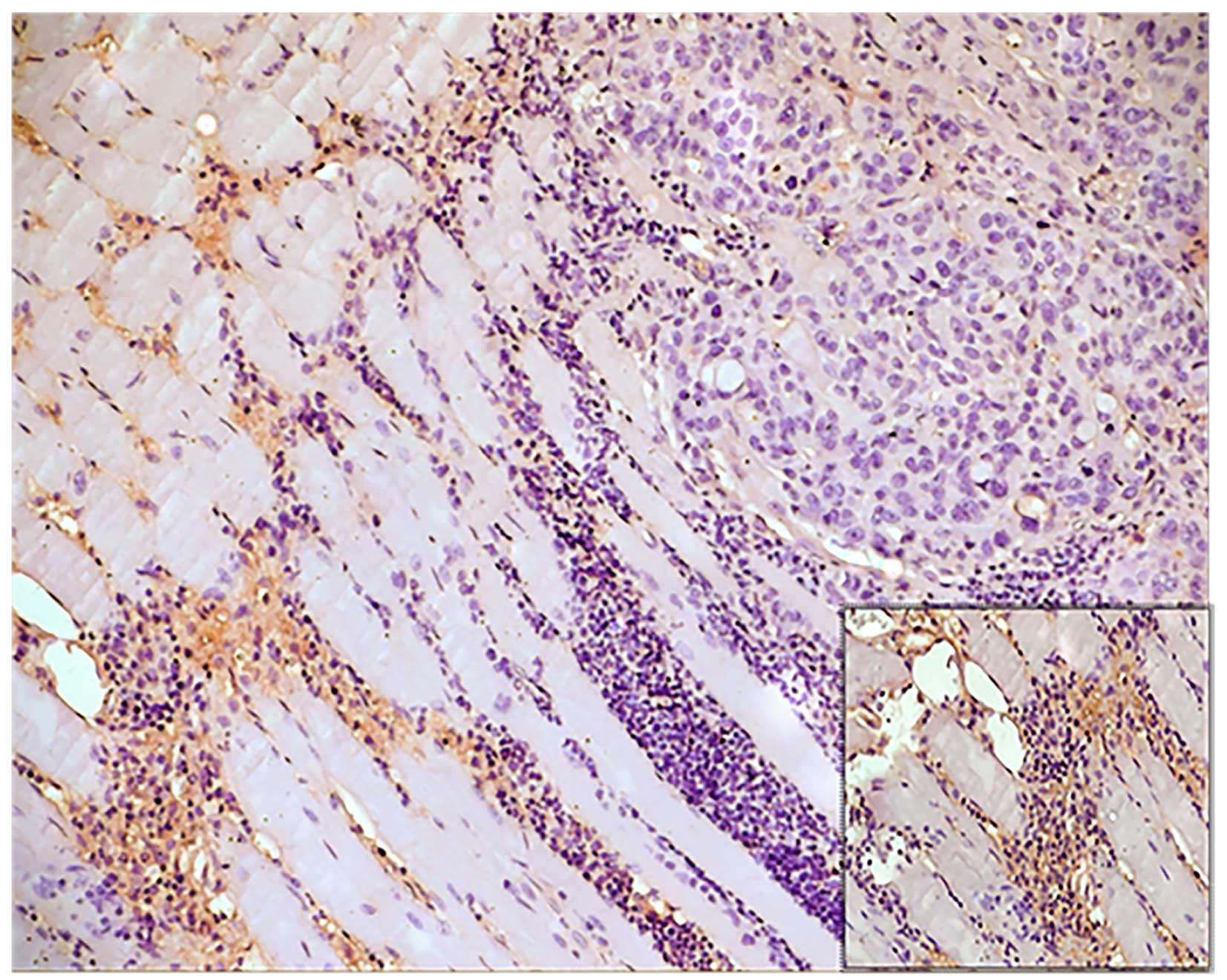
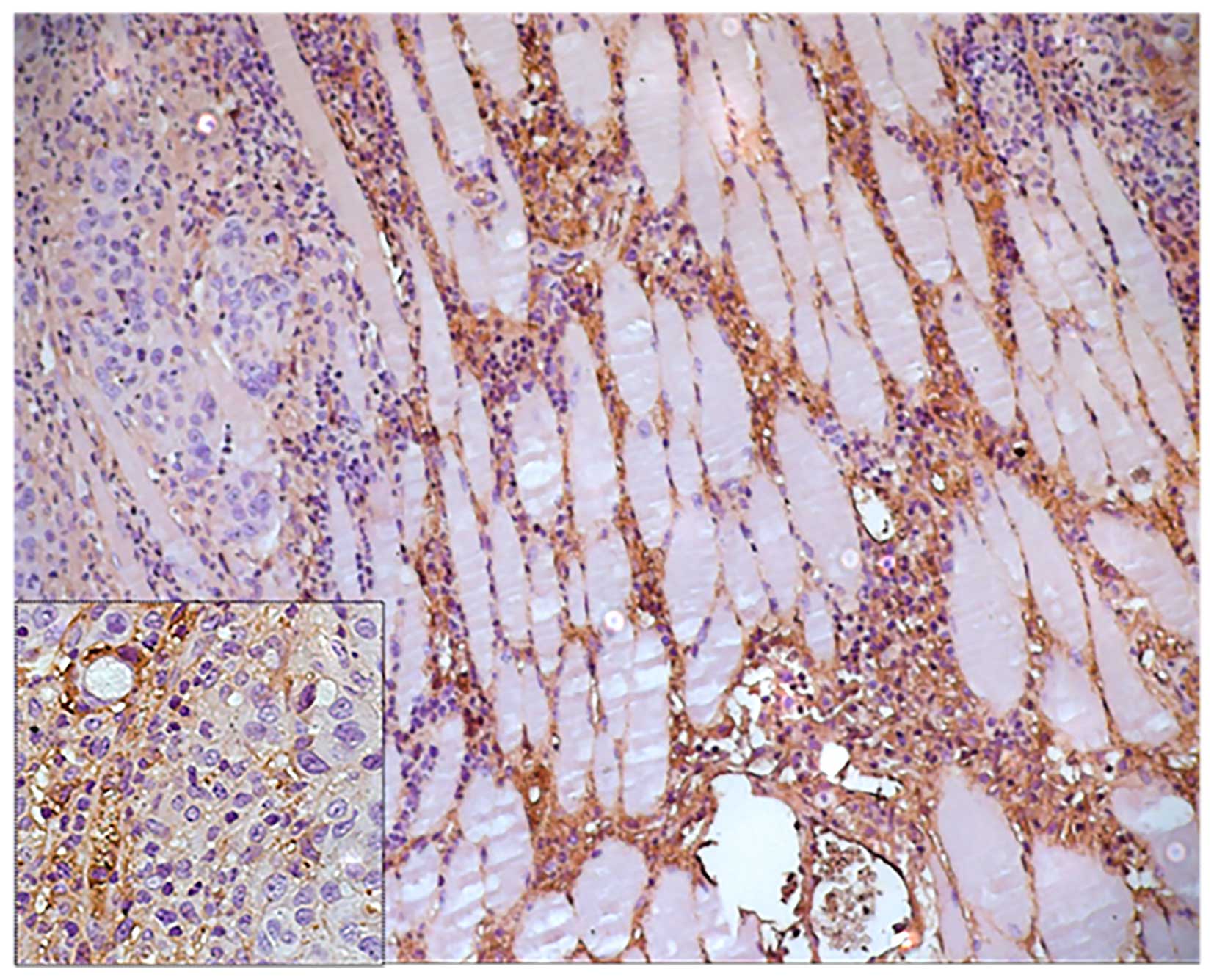
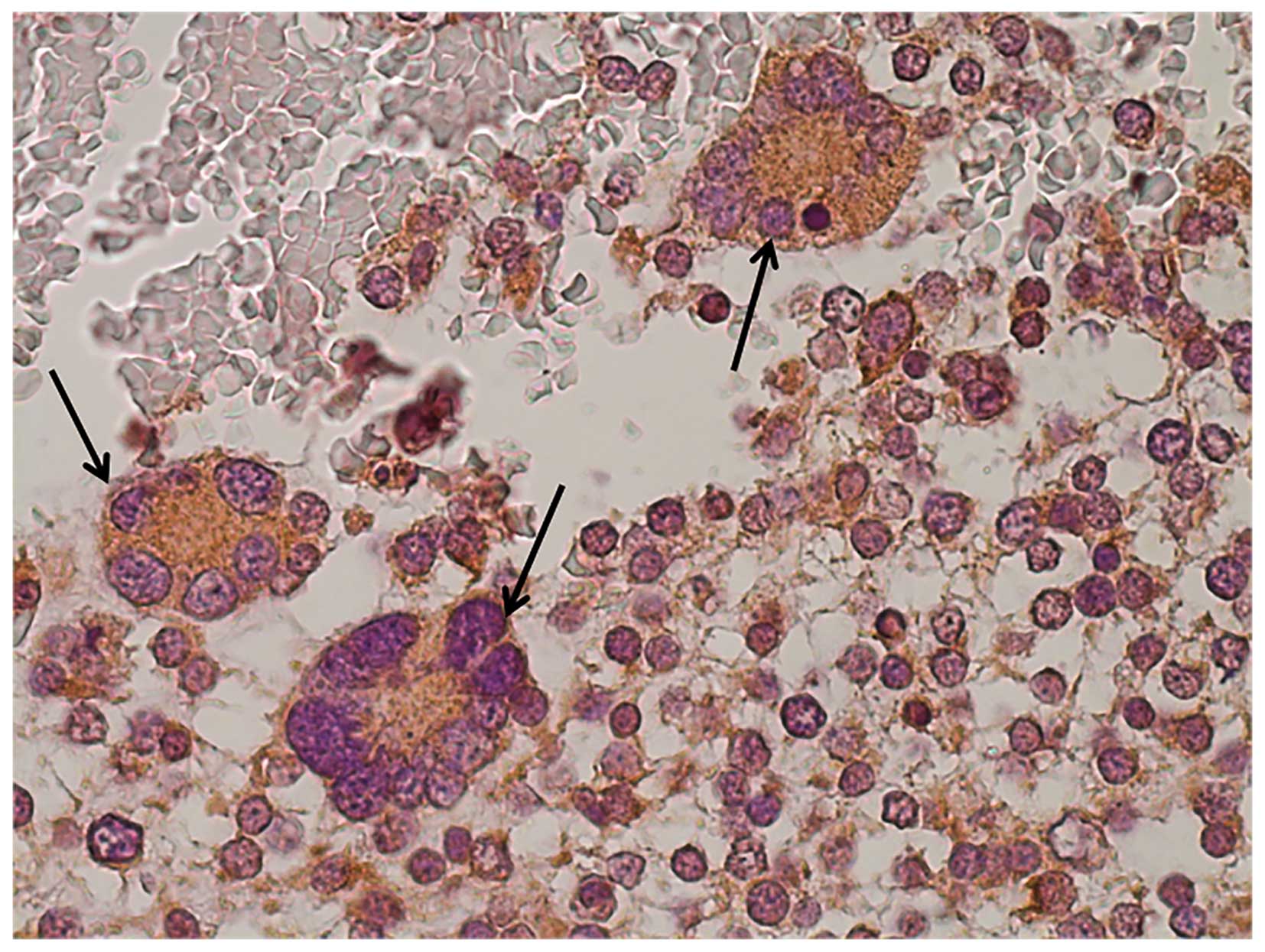
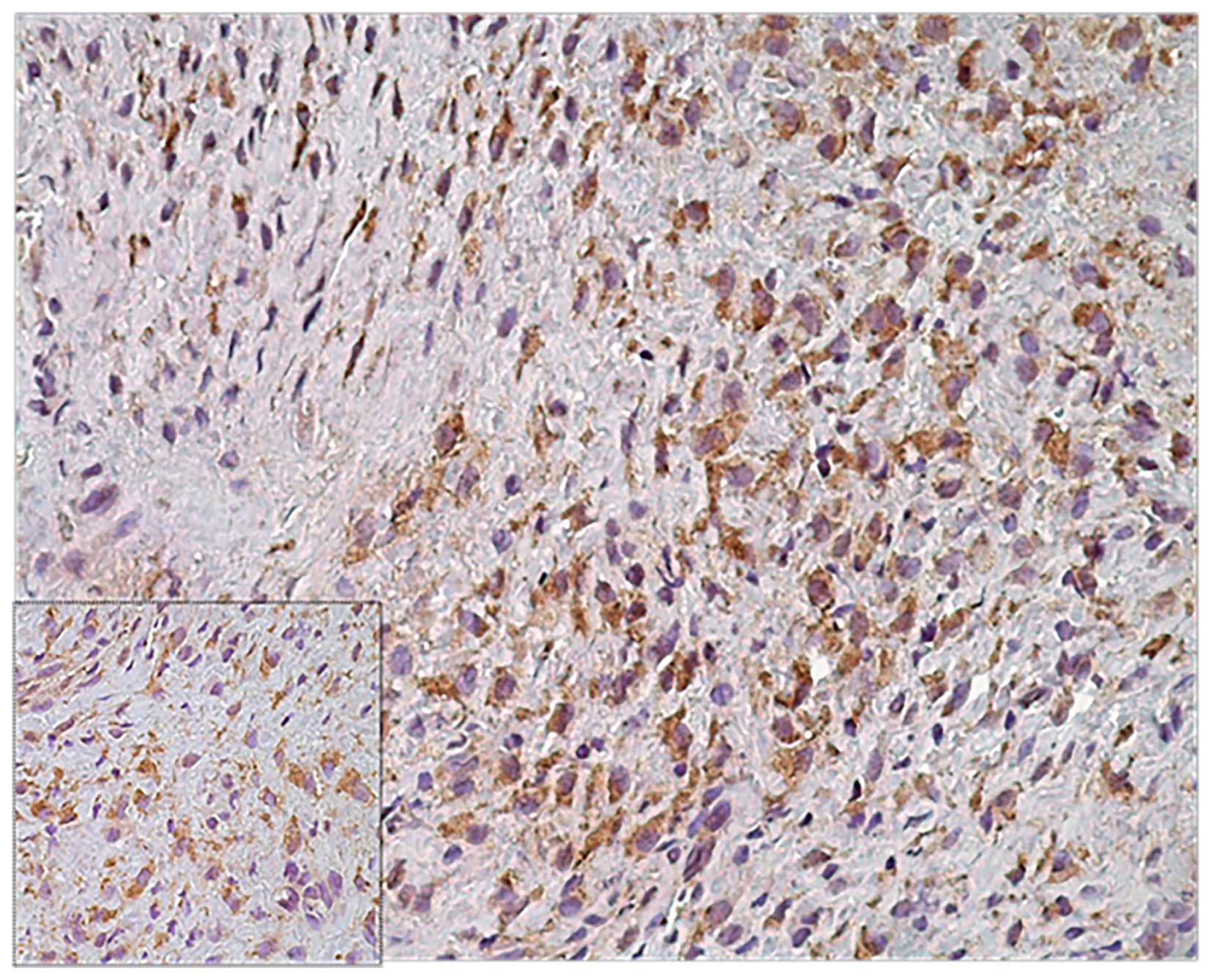
|
1
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: Therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis: An organizing
principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:273–286. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ellis LM, Liu W and Wilson M:
Down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in human
colon carcinoma cell lines by antisense transfection decreases
endothelial cell proliferation. Surgery. 120:871–878. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gerber HP, Kowalski J, Sherman D, Eberhard
DA and Ferrara N: Complete inhibition of rhabdomyosarcoma xenograft
growth and neovascularization requires blockade of both tumor and
host vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res. 60:6253–6258.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett
N, Phillips HS and Ferrara N: Inhibition of vascular endothelial
growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth ‘in
vivo’. Nature. 362:841–844. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Klohs WD and Hamby JM: Antiangiogenic
agents. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 10:544–549. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Prewett M, Huber J, Li Y, Santiago A,
O'Connor W, King K, Overholser J, Hooper A, Pytowski B, Witte L, et
al: Antivascular endothelial growth factor receptor (fetal liver
kinase 1) monoclonal antibody inhibits tumor angiogenesis and
growth of several mouse and human tumors. Cancer Res. 59:5209–5218.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ferrara N and Davis-Smyth T: The biology
of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr Rev. 18:4–25. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sato Y, Kanno S, Oda N, Abe M, Ito M,
Shitara K and Shibuya M: Properties of two VEGF receptors, Flt-1
and KDR, in signal transduction. Ann NY Acad Sci. 902:201–205.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ferrara N: The role of VEGF in the
regulation of physiological and pathological angiogenesis. EXS.
94:209–231. 2005.
|
|
11
|
Tang RF, Itakura J, Aikawa T, Matsuda K,
Fujii H, Korc M and Matsumoto Y: Overexpression of lymphangiogenic
growth factor VEGF-C in human pancreatic cancer. Pancreas.
22:285–292. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rydén L, Linderholm B, Nielsen NH, Emdin
S, Jönsson PE and Landberg G: Tumor specific VEGF-A and VEGFR2/KDR
protein are co-expressed in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
82:147–154. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Decaussin M, Sartelet H, Robert C, Moro D,
Claraz C, Brambilla C and Brambilla E: Expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its two receptors
(VEGF-R1-Flt1 and VEGF-R2-Flk1/KDR) in non-small cell lung
carcinomas (NSCLCs): Correlation with angiogenesis and survival. J
Pathol. 188:369–377. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun J, Wang DA, Jain RK, Carie A, Paquette
S, Ennis E, Blaskovich MA, Baldini L, Coppola D, Hamilton AD, et
al: Inhibiting angiogenesis and tumorigenesis by a synthetic
molecule that blocks binding of both VEGF and PDGF to their
receptors. Oncogene. 24:4701–4709. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wood JM, Bold G, Buchdunger E, Cozens R,
Ferrari S, Frei J, Hofmann F, Mestan J, Mett H, O'Reilly T, et al:
PTK787/ZK 222584, a novel and potent inhibitor of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, impairs
vascular endothelial growth factor-induced responses and tumor
growth after oral administration. Cancer Res. 60:2178–2189.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wedge SR, Ogilvie DJ, Dukes M, Kendrew J,
Curwen JO, Hennequin LF, Thomas AP, Stokes ES, Curry B, Richmond
GH, et al: ZD4190: An orally active inhibitor of vascular
endothelial growth factor signaling with broad-spectrum antitumor
efficacy. Cancer Res. 60:970–975. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev.
25:581–611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
El-Mousawi M, Tchistiakova L, Yurchenko L,
Pietrzynski G, Moreno M, Stanimirovic D, Ahmad D and Alakhov V: A
vascular endothelial growth factor high affinity receptor
1-specific peptide with antiangiogenic activity identified using a
phage display peptide library. J Biol Chem. 278:46681–46691. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gonçalves M, Estieu-Gionnet K, Berthelot
T, Laïn G, Bayle M, Canron X, Betz N, Bikfalvi A and Déléris G:
Design, synthesis, and evaluation of original carriers for
targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor interactions.
Pharm Res. 22:1411–1421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Failla CM, Odorisio T, Cianfarani F,
Schietroma C, Puddu P and Zambruno G: Placenta growth factor is
induced in human keratinocytes during wound healing. J Invest
Dermatol. 115:388–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Green CJ, Lichtlen P, Huynh NT, Yanovsky
M, Laderoute KR, Schaffner W and Murphy BJ: Placenta growth factor
gene expression is induced by hypoxia in fibroblasts: A central
role for metal transcription factor-1. Cancer Res. 61:2696–2703.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Larcher F, Franco M, Bolontrade M,
Rodriguez-Puebla M, Casanova L, Navarro M, Yancopoulos G, Jorcano
JL and Conti CJ: Modulation of the angiogenesis response through
Ha-ras control, placenta growth factor, and angiopoietin expression
in mouse skin carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 37:83–90. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carmeliet P, De Smet F, Loges S and
Mazzone M: Branching morphogenesis and antiangiogenesis candidates:
Tip cells lead the way. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 6:315–326. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li B, Sharpe EE, Maupin AB, Teleron AA,
Pyle AL, Carmeliet P and Young PP: VEGF and PlGF promote adult
vasculogenesis by enhancing EPC recruitment and vessel formation at
the site of tumor neovascularization. FASEB J. 20:1495–1497. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Podar K and Anderson KC: The
pathophysiologic role of VEGF in hematologic malignancies:
Therapeutic implications. Blood. 105:1383–1395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Youssoufian H, Hicklin DJ and Rowinsky EK:
Review: Monoclonal antibodies to the vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor-2 in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
13:S5544–S5548. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Calvani M, Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B,
Shoemaker RH and Melillo G: Hypoxic induction of an
HIF-1alpha-dependent bFGF autocrine loop drives angiogenesis in
human endothelial cells. Blood. 107:2705–2712. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Waldner MJ, Wirtz S, Jefremow A, Warntjen
M, Neufert C, Atreya R, Becker C, Weigmann B, Vieth M, Rose-John S,
et al: VEGF receptor signaling links inflammation and tumorigenesis
in colitis-associated cancer. J Exp Med. 207:2855–2868. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Albuquerque RJC, Hayashi T, Cho WG,
Kleinman ME, Dridi S, Takeda A, Baffi JZ, Yamada K, Kaneko H, Green
MG, et al: Alternatively spliced vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-2 is an essential endogenous inhibitor of lymphatic vessel
growth. Nat Med. 15:1023–1030. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Becker J, Pavlakovic H, Ludewig F, Wilting
F, Weich HA, Albuquerque R, Ambati J and Wilting J: Neuroblastoma
progression correlates with downregulation of the lymphangiogenesis
inhibitor sVEGFR-2. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1431–1441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Petrova TV, Bono P, Holnthoner W, Chesnes
J, Pytowski B, Sihto H, Laakkonen P, Heikkilä P, Joensuu H and
Alitalo K: VEGFR-3 expression is restricted to blood and lymphatic
vessels in solid tumors. Cancer Cell. 13:554–556. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Laakkonen P, Waltari M, Holopainen T,
Takahashi T, Pytowski B, Steiner P, Hicklin D, Persaud K, Tonra JR,
Witte L, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 is
involved in tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Res. 67:593–599.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
He Y, Rajantie I, Ilmonen M, Makinen T,
Karkkainen MJ, Haiko P, Salven P and Alitalo K: Preexisting
lymphatic endothelium but not endothelial progenitor cells are
essential for tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis.
Cancer Res. 64:3737–3740. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Achen MG and Stacker SA: Targeting tumor
stroma. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:4462008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He Y, Rajantie I, Pajusola K, Jeltsch M,
Holopainen T, Yla-Herttuala S, Harding T, Jooss K, Takahashi T and
Alitalo K: Vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor
3-mediated activation of lymphatic endothelium is crucial for tumor
cell entry and spread via lymphatic vessels. Cancer Res.
65:4739–4746. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gerber HP and Ferrara N: Pharmacology and
pharmacodynamics of bevacizumab as monotherapy or in combination
with cytotoxic therapy in preclinical studies. Cancer Res.
65:671–680. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J,
Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R and Johnson DH:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miles DW, Chan A, Dirix LY, Cortés J,
Pivot X, Tomczak P, Delozier T, Sohn JH, Provencher L, Puglisi F,
et al: Phase III study of bevacizumab plus docetaxel compared with
placebo plus docetaxel for the first-line treatment of human
epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:3239–3247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Robert NJ, Diéras V, Glaspy J, Brufsky AM,
Bondarenko I, Lipatov ON, Perez EA, Yardley DA, Chan SY, Zhou X, et
al: RIBBON-1: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase
III trial of chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for
first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor
2-negative, locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 29:1252–1260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, Dickler M,
Cobleigh M, Perez EA, Shenkier T, Cella D and Davidson NE:
Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 357:2666–2676. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Valachis A, Polyzos NP, Patsopoulos NA,
Georgoulias V, Mavroudis D and Mauri D: Bevacizumab in metastatic
breast cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 122:1–7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pivot X, Schneeweiss A, Verma S, Thomssen
C, Passos-Coelho JL, Benedetti G, Ciruelos E, von Moos R, Chang HT,
Duenne AA, et al: Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in combination
with docetaxel for the first-line treatment of elderly patients
with locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: Results from
AVADO. Eur J Cancer. 47:2387–2395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Vach W, Høilund-Carlsen PF, Fischer BM,
Gerke O and Weber W: How to study optimal timing of PET/CT for
monitoring of cancer treatment. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 1:54–62.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rakheja R, Ciarallo A, Alabed YZ and
Hickeson M: Intravenous administration of diazepam significantly
reduces brown fat activity on 18F-FDG PET/CT. Am J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 1:29–35. 2011.
|
|
46
|
Eary JF, Hawkins DS, Rodler ET and Conrad
EUI III: (18)F-FDG PET in sarcoma treatment response imaging. Am J
Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 1:47–53. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Iagaru A: 18F-FDG PET/CT: Timing for
evaluation of response to therapy remains a clinical challenge. Am
J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 1:63–64. 2011.
|
|
48
|
Mendel DB, Schreck RE, West DC, Li G,
Strawn LM, Tanciongco SS, Vasile S, Shawver LK and Cherrington JM:
The angiogenesis inhibitor SU5416 has long-lasting effects on
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor phosphorylation and
function. Clin Cancer Res. 6:4848–4858. 2000.
|
|
49
|
Laird AD, Vajkoczy P, Shawver LK, Thurnher
A, Liang C, Mohammadi M, Schlessinger J, Ullrich A, Hubbard SR,
Blake RA, et al: SU6668 is a potent antiangiogenic and antitumor
agent that induces regression of established tumors. Cancer Res.
60:4152–4160. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Drevs J, Hofmann I, Hugenschmidt H, Wittig
C, Madjar H, Müller M, Wood J, Martiny-Baron G, Unger C and Marmé
D: Effects of PTK787/ZK 222584, a specific inhibitor of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, on primary
tumor, metastasis, vessel density, and blood flow in a murine renal
cell carcinoma model. Cancer Res. 60:4819–4824. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Davidoff AM, Leary MA, Ng CY and Vanin EF:
Gene therapy-mediated expression by tumor cells of the angiogenesis
inhibitor flk-1 results in inhibition of neuroblastoma growth in
vivo. J Pediatr Surg. 36:30–36. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, Man S, Clark
K, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P and Kerbel RS: Continuous low-dose therapy
with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained
tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest.
105:R15–R24. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee CG, Heijn M, di Tomaso E,
Griffon-Etienne G, Ancukiewicz M, Koike C, Park KR, Ferrara N, Jain
RK, Suit HD, et al: Anti-Vascular endothelial growth factor
treatment augments tumor radiation response under normoxic or
hypoxic conditions. Cancer Res. 60:5565–5570. 2000.
|
|
54
|
Kozin SV, Boucher Y, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P,
Jain RK and Suit HD: Vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-2-blocking antibody potentiates radiation-induced
long-term control of human tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 61:39–44.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jain RK: Normalizing tumor vasculature
with anti-angiogenic therapy: A new paradigm for combination
therapy. Nat Med. 7:987–989. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yuan F, Chen Y, Dellian M, Safabakhsh N,
Ferrara N and Jain RK: Time-dependent vascular regression and
permeability changes in established human tumor xenografts induced
by an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability
factor antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:14765–14770. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Pham CD, Roberts TP, van Bruggen N, Melnyk
O, Mann J, Ferrara N, Cohen RL and Brasch RC: Magnetic resonance
imaging detects suppression of tumor vascular permeability after
administration of antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor.
Cancer Invest. 16:225–230. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Willett CG, Boucher Y, di Tomaso E, Duda
DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, Chung DC, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Kozin SV, et
al: Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has
antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med. 10:145–147.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W,
Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S,
Holmgren E, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2335–2342. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Escudier B, Bellmunt J, Négrier S, Bajetta
E, Melichar B, Bracarda S, Ravaud A, Golding S, Jethwa S and
Sneller V: Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a
in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (AVOREN): Final
analysis of overall survival. J Clin Oncol. 28:2144–2150. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen
T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WKA, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen
R, et al: Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in
recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 27:4733–4740. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Kreisl TN, Kim L, Moore K, Duic P, Royce
C, Stroud I, Garren N, Mackey M, Butman JA, Camphausen K, et al:
Phase II trial of single-agent bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab
plus irinotecan at tumor progression in recurrent glioblastoma. J
Clin Oncol. 27:740–745. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
63
|
Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, Stadler
WM, Vaena DA, Ou SS, Archer L, Atkins JN, Picus J, Czaykowski P, et
al: Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa
monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB
90206. J Clin Oncol. 26:5422–5428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM, Hwu P,
Schwartzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, Steinberg SM, Chen HX and
Rosenberg SA: A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular
endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N
Engl J Med. 349:427–434. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Van Meter ME and Kim ES: Bevacizumab:
Current updates in treatment. Curr Opin Oncol. 22:586–591. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Keunen O, Johansson M, Oudin A, Sanzey M,
Rahim SA, Fack F, Thorsen F, Taxt T, Bartos M, Jirik R, et al:
Anti-VEGF treatment reduces blood supply and increases tumor cell
invasion in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:3749–3754.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Artico M, Cervoni L, Celli P, Salvati M
and Palma L: Supratentorial glioblastoma in children: A series of
27 surgically treated cases. Childs Nerv Syst. 9:7–9. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bruns CJ, Shrader M, Harbison MT, Portera
C, Solorzano CC, Jauch KW, Hicklin DJ, Radinsky R and Ellis LM:
Effect of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2
antibody DC101 plus gemcitabine on growth, metastasis and
angiogenesis of human pancreatic cancer growing orthotopically in
nude mice. Int J Cancer. 102:101–108. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shaheen RM, Tseng WW, Vellagas R, Liu W,
Ahmad SA, Jung YD, Reinmuth N, Drazan KE, Bucana CD, Hicklin DJ, et
al: Effects of an antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-2 on survival, tumor vascularity, and apoptosis in a
murine model of colon carcinomatosis. Int J Oncol. 18:221–226.
2001.
|
|
70
|
Spratlin J: Ramucirumab (IMC-1121B):
Monoclonal antibody inhibition of vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor-2. Curr Oncol Rep. 13:97–102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Demetri GD, van Oosterom AT, Garrett CR,
Blackstein ME, Shah MH, Verweij J, McArthur G, Judson IR, Heinrich
MC, Morgan JA, et al: Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients
with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of
imatinib: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 368:1329–1338.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Rosenberg J,
Bukowski RM, Curti BD, George DJ, Hudes GR, Redman BG, Margolin KA
and Wilding G: Sunitinib efficacy against advanced renal cell
carcinoma. J Urol. 178:1883–1887. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik
C, Oudard S, Siebels M, Negrier S, Chevreau C, Solska E, Desai AA,
et al; TARGET Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell
renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:125–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al; SHARP Investigators Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:378–390. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Gruber BL, Marchese MJ and Kew R:
Angiogenic factors stimulate mast-cell migration. Blood.
86:2488–2493. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Thomas AL, Morgan B, Drevs J, Jivan A,
Buchert M, Horsfield M, et al: Pharmacodynamic results using
dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of 2 Phase 1
studies of the VEGF inhibitor PTK787/ZK 222584 in patients with
liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Proc ASCO. 20:2792001.
|
|
77
|
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW and Loeffler
JS: Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for
cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 3:24–40. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Burris H III and Rocha-Lima C: New
therapeutic directions for advanced pancreatic cancer: Targeting
the epidermal growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor
pathways. Oncologist. 13:289–298. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bergers G and Hanahan D: Modes of
resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:592–603.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Ellis LM and Hicklin DJ: Pathways
mediating resistance to vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted
therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6371–6375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shojaei F and Ferrara N: Role of the
microenvironment in tumor growth and in refractoriness/resistance
to anti-angiogenic therapies. Drug Resist Updat. 11:219–230. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Relf M, LeJeune S, Scott PA, Fox S, Smith
K, Leek R, Moghaddam A, Whitehouse R, Bicknell R and Harris AL:
Expression of the angiogenic factors vascular endothelial cell
growth factor, acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor, tumor
growth factor β-1, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor,
placenta growth factor, and pleiotrophin in human primary breast
cancer and its relation to angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 57:963–969.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Christofori G, Naik P and Hanahan D:
Vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors, flt-1 and
flk-1, are expressed in normal pancreatic islets and throughout
islet cell tumorigenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 9:1760–1770.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Inoue M, Hager JH, Ferrara N, Gerber HP
and Hanahan D: VEGF-A has a critical, nonredundant role in
angiogenic switching and pancreatic β cell carcinogenesis. Cancer
Cell. 1:193–202. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Joyce JA, Laakkonen P, Bernasconi M,
Bergers G, Ruoslahti E and Hanahan D: Stage-specific vascular
markers revealed by phage display in a mouse model of pancreatic
islet tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 4:393–403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Bergers G, Javaherian K, Lo KM, Folkman J
and Hanahan D: Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage
carcinogenesis in mice. Science. 284:808–812. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH,
Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during
carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2:737–744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N,
Bergsland E and Hanahan D: Benefits of targeting both pericytes and
endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors.
J Clin Invest. 111:1287–1295. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
90
|
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs
H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M,
et al: Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2
for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med.
344:783–792. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Hillan KJ: The role of VEGF expression in
response to bevacizumab plus capcitabine in metastatic breast
cancer (MBC). J Clin Oncol. 21:S2842003.
|
|
92
|
Gobbi G, Mirandola P, Micheloni C,
Solenghi E, Sponzilli I, Artico M, Soda G, Zanelli G, Pelusi G,
Fiorini T, et al: Expression of HLA class I antigen and proteasome
subunits LMP-2 and LMP-10 in primary vs. metastatic breast
carcinoma lesions. Int J Oncol. 25:1625–1629. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jubb AM, Hurwitz HI, Bai W, Holmgren EB,
Tobin P, Guerrero AS, Kabbinavar F, Holden SN, Novotny WF, Frantz
GD, et al: Impact of vascular endothelial growth factor-A
expression, thrombospondin-2 expression, and microvessel density on
the treatment effect of bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:217–227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Nagengast WB, de Korte MA, Oude Munnink
TH, Timmer-Bosscha H, den Dunnen WF, Hollema H, de Jong JR, Jensen
MR, Quadt C, Garcia-Echeverria C, et al: 89Zr-bevacizumab PET of
early antiangiogenic tumor response to treatment with HSP90
inhibitor NVP-AUY922. J Nucl Med. 51:761–767. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Christoforidis JB, Carlton MM, Knopp MV
and Hinkle GH: PET/CT imaging of I-124-radiolabeled bevacizumab and
ranibizumab after intravitreal injection in a rabbit model. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:5899–5903. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Nayak TK, Garmestani K, Baidoo KE, Milenic
DE and Brechbiel MW: PET imaging of tumor angiogenesis in mice with
VEGF-A-targeted (86)Y-CHX-A″-DTPA-bevacizumab. Int J Cancer.
128:920–926. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Paudyal B, Paudyal P, Oriuchi N, Hanaoka
H, Tominaga H and Endo K: Positron emission tomography imaging and
biodistribution of vascular endothelial growth factor with
64Cu-labeled bevacizumab in colorectal cancer xenografts. Cancer
Sci. 102:117–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Nagengast WB, Hooge MN, van Straten EM,
Kruijff S, Brouwers AH, den Dunnen WF, de Jong JR, Hollema H,
Dierckx RA, Mulder NH, et al: VEGF-SPECT with
111In-bevacizumab in stage III/IV melanoma patients. Eur
J Cancer. 47:1595–1602. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhang L, Xu JS, Sanders VM, Letson AD,
Roberts CJ and Xu RX: Multifunctional microbubbles for image-guided
anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. J Biomed Opt1.
5:0305152010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Terwisscha van Scheltinga AG, van Dam GM,
Nagengast WB, Ntziachristos V, Hollema H, Herek JL, Schröder CP,
Kosterink JG, Lub-de Hoog MN and de Vries EG: Intraoperative
near-infrared fluorescence tumor imaging with vascular endothelial
growth factor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
targeting antibodies. J Nucl Med. 52:1778–1785. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Nagengast WB, de Vries EG, Hospers GA,
Mulder NH, de Jong JR, Hollema H, Brouwers AH, van Dongen GA, Perk
LR and Lub-de Hooge MN: In vivo VEGF imaging with radiolabeled
bevacizumab in a human ovarian tumor xenograft. J Nucl Med.
48:1313–1319. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Helisch A, Förster GJ, Reber H, Buchholz
HG, Arnold R, Göke B, Weber MM, Wiedenmann B, Pauwels S, Haus U, et
al: Pre-therapeutic dosimetry and biodistribution of
86Y-DOTA-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide versus 111In-pentetreotide in
patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 31:1386–1392. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Scheer MG, Stollman TH, Boerman OC,
Verrijp K, Sweep FC, Leenders WP, Ruers TJ and Oyen WJ: Imaging
liver metastases of colorectal cancer patients with radiolabelled
bevacizumab: Lack of correlation with VEGF-A expression. Eur J
Cancer. 44:1835–1840. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Vogl G, Bartel H, Dietze O and
Hauser-Kronberger C: HER2 is unlikely to be involved in directly
regulating angiogenesis in human breast cancer. Appl
Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 14:138–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Kostopoulos I, Arapantoni-Dadioti P, Gogas
H, Papadopoulos S, Malamou-Mitsi V, Scopa CD, Markaki S, Karagianni
E, Kyriakou V, Margariti A, et al: Evaluation of the prognostic
value of HER-2 and VEGF in breast cancer patients participating in
a randomized study with dose-dense sequential adjuvant
chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 96:251–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Liu Y, Tamimi RM, Collins LC, Schnitt SJ,
Gilmore HL, Connolly JL and Colditz GA: The association between
vascular endothelial growth factor expression in invasive breast
cancer and survival varies with intrinsic subtypes and use of
adjuvant systemic therapy: Results from the Nurses' Health Study.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 129:175–184. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Oosting SF, Brouwers AH, Van Es SC,
Nagengast WB, Oude Munnink TH, Lub-de Hooge MN, Hollema H, de Jong
JR, de Jong IJ, de Haas S, et al: 89Zr-bevacizumab PET imaging in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients before and during
antiangiogenic treatment. J Clin Oncol. 30(Suppl): 105812012.
|
|
108
|
Bluff JE, Menakuru SR, Cross SS, Higham
SE, Balasubramanian SP, Brown NJ, Reed MW and Staton CA:
Angiogenesis is associated with the onset of hyperplasia in human
ductal breast disease. Br J Cancer. 101:666–672. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Perk LR, Visser OJ, Stigter-van Walsum M,
Vosjan MJ, Visser GW, Zijlstra JM, Huijgens PC and van Dongen GA:
Preparation and evaluation of (89)Zr-Zevalin for monitoring of
(90)Y-Zevalin biodistribution with positron emission tomography.
Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 33:1337–1345. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Herzog H, Tellmann L, Scholten B, Coenen
HH and Qaim SM: PET imaging problems with the non-standard positron
emitters Yttrium-86 and Iodine-124. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
52:159–165. 2008.
|
|
111
|
Buchholz HG, Herzog H, Förster GJ, Reber
H, Nickel O, Rösch F and Bartenstein P: PET imaging with
yttrium-86: Comparison of phantom measurements acquired with
different PET scanners before and after applying background
subtraction. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 30:716–720. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Palm S, Enmon RM Jr, Matei C, Kolbert KS,
Xu S, Zanzonico PB, Finn RL, Koutcher JA, Larson SM and Sgouros G:
Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of (86)Y-Trastuzumab for (90)Y
dosimetry in an ovarian carcinoma model: Correlative MicroPET and
MRI. J Nucl Med. 44:1148–1155. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
O'Connor MK, Li H, Rhodes DJ, Hruska CB,
Clancy CB and Vetter RJ: Comparison of radiation exposure and
associated radiation-induced cancer risks from mammography and
molecular imaging of the breast. Med Phys. 37:6187–6198. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
De Jong JR, Warnders FJ, Nagengast WB,
Dierckx RAJO, Hospers GAP, Brouwers AH, De Vries EGE and De Hooge
MN: Radiation dosimetry of 111In-bevacizumab for
VEGF-SPECT in melanoma patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
37(Suppl): S477. 2010.
|
|
115
|
Börjesson PK, Jauw YW, de Bree R, Roos JC,
Castelijns JA, Leemans CR, van Dongen GA and Boellaard R: Radiation
dosimetry of 89Zr-labeled chimeric monoclonal antibody U36 as used
for immuno-PET in head and neck cancer patients. J Nucl Med.
50:1828–1836. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Murano T, Minamimoto R, Senda M, Uno K,
Jinnouchi S, Fukuda H, Iinuma T, Tsukamoto E, Terauchi T, Yoshida
T, et al: Radiation exposure and risk-benefit analysis in cancer
screening using FDG-PET: Results of a Japanese nationwide survey.
Ann Nucl Med. 25:657–666. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Gaykema SB, Brouwers AH, Lub-de Hooge MN,
Pleijhuis RG, Timmer-Bosscha H, Pot L, van Dam GM, van der Meulen
SB, de Jong JR, Bart J, et al: 89Zr-bevacizumab PET imaging in
primary breast cancer. J Nucl Med. 54:1014–1018. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Collingridge DR, Carroll VA, Glaser M,
Aboagye EO, Osman S, Hutchinson OC, Barthel H, Luthra SK, Brady F,
Bicknell R, et al: The development of [(124)I]iodinated-VG76e: A
novel tracer for imaging vascular endothelial growth factor in vivo
using positron emission tomography. Cancer Res. 62:5912–5919.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Jayson GC, Zweit J, Jackson A, Mulatero C,
Julyan P, Ranson M, Broughton L, Wagstaff J, Hakannson L,
Groenewegen G, et al; European Organisation for Research and
Treatment of Cancer Biological Therapeutic Development Group.
Molecular imaging and biological evaluation of HuMV833 anti-VEGF
antibody: Implications for trial design of antiangiogenic
antibodies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 94:1484–1493. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Chan C, Sandhu J, Guha A, Scollard DA,
Wang J, Chen P, Bai K, Lee L and Reilly RM: A human
transferrin-vascular endothelial growth factor (hnTf-VEGF) fusion
protein containing an integrated binding site for (111)In for
imaging tumor angiogenesis. J Nucl Med. 46:1745–1752.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Backer MV, Levashova Z, Patel V, Jehning
BT, Claffey K, Blankenberg FG and Backer JM: Molecular imaging of
VEGF receptors in angiogenic vasculature with single-chain
VEGF-based probes. Nat Med. 13:504–509. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Blankenberg FG, Backer MV, Levashova Z,
Patel V and Backer JM: In vivo tumor angiogenesis imaging with
site-specific labeled (99m)Tc-HYNIC-VEGF. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 33:841–848. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Wang H, Cai W, Chen K, Li ZB, Kashefi A,
He L and Chen X: A new PET tracer specific for vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor 2. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 34:2001–2010.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Hsu AR, Cai W, Veeravagu A, Mohamedali KA,
Chen K, Kim S, Vogel H, Hou LC, Tse V, Rosenblum MG, et al:
Multimodality molecular imaging of glioblastoma growth inhibition
with vasculature-targeting fusion toxin VEGF121/rGel. J Nucl Med.
48:445–454. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Cai W and Chen X: Multimodality imaging of
vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor expression. Front Biosci. 12:4267–4279. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Backer MV and Backer JM: Imaging key
biomarkers of tumor angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2:502–515. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|