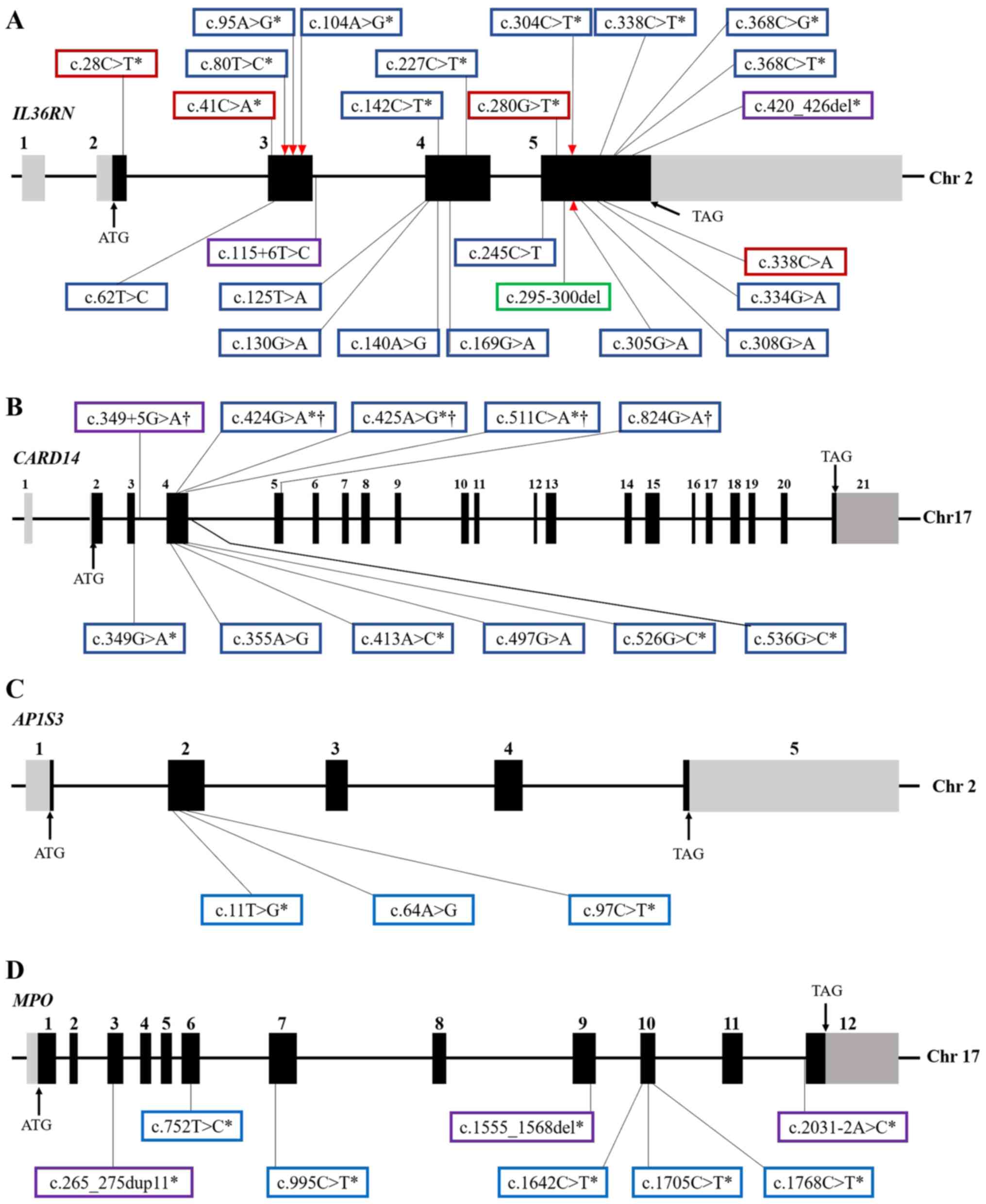
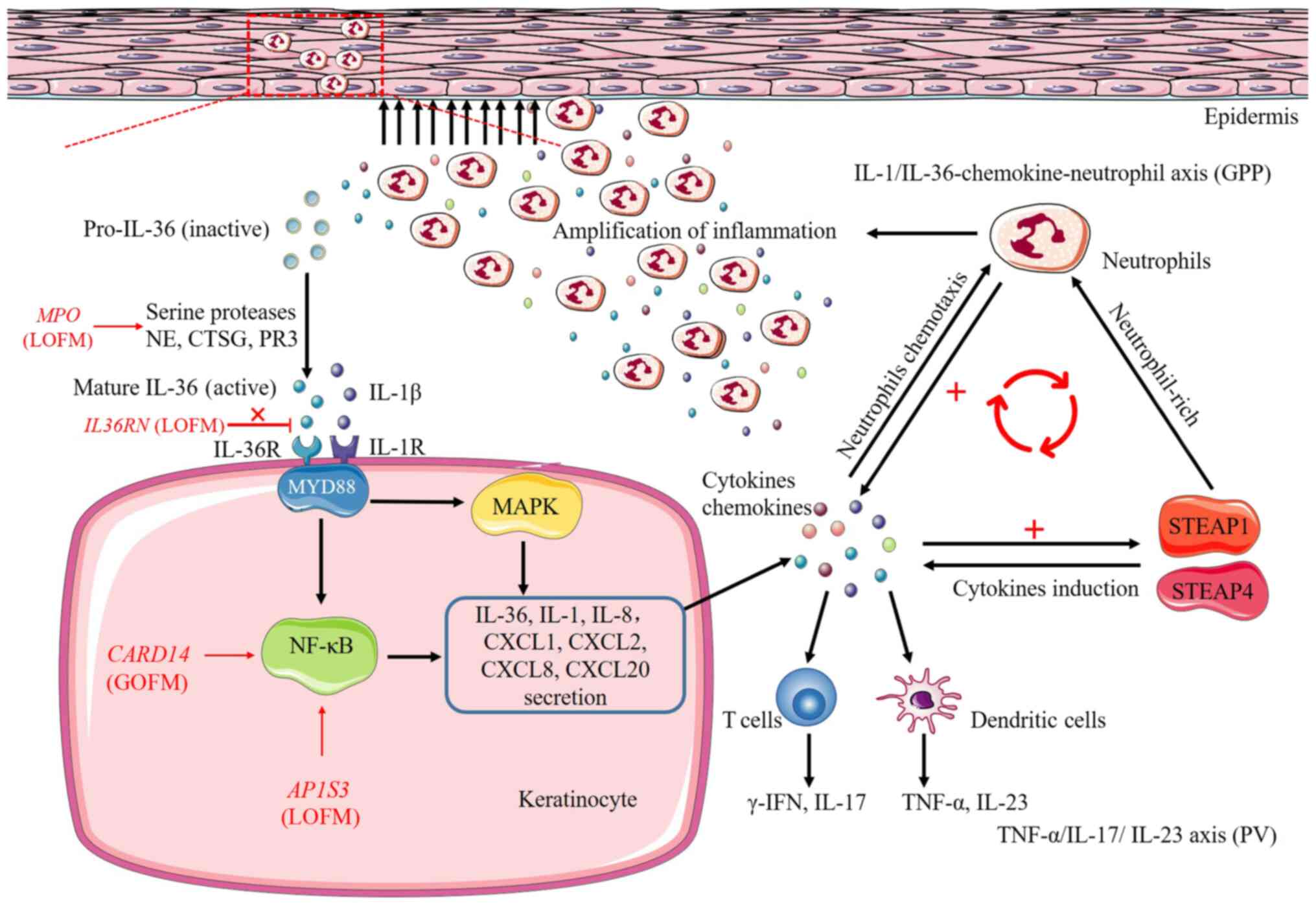
|
1
|
Navarini AA, Burden AD, Capon F, Mrowietz
U, Puig L, Köks S, Kingo K, Smith C and Barker JN; ERASPEN Network:
European consensus statement on phenotypes of pustular psoriasis. J
Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 31:1792–1799. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baker H and Ryan TJ: Generalized pustular
psoriasis. A clinical and epidemiological study of 104 cases. Br J
Dermatol. 80:771–793. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ohkawara A, Yasuda H, Kobayashi H, Inaba
Y, Ogawa H, Hashimoto I and Imamura S: Generalized pustular
psoriasis in Japan: Two distinct groups formed by differences in
symptoms and genetic background. Acta Derm Venereol. 76:68–71.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Augey F, Renaudier P and Nicolas JF:
Generalized pustular psoriasis (Zumbusch): A French epidemiological
survey. Eur J Dermatol. 16:669–673. 2006.
|
|
5
|
Ito T, Takahashi H, Kawada A, Iizuka H,
Nakagawa H, Japanese Society For and Psoriasis Research:
Epidemiological survey from 2009 to 2012 of psoriatic patients in
Japanese society for psoriasis research. J Dermatol. 45:293–301.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Takahashi H, Nakamura K, Kaneko F and
Nakagawa H: Analysis of psoriasis patients registered with the
Japanese society for psoriasis research from 2002-2008. J Dermatol.
38:1125–1129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen L, Huang X, Xiao Y, Su J, Shen M and
Chen X: Prevalence and risk factors of atopic dermatitis,
psoriasis, acne, and urticaria in China. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao
Yi Xue Ban. 45:449–455. 2020.In English, Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Talaee R, Hajheydari Z, Moghaddam AY,
Moraveji SA and Ravandi BF: Prevalence of oral mucosal lesions and
their association with severity of psoriasis among psoriatic
patients referred to dermatology clinic: A cross-sectional study in
Kashan/Iran. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 5:978–982. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Griffiths CE and Barker JN: Pathogenesis
and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 370:263–271. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Steffen C: William John Munro and Munro's
abscess, and Franz Kogoj and Kogoj's spongiform pustule. Am J
Dermatopathol. 24:364–368. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Crowley JJ, Pariser DM and Yamauchi PS: A
brief guide to pustular psoriasis for primary care providers.
Postgrad Med. 1–15. 2020.Online Ahead of Print.
|
|
12
|
Benjegerdes KE, Hyde K, Kivelevitch D and
Mansouri B: Pustular psoriasis: Pathophysiology and current
treatment perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 6:131–144. 2016.
|
|
13
|
Sugiura K, Takemoto A, Yamaguchi M,
Takahashi H, Shoda Y, Mitsuma T, Tsuda K, Nishida E, Togawa Y,
Nakajima K, et al: The majority of generalized pustular psoriasis
without psoriasis vulgaris is caused by deficiency of
interleukin-36 receptor antagonist. J Invest Dermatol.
133:2514–2521. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boehner A, Navarini AA and Eyerich K:
Generalized pustular psoriasis-a model disease for specific
targeted immunotherapy, systematic review. Exp Dermatol.
27:1067–1077. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li M, Han J, Lu Z, Li H, Zhu K, Cheng R,
Jiao Q, Zhang C, Zhu C, Zhuang Y, et al: Prevalent and rare
mutations in IL-36RN gene in Chinese patients with generalized
pustular psoriasis and psoriasis vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol.
133:2637–2639. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li X, Chen M, Fu X, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Yu G,
Yu Y, Qin P, Wu W, Pan F, et al: Mutation analysis of the IL36RN
gene in Chinese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis
with/without psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci. 76:132–138. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hussain S, Berki DM, Choon SE, Burden AD,
Allen MH, Arostegui JI, Chaves A, Duckworth M, Irvine AD,
Mockenhaupt M, et al: IL36RN mutations define a severe
autoinflammatory phenotype of generalized pustular psoriasis. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 135:1067–1070.e9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Marrakchi S, Guigue P, Renshaw BR, Puel A,
Pei XY, Fraitag S, Zribi J, Bal E, Cluzeau C, Chrabieh M, et al:
Interleukin-36-receptor antagonist deficiency and generalized
pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 365:620–628. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jordan CT, Cao L, Roberson ED, Pierson KC,
Yang CF, Joyce CE, Ryan C, Duan S, Helms CA, Liu Y, et al: PSORS2
is due to mutations in CARD14. Am J Hum Genet. 90:784–795. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Setta-Kaffetzi N, Simpson MA, Navarini AA,
Patel VM, Lu HC, Allen MH, Duckworth M, Bachelez H, Burden AD,
Choon SE, et al: AP1S3 mutations are associated with pustular
psoriasis and impaired Toll-like receptor 3 trafficking. Am J Hum
Genet. 94:790–797. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vergnano M, Mockenhaupt M, Benzian-Olsson
N, Paulmann M, Grys K, Mahil SK, Chaloner C, Barbosa IA, August S,
Burden AD, et al: Loss-of-function myeloperoxidase mutations are
associated with increased neutrophil counts and pustular skin
disease. Am J Hum Genet. 107:539–543. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Twelves S, Mostafa A, Dand N, Burri E,
Farkas K, Wilson R, Cooper HL, Irvine AD, Oon HH, Kingo K, et al:
Clinical and genetic differences between pustular psoriasis
subtypes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 143:1021–1026. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Mössner R, Wilsmann-Theis D, Oji V,
Gkogkolou P, Löhr S, Schulz P, Körber A, Prinz JC, Renner R,
Schäkel K, et al: The genetic basis for most patients with pustular
skin disease remains elusive. Br J Dermatol. 178:740–748. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sugiura K, Muto M and Akiyama M: CARD14
c.526G>C (p.Asp176His) is a significant risk factor for
generalized pustular psoriasis with psoriasis vulgaris in the
Japanese cohort. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1755–1757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li L, You J, Fu X, Wang Z, Sun Y, Liu H
and Zhang F: Variants of CARD14 are predisposing factors for
generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) with psoriasis vulgaris but
not for GPP alone in a Chinese population. Br J Dermatol.
180:425–426. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mahil SK, Twelves S, Farkas K,
Setta-Kaffetzi N, Burden AD, Gach JE, Irvine AD, Képíró L,
Mockenhaupt M, Oon HH, et al: AP1S3 mutations cause skisn
autoinflammation by disrupting keratinocyte autophagy and
up-regulating IL-36 production. J Invest Dermatol. 136:2251–2259.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Towne JE, Garka KE, Renshaw BR, Virca GD
and Sims JE: Interleukin (IL)-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal
through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP to activate the pathway leading to
NF-kappaB and MAPKs. J Biol Chem. 279:13677–13688. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Buhl AL and Wenzel J: Interleukin-36 in
infectious and inflammatory skin diseases. Front Immunol.
10:11622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Johnston A, Xing X, Wolterink L, Barnes
DH, Yin Z, Reingold L, Kahlenberg JM, Harms PW and Gudjonsson JE:
IL-1 and IL-36 are dominant cytokines in generalized pustular
psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 140:109–120. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Onoufriadis A, Simpson MA, Pink AE, Di
Meglio P, Smith CH, Pullabhatla V, Knight J, Spain SL, Nestle FO,
Burden AD, et al: Mutations in IL36RN/IL1F5 are associated with the
severe episodic inflammatory skin disease known as generalized
pustular psoriasis. Am J Hum Genet. 89:432–437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Furue K, Yamamura K, Tsuji G, Mitoma C,
Uchi H, Nakahara T, Kido-Nakahara M, Kadono T and Furue M:
Highlighting interleukin-36 signalling in plaque psoriasis and
pustular psoriasis. Acta Derm Venereol. 98:5–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cowen EW and Goldbach-Mansky R: DIRA,
DITRA, and new insights into pathways of skin inflammation: What's
in a name? Arch Dermatol. 148:381–384. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aksentijevich I, Masters SL, Ferguson PJ,
Dancey P, Frenkel J, van Royen-Kerkhoff A, Laxer R, Tedgård U,
Cowen EW, Pham TH, et al: An autoinflammatory disease with
deficiency of the interleukin-1-receptor antagonist. N Engl J Med.
360:2426–2437. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Reddy S, Jia S, Geoffrey R, Lorier R,
Suchi M, Broeckel U, Hessner MJ and Verbsky J: An autoinflammatory
disease due to homozygous deletion of the IL1RN locus. N Engl J
Med. 360:2438–2444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sugiura K, Takeichi T, Kono M, Ogawa Y,
Shimoyama Y, Muro Y and Akiyama M: A novel IL36RN/IL1F5 homozygous
nonsense mutation, p.Arg10X, in a Japanese patient with adult-onset
generalized pustular psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 167:699–701. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kanazawa N, Nakamura T, Mikita N and
Furukawa F: Novel IL36RN mutation in a Japanese case of early onset
generalized pustular psoriasis. J Dermatol. 40:749–751. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Farooq M, Nakai H, Fujimoto A, Fujikawa H,
Matsuyama A, Kariya N, Aizawa A, Fujiwara H, Ito M and Shimomura Y:
Mutation analysis of the IL36RN gene in 14 Japanese patients with
generalized pustular psoriasis. Hum Mutat. 34:176–183. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tauber M, Bal E, Pei XY, Madrange M,
Khelil A, Sahel H, Zenati A, Makrelouf M, Boubridaa K, Chiali A, et
al: IL36RN mutations affect protein expression and function: A
basis for genotype-phenotype correlation in pustular diseases. J
Invest Dermatol. 136:1811–1819. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Setta-Kaffetzi N, Navarini AA, Patel VM,
Pullabhatla V, Pink AE, Choon SE, Allen MA, Burden AD, Griffiths
CE, Seyger MM, et al: Rare pathogenic variants in IL36RN underlie a
spectrum of psoriasis-associated pustular phenotypes. J Invest
Dermatol. 133:1366–1369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sugiura K, Nakasuka A, Kono H, Kono M and
Akiyama M: Impetigo herpetiformis with IL36RN mutations in a
Chinese patient: A founder haplotype of c.115+6T>C in East Asia.
J Dermatol Sci. 79:319–320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shiratori T, Fukai K, Yasumizu M, Taguchi
R, Tsuruta D, Abe Y, Hozumi Y and Suzuki T: IL36RN gene analysis of
two Japanese patients with generalized pustular psoriasis. Int J
Dermatol. 54:e60–e62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Cheng R, Lu Z, Guo Y, Yan M, Liang
J, Huang P, Li M and Yao Z: Clinical profiles of pediatric patients
with GPP alone and with different IL36RN genotypes. J Dermatol Sci.
85:235–240. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Renert-Yuval Y, Horev L, Babay S, Tams S,
Ramot Y, Zlotogorski A and Molho-Pessach V: IL36RN mutation causing
generalized pustular psoriasis in a Palestinian patient. Int J
Dermatol. 53:866–868. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ueda Y, Komine M, Kamiya K, Tsuda H,
Maekawa T, Murata S and Ohtsuki M: Generalized pustular psoriasis
in a 92-year-old man with a homozygous nonsense mutation in IL36RN.
J Dermatol. 45:326–328. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ellingford JM, Black GC, Clayton TH, Judge
M, Griffiths CE and Warren RB: A novel mutation in IL36RN underpins
childhood pustular dermatosis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
30:302–305. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Rossi-Semerano L, Piram M, Chiaverini C,
De Ricaud D, Smahi A and Koné-Paut I: First clinical description of
an infant with interleukin-36-receptor antagonist deficiency
successfully treated with anakinra. Pediatrics. 132:e1043–e1047.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Körber A, Mössner R, Renner R, Sticht H,
Wilsmann-Theis D, Schulz P, Sticherling M, Traupe H and Hüffmeier
U: Mutations in IL36RN in patients with generalized pustular
psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 133:2634–2637. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Takeichi T, Togawa Y, Okuno Y, Taniguchi
R, Kono M, Matsue H, Sugiura K and Akiyama M: A newly revealed
IL36RN mutation in sibling cases complements our IL36RN mutation
statistics for generalized pustular psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci.
85:58–60. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wang TS, Chiu HY, Hong JB, Chan CC, Lin SJ
and Tsai TF: Correlation of IL36RN mutation with different clinical
features of pustular psoriasis in Chinese patients. Arch Dermatol
Res. 308:55–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Abbas O, Itani S, Ghosn S, Kibbi AG,
Fidawi G, Farooq M, Shimomura Y and Kurban M: Acrodermatitis
continua of Hallopeau is a clinical phenotype of DITRA: Evidence
that it is a variant of pustular psoriasis. Dermatology. 226:28–31.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sugiura K, Endo K, Akasaka T and Akiyama
M: Successful treatment with infliximab of sibling cases with
generalized pustular psoriasis caused by deficiency of
interleukin-36 receptor antagonist. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
29:2054–2056. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Song HS, Yun SJ, Park S and Lee ES: Gene
mutation analysis in a Korean patient with early-onset and
recalcitrant generalized pustular psoriasis. Ann Dermatol.
26:424–425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liang J, Zhang H, Guo Y, Yang K, Ni C, Yu
H, Kong X, Li M, Lu Z and Yao Z: Coinheritance of generalized
pustular psoriasis and familial Behçet-like autoinflammatory
syndrome with variants in IL36RN and TNFAIP3 in the heterozygous
state. J Dermatol. 46:907–910. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Scudiero I, Zotti T, Ferravante A,
Vessichelli M, Vito P and Stilo R: Alternative splicing of
CARMA2/CARD14 transcripts generates protein variants with
differential effect on NF-κB activation and endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced cell death. J Cell Physiol. 226:3121–3131. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bertin J, Wang L, Guo Y, Jacobson MD,
Poyet JL, Srinivasula SM, Merriam S, DiStefano PS and Alnemri ES:
CARD11 and CARD14 are novel caspase recruitment domain
(CARD)/membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family members
that interact with BCL10 and activate NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem.
276:11877–11882. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jordan CT, Cao L, Roberson ED, Duan S,
Helms CA, Nair RP, Duffin KC, Stuart PE, Goldgar D, Hayashi G, et
al: Rare and common variants in CARD14, encoding an epidermal
regulator of NF-kappaB, in psoriasis. Am J Hum Genet. 90:796–808.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Qin P, Zhang Q, Chen M, Fu X, Wang C, Wang
Z, Yu G, Yu Y, Li X, Sun Y, et al: Variant analysis of CARD14 in a
Chinese Han population with psoriasis vulgaris and generalized
pustular psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 134:2994–2996. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Berki DM, Liu L, Choon SE, David Burden A,
Griffiths CEM, Navarini AA, Tan ES, Irvine AD, Ranki A, Ogo T, et
al: Activating CARD14 mutations are associated with generalized
pustular psoriasis but rarely account for familial recurrence in
psoriasis vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 135:2964–2970. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Haskamp S, Bruns H, Hahn M, Hoffmann M,
Gregor A, Löhr S, Hahn J, Schauer C, Ringer M, Flamann C, et al:
Myeloperoxidase modulates inflammation in generalized pustular
psoriasis and additional rare pustular skin diseases. Am J Hum
Genet. 107:527–538. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
De Argila D, Dominguez JD,
Lopez-Estebaranz JL and Iglesias L: Pustular psoriasis in a patient
with myeloperoxidase deficiency. Dermatology. 193:2701996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Stendahl O, Coble BI, Dahlgren C, Hed J
and Molin L: Myeloperoxidase modulates the phagocytic activity of
polymorphonuclear neutrophil leukocytes. Studies with cells from a
myeloperoxidase-deficient patient. J Clin Invest. 73:366–373. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kizaki M, Miller CW, Selsted ME and
Koeffler HP: Myeloperoxidase (MPO) gene mutation in hereditary MPO
deficiency. Blood. 83:1935–1940. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Marchetti C, Patriarca P, Solero GP,
Baralle FE and Romano M: Genetic studies on myeloperoxidase
deficiency in Italy. Jpn J Infect Dis. 57:S10–S12. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Marchetti C, Patriarca P, Solero GP,
Baralle FE and Romano M: Genetic characterization of
myeloperoxidase deficiency in Italy. Hum Mutat. 23:496–505. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Akiyama M, Takeichi T, McGrath JA and
Sugiura K: Autoinflammatory keratinization diseases. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 140:1545–1547. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Akiyama M: Early-onset generalized
pustular psoriasis is representative of autoinflammatory
keratinization diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 143:809–810. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kanazawa N: Designation of
autoinflammatory skin manifestations with specific genetic
backgrounds. Front Immunol. 11:4752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Takeichi T and Akiyama M: Familial or
sporadic porokeratosis as an autoinflammatory keratinization
disease. J Dermatol. 46. pp. e125–e126. 2019, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Liang Y, Xing X, Beamer MA, Swindell WR,
Sarkar MK, Roberts LW, Voorhees JJ, Kahlenberg JM, Harms PW,
Johnston A and Gudjonsson JE: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigens
of the prostate comprise a novel inflammatory nexus in patients
with pustular skin disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
139:1217–1227. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ogawa E, Sato Y, Minagawa A and Okuyama R:
Pathogenesis of psoriasis and development of treatment. J Dermatol.
45:264–272. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Nestle FO, Conrad C, Tun-Kyi A, Homey B,
Gombert M, Boyman O, Burg G, Liu YJ and Gilliet M: Plasmacytoid
predendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon-alpha
production. J Exp Med. 202:135–143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Mudigonda P, Mudigonda T, Feneran AN,
Alamdari HS, Sandoval L and Feldman SR: Interleukin-23 and
interleukin-17: Importance in pathogenesis and therapy of
psoriasis. Dermatol Online J. 18:12012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Coimbra S, Oliveira H, Reis F, Belo L,
Rocha S, Quintanilha A, Figueiredo A, Teixeira F, Castro E,
Rocha-Pereira P and Santos-Silva A: Interleukin (IL)-22, IL-17,
IL-23, IL-8, vascular endothelial growth factor and tumour necrosis
factor-α levels in patients with psoriasis before, during and after
psoralen-ultraviolet A and narrowband ultraviolet B therapy. Br J
Dermatol. 163:1282–1290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Grine L, Dejager L, Libert C and
Vandenbroucke RE: An inflammatory triangle in psoriasis: TNF, type
I IFNs and IL-17. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 26:25–33. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Fanoni D, Venegoni L, Vergani B, Tavecchio
S, Cattaneo A, Leone BE, Berti E and Marzano AV: Evidence for a
role of auto-inflammation in early-phase psoriasis. Clin Exp
Immunol. 198:283–291. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hüffmeier U, Wätzold M, Mohr J, Schön MP
and Mössner R: Successful therapy with anakinra in a patient with
generalized pustular psoriasis carrying IL36RN mutations. Br J
Dermatol. 170:202–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Mansouri B, Richards L and Menter A:
Treatment of two patients with generalized pustular psoriasis with
the interleukin-1β inhibitor gevokizumab. Br J Dermatol.
173:239–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Skendros P, Papagoras C, Lefaki I,
Giatromanolaki A, Kotsianidis I, Speletas M, Bocly V, Theodorou I,
Dalla V and Ritis K: Successful response in a case of severe
pustular psoriasis after interleukin-1β inhibition. Br J Dermatol.
176:212–215. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, Burden
AD, Tsai TF, Morita A, Turki H, Hall DB, Shear M, Baum P, et al:
Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of
generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 380:981–983. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Fialová J, Vojáčková N, Vaňousová D and
Hercogová J: Juvenile generalized pustular psoriasis treated with
etanercept. Dermatol Ther. 27:105–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Esposito M, Mazzotta A, Casciello C and
Chimenti S: Etanercept at different dosages in the treatment of
generalized pustular psoriasis: A case series. Dermatology.
216:355–360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Viguier M, Aubin F, Delaporte E, Pagès C,
Paul C, Beylot-Barry M, Goujon C, Rybojad M and Bachelez H; Groupe
de Recherche sur le Psoriasis de la Société Française de
Dermatologie: Efficacy and safety of tumor necrosis factor
inhibitors in acute generalized pustular psoriasis. Arch Dermatol.
148:1423–1425. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Saikaly SK and Mattes M: Biologics and
pediatric generalized pustular psoriasis: An emerging therapeutic
trend. Cureus. 8:e6522016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Cuperus E, Koevoets R, van der Smagt JJ,
Toonstra J, de Graaf M, Frenkel J and Pasmans SGMA: Juvenile
interleukin-36 receptor antagonist deficiency (DITRA) with
c.80T>C (p.Leu27Pro) mutation successfully treated with
etanercept and acitretin. JAAD Case Rep. 4:192–195. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Adachi A, Komine M, Hirano T, Tsuda H,
Karakawa M, Murata S and Ohtsuki M: Case of generalized pustular
psoriasis exacerbated during pregnancy, successfully treated with
infliximab. J Dermatol. 43:1439–1440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Pan J, Qiu L, Xiao T and Chen HD: Juvenile
generalized pustular psoriasis with IL36RN mutation treated with
short-term infliximab. Dermatol Ther. 29:164–167. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Morita A, Yamazaki F, Matsuyama T,
Takahashi K, Arai S, Asahina A, Imafuku S, Nakagawa H, Hasegawa Y,
Williams D, et al: Adalimumab treatment in Japanese patients with
generalized pustular psoriasis: Results of an open-label phase 3
study. J Dermatol. 45:1371–1380. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Matsumoto A, Komine M, Karakawa M,
Kishimoto M and Ohtsuki M: Adalimumab administration after
infliximab therapy is a successful treatment strategy for
generalized pustular psoriasis. J Dermatol. 44:202–204. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Egawa G, Honda T and Kabashima K:
Long-term efficacy of ixekizumab in erythrodermic and generalized
pustular psoriasis patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
33:2592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wilsmann-Theis D, Schnell LM,
Ralser-Isselstein V, Bieber T, Schön MP, Hüffmeier U and Mössner R:
Successful treatment with interleukin-17A antagonists of
generalized pustular psoriasis in patients without IL36RN
mutations. J Dermatol. 45:850–854. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Okubo Y, Mabuchi T, Iwatsuki K, Elmaraghy
H, Torisu-Itakura H, Morisaki Y and Nakajo K: Long-term efficacy
and safety of ixekizumab in Japanese patients with erythrodermic or
generalized pustular psoriasis: Subgroup analyses of an open-label,
phase 3 study (UNCOVER-J). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
33:325–332. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Ho PH and Tsai TF: Successful treatment of
refractory juvenile generalized pustular psoriasis with secukinumab
monotherapy: A case report and review of published work. J
Dermatol. 45:1353–1356. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Imafuku S, Honma M, Okubo Y, Komine M,
Ohtsuki M, Morita A, Seko N, Kawashima N, Ito S, Shima T and
Nakagawa H: Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in patients with
generalized pustular psoriasis: A 52-week analysis from phase III
open-label multi-center Japanese study. J Dermatol. 43:1011–1017.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Gabeff R, Safar R, Leducq S, Maruani A,
Sarrabay G, Touitou I and Samimi M: Successful therapy with
secukinumab in a patient with generalized pustular psoriasis
carrying homozygous IL36RN p.His32Arg mutation. Int J Dermatol.
58:e16–e17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Yamasaki K, Nakagawa H, Kubo Y and Ootaki
K; Japanese Brodalumab Study Group: Efficacy and safety of
brodalumab in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis and
psoriatic erythroderma: Results from a 52-week, open-label study.
Br J Dermatol. 176:741–751. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Storan ER, O'Gorman SM and Markham T:
Generalized pustular psoriasis treated with ustekinumab. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 41:689–690. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Arakawa A, Ruzicka T and Prinz JC:
Therapeutic efficacy of interleukin 12/interleukin 23 blockade in
generalized pustular psoriasis regardless of IL36RN mutation
status. JAMA Dermatol. 152:825–828. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Viguier M, Guigue P, Pages C, Smahi A and
Bachelez H: Successful treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis
with the interleukin-1-receptor antagonist Anakinra: Lack of
correlation with IL1RN mutations. Ann Intern Med. 153:66–67. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|