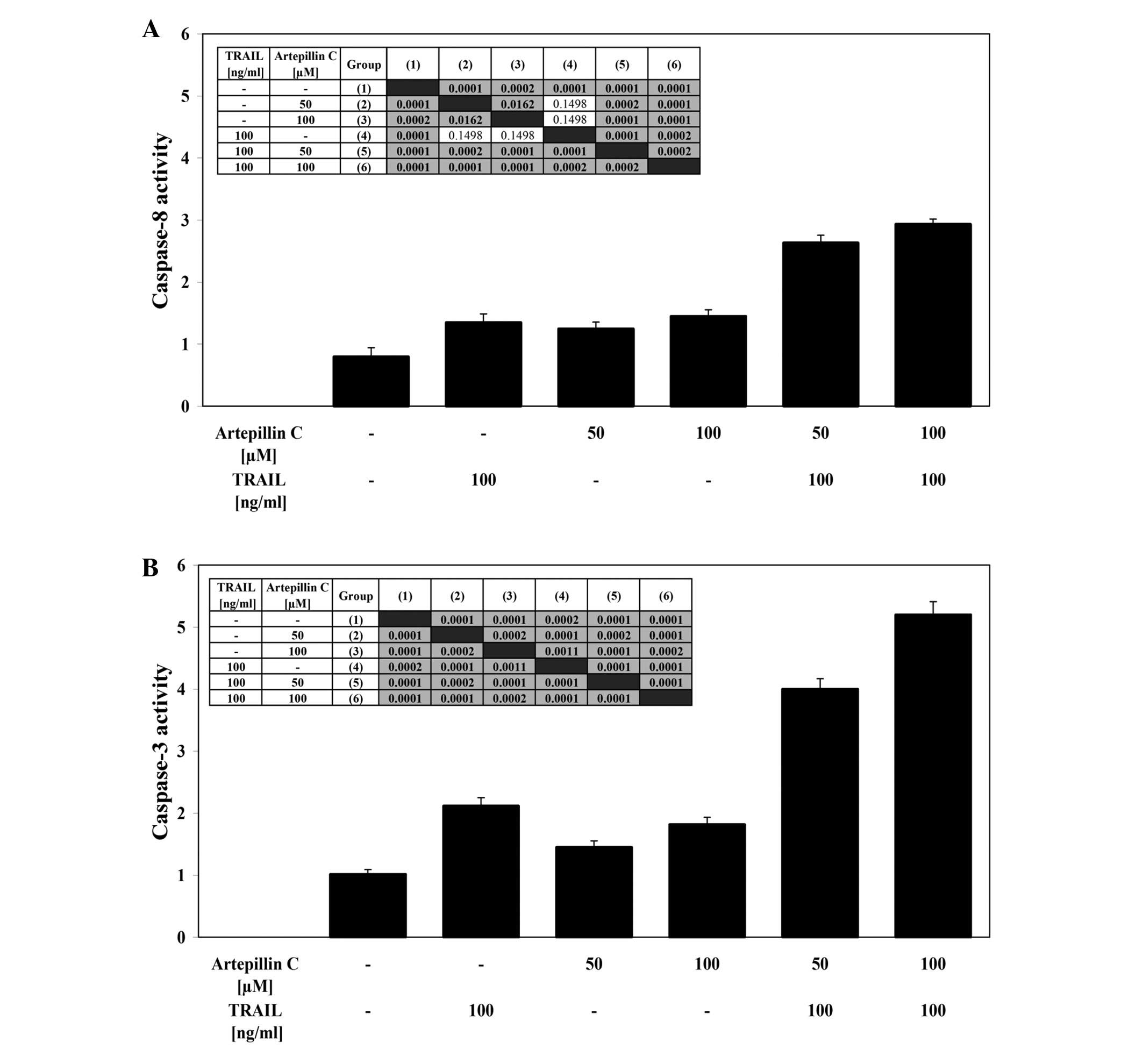
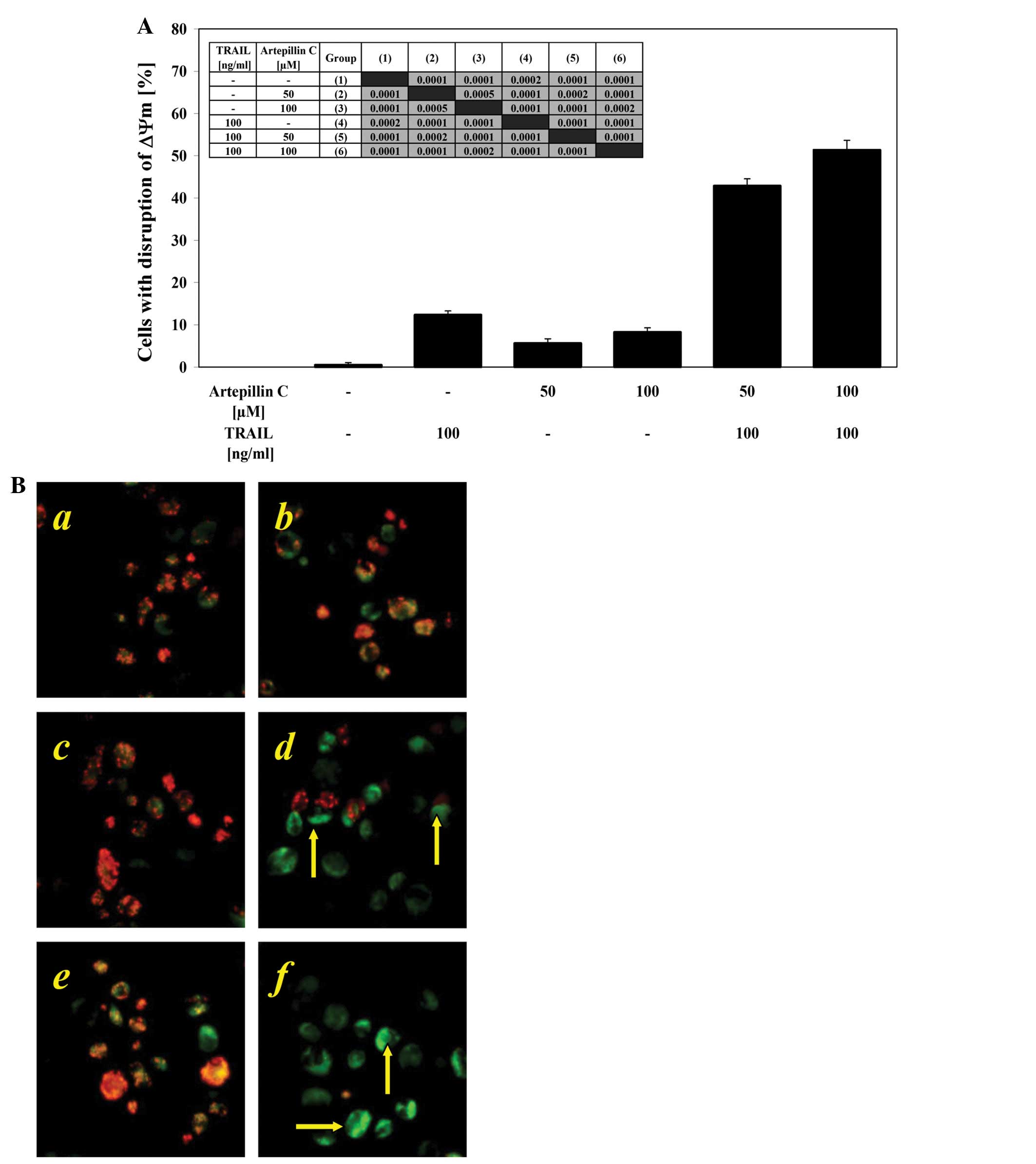
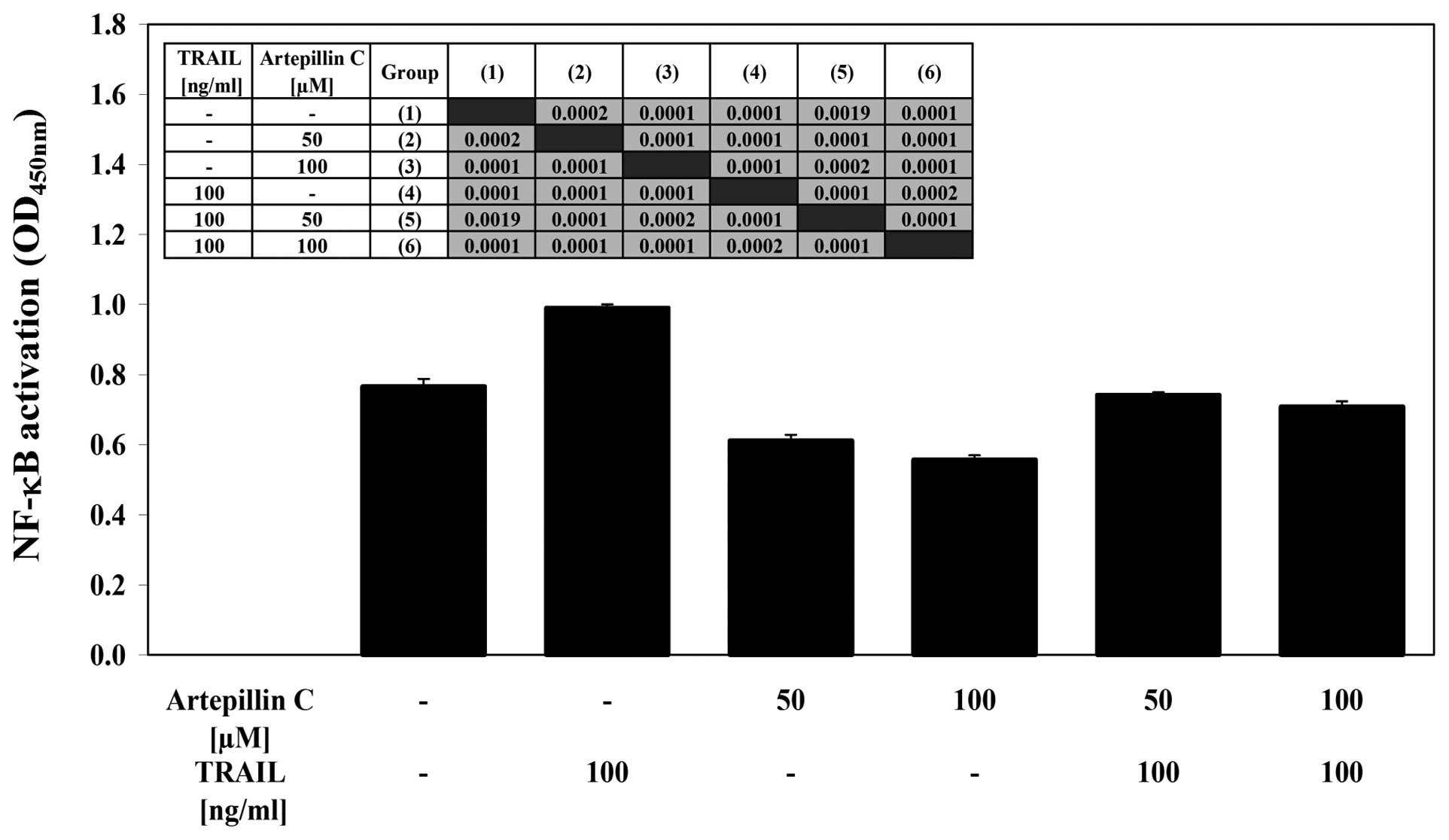
|
1
|
Lee JY, Huerta-Yepez S, Vega M, Baritaki
S, Spandidos DA and Bonavida B: The NO TRAIL to YES TRAIL in cancer
therapy (Review). Int J Oncol. 31:685–691. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Voelkel-Johnson C: TRAIL-mediated
signaling in prostate, bladder and renal cancer. Nat Rev Urol.
8:417–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baritaki S, Katsman A, Chatterjee D, Yeung
KC, Spandidos DA and Bonavida B: Regulation of tumor cell
sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by the metastatic suppressor
Raf kinase inhibitor protein via Yin Yang 1 inhibition and death
receptor 5 up-regulation. J Immunol. 179:5441–5453. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baritaki S, Huerta-Yepez S, Sakai T,
Spandidos DA and Bonavida B: Chemotherapeutic drugs sensitize
cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis: up-regulation of DR5 and
inhibition of Yin Yang 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1387–1399. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baritaki S, Suzuki E, Umezawa K, Spandidos
DA, Berenson J, Daniels TR, Penichet ML, Jazirehi AR, Palladino M
and Bonavida B: Inhibition of Yin Yang 1-dependent repressor
activity of DR5 transcription and expression by the novel
proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 contributes to its TRAIL-enhanced
apoptosis in cancer cells. J Immunol. 180:6199–6210. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Szliszka E and Krol W: The role of dietary
polyphenols in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing
ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis for cancer chemoprevention. Eur J
Cancer Prev. 20:63–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Szliszka E, Bronikowska J, Majcher A,
Miszkiewicz J and Krol W: Enhanced sensitivity of
hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells to tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) mediated
cytotoxicity by taxanes. CEJ Urol. 62:29–34. 2009.
|
|
8
|
Szliszka E, Bronikowska J, Czuba ZP and
Krol W: Isoflavones augment the effect of tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) on prostate cancer
cells. CEJ Urol. 63:182–186. 2010.
|
|
9
|
Szliszka E, Gebka J, Bronikowska J and
Krol W: Dietary flavones enhance the effect of tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) on bladder cancer
cells. CEJ Urol. 63:138–143. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Lee SJ, Noh HJ, Sung EG, Song IH, Kim JY,
Kwon TK and Lee TJ: Berberine sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis
through proteasome-mediated downregulation of c-FLIP and Mcl-1
proteins. Int J Oncol. 38:485–492. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fujiwara J, Sowa Y, Horinaka M, Koyama M,
Wakada M, Miki T and Sakai T: The anti-obesity drug orlistat
promotes sensitivity to TRAIL by two different pathways in
hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
40:1483–1491. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, Nakata
S, Wakada M and Sakai T: The dietary flavonoid apigenin sensitizes
malignant tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:945–951. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jung YH, Heo J, Lee YJ, Kwon TK and Kim
YH: Quercetin enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer
cells via increased protein stability of death receptor 5. Life
Sci. 86:351–357. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Mazur B, Paradysz A
and Krol W: Chalcones and dihydrochalcones augment TRAIL-mediated
apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Molecules. 15:5336–5353. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Sedek L, Paradysz A
and Krol W: Enhanced TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer
cells by the bioactive compounds neobavaisoflavone and psoralidin
isolated from Psoralea corylifolia. Pharmacol Rep.
63:139–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Bronikowska J,
Mertas A, Paradysz A and Krol W: Ethanolic extract of propolis
(EEP) augments TRAIL-induced apoptotic death in prostate cancer
cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:5351722011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szliszka E, Zydowicz G, Janoszka B, Dobosz
C, Kowalczyk-Ziomek G and Krol W: Ethanolic extract of Brazilian
green propolis sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 38:941–953. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szliszka E and Krol W: Soy isoflavones
augment the effect of TRAIL-mediated apoptotic death in prostate
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 26:533–541. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Szliszka E, Helewski KJ, Mizgala E and
Krol W: The dietary flavonol fisetin enhances the
apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL in prostate cancer cells. Int
J Oncol. 39:771–779. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Mertas A, Paradysz A
and Krol W: The dietary isoflavone biochanin-A sensitizes prostate
cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Urol Oncol. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.01.019.
2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park YK, Paredes-Guzman JF, Aguiar CL,
Alencar SM and Fujiwara FY: Chemical constituents in Baccharis
dracunculifolia as the main botanical origin of southeastern
Brazilian propolis. J Agric Food Chem. 52:1100–1113. 2004.
|
|
22
|
Matsuda AH and de Almeida-Muradian LB:
Validated method for the quantification of artepillin C in
Brazilian propolis. Phytochem Anal. 19:179–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Sousa JP, Leite MF, Jorge RF, Resende
DO, da Silva Filho AA, Furtado NA, Soares AE, Spadaro AC, de
Magalhaes PM and Bastos JK: Seasonality role on the phenolics from
cultivated Baccharis dracunculifolia. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:4642892011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsuno T, Jung SK, Matsumoto Y, Saito M
and Morikawa J: Preferential cytotoxicity to tumor cells of
3,5-diprenyl-4-hydroxycinnamic acid (artepillin C) isolated from
propolis. Anticancer Res. 17:3565–3568. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kimoto T, Arai S, Kohguchi M, Aga M,
Nomura Y, Micallef MJ, Kurimoto M and Mito K: Apoptosis and
suppression of tumor growth by artepillin C extracted from
Brazilian propolis. Cancer Detect Prev. 22:506–515. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kimoto T, Aga M, Hino K, Koya-Miyata S,
Yamamoto Y, Micallef MJ, Hanaya T, Arai S, Ikeda M and Kurimoto M:
Apoptosis of human leukemia cells induced by artepillin C, an
active ingredient of Brazilian propolis. Anticancer Res.
21:221–228. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ahn MR, Kunimasa K, Ohta T, Kumazawa S,
Kamihira M, Kaji K, Uto Y, Hori H, Nagasawa H and Nakayama T:
Suppression of tumor-induced angiogenesis by Brazilian propolis:
major component artepillin C inhibits in vitro tube formation and
endothelial cell proliferation. Cancer Lett. 252:235–243. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paulino N, Abreu SR, Uto Y, Koyama D,
Nagasawa H, Hori H, Dirsch VM, Vollmar AM, Scremin A and Bretz WA:
Anti-inflammatory effects of a bioavailable compound, Artepillin C,
in Brazilian propolis. Eur J Pharmacol. 587:296–301. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ahn MR, Kunimasa K, Kumazawa S, Nakayama
T, Kaji K, Uto Y, Hori H, Nagasawa H and Ohta T: Correlation
between antiangiogenic activity and antioxidant activity of various
components from propolis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 53:643–651. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Izuta H, Narahara Y, Shimazawa M, Mishima
S, Kondo S and Hara H: 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical
scavenging activity of bee products and their constituents
determined by ESR. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:1947–1951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Messerli SM, Ahn MR, Kunimasa K,
Yanagihara M, Tatefuji T, Hashimoto K, Mautner V, Uto Y, Hori H,
Kumazawa S, Kaji K, Ohta T and Maruta H: Artepillin C (ARC) in
Brazilian green propolis selectively blocks oncogenic PAK1
signaling and suppresses the growth of NF tumors in mice. Phytother
Res. 23:423–427. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Simoes-Ambrosio LM, Gregorio LE, Sousa JP,
Figueiredo-Rinhel AS, Azzolini AE, Bastos JK and Lucisano-Valim YM:
The role of seasonality on the inhibitory effect of Brazilian green
propolis on the oxidative metabolism of neutrophils. Fitoterapia.
81:1102–1108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Azevedo Bentes Monteiro Neto M, de
Souza Lima IM, Furtado RA, Bastos JK, da Silva Filho AA and Tavares
DC: Antigenotoxicity of artepillin C in vivo evaluated by the
micronucleus and comet assays. J Appl Toxicol. 31:714–719.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fonseca YM, Marquele-Oliveira F, Vicentini
FT, Furtado NA, Sousa JP, Lucisano-Valim YM and Fonseca MJ:
Evaluation of the potential of Brazilian propolis against
UV-induced oxidative stress. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2011:8639172010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moura SA, Negri G, Salatino A, Lima LD,
Dourado LP, Mendes JB, Andrade SP, Ferreira MA and Cara DC: Aqueous
extract of Brazilian green propolis: primary components, evaluation
of inflammation and wound healing by using subcutaneous implanted
sponges. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:7482832011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Watanabe MA, Amarante MK, Conti BJ and
Sforcin JM: Cytotoxic constituents of propolis inducing anticancer
effects: a review. J Pharm Pharmacol. 63:1378–1386. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Androutsopoulos VP, Ruparelia K, Arroo RR,
Tsatsakis AM and Spandidos DA: CYP1-mediated antiproliferative
activity of dietary flavonoids in MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells.
Toxicology. 264:162–170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Androutsopoulos VP, Papakyriakou A,
Vourloumis D, Tsatsakis AM and Spandidos DA: Dietary flavonoids in
cancer therapy and prevention: substrates and inhibitors of
cytochrome P450 CYP1 enzymes. Pharmacol Ther. 126:9–20. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Androutsopoulos VP, Papakyriakou A,
Vourloumis D and Spandidos DA: Comparative CYP1A1 and CYP1B1
substrate and inhibitor profile of dietary flavonoids. Bioorg Med
Chem. 19:2842–2849. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Davalli P, Rizzi F, Caldara GF, Davoli S,
Corti A, Silva A, Astancolle S, Vitale M, Bettuzzi S, Arcari M and
Azzali G: Chronic administration of green tea extract to TRAMP mice
induces the collapse of Golgi apparatus in prostate secretory cells
and results in alterations of protein post-translational
processing. Int J Oncol. 39:1521–1527. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Onoda C, Kuribayashi K, Nirasawa S, Tsuji
N, Tanaka M, Kobayashi D and Watanabe N:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis in gastric cancer
cell lines by down-regulating survivin expression. Int J Oncol.
38:1403–1408. 2011.
|
|
42
|
Teiten MH, Gaascht F, Cronauer M, Henry E,
Dicato M and Diederich M: Anti-proliferative potential of curcumin
in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells occurs through
modulation of the Wingless signaling pathway. Int J Oncol.
38:603–611. 2011.
|
|
43
|
Miki H, Uehara N, Kimura A, Sasaki T, Yuri
T, Yoshizawa K and Tsubura A: Resveratrol induces apoptosis via
ROS-triggered autophagy in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
40:1020–1028. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Marech I, Vacca A, Ranieri G, Gnoni A and
Dammacco F: Novel strategies in the treatment of
castration-resistant prostate cancer (Review). Int J Oncol.
40:1313–1320. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Venkateswaran V and Klotz LH: Diet and
prostate cancer: mechanisms of action and implications for
chemoprevention. Nat Rev Urol. 7:442–453. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bronikowska J, Szliszka E, Czuba ZP,
Zwolinski D, Szmydki B and Krol W: The combination of TRAIL and
isoflavones enhances apoptosis in cancer cells. Molecules.
15:2000–2015. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Domino M, Mazur B,
Zydowicz G and Krol W: Ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP) enhances
the apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL in cancer cells.
Molecules. 14:738–754. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Szliszka E, Skaba D, Czuba ZP and Krol W:
Inhibition of inflammatory mediators by neobavaisoflavone in
activated RAW264.7 macrophages. Molecules. 16:3701–3712. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Kawczyk-Krupka A,
Sieron-Stoltny A, Sieron A and Krol W: Chlorin-based photodynamic
therapy enhances the effect of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in bladder cancer cells. Med Sci
Monit. 18:BR47–BR53. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Szliszka E, Mazur B, Zydowicz G, Czuba ZP
and Krol W: TRAIL-induced apoptosis and expression of death
receptor TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in bladder cancer cells. Folia
Histochem Cytobiol. 47:579–585. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Akao Y, Maruyama H, Matsumoto K, Ohguchi
K, Nishizawa K, Sakamoto T, Araki Y, Mishima S and Nozawa Y: Cell
growth inhibitory effect of cinnamic acid derivatives from propolis
on human tumor cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull. 26:1057–1059. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yoshida T, Konishi M, Horinaka M, Yasuda
T, Goda AE, Taniguchi H, Yano K, Wakada M and Sakai T: Kaempferol
sensitizes colon cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 375:129–133. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li X, Wang JN, Huang JM, Xiong XK, Chen
MF, Ong CN, Shen HM and Yang XF: Chrysin promotes tumor necrosis
factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induced
apoptosis in human cancer cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 25:630–635.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Baritaki S, Militello L, Malaponte G,
Spandidos DA, Salcedo M and Bonavida B: The anti-CD20 mAb LFB-R603
interrupts the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/RKIP/PTEN resistance loop
in B-NHL cells: Role in sensitization to TRAIL apoptosis. Int J
Oncol. 38:1683–1694. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|