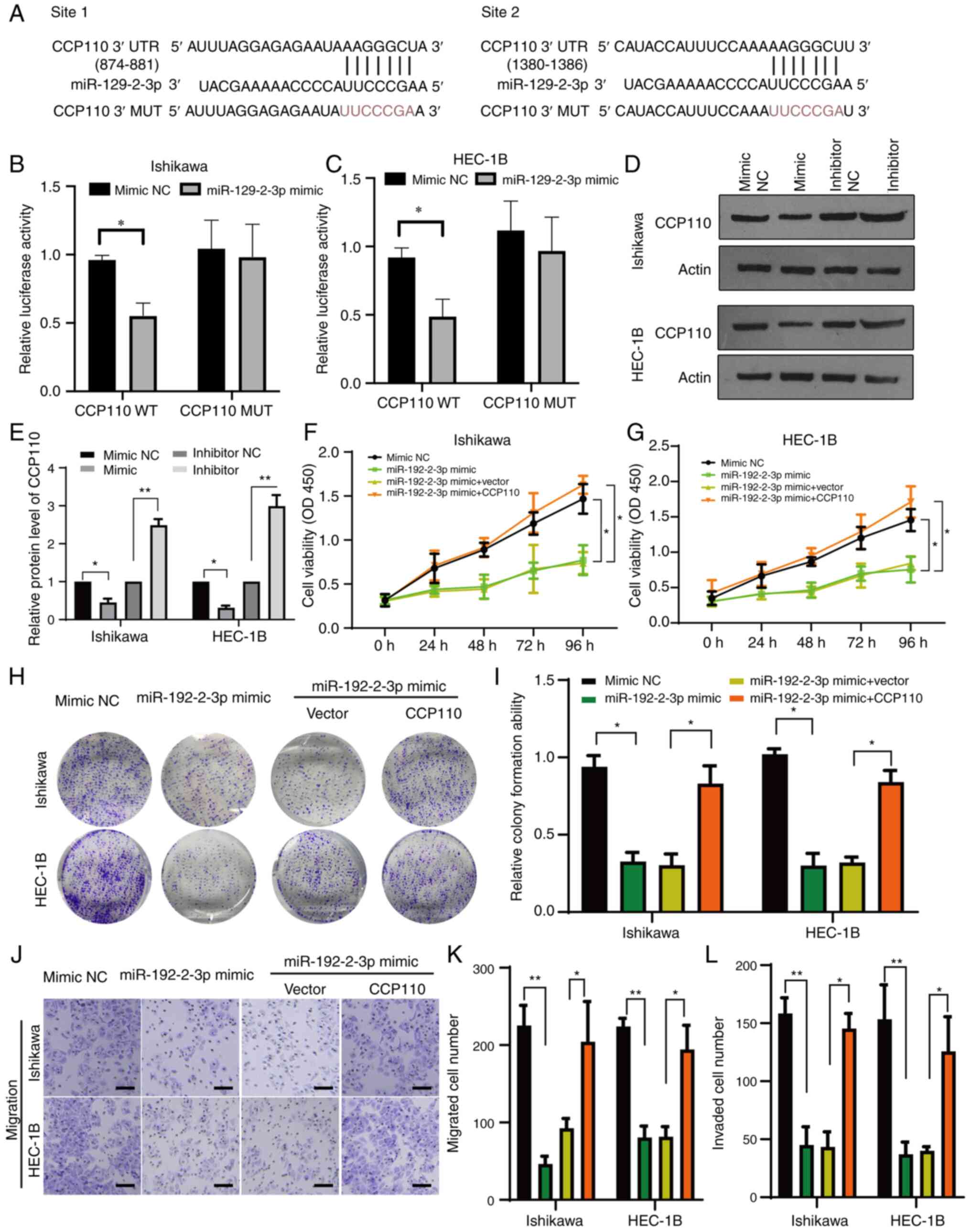
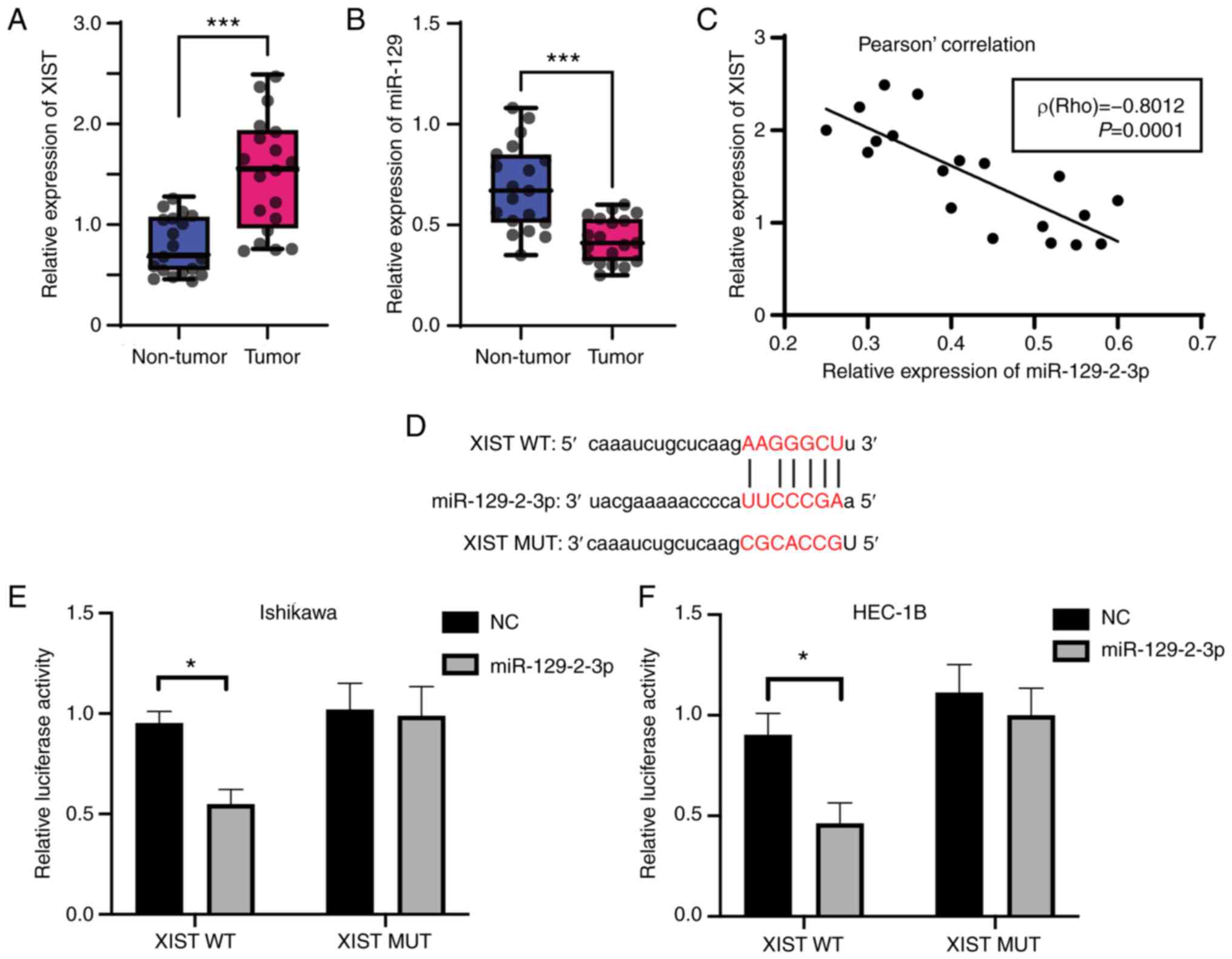
|
1
|
Moore K and Brewer MA: Endometrial cancer:
Is this a new disease? Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 37:435–442.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Amant F, Mirza MR, Koskas M and Creutzberg
CL: Cancer of the corpus uteri. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 143 (Suppl
2):S37–S50. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Urick ME and Bell DW: Clinical
actionability of molecular targets in endometrial cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 19:510–521. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sorosky JI: Endometrial cancer. Obstet
Gynecol. 120:383–397. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Practice Bulletin No. 149. Endometrial
cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 125:1006–1026. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
ACOG committee opinion no. 557. Management
of acute abnormal uterine bleeding in nonpregnant reproductive-aged
women. Obstet Gynecol. 121:891–896. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C,
Abu-Rustum N and Darai E: Endometrial cancer. Lancet.
387:1094–1108. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tran AQ and Gehrig P: Recent advances in
endometrial cancer. F1000Res. 6(81)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tsikouras P, Bouchlariotou S, Vrachnis N,
Dafopoulos A, Galazios G, Csorba R and von Tempelhoff GF:
Endometrial cancer: Molecular and therapeutic aspects. Eur J Obstet
Gynecol Reprod Biol. 169:1–9. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bell DW and Ellenson LH: Molecular
genetics of endometrial carcinoma. Annu Rev Pathol. 14:339–367.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Caponio MA, Addati T, Popescu O, Petroni
S, Rubini V, Centrone M, Trojano G and Simone G: P16(INK4a) protein
expression in endocervical, endometrial and metastatic
adenocarcinomas of extra-uterine origin: Diagnostic and clinical
considerations. Cancer Biomark. 14:169–175. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fukasawa K: Centrosome amplification,
chromosome instability and cancer development. Cancer Lett.
230:6–19. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sluder G and Nordberg JJ: The good, the
bad and the ugly: The practical consequences of centrosome
amplification. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 16:49–54. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
D'Angiolella V, Donato V, Vijayakumar S,
Saraf A, Florens L, Washburn MP, Dynlacht B and Pagano M:
SCF(Cyclin F) controls centrosome homeostasis and mitotic fidelity
through CP110 degradation. Nature. 466:138–142. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tsang WY, Spektor A, Luciano DJ, Indjeian
VB, Chen Z, Salisbury JL, Sánchez I and Dynlacht BD: CP110
cooperates with two calcium-binding proteins to regulate
cytokinesis and genome stability. Mol Biol Cell. 17:3423–3434.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li J, D'Angiolella V, Seeley ES, Kim S,
Kobayashi T, Fu W, Campos EI, Pagano M and Dynlacht BD: USP33
regulates centrosome biogenesis via deubiquitination of the
centriolar protein CP110. Nature. 495:255–259. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wei Y, Li M, Yu S, Ye M,
Zhang H, Chen S, Liu W and Zhang J: MiR-129-3p promotes docetaxel
resistance of breast cancer cells via CP110 inhibition. Sci Rep.
5(15424)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bijnsdorp IV, Hodzic J, Lagerweij T,
Westerman B, Krijgsman O, Broeke J, Verweij F, Nilsson RJA,
Rozendaal L, van Beusechem VW, et al: miR-129-3p controls
centrosome number in metastatic prostate cancer cells by repressing
CP110. Oncotarget. 7:16676–16687. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hu S, Danilov AV, Godek K, Orr B, Tafe LJ,
Rodriguez-Canales J, Behrens C, Mino B, Moran CA, Memoli VA, et al:
CDK2 inhibition causes anaphase catastrophe in lung cancer through
the centrosomal protein CP110. Cancer Res. 75:2029–2038.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kwon SC, Baek SC, Choi YG, Yang J, Lee YS,
Woo JS and Kim VN: Molecular basis for the single-nucleotide
precision of primary microRNA processing. Mol Cell. 73:505–518
e505. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Widodo, Djati MS and Rifa'I M: Role of
MicroRNAs in carcinogenesis that potential for biomarker of
endometrial cancer. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 7:9–13. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Banno K, Kisu I, Yanokura M, Masuda K,
Ueki A, Kobayashi Y, Susumu N and Aoki D: Epigenetics and genetics
in endometrial cancer: New carcinogenic mechanisms and relationship
with clinical practice. Epigenomics. 4:147–162. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yanokura M, Banno K, Iida M, Irie H, Umene
K, Masuda K, Kobayashi Y, Tominaga E and Aoki D: MicroRNAS in
endometrial cancer: Recent advances and potential clinical
applications. EXCLI J. 14:190–198. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cohn DE, Fabbri M, Valeri N, Alder H,
Ivanov I, Liu CG, Croce CM and Resnick KE: Comprehensive miRNA
profiling of surgically staged endometrial cancer. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 202:656 e651–e658. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Montagnana M, Benati M, Danese E, Giudici
S, Perfranceschi M, Ruzzenenete O, Salvagno GL, Bassi A, Gelati M,
Paviati E, et al: Aberrant microRNA expression in patients with
endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 27:459–466.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li L and Ma L: Upregulation of miR-582-5p
regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting AKT3 in
human endometrial carcinoma. Saudi J Biol Sci. 25:965–970.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu Z, Nian Z, Jingjing Z, Tao L and Quan
L: MicroRNA-424/E2F6 feedback loop modulates cell invasion,
migration and EMT in endometrial carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:114281–114291. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Huang YW, Liu JC, Deatherage DE, Luo J,
Mutch DG, Goodfellow PJ, Miller DS and Huang THM: Epigenetic
repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4
oncogene in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 69:9038–9046.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shan T, Uyar DS, Wang LS, Mutch DG, Huang
THM, Rader JS, Sheng X and Huang YW: SOX11 hypermethylation as a
tumor biomarker in endometrial cancer. Biochimie. 162:8–14.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
He WP, Chen YY, Wu LX, Guo YY, You ZS and
Yang GF: A novel necroptosis-related lncRNA signature for
predicting prognosis and anti-cancer treatment response in
endometrial cancer. Front Immunol. 13(1018544)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ong MS, Cai W, Yuan Y, Leong HC, Tan TZ,
Mohammad A, You ML, Arfuso F, Goh BC, Warrier S, et al: ‘Lnc’-ing
Wnt in female reproductive cancers: therapeutic potential of long
non-coding RNAs in Wnt signalling. Br J Pharmacol. 174:4684–4700.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hosseini ES, Meryet-Figuiere M,
Sabzalipoor H, Kashani HH, Nikzad H and Asemi Z: Dysregulated
expression of long noncoding RNAs in gynecologic cancers. Mol
Cancer. 16(107)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xie P, Cao H, Li Y, Wang J and Cui Z:
Knockdown of lncRNA CCAT2 inhibits endometrial cancer cells growth
and metastasis via sponging miR-216b. Cancer Biomark. 21:123–133.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Guo C, Song WQ, Sun P, Jin L and Dai HY:
LncRNA-GAS5 induces PTEN expression through inhibiting miR-103 in
endometrial cancer cells. J Biomed Sci. 22(100)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun MY, Zhu JY, Zhang CY, Zhang M, Song
YN, Rahman K, Zhang LJB and Zhang H: Autophagy regulated by lncRNA
HOTAIR contributes to the cisplatin-induced resistance in
endometrial cancer cells. Biotechnol Lett. 39:1477–1484.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Brown CJ, Hendrich BD, Rupert JL,
Lafrenière RG, Xing Y, Lawrence J and Willard HF: The human XIST
gene: Analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains
conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell.
71:527–542. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yang Z, Jiang X, Jiang X and Zhao H:
X-inactive-specific transcript: A long noncoding RNA with complex
roles in human cancers. Gene. 679:28–35. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Mutzel V and Schulz EG: Dosage sensing,
threshold responses, and epigenetic memory: A systems biology
perspective on random X-Chromosome inactivation. Bioessays.
42(e1900163)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Creytens D: NKX2.2 immunohistochemistry in
the distinction of Ewing sarcoma from cytomorphologic mimics:
Diagnostic utility and pitfalls-Comment on Russell-Goldman et
al. Cancer Cytopathol. 127(202)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4(e05005)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang X: Improving microRNA target
prediction by modeling with unambiguously identified
microRNA-target pairs from CLIP-ligation studies. Bioinformatics.
32:1316–1322. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:D92–D97. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg
L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M
and Rajewsky N: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat
Genet. 37:495–500. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhang R, Xia LQ, Lu WW, Zhang J and Zhu
JS: LncRNAs and cancer. Oncol Lett. 12:1233–1239. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jali I, Vanamamalai VK, Garg P, Navarrete
P, Gutierrez-Adan A and Sharma S: Identification and differential
expression of long non-coding RNAs and their association with XIST
gene during early embryonic developmental stages of Bos taurus. Int
J Biol Macromol. 229:896–908. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Raglan O, Kalliala I, Markozannes G,
Cividini S, Gunter MJ, Nautiyal J, Gabra H, Paraskevaidis E,
Martin-Hirsch P, Tsilidis KK and Kyrgiou M: Risk factors for
endometrial cancer: An umbrella review of the literature. Int J
Cancer. 145:1719–1730. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Banno K, Kisu I, Yanokura M, Tsuji K,
Masuda K, Ueki A, Kobayashi Y, Yamagami W, Nomura H, Tominaga E, et
al: Biomarkers in endometrial cancer: Possible clinical
applications (Review). Oncol Lett. 3:1175–1180. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Schmidt TI, Kleylein-Sohn J, Westendorf J,
Clech ML, Lavoie SB, Stierhof YD and Nigg EA: Control of centriole
length by CPAP and CP110. Curr Biol. 19:1005–1011. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Spektor A, Tsang WY, Khoo D and Dynlacht
BD: Cep97 and CP110 suppress a cilia assembly program. Cell.
130:678–690. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Plotnikova OV, Golemis EA and Pugacheva
EN: Cell cycle-dependent ciliogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res.
68:2058–2061. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Michaud EJ and Yoder BK: The primary
cilium in cell signaling and cancer. Cancer Res. 66:6463–6467.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Fesler A, Zhai H and Ju J: miR-129 as a
novel therapeutic target and biomarker in gastrointestinal cancer.
Onco Targets Ther. 7:1481–1485. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Tsai CH, Liu SC, Wang YH, Su CM, Huang CC,
Hsu CJ and Tang CH: Osteopontin inhibition of miR-129-3p enhances
IL-17 expression and monocyte migration in rheumatoid arthritis.
Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1861:15–22. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Chen R, Ye B, Xie H, Huang Y, Wu Z, Wu H,
Wang X, Miao H and Liang W: miR-129-3p alleviates chondrocyte
apoptosis in knee joint fracture-induced osteoarthritis through
CPEB1. J Orthop Surg Res. 15(552)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zou Y and Kong M: Tetrahydroxy stilbene
glucoside alleviates palmitic acid-induced inflammation and
apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by regulating miR-129-3p/Smad3
signaling. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 24(5)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wang B, Li Y and You C: MiR-129-3p
targeting of MCU protects against glucose fluctuation-mediated
neuronal damage via a mitochondrial-dependent intrinsic apoptotic
pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 14:153–163. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Jia Y, Gao Y and Dou J: Effects of
miR-129-3p on biological functions of prostate cancer cells through
targeted regulation of Smad3. Oncol Lett. 19:1195–1202.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang M, Jiang D, Xie X, He Y, Lv M and
Jiang X: miR-129-3p inhibits NHEJ pathway by targeting SAE1 and
represses gastric cancer progression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
12:1539–1547. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shaker OG, Abdelwahed MY, Ahmed NA, Hassan
EA, Ahmed TI, Abousarie MA and Ayoub SE: Evaluation of serum long
noncoding RNA NEAT and MiR-129-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma.
IUBMB Life. 71:1571–1578. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhai J, Qu S, Li X, Zhong J, Chen X, Qu Z
and Wu D: miR-129 suppresses tumor cell growth and invasion by
targeting PAK5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:161–167. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zhang D, Cao J, Zhong Q, Zeng L, Cai C,
Lei L, Zhang W and Liu F: Long noncoding RNA PCAT-1 promotes
invasion and metastasis via the miR-129-5p-HMGB1 signaling pathway
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 95:1187–1193.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Chen C, Jiang J, Fang M, Zhou L, Chen Y,
Zhou J, Song Y, Kong G, Zhang B, Jiang B, et al: MicroRNA-129-2-3p
directly targets Wip1 to suppress the proliferation and invasion of
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Cancer. 11:3216–3224.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Chen X, Xiong D, Ye L, Wang K, Huang L,
Mei S, Wu J, Chen S, Lai X, Zheng L and Wang M: Up-regulated lncRNA
XIST contributes to progression of cervical cancer via regulating
miR-140-5p and ORC1. Cancer Cell Int. 19(45)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Xu Z, Xu J, Lu H, Lin B, Cai S, Guo J,
Zang F and Chen R: LARP1 is regulated by the XIST/miR-374a axis and
functions as an oncogene in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 38:3659–3667. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Wang H, Shen Q, Zhang X, Yang C, Cui S,
Sun Y, Wang L, Fan X and Xu S: The long non-coding RNA XIST
controls non-small cell lung cancer proliferation and invasion by
modulating miR-186-5p. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:2221–2229.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zhang YL, Li XB, Hou YX, Fang NZ, You JC
and Zhou QH: The lncRNA XIST exhibits oncogenic properties via
regulation of miR-449a and Bcl-2 in human non-small cell lung
cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:371–381. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Fang J, Sun CC and Gong C: Long noncoding
RNA XIST acts as an oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer by
epigenetically repressing KLF2 expression. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 478:811–817. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Chen Z, Hu X, Wu Y, Cong L, He X, Lu J,
Feng J and Liu D: Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes the development
of esophageal cancer by sponging miR-494 to regulate CDK6
expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:2228–2236. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wang H, Li H, Yu Y, Jiang Q, Zhang R, Sun
H, Xing W and Li Y: Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes the
progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through sponging
miR-129-5p and upregulating CCND1 expression. Cell Cycle. 20:39–53.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Tang Y, He R, An J, Deng P, Huang L and
Yang W: lncRNA XIST interacts with miR-140 to modulate lung cancer
growth by targeting iASPP. Oncol Rep. 38:941–948. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wang W, Shen H, Cao G and Huang J: Long
non-coding RNA XIST predicts poor prognosis and promotes malignant
phenotypes in osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett. 17:256–262. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Han J and Shen X: Long noncoding RNAs in
osteosarcoma via various signaling pathways. J Clin Lab Anal.
34(e23317)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Wu D, Nie X, Ma C, Liu X, Liang X, An Y,
Zhao B and Wu X: RSF1 functions as an oncogene in osteosarcoma and
is regulated by XIST/miR-193a-3p axis. Biomed Pharmacother.
95:207–214. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Xu T, Jiang W, Fan L, Gao Q and Li G:
Upregulation of long noncoding RNA Xist promotes proliferation of
osteosarcoma by epigenetic silencing of P21. Oncotarget.
8:101406–101417. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Yang C, Wu K, Wang S and Wei G: Long
non-coding RNA XIST promotes osteosarcoma progression by targeting
YAP via miR-195-5p. J Cell Biochem. 119:5646–5656. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Zhang R and Xia T: Long non-coding RNA
XIST regulates PDCD4 expression by interacting with miR-21-5p and
inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth and metastasis. Int J Oncol.
51:1460–1470. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|