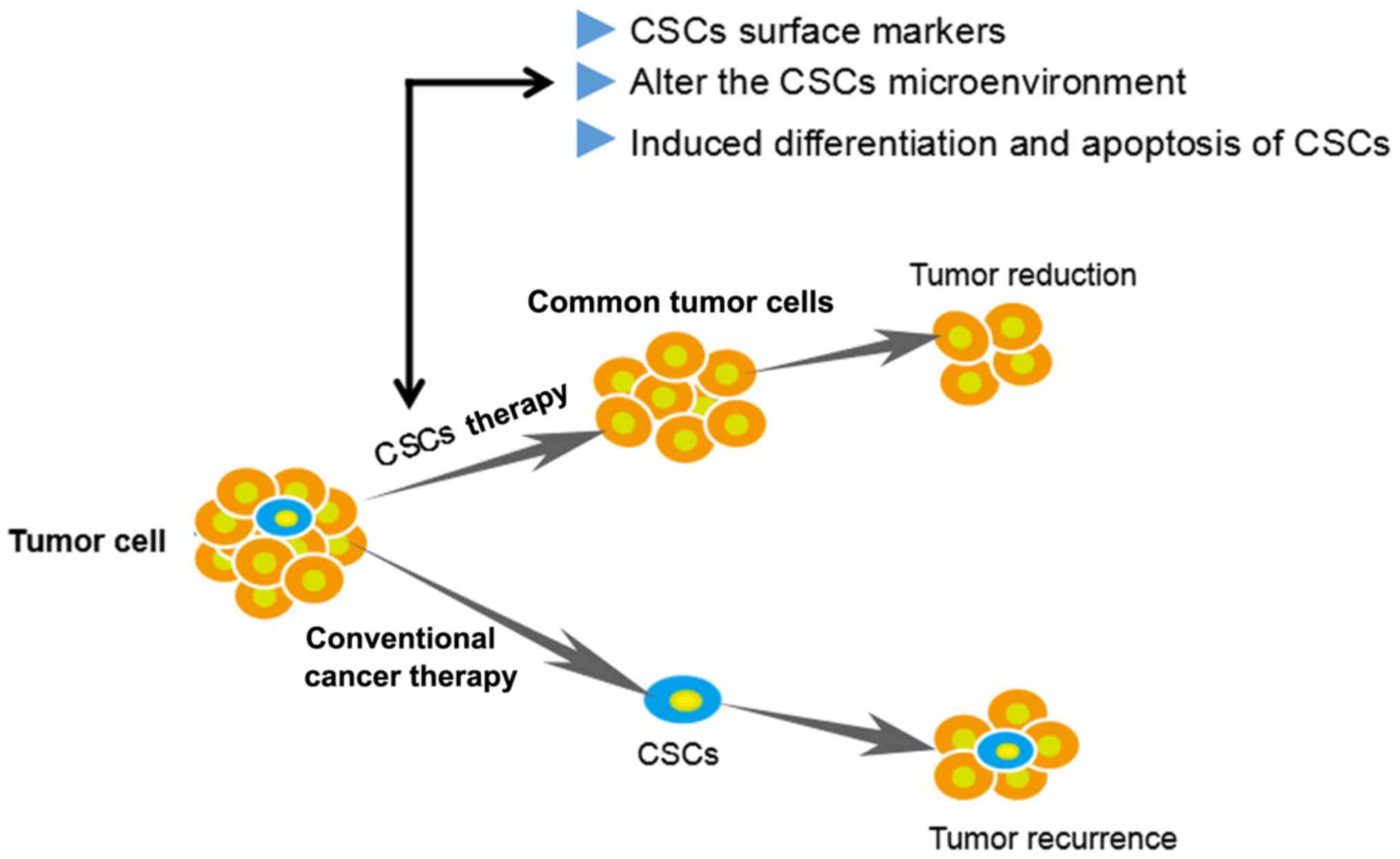
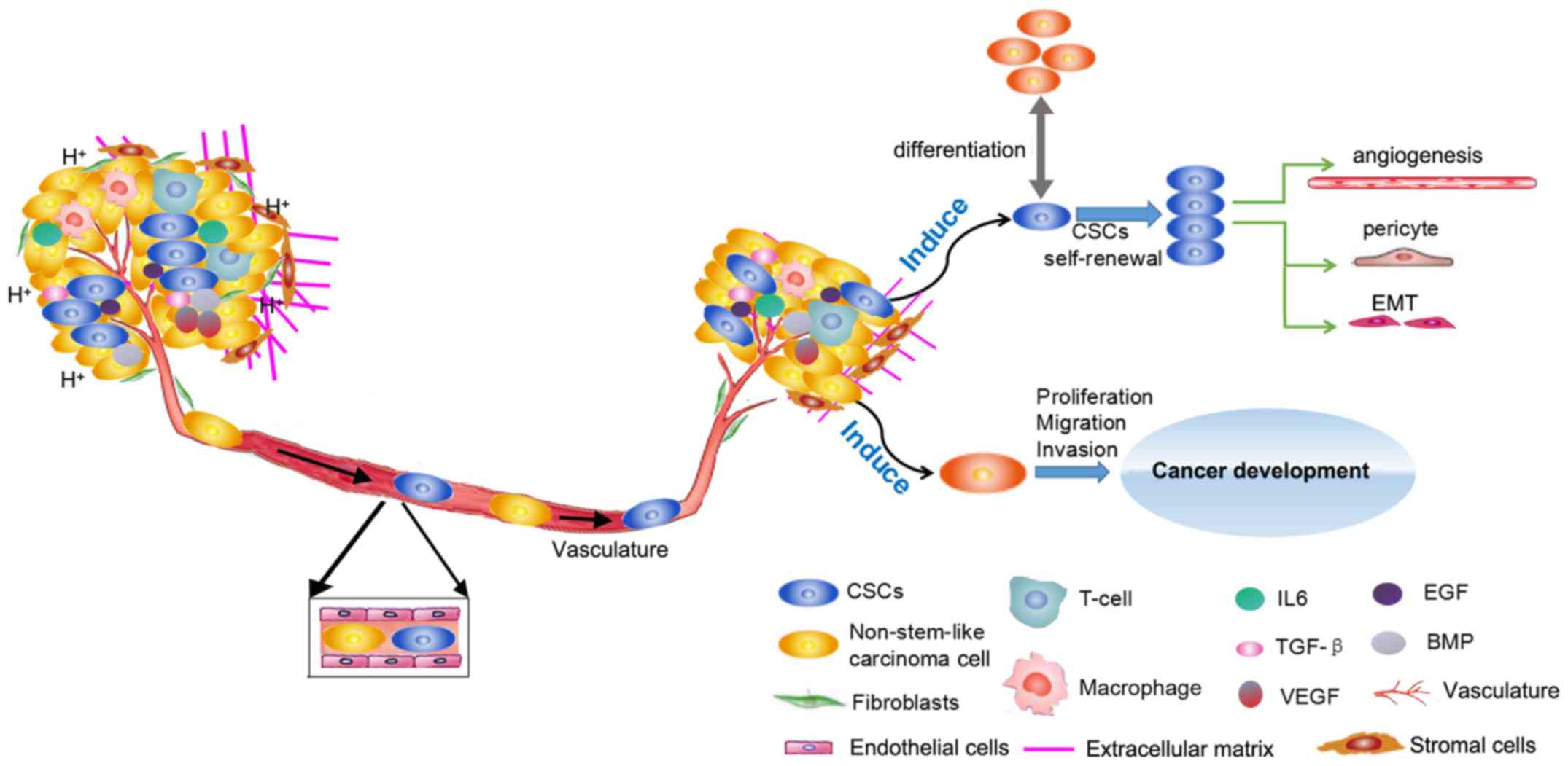
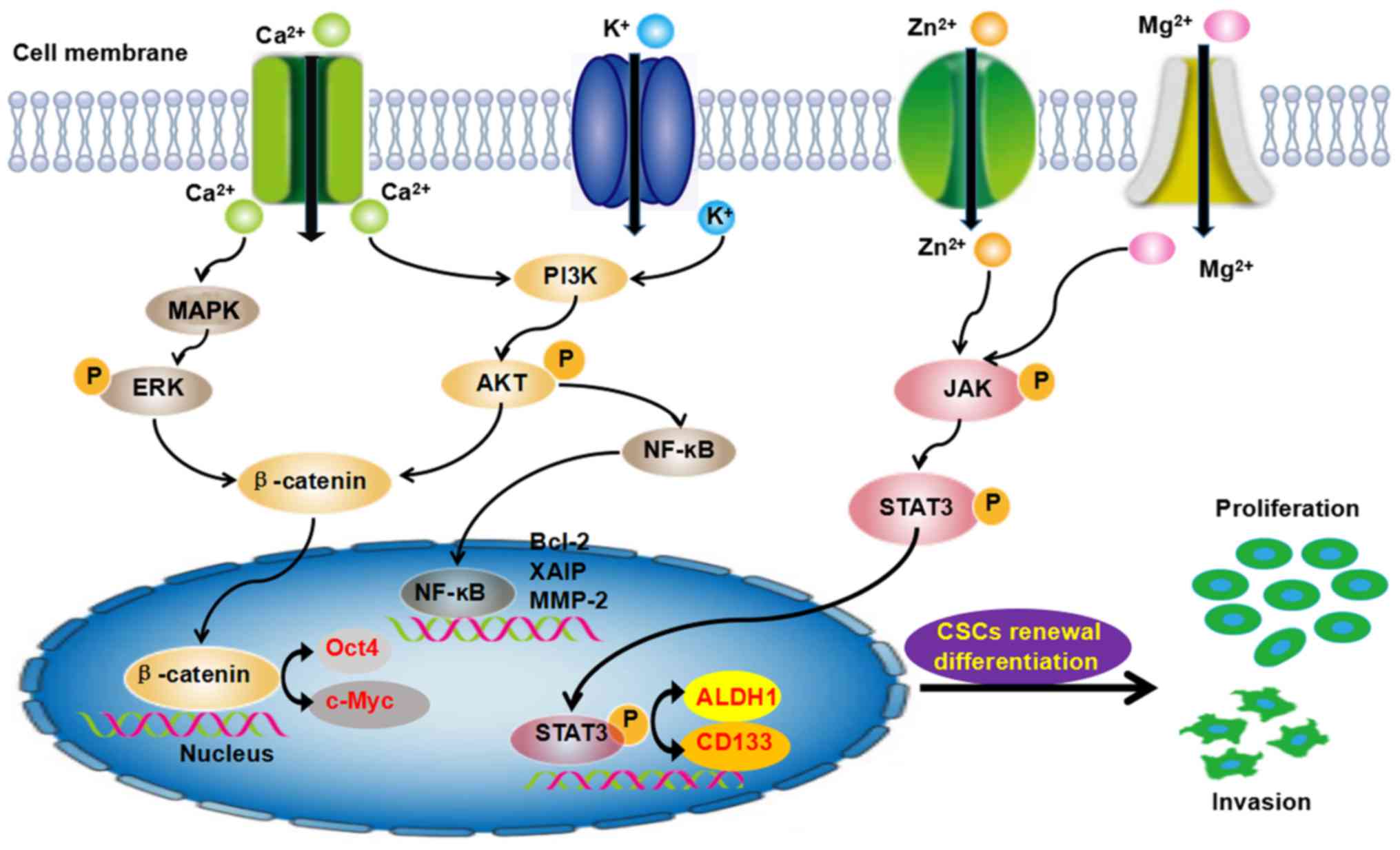
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hardingham JE, Grover P, Winter M, Hewett
PJ, Price TJ and Thierry B: Detection and clinical significance of
circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer - 20 years of
progress. Mol Med. 21(Suppl 1): S25–S31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Shiozawa Y, Nie B, Pienta KJ, Morgan TM
and Taichman RS: Cancer stem cells and their role in metastasis.
Pharmacol Ther. 138:285–293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dalerba P, Cho RW and Clarke MF: Cancer
stem cells: Models and concepts. Annu Rev Med. 58:267–284. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fan ST, Yang ZF, Ho DW, Ng MN, Yu WC and
Wong J: Prediction of posthepatectomy recurrence of hepatocellular
carcinoma by circulating cancer stem cells: A prospective study.
Ann Surg. 254:569–576. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chinn SB, Darr OA, Peters RD and Prince
ME: The role of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem
cells in tumorigenesis, metastasis, and treatment failure. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 3:902012.
|
|
7
|
Nandy SB and Lakshmanaswamy R: Cancer stem
cells and metastasis. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 151:137–176. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ribatti D: Cancer stem cells and tumor
angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 321:13–17. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marusyk A, Almendro V and Polyak K:
Intra-tumour heterogeneity: A looking glass for cancer? Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:323–334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ansieau S: EMT in breast cancer stem cell
generation. Cancer Lett. 338:63–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wei J, Wu A, Kong LY, Wang Y, Fuller G,
Fokt I, Melillo G, Priebe W and Heimberger AB: Hypoxia potentiates
glioma-mediated immunosuppression. PLoS One. 6:e161952011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Salnikov AV, Liu L, Platen M, Gladkich J,
Salnikova O, Ryschich E, Mattern J, Moldenhauer G, Werner J,
Schemmer P, et al: Hypoxia induces EMT in low and highly aggressive
pancreatic tumor cells but only cells with cancer stem cell
characteristics acquire pronounced migratory potential. PLoS One.
7:e463912012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takanami I, Inoue Y and Gika M: G-protein
inwardly rectifying potassium channel 1 (GIRK 1) gene expression
correlates with tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer.
BMC Cancer. 4:79–85. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stringer BK, Cooper AG and Shepard SB:
Overexpression of the G-protein inwardly rectifying potassium
channel 1 (GIRK1) in primary breast carcinomas correlates with
axillary lymph node metastasis. Cancer Res. 61:582–588.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Wang H, Qian Z, Feng B, Zhao X,
Jiang X and Tao J: Low-voltage-activated T-type Ca2+
channel inhibitors as new tools in the treatment of glioblastoma:
The role of endostatin. Pflugers Arch. 466:811–818. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang XT, Nagaba Y, Cross HS, Wrba F, Zhang
L and Guggino SE: The mRNA of L-type calcium channel elevated in
colon cancer: Protein distribution in normal and cancerous colon.
Am J Pathol. 157:1549–1562. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vanden Abeele F, Lemonnier L, Thébault S,
Lepage G, Parys JB, Shuba Y, Skryma R and Prevarskaya N: Two types
of store-operated Ca2+ channels with different
activation modes and molecular origin in LNCaP human prostate
cancer epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 279:30326–30337. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Catterall WA and Zheng N: Deciphering
voltage-gated Na(+) and Ca(2+) channels by studying prokaryotic
ancestors. Trends Biochem Sci. 40:526–534. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
González C, Baez-Nieto D, Valencia I,
Oyarzún I, Rojas P, Naranjo D and Latorre R: K(+) channels:
Function-structural overview. Compr Physiol. 2:2087–2149. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Firth AL, Remillard CV, Platoshyn O,
Fantozzi I, Ko EA and Yuan JX: Functional ion channels in human
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: Voltage-dependent cation
channels. Pulm Circ. 1:48–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Voglis G and Tavernarakis N: The role of
synaptic ion channels in synaptic plasticity. EMBO Rep.
7:1104–1110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hua SZ, Gottlieb PA, Heo J and Sachs F: A
mechanosensitive ion channel regulating cell volume. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 298:C1424–C1430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sardini A, Amey JS, Weylandt KH, Nobles M,
Valverde MA and Higgins CF: Cell volume regulation and
swelling-activated chloride channels. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1618:153–162. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Subramanyam P and Colecraft HM: Ion
channel engineering: Perspectives and strategies. J Mol Biol.
427:190–204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Grosse W, Essen LO and Koert U: Strategies
and perspectives in ion-channel engineering. ChemBioChem.
12:830–839. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang B, Cao L, Liu J, Xu Y, Milne G, Chan
W, Heys SD, McCaig CD and Pu J: Low expression of chloride channel
accessory 1 predicts a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Cancer.
121:1570–1580. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ievglevskyi O, Isaev D, Netsyk O, Romanov
A, Fedoriuk M, Maximyuk O, Isaeva E, Akaike N and Krishtal O:
Acid-sensing ion channels regulate spontaneous inhibitory activity
in the hippocampus: Possible implications for epilepsy. Philos
Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 371:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Feske S, Wulff H and Skolnik EY: Ion
channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol.
33:291–353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bulman DE: Phenotype variation and
newcomers in ion channel disorders. Hum Mol Genet. 6:1679–1685.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu J, Yang Y, Xie R, Liu J, Nie X, An J,
Wen G, Liu X, Jin H and Tuo B: The NCX1/TRPC6 complex mediates
TGFβ-driven migration and invasion of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 78:2564–2576. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moharil RB, Dive A, Khandekar S and
Bodhade A: Cancer stem cells: An insight. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol.
21:4632017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peters T: Calcium in physiological and
pathological cell function. Eur Neurol. 25(Suppl 1): 27–44. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Monteith GR, Davis FM and Roberts-Thomson
SJ: Calcium channels and pumps in cancer: Changes and consequences.
J Biol Chem. 287:31666–31673. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
D'Ascenzo M, Piacentini R, Casalbore P,
Budoni M, Pallini R, Azzena GB and Grassi C: Role of L-type
Ca2+ channels in neural stem/progenitor cell
differentiation. Eur J Neurosci. 23:935–944. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stewart TA, Yapa KT and Monteith GR:
Altered calcium signaling in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1848B:2502–2511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xie J, Pan H, Yao J, Zhou Y and Han W:
SOCE and cancer: Recent progress and new perspectives. Int J
Cancer. 138:2067–2077. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Prakriya M and Lewis RS: Store-operated
calcium channels. Physiol Rev. 95:1383–1436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee SH, Rigas NK, Lee CR, Bang A, Srikanth
S, Gwack Y, Kang MK, Kim RH, Park NH and Shin KH: Orai1 promotes
tumor progression by enhancing cancer stemness via NFAT signaling
in oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget.
7:43239–43255. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao W, Wang L, Han H, Jin K, Lin N, Guo
T, Chen Y, Cheng H, Lu F, Fang W, et al: 1B50-1, a mAb raised
against recurrent tumor cells, targets liver tumor-initiating cells
by binding to the calcium channel α2δ1 subunit. Cancer Cell.
23:541–556. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu M, Inoue K, Leng T, Guo S and Xiong
ZG: TRPM7 channels regulate glioma stem cell through STAT3 and
Notch signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 26:2773–2781. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Morelli MB, Nabissi M, Amantini C,
Farfariello V, Ricci-Vitiani L, di Martino S, Pallini R, Larocca
LM, Caprodossi S, Santoni M, et al: The transient receptor
potential vanilloid-2 cation channel impairs glioblastoma stem-like
cell proliferation and promotes differentiation. Int J Cancer.
131:E1067–E1077. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Curci A, Mele A, Camerino GM, Dinardo MM
and Tricarico D: The large conductance Ca(2+) -activated K(+)
(BKCa) channel regulates cell proliferation in SH-SY5Y
neuroblastoma cells by activating the staurosporine-sensitive
protein kinases. Front Physiol. 5:4762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rosa P, Sforna L, Carlomagno S, Mangino G,
Miscusi M, Pessia M, Franciolini F, Calogero A and Catacuzzeno L:
Overexpression of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium
channels in human glioblastoma stem-like cells and their role in
cell migration. J Cell Physiol. 232:2478–2488. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang YY, Yue J, Che H, Sun HY, Tse HF and
Li GR: BKCa and hEag1 channels regulate cell proliferation and
differentiation in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. J Cell Physiol. 229:202–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Nio K, Yamashita T and Kaneko S: The
evolving concept of liver cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer. 16:42017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Heubach JF, Graf EM, Leutheuser J, Bock M,
Balana B, Zahanich I, Christ T, Boxberger S, Wettwer E and Ravens
U: Electrophysiological properties of human mesenchymal stem cells.
J Physiol. 554:659–672. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li G-R, Sun H, Deng X and Lau CP:
Characterization of ionic currents in human mesenchymal stem cells
from bone marrow. Stem Cells. 23:371–382. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang S-P, Wang J-A, Luo R-H, Cui W-Y and
Wang H: Potassium channel currents in rat mesenchymal stem cells
and their possible roles in cell proliferation. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 35:1077–1084. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pardo LA and Stühmer W: The roles of K(+)
channels in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:39–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wang ZH, Shen B, Yao HL, Jia YC, Ren J,
Feng YJ and Wang YZ: Blockage of intermediate-conductance-Ca(2+)
-activated K(+) channels inhibits progression of human endometrial
cancer. Oncogene. 26:5107–5114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rao VR, Perez-Neut M, Kaja S and Gentile
S: Voltage-gated ion channels in cancer cell proliferation. Cancers
(Basel). 7:849–875. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Šatková J and Bébarová M: Functional
impact of hERG: From physiological role to target of anticancer
therapy. Vnitr Lek. 63:114–123. 2017.In Czech.
|
|
54
|
Li H, Liu L, Guo L, Zhang J, Du W, Li X,
Liu W, Chen X and Huang S: HERG K+ channel expression in
CD34+/CD38−/CD123(high) cells and primary
leukemia cells and analysis of its regulation in leukemia cells.
Int J Hematol. 87:387–392. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jehle J, Schweizer PA, Katus HA and Thomas
D: Novel roles for hERG K(+) channels in cell proliferation and
apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2:e1932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kubota D, Orita H, Yoshida A, Gotoh M,
Kanda T, Tsuda H, Hasegawa T, Katai H, Shimada Y, Kaneko K, et al:
Pfetin as a prognostic biomarker for gastrointestinal stromal
tumor: Validation study in multiple clinical facilities. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 41:1194–1202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li L, Duan T, Wang X, Zhang RH, Zhang M,
Wang S, Wang F, Wu Y, Huang H and Kang T: KCTD12 Regulates
colorectal cancer cell stemness through the ERK pathway. Sci Rep.
6:204602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jentsch TJ, Stein V, Weinreich F and
Zdebik AA: Molecular structure and physiological function of
chloride channels. Physiol Rev. 82:503–568. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nako Y, Shiozaki A, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S,
Konishi H, Iitaka D, Ishii H, Ikoma H, Kubota T, Fujiwara H, et al:
Enhancement of the cytocidal effects of hypotonic solution using a
chloride channel blocker in pancreatic cancer cells. Pancreatology.
12:440–448. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Soroceanu L, Manning TJ Jr and Sontheimer
H: Modulation of glioma cell migration and invasion using Cl(−) and
K(+) ion channel blockers. J Neurosci. 19:5942–5954. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Setti M, Savalli N, Osti D, Richichi C,
Angelini M, Brescia P, Fornasari L, Carro MS, Mazzanti M and
Pelicci G: Functional role of CLIC1 ion channel in
glioblastoma-derived stem/progenitor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst.
105:1644–1655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Deng YJ, Tang N, Liu C, Zhang JY, An SL,
Peng YL, Ma LL, Li GQ, Jiang Q, Hu CT, et al: CLIC4, ERp29, and
Smac/DIABLO derived from metastatic cancer stem-like cells stratify
prognostic risks of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:3809–3817. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Higgins CF: Volume-activated chloride
currents associated with the multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. J
Physiol. 482(Suppl): 31S–36S. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhao L, Zhao Y, Schwarz B, Mysliwietz J,
Hartig R, Camaj P, Bao Q, Jauch KW, Guba M, Ellwart JW, et al:
Verapamil inhibits tumor progression of chemotherapy-resistant
pancreatic cancer side population cells. Int J Oncol. 49:99–110.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Comes N, Bielanska J, Vallejo-Gracia A,
Serrano-Albarrás A, Marruecos L, Gómez D, Soler C, Condom E, Ramón
Y, Cajal S, Hernández-Losa J, et al: The voltage-dependent K(+)
channels Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 in human cancer. Front Physiol. 4:2832013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fraser SP, Grimes JA and Djamgoz MB:
Effects of voltage-gated ion channel modulators on rat prostatic
cancer cell proliferation: Comparison of strongly and weakly
metastatic cell lines. Prostate. 44:61–76. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
D'Alessandro G, Grimaldi A, Chece G,
Porzia A, Esposito V, Santoro A, Salvati M, Mainiero F, Ragozzino
D, Di Angelantonio S, et al: KCa3.1 channel inhibition sensitizes
malignant gliomas to temozolomide treatment. Oncotarget.
7:30781–30796. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kang MK and Kang SK: Pharmacologic
blockade of chloride channel synergistically enhances apoptosis of
chemotherapeutic drug-resistant cancer stem cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 373:539–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gritti M, Würth R, Angelini M, Barbieri F,
Peretti M, Pizzi E, Pattarozzi A, Carra E, Sirito R, Daga A, et al:
Metformin repositioning as antitumoral agent: Selective
antiproliferative effects in human glioblastoma stem cells, via
inhibition of CLIC1-mediated ion current. Oncotarget.
5:11252–11268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chiu LY, Ko JL, Lee YJ, Yang TY, Tee YT
and Sheu GT: L-type calcium channel blockers reverse docetaxel and
vincristine-induced multidrug resistance independent of ABCB1
expression in human lung cancer cell lines. Toxicol Lett.
192:408–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Firuzi O, Javidnia K, Mansourabadi E, Saso
L, Mehdipour AR and Miri R: Reversal of multidrug resistance in
cancer cells by novel asymmetrical 1,4-dihydropyridines. Arch Pharm
Res. 36:1392–1402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B,
Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, Minden M, Paterson B, Caligiuri MA and
Dick JE: A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after
transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 367:645–648. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bonnet D and Dick JE: Human acute myeloid
leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a
primitive hema-topoietic cell. Nat Med. 3:730–737. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hu G, Li F, Ouyang K, Xie F, Tang X, Wang
K, Han S, Jiang Z, Zhu M, Wen D, et al: Intrinsic gemcitabine
resistance in a novel pancreatic cancer cell line is associated
with cancer stem cell-like phenotype. Int J Oncol. 40:798–806.
2012.
|
|
75
|
de la Mare JA, Sterrenberg JN, Sukhthankar
MG, Chiwakata MT, Beukes DR, Blatch GL and Edkins AL: Assessment of
potential anti-cancer stem cell activity of marine algal compounds
using an in vitro mammosphere assay. Cancer Cell Int. 13:392013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kise K, Kinugasa-Katayama Y and Takakura
N: Tumor micro-environment for cancer stem cells. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 99B:197–205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Broz ML, Binnewies M, Boldajipour B,
Nelson AE, Pollack JL, Erle DJ, Barczak A, Rosenblum MD, Daud A,
Barber DL, et al: Dissecting the tumor myeloid compartment reveals
rare activating antigen-presenting cells critical for T cell
immunity. Cancer Cell. 26:638–652. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ishiwata T: Cancer stem cells and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Novel therapeutic targets for
cancer. Pathol Int. 66:601–608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Plaks V, Kong N and Werb Z: The cancer
stem cell niche: How essential is the niche in regulating stemness
of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell. 16:225–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Wang L, Fan J, Hitron JA, Son YO, Wise JT,
Roy RV, Kim D, Dai J, Pratheeshkumar P, Zhang Z, et al: Cancer
stem-like cells accumulated in nickel-induced malignant
transformation. Toxicol Sci. 151:376–387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Oskarsson T, Batlle E and Massagué J:
Metastatic stem cells: Sources, niches, and vital pathways. Cell
Stem Cell. 14:306–321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Tian Y, Bresenitz P, Reska A, El Moussaoui
L, Beier CP and Gründer S: Glioblastoma cancer stem cell lines
express functional acid sensing ion channels ASIC1a and ASIC3. Sci
Rep. 7:136742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Shiozaki A, Kudou M, Ichikawa D, Fujiwara
H, Shimizu H, Ishimoto T, Arita T, Kosuga T, Konishi H, Komatsu S,
et al: Esophageal cancer stem cells are suppressed by tranilast, a
TRPV2 channel inhibitor. J Gastroenterol. 53:197–207. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Bao B, Azmi AS, Li Y, Ahmad A, Ali S,
Banerjee S, Kong D and Sarkar FH: Targeting CSCs in tumor
microenvironment: The potential role of ROS-associated miRNAs in
tumor aggressiveness. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:22–35. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|