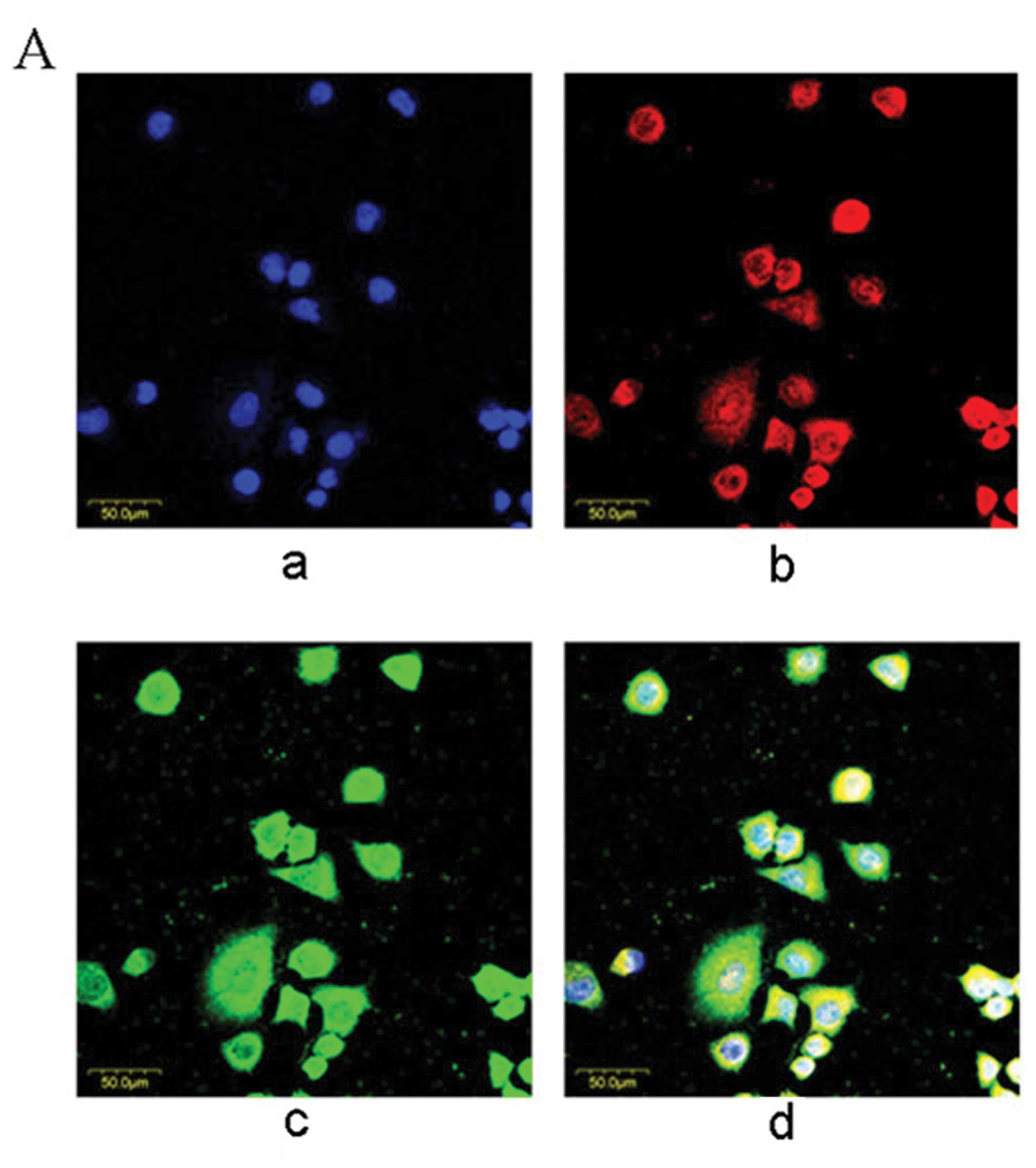
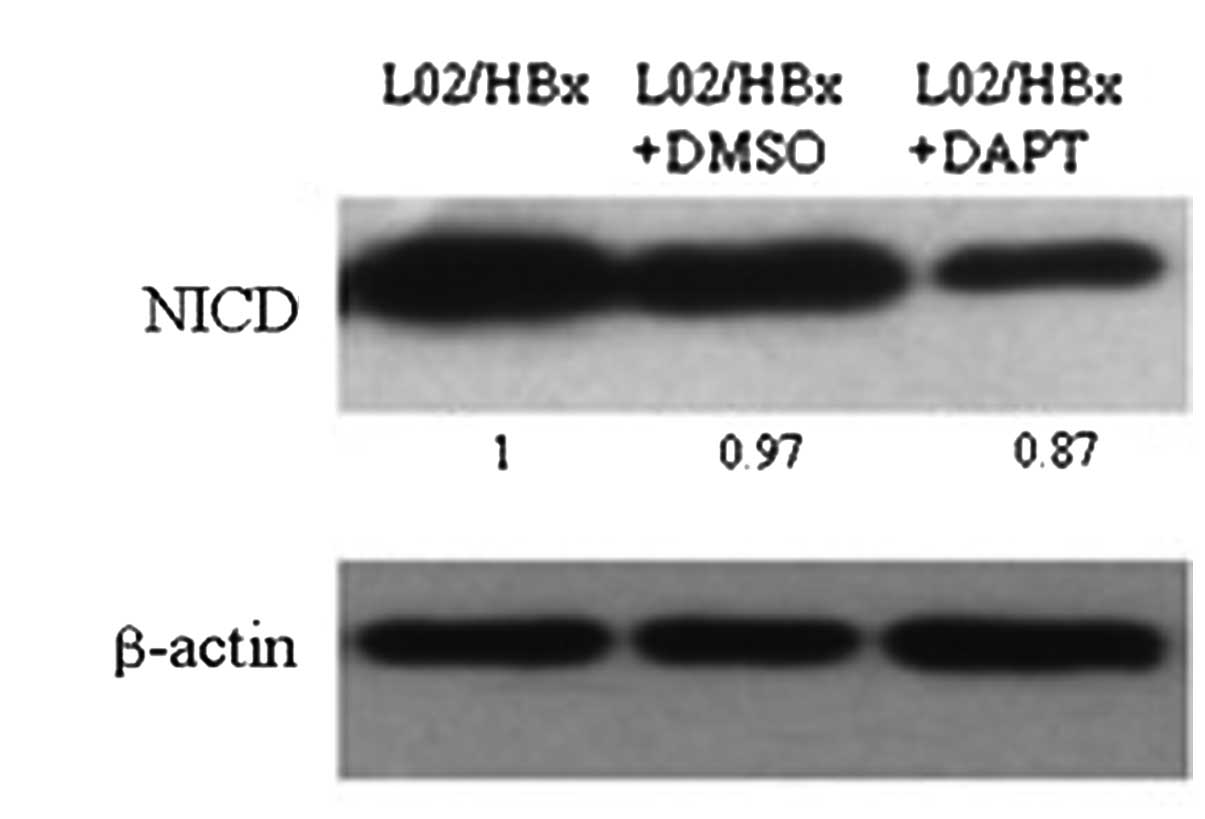
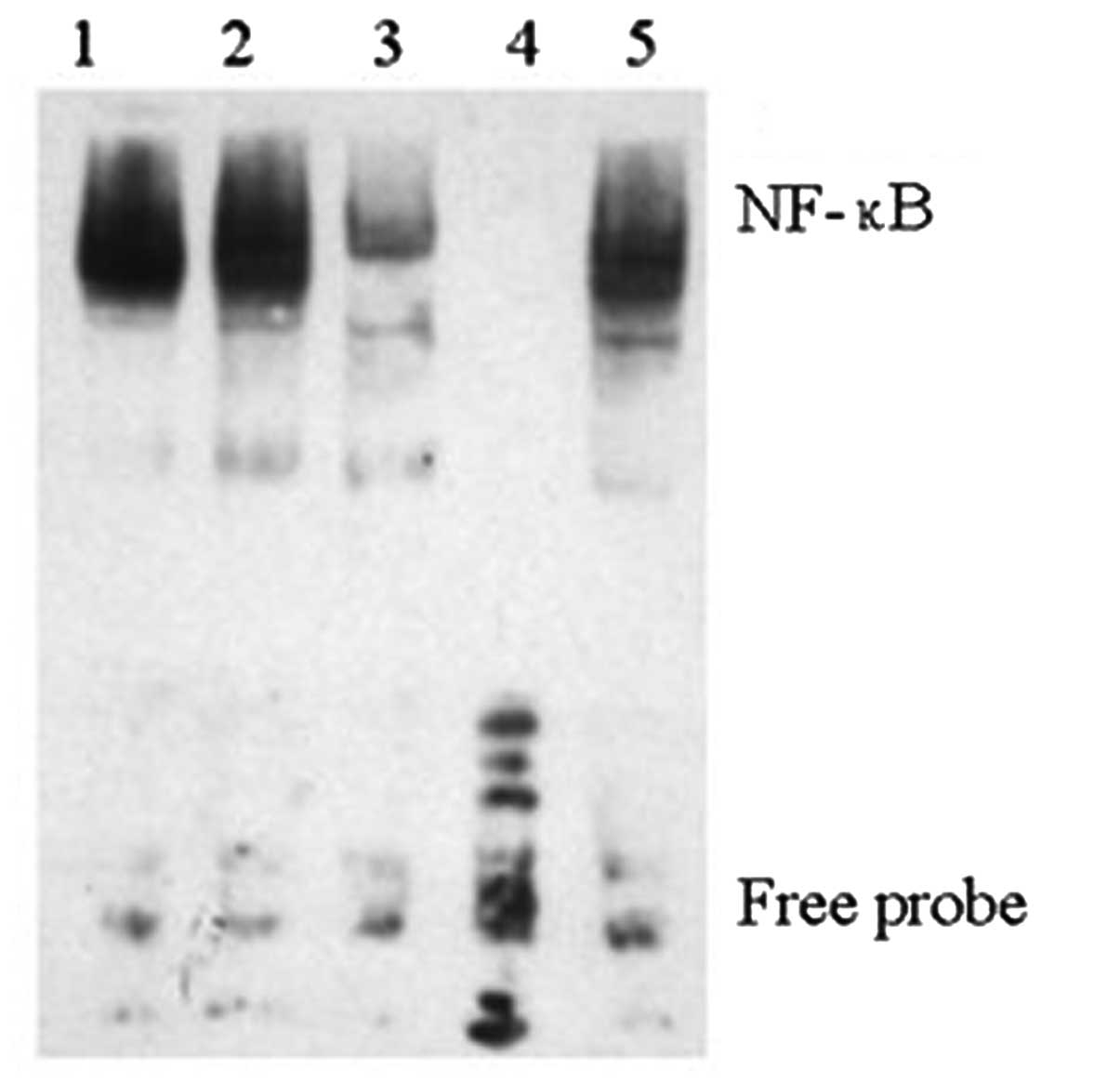
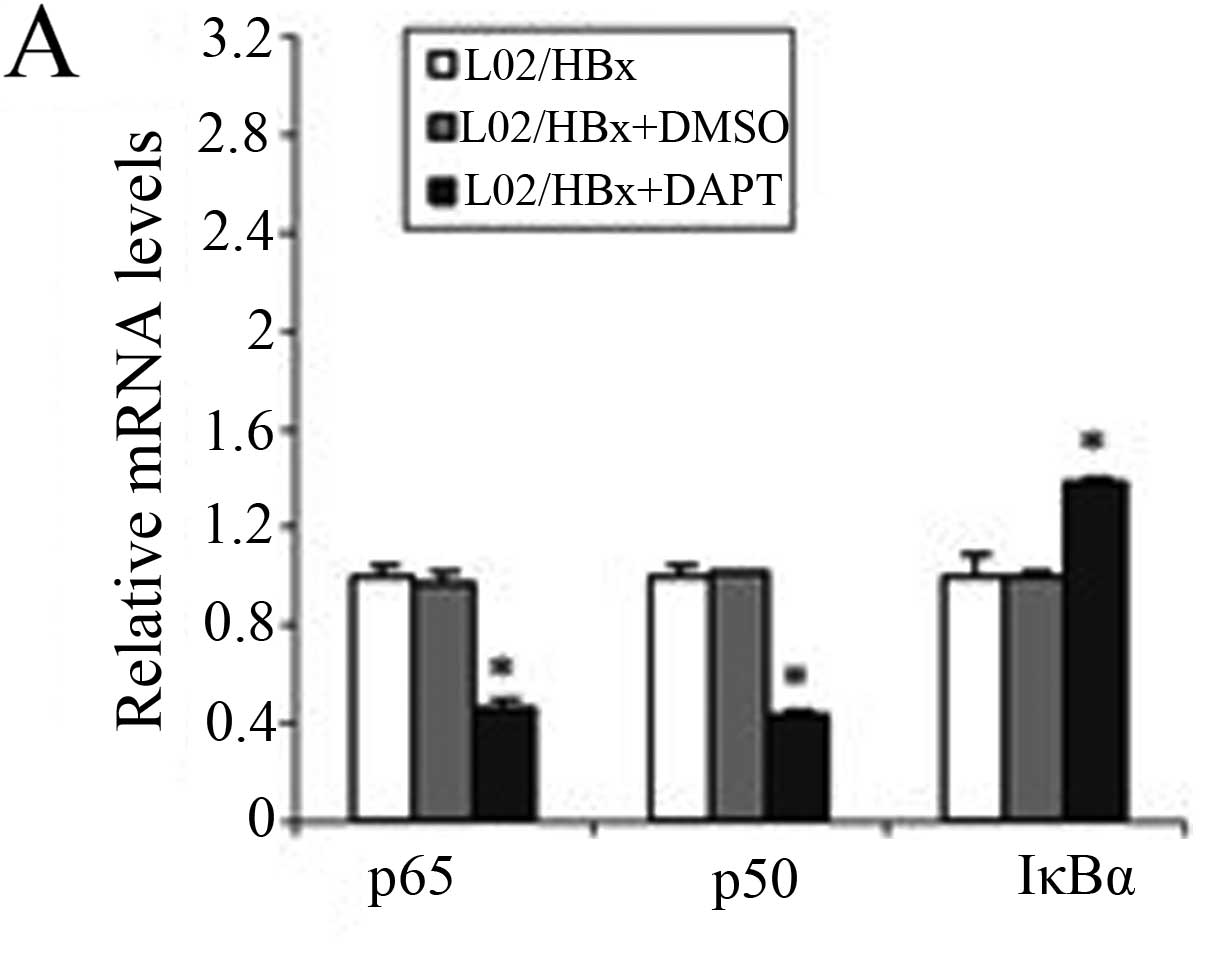
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Melissa M, et al: Global
Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Hashem BE and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Feitelson MA and Duan LX: Hepatitis B
virus X antigen in the pathogenesis of chronic infections and the
development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol.
150:1141–1157. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Wang F, Zhou H, Xia X, et al: Activated
Notch signaling is required for hepatitis B virus X protein to
promote proliferation and survival of human hepatic cells. Cancer
Lett. 298:64–73. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lai EC: Notch signaling: control of cell
communication and cell fate. Development. 131:965–973. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Miele L: Notch signaling. Clin Cancer Res.
12:1074–1079. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Miele L, Golde T and Osborne B: Notch
signaling in cancer. Curr Mol Med. 6:905–918. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kopan R and Ilagan MX: Gamma-secretase:
proteasome of the membrane? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:499–504. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Berman JN and Look AT: Targeting
transcription factors in acute leukemia in children. Curr Drug
Targets. 8:727–737. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Rangarajan A, Talora C, Okuyama R, et al:
Notch signaling is a direct determinant of keratinocyte growth
arrest and entry into differentiation. EMBO J. 20:3427–3436. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ronchini C and Capobianco AJ: Induction of
cyclin D1 transcription and CDK2 activity by Notch(ic): implication
for cell cycle disruption in transformation by Notch(ic). Mol Cell
Biol. 1:5925–5934. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Baonza A and Freeman M: Control of cell
proliferation in the Drosophila eye by Notch signaling. Dev Cell.
8:529–539. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Cheng P, Zlobin A, Volgina V, et al:
Notch-1 regulates NF-kappaB activity in hemopoietic progenitor
cells. J Immunol. 167:4458–4467. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Klinakis A, Szabolcs M, Politi K, et al:
Myc is a Notch1 transcriptional target and a requisite for
Notch1-induced mammary tumorigenesis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:9262–9267. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Diao J, Garces R and Richardson CD: X
protein of hepatitis B virus modulates cytokine and growth factor
related signal transduction pathways during the course of viral
infections and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
12:189–205. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Seto E, Mitchell PJ and Yen TS:
Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2
and other transcription factors. Nature. 344:72–74. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Lucito R and Schneider RJ: Hepatitis B
virus X protein activates transcription factor NF-kappa B without a
requirement for protein kinase C. J Virol. 66:983–991.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Meyer M, Caselmann WH, Schluter V, et al:
Hepatitis B virus transactivator MHBst: activation of NF-kappa B,
selective inhibition by antioxidants and integral membrane
localization. EMBO J. 11:2991–3001. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Campbell KJ and Perkins ND: Regulation of
NF-kappaB function. Biochem Soc Symp. 73:165–180. 2006.
|
|
20.
|
Perkins ND: Integrating cell-signalling
pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:49–62. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Maniati E, Bossard M, Cook N, et al:
Crosstalk between the canonical NF-κB and Notch signaling pathways
inhibits PPARγ expression and promotes pancreatic cancer
progression in mice. J Clin Invest. 121:4685–4699. 2011.
|
|
22.
|
Pan H, Zhou W, He W, et al: Genistein
inhibits MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cell growth by
inhibiting NF-κB activity via the Notch-1 pathway. Int J Mol Med.
30:337–343. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Schwarzer R, Dörken B and Jundt F: Notch
is an essential upstream regulator of NF-κB and is relevant for
survival of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Leukemia. 26:806–813.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Cheng B, Zheng Y, Guo XR, et al: Hepatitis
B viral X protein alters the biological features and expressions of
DNA repair enzymes in LO2 cells. Liver Int. 30:319–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, et al:
Activated K-ras and INK4a/Arf deficiency cooperate during the
development of pancreatic cancer by activation of Notch and NF-κB
signaling pathways. PLoS One. 6:e205372011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Berasain C, Castillo J, Perugorria MJ, et
al: Infammation and liver cancer: new molecular links. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1155:206–221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Lupberger J and Hildt E: Hepatitis B
virus-induced concogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 13:74–81. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Qiao L, Zhang H, Yu J, et al: Constitutive
activation of NF-kappaB in human hepatocellular carcinoma: evidence
of a cytoprotective role. Hum Gene Ther. 17:280–290. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Gao J, Chen C, Hong L, et al: Expression
of Jagged1 and its association with hepatitis B virus X protein in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 356:341–347.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Karin M: NF-kappaB and cancer: mechanisms
and targets. Mol Carcinog. 45:355–361. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Luedde T and Schwabe RF: NF-κB in the
liver - linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:108–118. 2011.
|
|
32.
|
Beg AA and Baldwin JR: The I kappa B
proteins: multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B
transcription factors. Genes Dev. 7:2064–2070. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Oakley F, Mann J, Ruddell RG, et al: Basal
expression of IkappaBalpha is controlled by the mammalian
transcriptional repressor RBP-J (CBF1) and its activator Notch1. J
Biol Chem. 278:24359–24370. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Monsalve E, Ruiz-García A, Baladrón V, et
al: Notch1 upregulates LPS-induced macrophage activation by
increasing NF-kappaB activity. Eur J Immunol. 39:2556–2570. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|