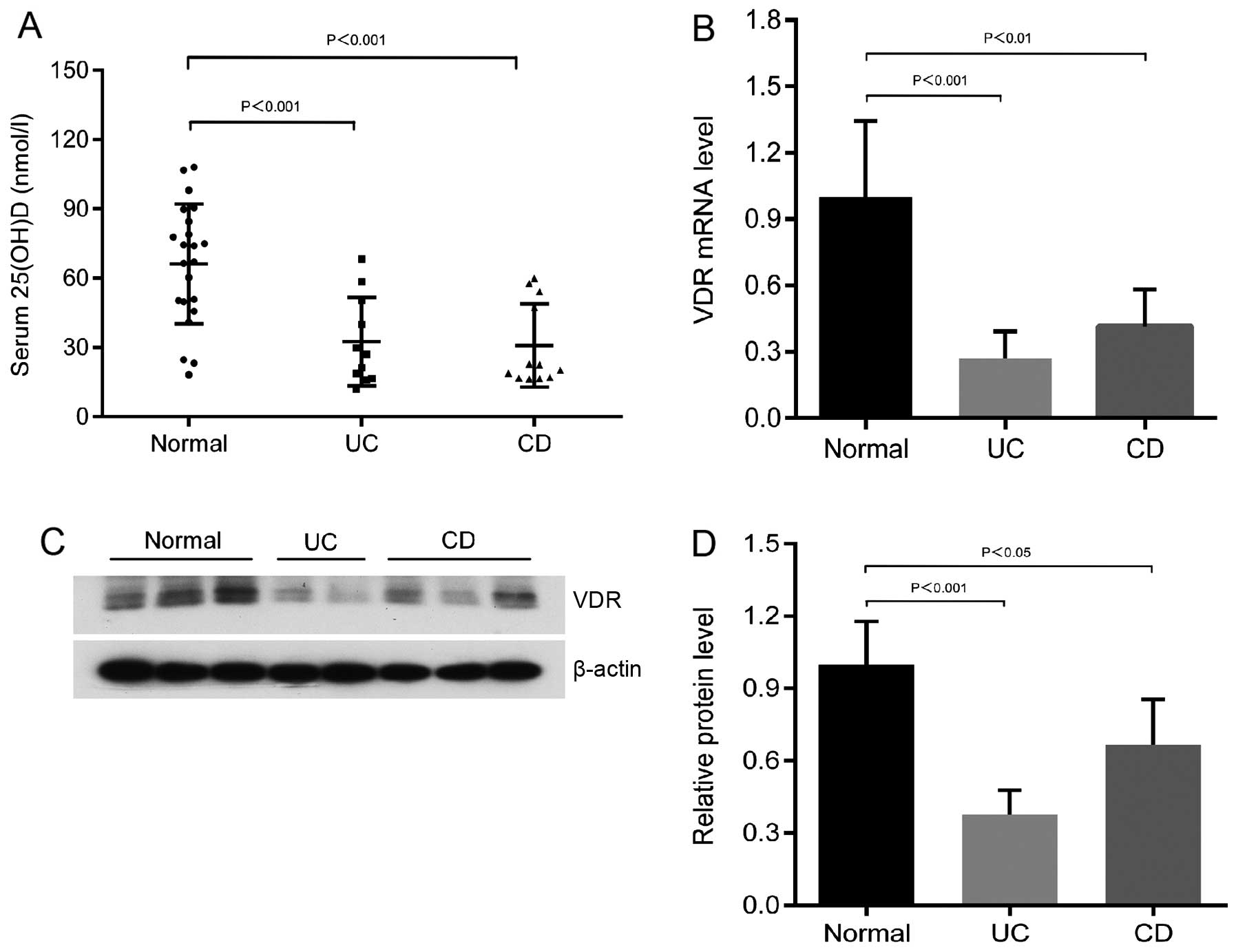
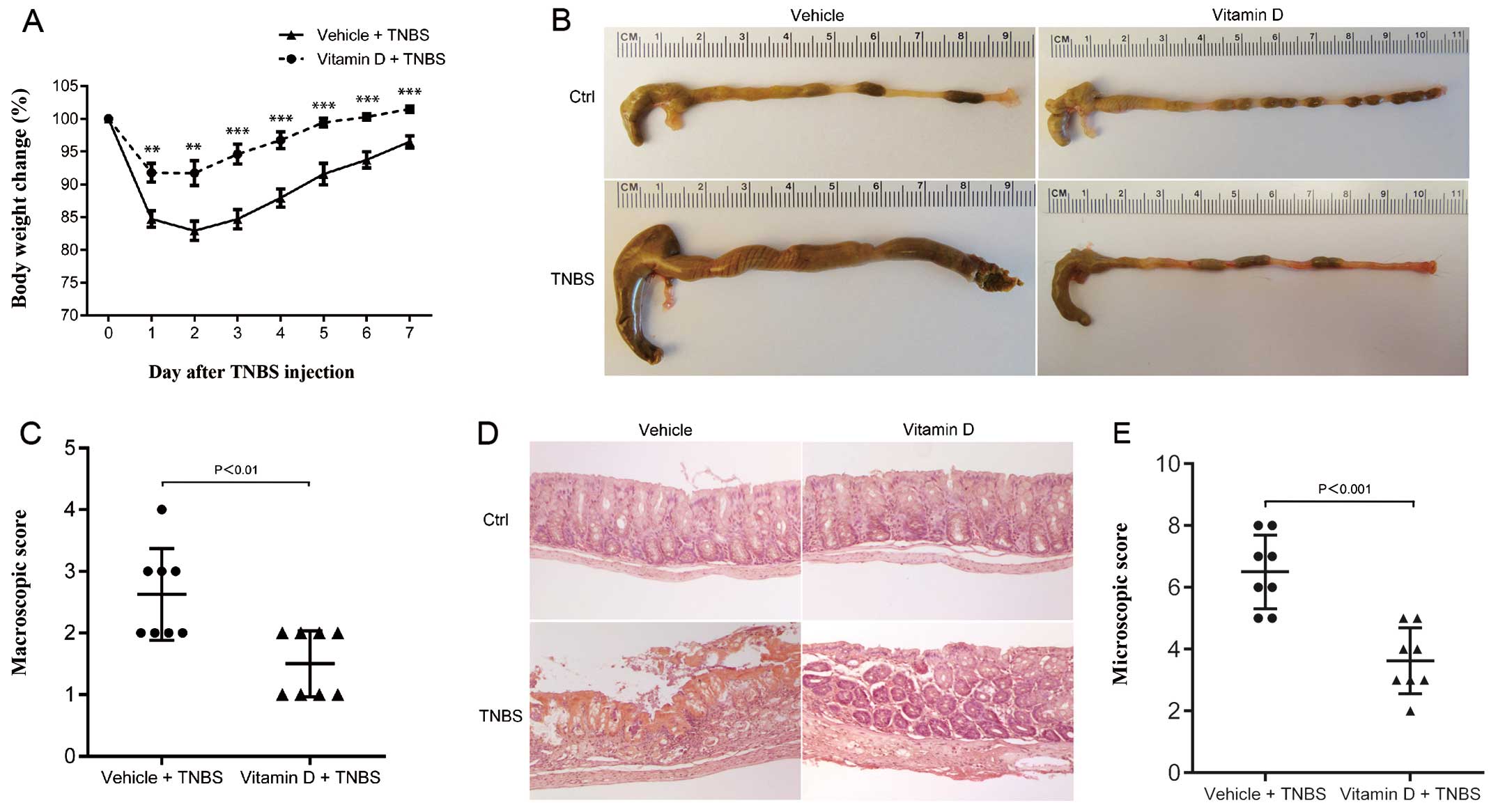
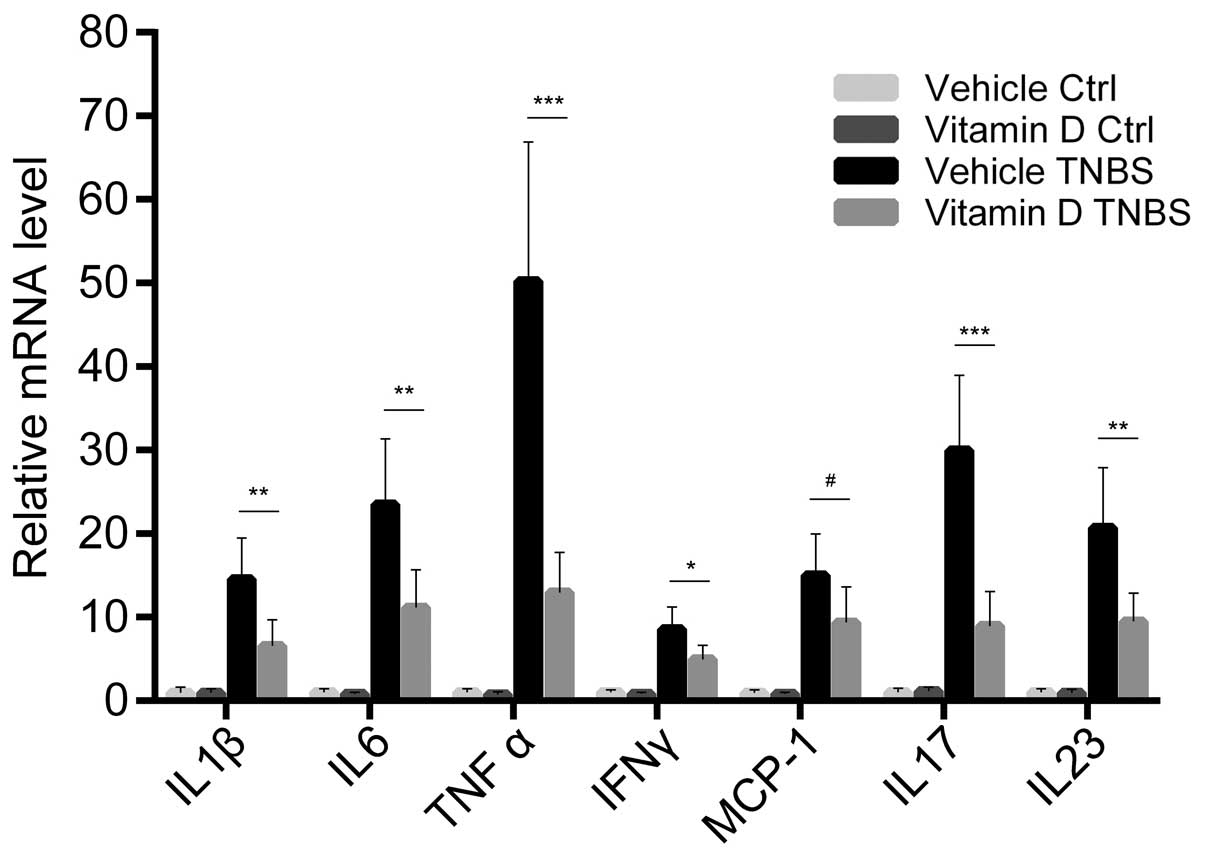
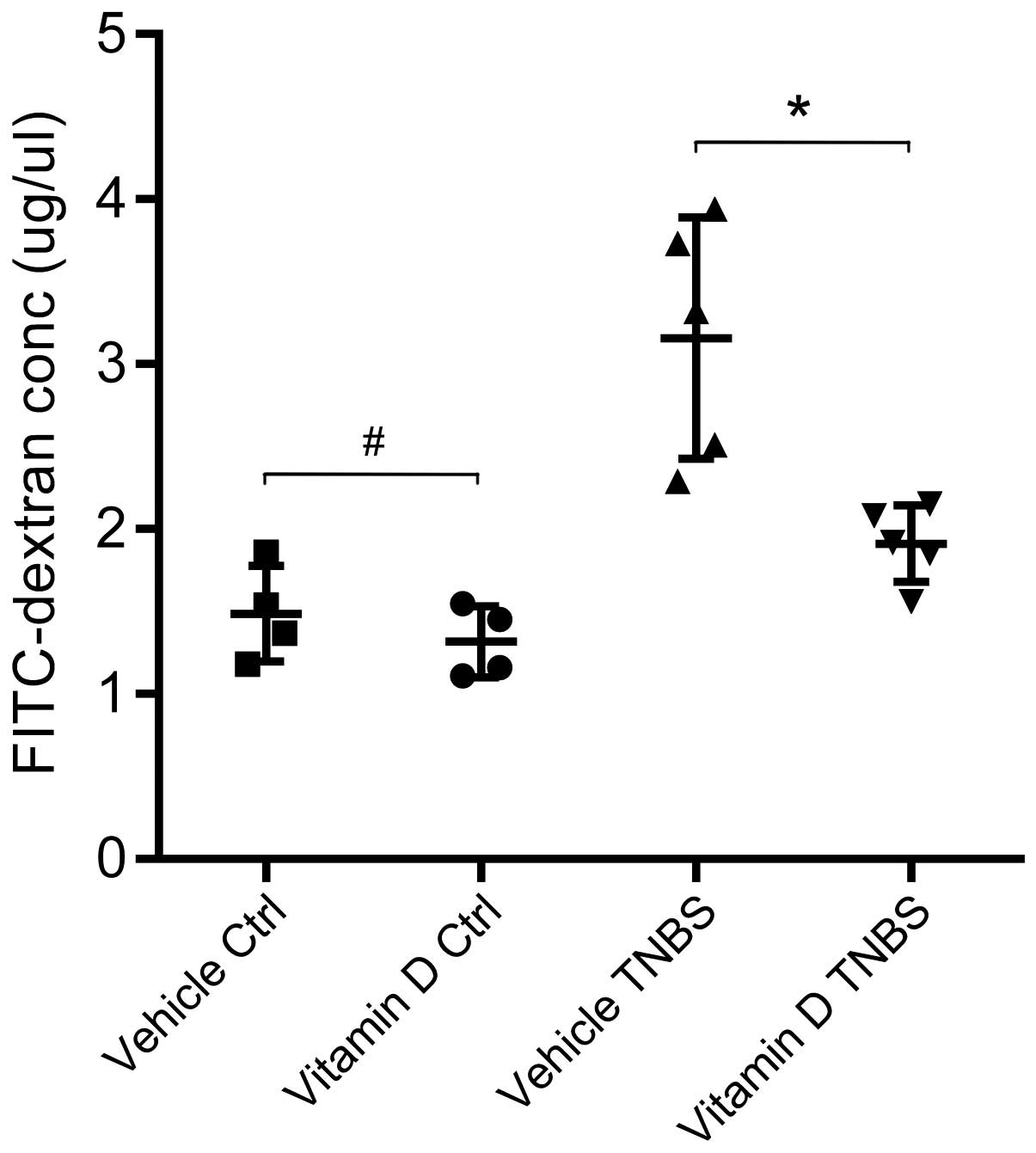
|
1
|
Tan B, Li P, Lv H, et al: Vitamin D Levels
and bone metabolism in Chinese adult patients with inflammatory
bowel disease. J Dig Dis. 15:116–123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Levin AD, Wadhera V, Leach ST, et al:
Vitamin D deficiency in children with inflammatory bowel disease.
Dig Dis Sci. 56:830–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Loftus EV Jr: Clinical epidemiology of
inflammatory bowel disease: incidence, prevalence, and
environmental influences. Gastroenterology. 126:1504–1517. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Wang ZT, Hu JJ, Fan R, Zhou J and
Zhong J: Polymorphisms of the vitamin D receptor gene and the risk
of inflammatory bowel disease: a meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res.
13:2598–2610. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xue LN, Xu KQ, Zhang W, Wang Q, Wu J and
Wang XY: Associations between vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and
susceptibility to ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease: a
meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 19:54–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kong J, Zhang ZY, Musch MW, et al: Novel
role of the vitamin D receptor in maintaining the integrity of the
intestinal mucosal barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 294:208–216. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Peterson LW and Artis D: Intestinal
epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune
homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:141–153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fasano A and Shea-Donohue T: Mechanisms of
disease: the role of intestinal barrier function in the
pathogenesis of gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases. Nat Clin
Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:416–422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gibson PR: Increased gut permeability in
Crohn’s disease: is TNF the link? Gut. 53:1724–1725. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Watson AJ, Chu S, Sieck L, et al:
Epithelial barrier function in vivo is sustained despite gaps in
epithelial layers. Gastroenterology. 129:902–912. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abraham C and Cho JH: Inflammatory bowel
disease. N Engl J Med. 361:2066–2078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su L, Nalle SC, Shen L, et al: TNFR2
activates MLCK-dependent tight junction dysregulation to cause
apoptosis-mediated barrier loss and experimental colitis.
Gastroenterology. 145:407–415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu W, Chen Y, Golan MA, et al: Intestinal
epithelial vitamin D receptor signaling inhibits experimental
colitis. J Clin Invest. 123:3983–3996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dirisina R, Katzman RB, Goretsky T, et al:
p53 and PUMA independently regulate apoptosis of intestinal
epithelial cells in patients and mice with colitis.
Gastroenterology. 141:1036–1045. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qiu W, Wu B, Wang X, et al: PUMA-mediated
intestinal epithelial apoptosis contributes to ulcerative colitis
in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 121:1722–1732. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bouillon R, Carmeliet G, Verlinden L, et
al: Vitamin D and human health: lessons from vitamin D receptor
null mice. Endocr Rev. 29:726–776. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wirtz S, Neufert C, Weigmann B and Neurath
MF: Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat
Protoc. 2:541–546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Appleyard CB and Wallace JL: Reactivation
of hapten-induced colitis and its prevention by anti-inflammatory
drugs. Am J Physiol. 269:G119–G125. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng S and Coyne D: Paricalcitol capsules
for the control of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney
disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 7:617–621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greenbaum LA, Benador N, Goldstein SL, et
al: Intravenous paricalcitol for treatment of secondary
hyperparathyroidism in children on hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis.
49:814–823. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harries AD, Brown R, Heatley RV, Williams
LA, Woodhead S and Rhodes J: Vitamin D status in Crohn’s disease:
association with nutrition and disease activity. Gut. 26:1197–1203.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moum B, Aadland E, Ekbom A and Vatn MH:
Seasonal variations in the onset of ulcerative colitis. Gut.
38:376–378. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Naderi N, Farnood A, Habibi M, et al:
Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in Iranian
patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
23:1816–1822. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cutolo M, Paolino S, Sulli A, Smith V,
Pizzorni C and Seriolo B: Vitamin D, steroid hormones, and
autoimmunity. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1317:39–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cantorna MT, McDaniel K, Bora S, Chen J
and James J: Vitamin D, immune regulation, the microbiota, and
inflammatory bowel disease. Exp Biol Med. 239:1524–1530. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cantorna MT and Mahon BD: Mounting
evidence for vitamin D as an environmental factor affecting
autoimmune disease prevalence. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
229:1136–1142. 2004.
|
|
27
|
Froicu M, Zhu Y and Cantorna MT: Vitamin D
receptor is required to control gastrointestinal immunity in IL-10
knockout mice. Immunology. 117:310–318. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nicholson I, Dalzell AM and El-Matary W:
Vitamin D as a therapy for colitis: a systematic review. J Crohns
Colitis. 6:405–411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han J, Flemington C, Houghton AB, et al:
Expression of bbc3, a pro-apoptotic BH3-only gene, is regulated by
diverse cell death and survival signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:11318–11323. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu J and Zhang L: PUMA, a potent killer
with or without p53. Oncogene. 27:S71–S83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Edelblum KL, Yan F, Yamaoka T and Polk DB:
Regulation of apoptosis during homeostasis and disease in the
intestinal epithelium. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 12:413–424. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|