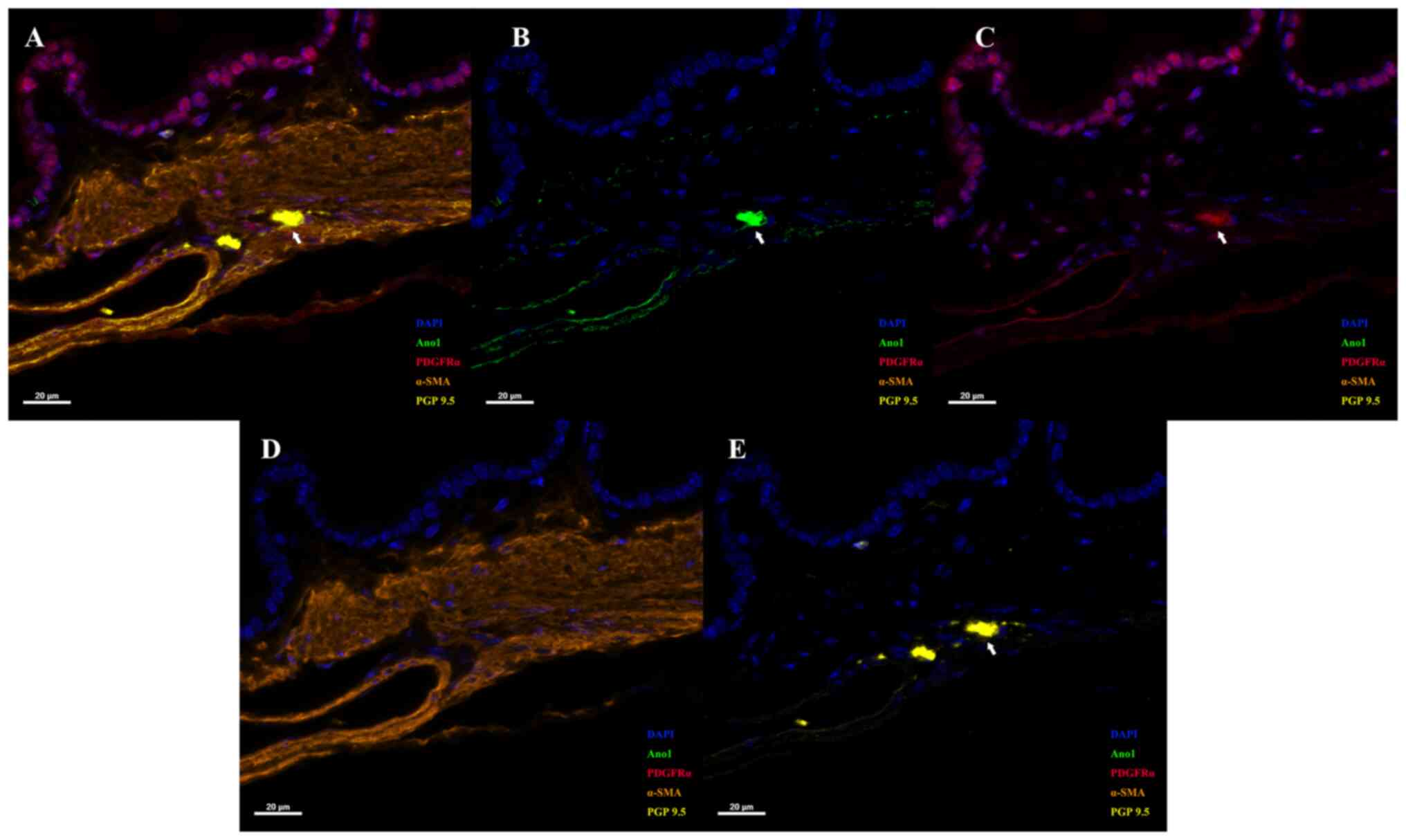
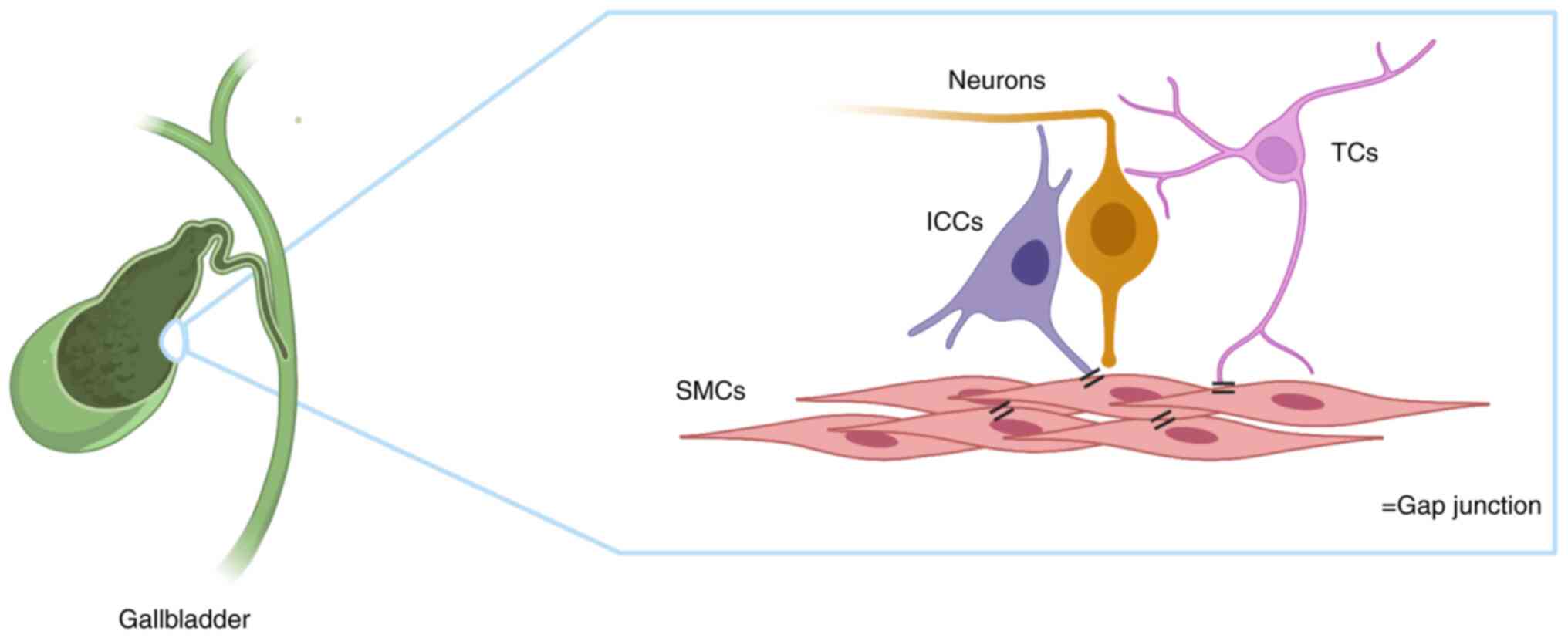
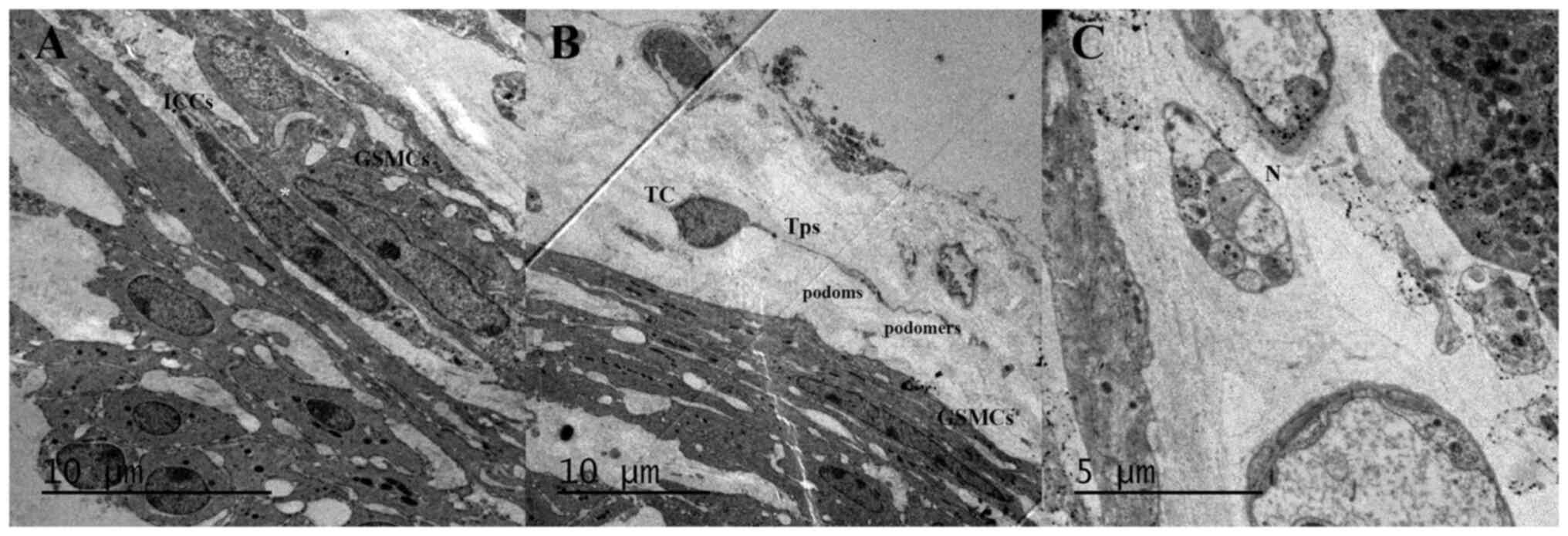
|
1
|
Boyer J: Bile formation and secretion.
Compr Physiol. 3:1035–1078. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lanzini A, Jazrawi RP and Northfield TC:
Simultaneous quantitative measurements of absolute gallbladder
storage and emptying during fasting and eating in humans.
Gastroenterology. 92:852–861. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Torsoli A, Corazziari E, Habib FI and
Cicala M: Pressure relationships within the human bile tract.
Normal and abnormal physiology. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl.
175:52–57. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lammert F, Gurusamy K, Ko CW, Miquel JF,
Méndez-Sánchez N, Portincasa P, van Erpecum KJ, van Laarhoven CJ
and Wang DQ: Gallstones. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160242016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gallaher J and Charles A: Acute
cholecystitis: A review. JAMA. 327:965–975. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bronkhorst MWGA, Terpstra V and Bouwman
LH: Polyp in the gallbladder. Gastroenterology. 141:e3–e4. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sanders KM, Koh S, Ro S and Ward SM:
Regulation of gastrointestinal motility-insights from smooth muscle
biology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:633–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huizinga JD, Zarate N and Farrugia G:
Physiology, injury, and recovery of interstitial cells of Cajal:
basic and clinical science. Gastroenterology. 137:1548–1556. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sanders KM, Koh SD and Ward SM:
Interstitial cells of cajal as pacemakers in the gastrointestinal
tract. Annu Rev Physiol. 68:307–343. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Horiguchi K and Komuro T: Ultrastructural
observations of fibroblast-like cells forming gap junctions in the
W/W(nu) mouse small intestine. J Auton Nerv Syst. 80:142–147. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Klemm MF and Lang RJ: Distribution of
Ca2+-activated K+ channel (SK2 and SK3)
immunoreactivity in intestinal smooth muscles of the guinea-pig.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 29:18–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Burnstock G: Autonomic neurotransmitters
and trophic factors. J Auton Nerv Syst. 7:213–217. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Spencer NJ and Hu H: Enteric nervous
system: Sensory transduction, neural circuits and gastrointestinal
motility. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:338–351. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Obermayr F, Hotta R, Enomoto H and Young
HM: Development and developmental disorders of the enteric nervous
system. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:43–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Popescu LM and Faussone-Pellegrini MS:
TELOCYTES-a case of serendipity: The winding way from interstitial
cells of Cajal (ICC), via interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) to
TELOCYTES. J Cell Mol Med. 14:729–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vannucchi MG, Traini C, Manetti M,
Ibba-Manneschi L and Faussone-Pellegrini MS: Telocytes express
PDGFRα in the human gastrointestinal tract. J Cell Mol Med.
17:1099–1108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rasmussen H, Rumessen JJ, Hansen A, Smedts
F and Horn T: Ultrastructure of Cajal-like interstitial cells in
the human detrusor. Cell Tissue Res. 335:517–527. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suciu L, Popescu LM, Gherghiceanu M,
Regalia T, Nicolescu MI, Hinescu ME and Faussone-Pellegrini MS:
Telocytes in human term placenta: Morphology and phenotype. Cells
Tissues Organs. 192:325–339. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vannucchi MG, Traini C, Guasti D, Del
Popolo G and Faussone-Pellegrini MS: Telocytes subtypes in human
urinary bladder. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2000–2008. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suciu LC, Popescu BO, Kostin S and Popescu
LM: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β-positive telocytes in
skeletal muscle interstitium. J Cell Mol Med. 16:701–707. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pieri L, Vannucchi MG and
Faussone-Pellegrini MS: Histochemical and ultrastructural
characteristics of an interstitial cell type different from ICC and
resident in the muscle coat of human gut. J Cell Mol Med.
12:1944–1955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen L and Yu B: Telocytes and
interstitial cells of Cajal in the biliary system. J Cell Mol Med.
22:3323–3329. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vannucchi MG: The telocytes: Ten years
after their introduction in the scientific literature. An update on
their morphology, distribution, and potential roles in the gut. Int
J Mol Sci. 21:44782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Jin M, Ma WH, Zhu Z and Wang X:
The history of telocyte discovery and understanding. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 913:1–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vannucchi MG and Faussone-Pellegrini MS:
The telocyte subtypes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 913:115–126. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cretoiu SM and Popescu LM: Telocytes
revisited. Biomol Concepts. 5:353–369. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhong X, Fu J, Song K, Xue N, Gong R, Sun
D, Luo H, He W, Pan X, Shen B and Du J: The role of TRPP2 in
agonist-induced gallbladder smooth muscle contraction. Sci China
Life Sci. 59:409–416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Morales S, Diez A, Puyet A, Camello PJ,
Camello-Almaraz C, Bautista JM and Pozo MJ: Calcium controls smooth
muscle TRPC gene transcription via the CaMK/calcineurin-dependent
pathways. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 292:C553–C563. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
McCarron JG, Olson ML, Rainbow RD,
MacMillan D and Chalmers S: Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptor regulation during
'quantal' Ca2+ release in smooth muscle. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 28:271–279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Quinn T, Feighery R and Baird AW: Role of
Rho-kinase in guinea-pig gallbladder smooth muscle contraction. Eur
J Pharmacol. 534:210–217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Balemba OB, Heppner TJ, Bonev AD, Nelson
MT and Mawe GM: Calcium waves in intact guinea pig gallbladder
smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
291:G717–G727. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan YY, Ji ZL, Zhao G, Jiang JR, Wang D
and Wang JM: Decreased SCF/c-kit signaling pathway contributes to
loss of interstitial cells of Cajal in gallstone disease. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 7:4099–4106. 2014.
|
|
33
|
Pasternak A, Gil K, Matyja A, Gajda M,
Sztefko K, Walocha JA, Kulig J and Thor P: Loss of gallbladder
interstitial Cajal-like cells in patients with cholelithiasis.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 25:e17–e24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liang J, Shao W, Liu Q, Lu Q, Gu A and
Jiang Z: Single cell RNA-sequencing reveals a murine gallbladder
cell transcriptome atlas during the process of cholesterol
gallstone formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7142712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cai WQ and Gabella G: The musculature of
the gall bladder and biliary pathways in the guinea-pig. J Anat.
136:237–250. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Horowitz A, Menice CB, Laporte R and
Morgan KG: Mechanisms of smooth muscle contraction. Physiol Rev.
76:967–1003. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ota N, Hirose H, Kato H, Maeda H and
Shiojiri N: Immunohistological analysis on distribution of smooth
muscle tissues in livers of various vertebrates with attention to
different liver architectures. Ann Anat. 233:1515942021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sanders KM: Chapter 1-Nerves, smooth
muscle cells and interstitial cells in the GI tract: Molecular and
cellular interactions. Clinical and Basic Neurogastroenterology and
Motility. 3–16. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sun X, Yu B, Xu L, Dong W and Luo H:
Interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine gallbladder. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 41:1218–1226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ahmadi O, Nicholson Mde L, Gould ML,
Mitchell A and Stringer MD: Interstitial cells of Cajal are present
in human extrahepatic bile ducts. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
25:277–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hinescu ME, Ardeleanu C, Gherghiceanu M
and Popescu LM: Interstitial Cajal-like cells in human gallbladder.
J Mol Histol. 38:275–284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pasternak A, Szura M, Gil K and Matyja A:
Interstitial cells of Cajal-systematic review. Folia Morphol
(Warsz). 75:281–286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lavoie B, Balemba OB, Nelson MT, Ward SM
and Mawe GM: Morphological and physiological evidence for
interstitial cell of Cajal-like cells in the guinea pig
gallbladder. J Physiol. 579:487–501. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gomez-Pinilla PJ, Gibbons SJ, Bardsley MR,
Lorincz A, Pozo MJ, Pasricha PJ, Van de Rijn M, West RB, Sarr MG,
Kendrick ML, et al: Ano1 is a selective marker of interstitial
cells of Cajal in the human and mouse gastrointestinal tract. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 296:G1370–G1381. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu MH, Sung TS, Kurahashi M, O'Kane LE,
O'Driscoll K, Koh SD and Sanders KM:
Na+-K+-Cl- cotransporter (NKCC) maintains the
chloride gradient to sustain pacemaker activity in interstitial
cells of Cajal. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
311:G1037–G1046. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pasternak A, Gajda M, Gil K, Matyja A,
Tomaszewski KA, Walocha JA, Kulig J and Thor P: Evidence of
interstitial Cajal-like cells in human gallbladder. Folia Histochem
Cytobiol. 50:581–585. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cantarero I, Luesma MJ, Alvarez-Dotu JM,
Muñoz E and Junquera C: Transmission electron microscopy as key
technique for the characterization of telocytes. Curr Stem Cell
Res. 11:410–414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Peri LE, Sanders KM and
Mutafova-Yambolieva VN: Differential expression of genes related to
purinergic signaling in smooth muscle cells, PDGFRα-positive cells,
and interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine colon.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 25:e609–e620. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu C, Huang X, Lu HL, Liu SH, Zang JY, Li
YJ, Chen J and Xu WX: Different distributions of interstitial cells
of Cajal and platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α positive
cells in colonic smooth muscle cell/interstitial cell of
Cajal/platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α positive cell
syncytium in mice. World J Gastroenterol. 24:4989–5004. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yeoh JW, Corrias A and Buist ML: A
mechanistic model of a PDGFRα(+) cell. J Theor Biol. 408:127–136.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bolton TB, Prestwich SA, Zholos AV and
Gordienko DV: Excitation-contraction coupling in gastrointestinal
and other smooth muscles. Annu Rev Physiol. 61:85–115. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang L, Bonev AD, Nelson MT and Mawe GM:
Ionic basis of the action potential of guinea pig gallbladder
smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 265:C1552–C1561. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shimada T: Voltage-dependent calcium
channel current in isolated gallbladder smooth muscle cells of
guinea pig. Am J Physiol. 264:G1066–G1076. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu Z and Shen W: Progesterone inhibits
L-type calcium currents in gallbladder smooth muscle cells. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:1838–1843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wu ZX, Yu BP, Xia H and Xu L: Emodin
increases Ca(2+) influx through L-type Ca(2+) channel in guinea pig
gallbladder smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 595:95–99. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Petkov GV, Balemba OB, Nelson MT and Mawe
GM: Identification of a spontaneously active,
Na+-permeable channel in guinea pig gallbladder smooth
muscle. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 289:G501–G507.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Parr E, Pozo MJ, Horowitz B, Nelson MT and
Mawe GM: ERG K+ channels modulate the electrical and
contractile activities of gallbladder smooth muscle. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 284:G392–G398. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wu ZX, Yu BP, Xu L and Xia H: Emodin
inhibits voltage-dependent potassium current in guinea pig
gallbladder smooth muscle. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
105:167–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jaggar JH, Mawe GM and Nelson MT:
Voltage-dependent K+ currents in smooth muscle cells
from mouse gallbladder. Am J Physiol. 274:G687–G693. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Vandenberg JI, Perry MD, Perrin MJ, Mann
SA, Ke Y and Hill AP: hERG K(+) channels: structure, function, and
clinical significance. Physiol Rev. 92:1393–1478. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ashcroft SJ and Ashcroft FM: Properties
and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 2:197–214.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang L, Bonev AD, Nelson MT and Mawe GM:
Activation of ATP-sensitive potassium currents in guinea-pig
gall-bladder smooth muscle by the neuropeptide CGRP. J Physiol.
478:483–491. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hemming JM, Guarraci FA, Firth TA,
Jennings LJ, Nelson MT and Mawe GM: Actions of histamine on muscle
and ganglia of the guinea pig gallbladder. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 279:G622–G630. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Pozo MJ, Pérez GJ, Nelson MT and Mawe GM:
Ca(2+) sparks and BK currents in gallbladder myocytes: Role in
CCK-induced response. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
282:G165–G174. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Dopico AM, Walsh JV Jr and Singer JJ:
Natural bile acids and synthetic analogues modulate large
conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channel
activity in smooth muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 119:251–273. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Song K, Zhong XG, Xia XM, Huang JH, Fan
YF, Yuan RX, Xue NR, Du J, Han WX, Xu AM and Shen B: Orai1 forms a
signal complex with SK3 channel in gallbladder smooth muscle.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 466:456–462. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kuo IY and Ehrlich BE: Signaling in muscle
contraction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7:a0060232015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wellman GC and Nelson MT: Signaling
between SR and plasmalemma in smooth muscle: Sparks and the
activation of Ca2+-sensitive ion channels. Cell Calcium.
34:211–229. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Putney JW: Capacitative calcium entry:
From concept to molecules. Immunol Rev. 231:10–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Berridge MJ: Capacitative calcium entry.
Biochem J. 312:1–11. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Quinn T, Molloy M, Smyth A and Baird AW:
Capacitative calcium entry in guinea pig gallbladder smooth muscle
in vitro. Life Sci. 74:1659–1669. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Morales S, Camello PJ, Rosado JA, Mawe GM
and Pozo MJ: Disruption of the filamentous actin cytoskeleton is
necessary for the activation of capacitative calcium entry in naive
smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal. 17:635–645. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Albert AP and Large WA: Store-operated
Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channels in smooth
muscle cells. Cell Calcium. 33:345–356. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Pan Z, Yang H and Reinach PS: Transient
receptor potential (TRP) gene superfamily encoding cation channels.
Hum Genomics. 5:108–116. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Mochizuki T, Wu G, Hayashi T, Xenophontos
SL, Veldhuisen B, Saris JJ, Reynolds DM, Cai Y, Gabow PA, Pierides
A, et al: PKD2, a gene for polycystic kidney disease that encodes
an integral membrane protein. Science. 272:1339–1342. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
González-Perrett S, Kim K, Ibarra C,
Damiano AE, Zotta E, Batelli M, Harris PC, Reisin IL, Arnaout MA
and Cantiello HF: Polycystin-2, the protein mutated in autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), is a
Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channel. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:1182–1187. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Zhao R, Zhou M, Li J, Wang X, Su K, Hu J,
Ye Y, Zhu J, Zhang G, Wang K, et al: Increased TRPP2 expression in
vascular smooth muscle cells from high-salt intake hypertensive
rats: The crucial role in vascular dysfunction. Mol Nutr Food Res.
59:365–372. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Spirli C, Locatelli L, Fiorotto R, Morell
CM, Fabris L, Pozzan T and Strazzabosco M: Altered store operated
calcium entry increases cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate
production and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2
phosphorylation in polycystin-2-defective cholangiocytes.
Hepatology. 55:856–868. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Balemba OB, Salter MJ, Heppner TJ, Bonev
AD, Nelson MT and Mawe GM: Spontaneous electrical rhythmicity and
the role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in the excitability of
guinea pig gallbladder smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 290:G655–G664. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Ehrlich BE and Watras J: Inositol
1,4,5-trisphosphate activates a channel from smooth muscle
sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 336:583–586. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Xu L, Lai FA, Cohn A, Etter E, Guerrero A,
Fay FS and Meissner G: Evidence for a Ca(2+)-gated
ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ release channel in visceral
smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:3294–3298. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
McCarron JG, Bradley KN, MacMillan D and
Muir TC: Sarcolemma agonist-induced interactions between InsP3 and
ryanodine receptors in Ca2+ oscillations and waves in
smooth muscle. Biochem Soc Trans. 31:920–924. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Camello-Almaraz C, Macias B, Gomez-Pinilla
PJ, Alcon S, Martin-Cano FE, Baba A, Matsuda T, Camello PJ and Pozo
MJ: Developmental changes in Ca2+ homeostasis and
contractility in gallbladder smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 296:C783–C791. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Somlyo AP and Somlyo AV: Ca2+
sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: Modulated by
G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev.
83:1325–1358. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Louie DS: Cholecystokinin-stimulated
intracellular signal transduction pathways. J Nutr. 124(8 Suppl):
1315S–1320S. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Yu P, Chen Q, Xiao Z, Harnett K, Biancani
P and Behar J: Signal transduction pathways mediating CCK-induced
gallbladder muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 275:G203–G211.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Parkman HP, Pagano AP and Ryan JP:
Subtypes of muscarinic receptors regulating gallbladder cholinergic
contractions. Am J Physiol. 276:G1243–G1250. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Büyükafşar K, Akça T, Nalan Tiftik R,
Sahan-Firat S and Aydin S: Contribution of Rho-kinase in human
gallbladder contractions. Eur J Pharmacol. 540:162–167. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Romański KW: Ovine model for clear-cut
study on the role of cholecystokinin in antral, small intestinal
and gallbladder motility. Pol J Pharmacol. 56:247–256. 2004.
|
|
90
|
Fleckenstein P, Bueno L, Fioramonti J and
Ruckebusch Y: Minute rhythm of electrical spike bursts of the small
intestine in different species. Am J Physiol. 242:G654–G659.
1982.
|
|
91
|
Romański KW: Characteristics and
cholinergic control of the 'minute rhythm' in ovine antrum, small
bowel and gallbladder. J Vet Med A Physiol Pathol Clin Med.
49:313–320. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Klein S, Seidler B, Kettenberger A, Sibaev
A, Rohn M, Feil R, Allescher HD, Vanderwinden JM, Hofmann F,
Schemann M, et al: Interstitial cells of Cajal integrate excitatory
and inhibitory neurotransmission with intestinal slow-wave
activity. Nat Commun. 4:16302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Fan Y, Wu S, Fu B, Weng C and Wang X: The
role of interstitial Cajal-like cells in the formation of
cholesterol stones in guinea pig gallbladder. Hepatol Int.
9:612–620. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Sanders KM, Ward SM and Koh SD:
Interstitial cells: Regulators of smooth muscle function. Physiol
Rev. 94:859–907. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Hwang SJ, Blair PJ, Britton FC, O'Driscoll
KE, Hennig G, Bayguinov YR, Rock JR, Harfe BD, Sanders KM and Ward
SM: Expression of anoctamin 1/TMEM16A by interstitial cells of
Cajal is fundamental for slow wave activity in gastrointestinal
muscles. J Physiol. 587:4887–4904. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Zhu MH, Kim TW, Ro S, Yan W, Ward SM, Koh
SD and Sanders KM: A Ca(2+)-activated Cl(-) conductance in
interstitial cells of Cajal linked to slow wave currents and
pacemaker activity. J Physiol. 587:4905–4918. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Pappas A and Wellman GC: Setting the pace
for GI motility: Ryanodine receptors and IP3 receptors within
interstitial cells of Cajal. Focus on 'intracellular
Ca2+ release from endoplasmic reticulum regulates slow
wave currents and pacemaker activity of interstitial cells of
Cajal'. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 308:C606–C607. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Koh SD, Sanders KM and Ward SM:
Spontaneous electrical rhythmicity in cultured interstitial cells
of cajal from the murine small intestine. J Physiol. 513:203–213.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Koh SD, Jun JY, Kim TW and Sanders KM: A
Ca(2+)-inhibited non-selective cation conductance contributes to
pacemaker currents in mouse interstitial cell of Cajal. J Physiol.
540:803–814. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Baker SA, Leigh WA, Del Valle G, De
Yturriaga IF, Ward SM, Cobine CA, Drumm BT and Sanders KM:
Ca2+ signaling driving pacemaker activity in submucosal
interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine colon. Elife.
10:e640992021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Sanders KM: Spontaneous electrical
activity and rhythmicity in gastrointestinal smooth muscles. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 1124:3–46. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Huang X, Lee SH, Lu H, Sanders KM and Koh
SD: Molecular and functional characterization of inwardly
rectifying K+ currents in murine proximal colon. J
Physiol. 596:379–391. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Kito Y, Mitsui R, Ward SM and Sanders KM:
Characterization of slow waves generated by myenteric interstitial
cells of Cajal of the rabbit small intestine. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 308:G378–G388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
104
|
Youm JB, Zheng H, Koh SD and Sanders KM:
Na-K-2Cl cotransporter and store-operated Ca2+ entry in
pacemaking by interstitial cells of Cajal. Biophys J. 117:767–779.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wouters M, De Laet A, Donck LV, Delpire E,
van Bogaert PP, Timmermans JP, de Kerchove d'Exaerde A, Smans K and
Vanderwinden JM: Subtractive hybridization unravels a role for the
ion cotransporter NKCC1 in the murine intestinal pacemaker. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 290:G1219–G1227. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Balemba OB, Bartoo AC, Nelson MT and Mawe
GM: Role of mitochondria in spontaneous rhythmic activity and
intracellular calcium waves in the guinea pig gallbladder smooth
muscle. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 294:G467–G476.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Blaustein MP and Lederer WJ:
Sodium/calcium exchange: Its physiological implications. Physiol
Rev. 79:763–854. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zheng H, Drumm BT, Zhu MH, Xie Y,
O'Driscoll KE, Baker SA, Perrino BA, Koh SD and Sanders KM:
Na(+)/Ca(2 +) exchange and pacemaker activity of interstitial cells
of Cajal. Front Physiol. 11:2302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Vanderwinden JM, Rumessen JJ, de Kerchove
d'Exaerde A Jr, Gillard K, Panthier JJ, de Laet MH and Schiffmann
SN: Kit-negative fibroblast-like cells expressing SK3, a
Ca2+-activated K+ channel, in the gut musculature in
health and disease. Cell Tissue Res. 310:349–358. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Gallego D, Hernández P, Clavé P and
Jiménez M: P2Y1 receptors mediate inhibitory purinergic
neuromuscular transmission in the human colon. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 291:G584–G594. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Kurahashi M, Zheng H, Dwyer L, Ward SM,
Koh SD and Sanders KM: A functional role for the 'fibroblast-like
cells' in gastrointestinal smooth muscles. J Physiol. 589:697–710.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Gallego D, Gil V, Martínez-Cutillas M,
Mañé N, Martín MT and Jiménez M: Purinergic neuromuscular
transmission is absent in the colon of P2Y(1) knocked out mice. J
Physiol. 590:1943–1956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Vogalis F and Goyal RK: Activation of
small conductance Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels by purinergic
agonists in smooth muscle cells of the mouse ileum. J Physiol.
502:497–508. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Kurahashi M, Mutafova-Yambolieva V, Koh SD
and Sanders KM: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α-positive
cells and not smooth muscle cells mediate purinergic
hyperpolarization in murine colonic muscles. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 307:C561–C570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Baker SA, Hennig GW, Ward SM and Sanders
KM: Temporal sequence of activation of cells involved in purinergic
neurotransmission in the colon. J Physiol. 593:1945–1963. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
116
|
Furness J: The enteric nervous system and
neurogastroenterology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:286–294.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Furness JB, Callaghan BP, Rivera LR and
Cho HJ: The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal
innervation: integrated local and central control. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 817:39–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Balemba OB, Salter MJ and Mawe GM:
Innervation of the extrahepatic biliary tract. Anat Rec A Discov
Mol Cell Evol Biol. 280:836–847. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Keast JR, Furness JB and Costa M:
Distribution of certain peptide-containing nerve fibres and
endocrine cells in the gastrointestinal mucosa in five mammalian
species. J Comp Neurol. 236:403–422. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Cai WQ and Gabella G: Innervation of the
gall bladder and biliary pathways in the guinea-pig. J Anat.
136:97–109. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Talmage EK, Pouliot WA, Schemann M and
Mawe GM: Structure and chemical coding of human, canine and opossum
gallbladder ganglia. Cell Tissue Res. 284:289–302. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Gilloteaux J, Pomerants B and Kelly TR:
Human gallbladder mucosa ultrastructure: Evidence of
intraepithelial nerve structures. Am J Anat. 184:321–333. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
De Giorgio R, Zittel TT, Parodi JE, Becker
JM, Brunicardi FC, Go VL, Brecha NC and Sternini C: Peptide
immunoreactivities in the ganglionated plexuses and nerve fibers
innervating the human gallbladder. J Auton Nerv Syst. 51:37–47.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
De Giorgio R, Parodi JE, Brecha NC,
Brunicardi FC, Becker JM, Go VL and Sternini C: Nitric oxide
producing neurons in the monkey and human digestive system. J Comp
Neurol. 342:619–627. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Mawe GM and Ellis LM: Chemical coding of
intrinsic and extrinsic nerves in the guinea pig gallbladder:
Distributions of PACAP and orphanin FQ. Anat Rec. 262:101–109.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Talmage EK, Pouliot WA, Cornbrooks EB and
Mawe GM: Transmitter diversity in ganglion cells of the guinea pig
gallbladder: An immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol.
317:45–56. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Sundler F, Alumets J, Håkanson R,
Ingemansson S, Fahrenkrug J and Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O: VIP
innervation of the gallbladder. Gastroenterology. 72:1375–1377.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Uemura S, Pompolo S, Furness JB and Hardy
KJ: Nitric oxide synthase in neurons of the human gall-bladder and
its colocalization with neuropeptides. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
12:257–265. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Hopton DS: The influence of the vagus
nerves on the biliary system. Br J Surg. 60:216–218. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Mawe GM, Moses PL, Saccone GTP and Pozo
MJ: Motility of the Biliary Tract. Textbook of Gastroenterology.
264–283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Schjoldager B, Molero X and Miller LJ:
Functional and biochemical characterization of the human
gallbladder muscularis cholecystokinin receptor. Gastroenterology.
96:1119–1125. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Xu D, Yu BP, Luo HS and Chen LD: Control
of gallbladder contractions by cholecystokinin through
cholecystokinin-a receptors on gallbladder interstitial cells of
Cajal. World J Gastroenterol. 14:2882–2887. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Mawe GM, Gokin AP and Wells DG: Actions of
cholecystokinin and norepinephrine on vagal inputs to ganglion
cells in guinea pig gallbladder. Am J Physiol. 267:G1146–G1151.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Behar J and Biancani P: Pharmacologic
characterization of excitatory and inhibitory cholecystokinin
receptors of the cat gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi.
Gastroenterology. 92:764–770. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Stengel PW and Cohen ML: Muscarinic
receptor knockout mice: Role of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
M(2), M(3), and M(4) in carbamylcholine-induced gallbladder
contractility. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 301:643–650. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Takahashi T, Kurosawa S and Owyang C:
Regulation of PI hydrolysis and cAMP formation by muscarinic M3
receptor in guinea pig gallbladder. Am J Physiol. 267:G523–G528.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Lee MC, Yang YC, Chen YC and Huang SC:
Muscarinic receptor M3 mediates human gallbladder contraction
through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and Rho kinase.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 48:205–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Patacchini R and Maggi CA: Effect of newly
developed tachykinin agonist and antagonists on the guinea pig
isolated gallbladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 261:191–194.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Yau WM: Mode of stimulation of gallbladder
contraction by substance K. Am J Physiol. 259:G838–G841.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
O'Riordan AM, Quinn T and Baird AW: Role
of prostaglandin E(2) and Ca(2+) in bradykinin induced contractions
of guinea-pig gallbladder in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 431:245–252.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Trevisani M, Amadesi S, Schmidlin F,
Poblete MT, Bardella E, Maggiore B, Harrison S, Figueroa CD,
Tognetto M, Navarra G, et al: Bradykinin B2 receptors mediate
contraction in the normal and inflamed human gallbladder in vitro.
Gastroenterology. 125:126–135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Andre E, Gazzieri D, Bardella E, Ferreira
J, Mori MA, Saul VV, Bader M, Calixto JB, De Giorgio R, Corinaldesi
R, et al: Expression and functional pharmacology of the bradykinin
B1 receptor in the normal and inflamed human gallbladder. Gut.
57:628–633. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Takahashi T, Kusunoki M, Ishikawa Y,
Kantoh M, Yamamura T and Utsunomiya J: Adenosine 5′-triphosphate
release evoked by electrical nerve stimulation from the guinea-pig
gallbladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 134:77–82. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Puchałowicz K, Tarnowski M,
Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Chlubek D and Dziedziejko V: P2X and P2Y
receptors-role in the pathophysiology of the nervous system. Int J
Mol Sci. 15:23672–23704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Bartoo AC, Nelson MT and Mawe GM: ATP
induces guinea pig gallbladder smooth muscle excitability via the
P2Y4 receptor and COX-1 activity. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 294:G1362–G1368. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Ruan HZ and Burnstock G: P2X2 and P2X3
receptor expression in the gallbladder of the guinea pig. Auton
Neurosci. 111:89–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Rasmussen TN, Harling H, Rehfeld JF and
Holst JJ: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a potent
regulator of biliary flow. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 9:215–220.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Kline LW and Pang PK: Cyclic AMP modulates
part of the relaxant action of calcitonin gene-related peptide in
guinea pig gallbladder strips. Regul Pept. 72:55–59. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Kline LW and Pang PK: Nitric oxide
modulates the calcitonin gene-related peptide-induced relaxation in
guinea pig gallbladder strips in vitro. Regul Pept. 50:207–212.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Gultekin H, Erdem SR, Emre-Aydingoz S and
Tuncer M: The role of nitric oxide in the electrical field
stimulation-induced contractions of sphincter of oddi and
gallbladder strips in Guinea pigs. J Pharmacol Sci. 101:240–244.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Alcón S, Morales S, Camello PJ, Salido GM,
Miller SM and Pozo MJ: Relaxation of canine gallbladder to nerve
stimulation involves adrenergic and non-adrenergic non-cholinergic
mechanisms. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 13:555–566. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Xue L, Farrugia G, Miller SM, Ferris CD,
Snyder SH and Szurszewski JH: Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide as
coneurotransmitters in the enteric nervous system: Evidence from
genomic deletion of biosynthetic enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:1851–1855. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Harmar AJ, Fahrenkrug J, Gozes I, Laburthe
M, May V, Pisegna JR, Vaudry D, Vaudry H, Waschek JA and Said SI:
Pharmacology and functions of receptors for vasoactive intestinal
peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide:
IUPHAR review 1. Br J Pharmacol. 166:4–17. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
154
|
Pálvölgyi A, Sári R, Németh J, Szabolcs A,
Nagy I, Hegyi P, Lonovics J and Szilvássy Z: Interplay between
nitric oxide and VIP in CCK-8-induced phasic contractile activity
in the rabbit sphincter of Oddi. World J Gastroenterol.
11:3264–3266. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Pang PK and Kline LW: Protein kinase C
mediates the contractile actions of pituitary adenylate cyclase
activating polypeptide in guinea pig gallbladder strips. Regul
Pept. 77:63–67. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Greaves RR, O'Donnell LJ, Battistini B,
Forget MA and Farthing MJ: The differential effect of VIP and PACAP
on guinea pig gallbladder in vitro. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
12:1181–1184. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Parkman HP, Pagano AP and Ryan JP: Dual
effects of PACAP on guinea pig gallbladder muscle via
PACAP-preferring and VIP/PACAP-preferring receptors. Am J Physiol.
272:G1433–G1438. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Fisher RS, Rock E, Levin G and Malmud L:
Effects of somatostatin on gallbladder emptying. Gastroenterology.
92:885–890. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Greenberg GR, McCloy RF, Adrian TE,
Chadwick VS, Baron JH and Bloom SR: Inhibition of pancreas and
gallbladder by pancreatic polypeptide. Lancet. 2:1280–1282. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Walker JP, Khalil T, Wiener I, Fagan CJ,
Townsend CM Jr, Greeley GH Jr and Thompson JC: The role of
neurotensin in human gallbladder motility. Ann Surg. 201:678–683.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Holzer P, Reichmann F and Farzi A:
Neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide in the
gut-brain axis. Neuropeptides. 46:261–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Chen Q, Lee K, Xiao Z, Biancani P and
Behar J: Mechanism of gallbladder relaxation in the cat: Role of
norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 285:475–479. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
McGowan BMC and Bloom SR: Peptide YY and
appetite control. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 4:583–588. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Hoentjen F, Hopman WP and Jansen JB:
Effect of circulating peptide YY on gallbladder emptying in humans.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 36:1086–1091. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Hazelwood RL: The pancreatic polypeptide
(PP-fold) family: Gastrointestinal, vascular, and feeding
behavioral implications. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 202:44–63. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Kojima S, Ueno N, Asakawa A, Sagiyama K,
Naruo T, Mizuno S and Inui A: A role for pancreatic polypeptide in
feeding and body weight regulation. Peptides. 28:459–463. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Vu MK, Van Oostayen JA, Biemond I and
Masclee AA: Effect of somatostatin on postprandial gallbladder
relaxation. Clin Physiol. 21:25–31. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Maselli MA, Piepoli AL, Pezzolla F, Caruso
ML and Lorusso D: Effect of somatostatin on human gallbladder
motility: An in vitro study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 11:47–53.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Milenov K, Vassileva M, Marinova D and
Kalfin R: Effect of neurotensin on the canine gallbladder motility:
In vivo and in vitro experiments. Neuropeptides. 25:233–239. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Yamasato T and Nakayama S: Effects of
neurotensin on the motility of the isolated gallbladder, bile duct
and ampulla in guinea-pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 148:101–106. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Feeley TM, Clanachan AS and Scott GW:
Contractility of human gallbladder muscle in vitro. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 1:607–616. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Lavoie B, Balemba OB, Godfrey C, Watson
CA, Vassileva G, Corvera CU, Nelson MT and Mawe GM: Hydrophobic
bile salts inhibit gallbladder smooth muscle function via
stimulation of GPBAR1 receptors and activation of KATP channels. J
Physiol. 588:3295–3305. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Jain AK, Stoll B, Burrin DG, Holst JJ and
Moore DD: Enteral bile acid treatment improves parenteral
nutrition-related liver disease and intestinal mucosal atrophy in
neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
302:G218–G224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
174
|
Yusta B, Matthews D, Flock GB, Ussher JR,
Lavoie B, Mawe GM and Drucker DJ: Glucagon-like peptide-2 promotes
gallbladder refilling via a TGR5-independent, GLP-2R-dependent
pathway. Mol Metab. 6:503–511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Kliewer SA and Mangelsdorf DJ: Bile acids
as hormones: The FXR-FGF15/19 pathway. Dig Dis. 33:327–331. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Everhart JE and Ruhl CE: Burden of
digestive diseases in the United States Part III: Liver, biliary
tract, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 136:1134–1144. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Cai JS, Qiang S and Bao-Bing Y: Advances
of recurrent risk factors and management of choledocholithiasis.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 52:34–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Behar J, Lee KY, Thompson WR and Biancani
P: Gallbladder contraction in patients with pigment and cholesterol
stones. Gastroenterology. 97:1479–1484. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Carey MC and Small DM: The physical
chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to
gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J Clin Invest.
61:998–1026. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Zheng Y, Xu M, Heianza Y, Ma W, Wang T,
Sun D, Albert CM, Hu FB, Rexrode KM, Manson JE and Qi L: Gallstone
disease and increased risk of mortality: Two large prospective
studies in US men and women. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 33:1925–1931.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Huang L, Ding C and Si X: Changes in the
interstitial cells of Cajal in the gallbladder of guinea pigs fed a
lithogenic diet. Exp Ther Med. 22:8232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Xiao ZL, Chen Q, Amaral J, Biancani P and
Behar J: Defect of receptor-G protein coupling in human gallbladder
with cholesterol stones. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
278:G251–G258. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Gao G, Ding ZQ and Zou SQ: The changes of
vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and VIPR expression in the
patients with cholesterol gallstone. J Clinc Surg. 12:224–226.
2004.
|
|
184
|
Wang HH, Portincasa P and Wang DQH: Update
on the molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of
cholecystokinin and cholecystokinin-1 receptor on the formation of
cholesterol gallstones. Curr Med Chem. 26:3407–3423. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Tan YY: Studies on the role of Cajal
interstitial cell in cholecystolithiasis and surgical methodology
of endoscopic minimal invasive cholecystolithotomy. Dongnan Daxue.
58–91. 2015.
|
|
186
|
Fu BB, Xu JH, Wu SD and Fan Y: Effect of
cholesterol on in vitro cultured interstitial Cajal-like cells
isolated from guinea pig gallbladders. World J Gastrointest Surg.
12:226–235. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Lavoie B, Nausch B, Zane EA, Leonard MR,
Balemba OB, Bartoo AC, Wilcox R, Nelson MT, Carey MC and Mawe GM:
Disruption of gallbladder smooth muscle function is an early
feature in the development of cholesterol gallstone disease.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 24. pp. e313–e324. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Chen Q, Amaral J, Biancani P and Behar J:
Excess membrane cholesterol alters human gallbladder muscle
contractility and membrane fluidity. Gastroenterology. 116:678–685.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Wang B, Ding YM, Wang CT and Wang WX: Role
of ROCK expression in gallbladder smooth muscle contraction. Mol
Med Rep. 12:2907–2911. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Xu QW, Freedman SM and Shaffer EA:
Inhibitory effect of bile salts on gallbladder smooth muscle
contractility in the guinea pig in vitro. Gastroenterology.
112:1699–1706. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Rutishauser SC: Effects of bile salts on
the motor activity of the guinea-pig gall-bladder in vitro. Q J Exp
Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 63:265–276. 1978.
|
|
192
|
Pasternak A, Matyja A, Gil K, Gajda M,
Tomaszewski KA, Gajda M, Tomaszewski KA, Matyja M, Walocha JA and
Kulig J: Interstitial cajal-like cells and bile lithogenicity in
the pathogenesis of gall-stone disease. Pol Przegl Chir.
85:311–316. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
193
|
Villanacci V, Del Sordo R, Salemme M,
Cadei M, Sidoni A and Bassotti G: The enteric nervous system in
patients with calculous and acalculous gallbladder. Dig Liver Dis.
48:792–795. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Fu Y, Pang L, Dai W, Wu S and Kong J:
Advances in the study of acute acalculous cholecystitis: A
comprehensive review. Dig Dis. 40:468–478. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
195
|
Cong P, Xiao ZL, Biancani P and Behar J:
Prostaglandins mediate tonic contraction of the guinea pig and
human gallbladder. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
292:G409–G418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
Xiao ZL, Amaral J, Biancani P and Behar J:
Impaired cytoprotective function of muscle in human gallbladders
with cholesterol stones. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
288:G525–G532. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Myers SI, Bartula LL, Colvin MP, Parkman
HP, Braverman AA and Ruggieri MR: Bile duct ligation induced acute
inflammation up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 content and PGE2 release
in guinea pig gallbladder smooth muscle cell cultures.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 72:327–333. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Parkman HP, James AN, Thomas RM, Bartula
LL, Ryan JP and Myers SI: Effect of indomethacin on gallbladder
inflammation and contractility during acute cholecystitis. J Surg
Res. 96:135–142. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
199
|
Jennings LJ and Mawe GM: PGE2
hyperpolarizes gallbladder neurons and inhibits synaptic potentials
in gallbladder ganglia. Am J Physiol. 274:G493–G502. 1998.
|
|
200
|
Parkman HP, James AN, Bogar LJ, Bartula
LL, Thomas RM, Ryan JP and Myers SI: Effect of acalculous
cholecystitis on gallbladder neuromuscular transmission and
contractility. J Surg Res. 88:186–192. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Xiao ZL, Andrada MJ, Biancani P and Behar
J: Reactive oxygen species (H(2)O(2)): Effects on the gallbladder
muscle of guinea pigs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
282:G300–G306. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Cullen JJ, Conklin JL, Ephgrave KS and
Oberley LW: The role of antioxidant enzymes in the control of
opossum gallbladder motility. J Surg Res. 86:155–161. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
203
|
Pozo MJ, Camello PJ and Mawe GM: Chemical
mediators of gallbladder dysmotility. Curr Med Chem. 11:1801–1812.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Jennings LJ, Salido GM, Pozo MJ, Davison
JS, Sharkey KA, Lea RW and Singh J: The source and action of
histamine in the isolated guinea-pig gallbladder. Inflamm Res.
44:447–453. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Al-Jiffry BO, Shaffer EA, Woods CM,
Menadue M, Young F, Oliver J, Thomas AC, Toouli J and Saccone GT:
Endogenous endothelin increases gallbladder tone and leads to acute
cholecystitis in the Australian possum. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
16:125–133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Huang SC, Lee MC, Wei CK and Huang SM:
Endothelin receptors in human and guinea-pig gallbladder muscle.
Regul Pept. 98:145–153. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Huang ZP, Qiu H, Yang Y and Yu BP: Effect
of neutrophils on gallbladder interstitial cajal-like cells in
guinea pig model of acute cholecystitis. Cell Physiol Biochem.
39:2033–2043. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Lin MJ, Chen L, Huang ZP, Qiu H and Yu BP:
Neutrophils injure gallbladder interstitial Cajal-like cells in a
guinea pig model of acute cholecystitis. J Cell Physiol.
234:4291–4301. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
209
|
Burns AJ, Herbert TM, Ward SM and Sanders
KM: Interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal
tract as revealed by c-Kit immunohistochemistry. Cell Tissue Res.
290:11–20. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Christensen J: A commentary on the
morphological identification of interstitial cells of Cajal in the
gut. J Auton Nerv Syst. 37:75–88. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Ward SM, Burke EP and Sanders KM: Use of
rhodamine 123 to label and lesion interstitial cells of Cajal in
canine colonic circular muscle. Anat Embryol (Berl). 182:215–224.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Mikkelsen HB, Thuneberg L and Wittrup IH:
Selective double staining of interstitial cells of Cajal and
macrophage-like cells in small intestine by an improved supravital
methylene blue technique combined with FITC-dextran uptake. Anat
Embryol (Berl). 178:191–195. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Xue C, Ward SM, Shuttleworth CW and
Sanders KM: Identification of interstitial cells in canine proximal
colon using NADH diaphorase histochemistry. Histochemistry.
99:373–384. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Huang Y, Mei F, Yu B, Zhang HJ, Han J,
Jiang ZY and Zhou DS: Distribution of the interstitial Cajal-like
cells in the gallbladder and extrahepatic biliary duct of the
guinea-pig. Acta Histochem. 111:157–165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
215
|
Vannucchi MG and Traini C: Interstitial
cells of Cajal and telocytes in the gut: Twins, related or simply
neighbor cells? Biomol Concepts. 7:93–102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Sugai M: Morphological studies of human
gallbladder. Nihon Heikatsukin Gakkai Zasshi. 21:119–138. 1985.In
Japanese. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
217
|
Hartshorne DJ, Ito M and Erdödi F: Myosin
light chain phosphatase: Subunit composition, interactions and
regulation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 19:325–341. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Mnh: Histologie du système nerveux de
l'homme et des vertébrés. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 57:8831998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
219
|
Cawston EE and Miller LJ: Therapeutic
potential for novel drugs targeting the type 1 cholecystokinin
receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 159:1009–1021. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
220
|
Zhang L, Bonev AD, Mawe GM and Nelson MT:
Protein kinase A mediates activation of ATP-sensitive K+ currents
by CGRP in gallbladder smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 267:G494–G499.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Luman W, Ardill JE, Armstrong E, Smith GD,
Brett L, Lessells AM, Haynes WG, Gray GA, Mickley EJ, Webb DJ and
Palmer KR: Nitric oxide and gall-bladder motor function. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 12:425–432. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Farrugia G, Miller SM, Rich A, Liu X,
Maines MD, Rae JL and Szurszewski JH: Distribution of heme
oxygenase and effects of exogenous carbon monoxide in canine
jejunum. Am J Physiol. 274:G350–G358. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Zhang ZH, Qin CK, Wu SD, Xu J, Cui XP,
Wang ZY and Xian GZ: Roles of sphincter of Oddi motility and serum
vasoactive intestinal peptide, gastrin and cholecystokinin
octapeptide. World J Gastroenterol. 20:4730–4736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Morales S, Camello PJ, Mawe GM and Pozo
MJ: Cyclic AMP-mediated inhibition of gallbladder contractility:
Role of K+ channel activation and Ca2+ signaling. Br J
Pharmacol. 143:994–1005. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Bitar KN and Makhlouf GM: Relaxation of
isolated gastric smooth muscle cells by vasoactive intestinal
peptide. Science. 216:531–533. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Choi M, Moschetta A, Bookout AL, Peng L,
Umetani M, Holmstrom SR, Suino-Powell K, Xu HE, Richardson JA,
Gerard RD, et al: Identification of a hormonal basis for
gallbladder filling. Nat Med. 12:1253–1255. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Yamasaki T, Chijiiwa K and Chijiiwa Y:
Somatostatin inhibits cholecystokinin-induced contraction of
isolated gallbladder smooth muscle cells. J Surg Res. 59:743–746.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Kaczmarek P, Singh V, Cashen DE, Yang L,
Berk S, Pasternak A, Xiong Y, Shen DM, Hutchins SM, Chapman K, et
al: Somatostatin receptor subtypes 2 and 5 mediate inhibition of
egg yolk-induced gall bladder emptying in mice. Neurogastroenterol
Motil. 22:204–209.e66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|