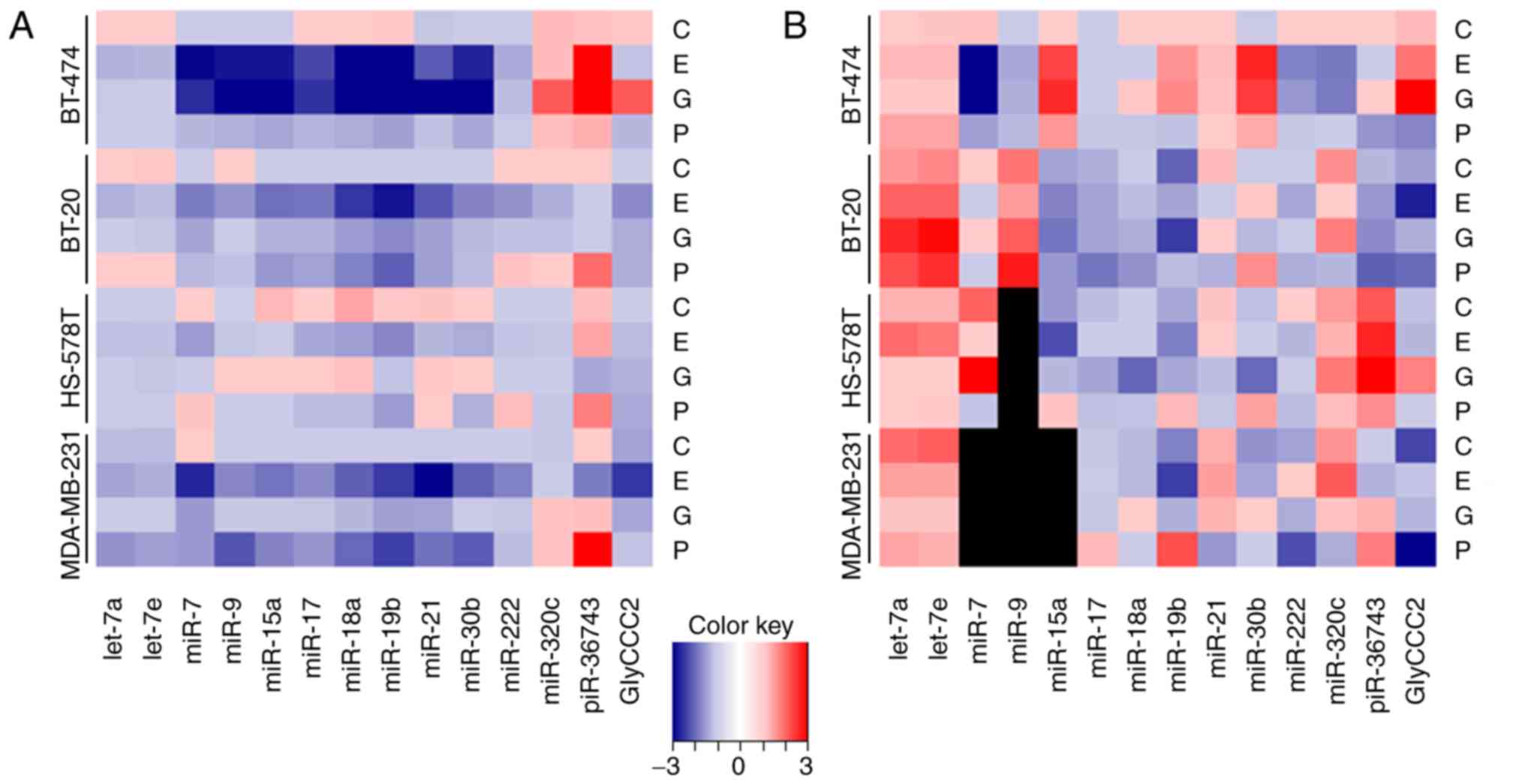
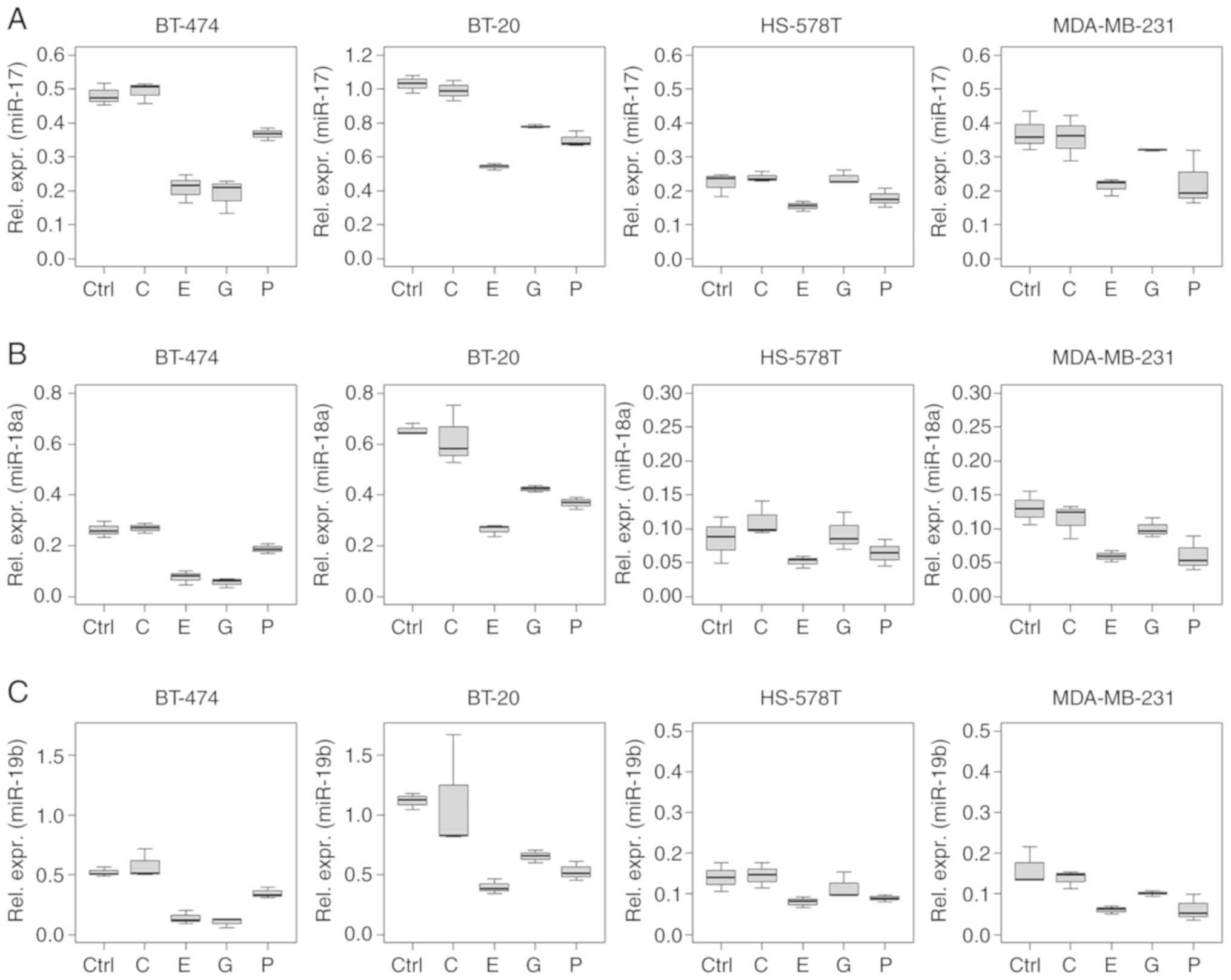
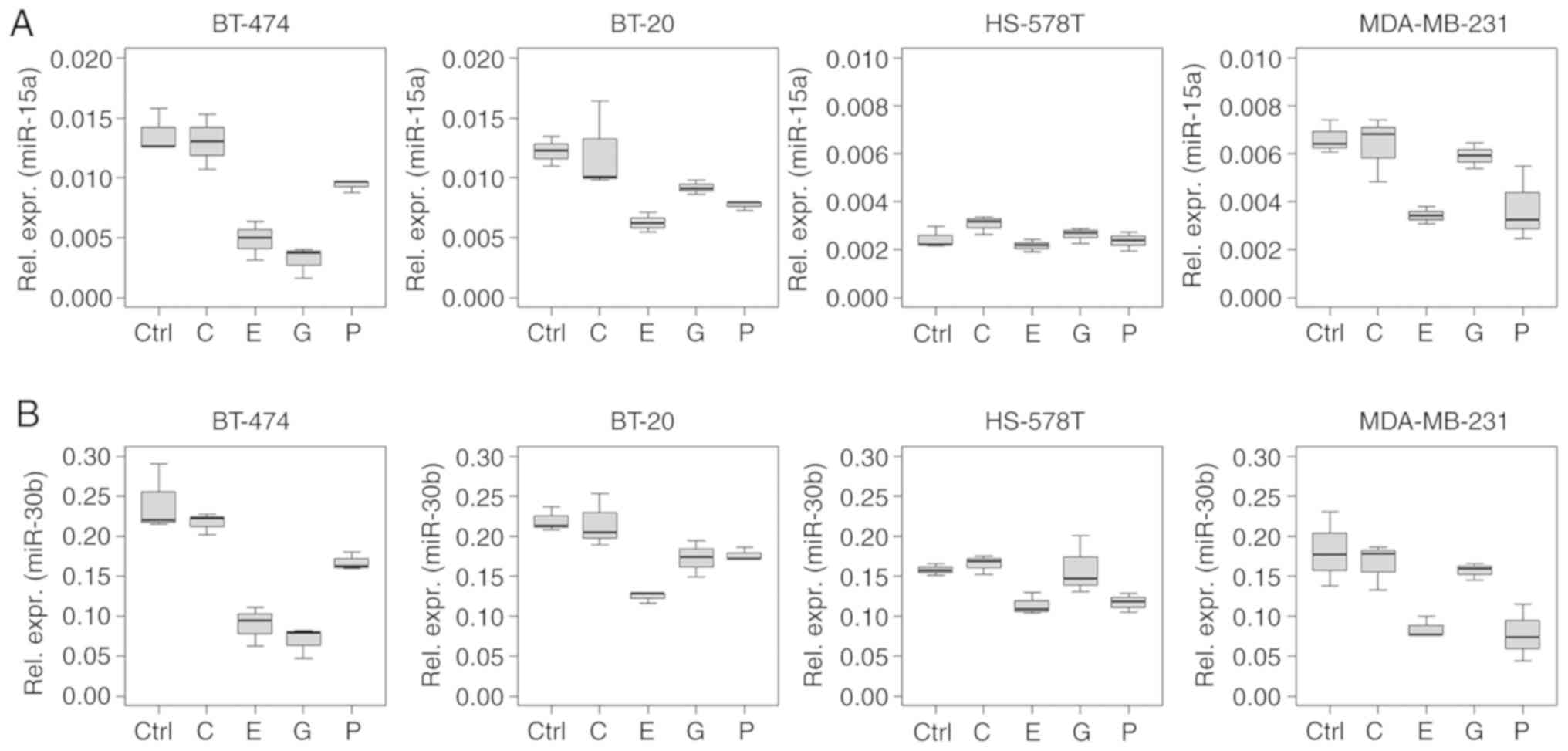
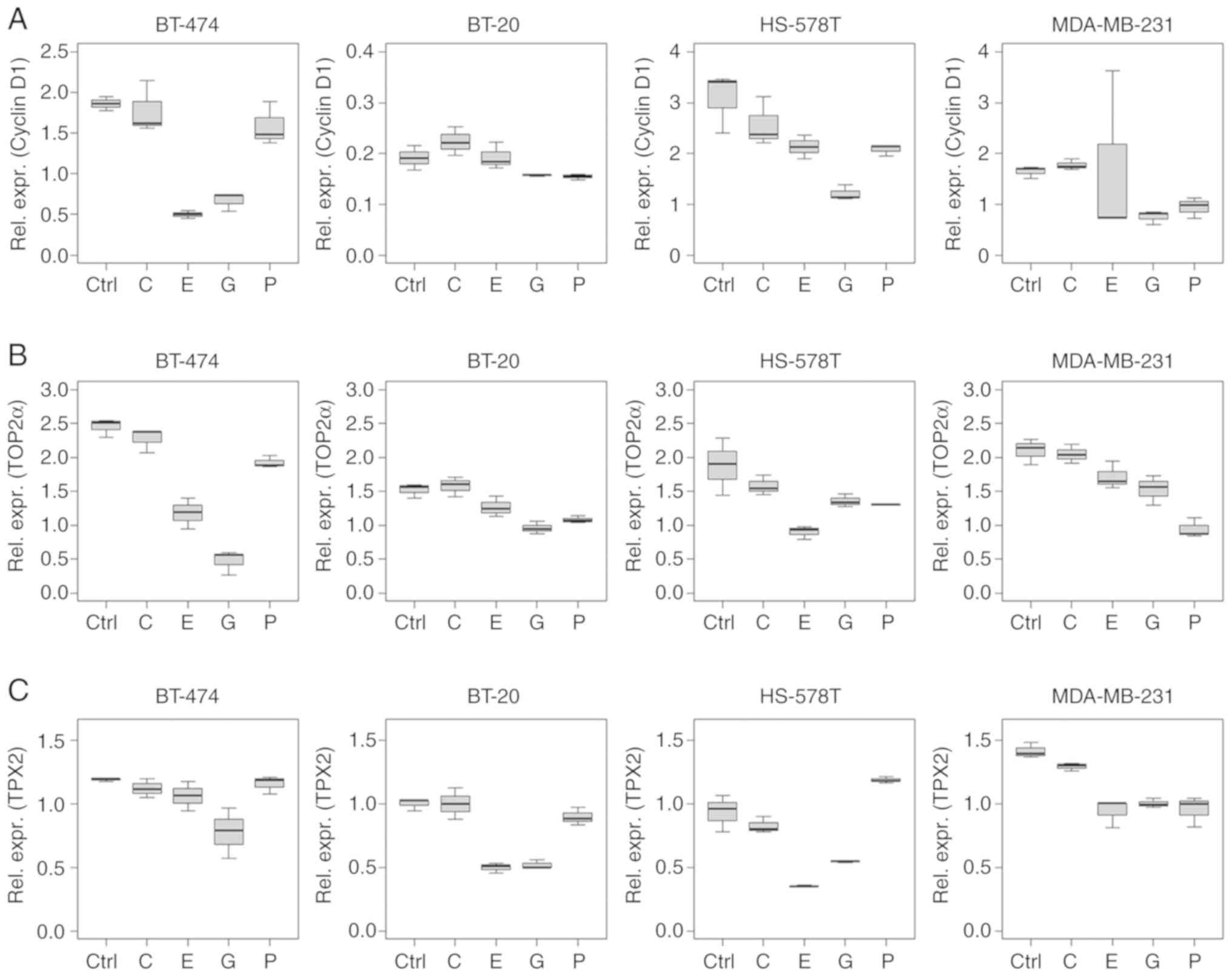
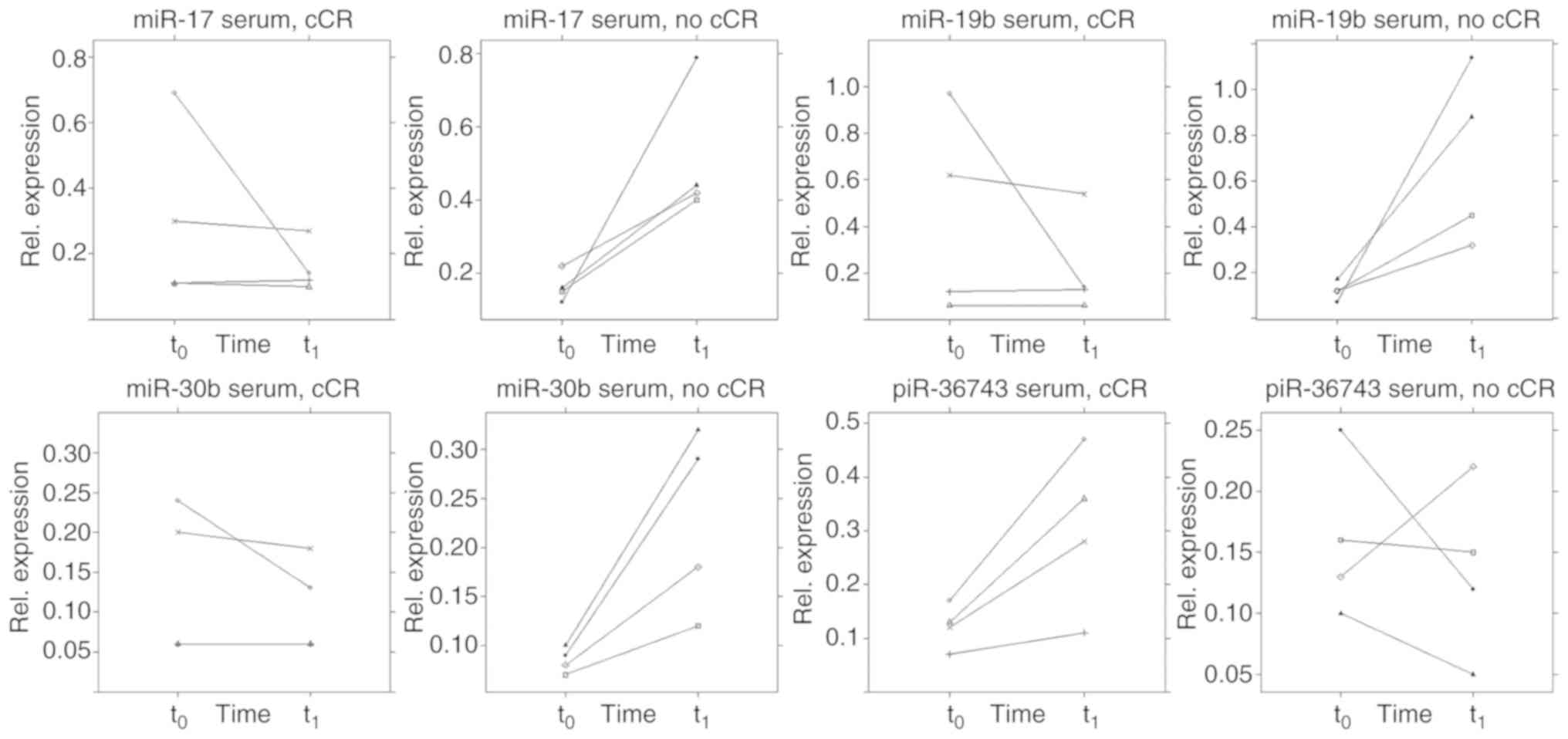
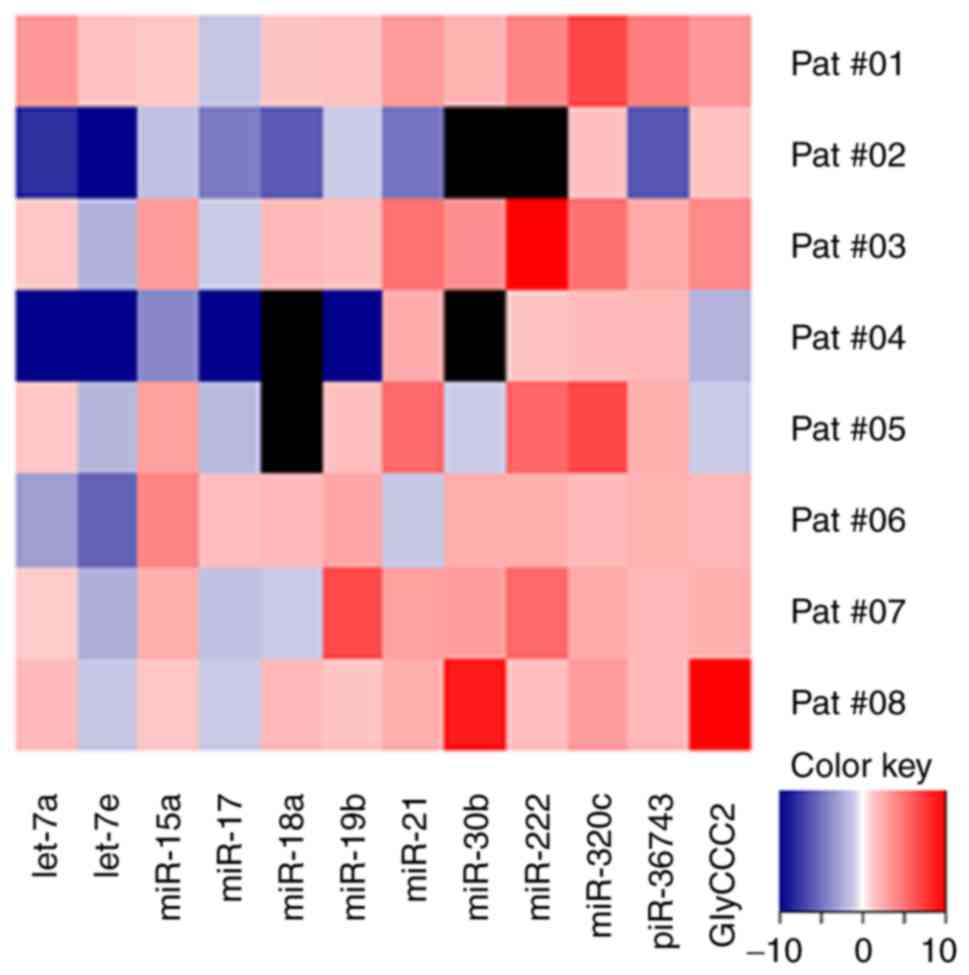
|
1
|
World Health Organization IAfRoC: Cancer
Today. 2018, https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
Accessed April 4, 2019.
|
|
2
|
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists'
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG): Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal
therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival:
An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 365:1687–1717. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C,
Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X and Perou CM: Phenotypic and
molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pérou CM, Sprlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sprlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber
RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ and Panel
Members: Tailoring therapies-improving the management of early
breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the
Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 20l5. Ann Oncol.
26:1533–1546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
American Cancer Society: Breast
CancerFacts &Figures. 2017-2018, American Cancer Society;
Atlanta, GA: 2017, https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-stati-stics/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures-2017-2018.pdf.
Accessed April 02, 2019.
|
|
9
|
Badve S, Dabbs DJ, Schnitt SJ, Baehner FL,
Decker T, Eusebi V, Fox SB, Ichihara S, Jacquemier J, Lakhani SR,
et al: Basal-like and triple-negative breast cancers: A critical
review with an emphasis on the implications for pathologists and
oncologists. Mod Pathol. 24:157–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Plasilova ML, Hayse B, Killelea BK,
Horowitz NR, Chagpar AB and Lannin DR: Features of triple-negative
breast cancer: Analysis of 38,813 cases from the national cancer
database. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e46142016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yeh J, Chun J, Schwartz S, Wang A, Kern E,
Guth AA, Axelrod D, Shapiro R and Schnabel F: Clinical
characteristics in patients with triple negative breast cancer. Int
J Breast Cancer. 2017:17961452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anders CK and Carey LA: Biology,
metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative
breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 9(Suppl 2): S73–S81. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Toft DJ and Cryns VL: Minireview:
Basal-like breast cancer: From molecular profiles to targeted
therapies. Mol Endocrinol. 25:199–211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Bertucci F, Finetti P, Cervera N, Esterni
B, Hermitte F, Viens P and Birnbaum D: How basal are
triple-negative breast cancers? Int J Cancer. 123:236–240. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Harbeck N and Gnant M: Breast cancer.
Lancet. 389:1134–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mieog JS, van der Hage JA and van de Velde
CJ: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for operable breast cancer. Br J Surg.
94:1189–1200. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mieog JS, van der Hage JA and van de Velde
CJ: Preoperative chemotherapy for women with operable breast
cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD0050022007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fisher B, Bryant J, Wolmark N, Mamounas E,
Brown A, Fisher ER, Wickerham DL, Begovic M, DeCillis A, Robidoux
A, et al: Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of
women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 16:2672–2685.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rastogi P, Anderson SJ, Bear HD, Geyer CE,
Kahlenberg MS, Robidoux A, Margolese RG, Hoehn JL, Vogel VG, Dakhil
SR, et al: Preoperative chemotherapy: Updates of National surgical
adjuvant breast and bowel project protocols B-18 and B-27. J Clin
Oncol. 26:778–785. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van der Hage JA, van de Velde CJ, Julien
JP, Tubiana-Hulin M, Vandervelden C and Duchateau L: Preoperative
chemotherapy in primary operable breast cancer: Results from the
European organization for research and treatment of cancer trial
10902. J Clin Oncol. 19:4224–4237. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU,
Costa SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, Gerber B, Eiermann W, Hilfrich
J, Huober J, et al: Definition and impact of pathologic complete
response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various
intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 30:1796–1804. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Berruti A, Amoroso V, Gallo F, Bertaglia
V, Simoncini E, Pedersini R, Ferrari L, Bottini A, Bruzzi P and
Sormani MP: Pathologic complete response as a potential surrogate
for the clinical outcome in patients with breast cancer after
neoadjuvant therapy: A meta-regression of 29 randomized prospective
studies. J Clin Oncol. 32:3883–3891. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, Mehta K,
Costantino JP, Wolmark N, Bonnefoi H, Cameron D, Gianni L,
Valagussa P, et al: Pathological complete response and long-term
clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis.
Lancet. 384:164–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Loibl S, Volz C, Mau C, Blohmer JU, Costa
SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, Gerber B, Hanusch C, Jackisch C, et
al: Response and prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 1,051
patients with infiltrating lobular breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 144:153–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Nüesch E, Loibl
S, Kaufmann M, Kümmel S, Fasching PA, Eiermann W, Blohmer JU, Costa
SD, et al: Impact of treatment characteristics on response of
different breast cancer phenotypes: Pooled analysis of the German
neo-adjuvant chemotherapy trials. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
125:145–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
von Minckwitz G, Blohmer JU, Costa SD,
Denkert C, Eidtmann H, Eiermann W, Gerber B, Hanusch C, Hilfrich J,
Huober J, et al: Response-guided neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31:3623–3630. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diagnosis and treatment of patients with
primary and metastatic breast cancer. http://www.ago-online.de.
Accessed April 2, 2019.
|
|
29
|
Marinovich ML, Houssami N, Macaskill P,
von Minckwitz G, Blohmer JU and Irwig L: Accuracy of ultrasound for
predicting pathologic response during neoadjuvant therapy for
breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 136:2730–2737. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chagpar AB, Middleton LP, Sahin AA,
Dempsey P, Buzdar AU, Mirza AN, Ames FC, Babiera GV, Feig BW, Hunt
KK, et al: Accuracy of physical examination, ultrasonography, and
mammography in predicting residual pathologic tumor size in
patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg.
243:257–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sadeghi-Naini A, Sannachi L, Tadayyon H,
Tran WT, Slodkowska E, Trudeau M, Gandhi S, Pritchard K, Kolios MC
and Czarnota GJ: Chemotherapy-response monitoring of breast cancer
patients using quantitative ultrasound-based Intra-tumour
heterogeneities. Sci Rep. 7:103522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amoroso V, Generali D, Buchholz T,
Cristofanilli M, Pedersini R, Curigliano G, Daidone MG, Di Cosimo
S, Dowsett M, Fox S, et al: International expert consensus on
primary systemic therapy in the management of early breast cancer:
Highlights of the fifth symposium on primary systemic therapy in
the management of operable breast cancer, Cremona, Italy 2013. J
Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2015:90–96. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andrè F,
Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B,
Green M, et al: Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term
survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:1275–1281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
von Minckwitz G, Blohmer JU, Raab G, Lohr
A, Gerber B, Heinrich G, Eidtmann H, Kaufmann M, Hilfrich J,
Jackisch C, et al: In vivo chemosensitivity-adapted preoperative
chemotherapy in patients with early-stage breast cancer: The
GEPARTRIO pilot study. Ann Oncol. 16:56–63. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hombach S and Kretz M: Non-coding RNAs:
Classification, biology and functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol.
937:3–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brosnan CA and Voinnet O: The long and the
short of noncoding RNAs. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:416–425. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS and Slack FJ:
Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:5–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Izzotti A, Carozzo S, Pulliero A,
Zhabayeva D, Ravetti JL and Bersimbaev R: Extracellular MicroRNA in
liquid biopsy: Applicability in cancer diagnosis and prevention. Am
J Cancer Res. 6:1461–1493. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qi P, Zhou XY and Du X: Circulating long
non-coding RNAs in cancer: Current status and future perspectives.
Mol Cancer. 15:392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang X, Cheng Y, Lu Q, Wei J, Yang H and
Gu M: Detection of stably expressed piRNAs in human blood. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:13353–13358. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fanale D, Castiglia M, Bazan V and Russo
A: Involvement of Non-coding RNAs in Chemo- and radioresistance of
colorectal cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 937:207–228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Magee P, Shi L and Garofalo M: Role of
microRNAs in chemo- resistance. Ann Transl Med. 3:3322015.
|
|
44
|
Wang YW, Zhang W and Ma R: Bioinformatic
identification of chemoresistance-associated microRNAs in breast
cancer based on microarray data. Oncol Rep. 39:1003–1010.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Malhotra A, Jain M, Prakash H, Vasquez KM
and Jain A: The regulatory roles of long non-coding RNAs in the
development of chemoresistance in breast cancer. Oncotarget.
8:110671–110684. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kao J, Salari K, Bocanegra M, Choi YL,
Girard L, Gandhi J, Kwei KA, Hernandez-Boussard T, Wang P, Gazdar
AF, et al: Molecular profiling of breast cancer cell lines defines
relevant tumor models and provides a resource for cancer gene
discovery. PLoS One. 4:e61462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ: Panel members:
Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer:
Highlights of the St Gallen international expert consensus on the
primary therapy of Early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol.
24:2206–2223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Elston CW and Ellis IO: Pathological
prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological
grade in breast cancer: Experience from a large study with
long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 19:403–410. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Busk PK: A tool for design of primers for
microRNA-specific quantitative RT-qPCR. BMC Bioinformatics.
15:292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Torres A, Torres K, Wdowiak P, Paszkowski
T and Maciejewski R: Selection and validation of endogenous
controls for microRNA expression studies in endometrioid
endometrial cancer tissues. Gynecol Oncol. 130:588–594. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bockmeyer CL, Säuberlich K, Wittig J, Eßer
M, Roeder SS, Vester U, Hoyer PF, Agustian PA, Zeuschner P, Amann
K, et al: Comparison of different normalization strategies for the
analysis of glomerular microRNAs in IgA nephropathy. Sci Rep.
6:319922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen L, Jin Y, Wang L, Sun F, Yang X, Shi
M, Zhan C, Shi Y and Wang Q: Identification of reference genes and
miRNAs for qRT-PCR in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med
Oncol. 34:22017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Masè M, Grasso M, Avogaro L, D'Amato E,
Tessarolo F, Graffigna A, Denti MA and Ravelli F: Selection of
reference genes is critical for miRNA expression analysis in human
cardiac tissue. A focus on atrial fibrillation. Sci Rep.
7:411272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C and
Neuvians TP: Determination of stable housekeeping genes,
differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:
BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations.
Biotechnol Lett. 26:509–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mestdagh P, Van Vlierberghe P, De Weer A,
Muth D, Westermann F, Speleman F and Vandesompele J: A novel and
universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome
Biol. 10:R642009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
D'Haene B, Mestdagh P, Hellemans J and
Vandesompele J: miRNA expression profiling: From reference genes to
global mean normalization. Methods Mol Biol. 822:261–272. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Schwarzenbach H, da Silva AM, Calin G and
Pantel K: Data Normalization strategies for MicroRNA
quantification. Clin Chem. 61:1333–1342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Erbes T, Hirschfeld M, Rücker G, Jaeger M,
Boas J, Iborra S, Mayer S, Gitsch G and Stickeler E: Feasibility of
urinary microRNA detection in breast cancer patients and its
potential as an innovative non-invasive biomarker. BMC Cancer.
15:1932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Marabita F, de Candia P, Torri A, Tegnér
J, Abrignani S and Rossi RL: Normalization of circulating microRNA
expression data obtained by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Brief
Bioinform. 17:204–212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
61
|
Song W, Zhang WH, Zhang H, Li Y, Zhang Y,
Yin W and Yang Q: Validation of housekeeping genes for the
normalization of RT-qPCR expression studies in oral squamous cell
carcinoma cell line treated by 5 kinds of chemotherapy drugs. Cell
Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand). 62:29–34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia
AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ and
Klenk DC: Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal
Biochem. 150:76–85. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Schägger H and von Jagow G: Tricine-sodium
dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the
separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal
Biochem. 166:368–379. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
R Core Team: R: A language and environment
for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing;
Vienna: 2018
|
|
65
|
Gao D, Qi X, Zhang X, Fang K, Guo Z and Li
L: hsa_ circRNA_0006528 as a competing endogenous RNA promotes
human breast cancer progression by sponging miR-75p and activating
the MAPK/ERK signalling pathway. Mol Carcinog. 58:554–564. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Gao D, Zhang X, Liu B, Meng D, Fang K, Guo
Z and Li L: Screening circular RNA related to chemotherapeutic
resistance in breast cancer. Epigenomics. 9:1175–1188. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Uhr K, Sieuwerts AM, de Weerd V, Smid M,
Hammerl D, Foekens JA and Martens JWM: Association of microRNA-7
and its binding partner CDR1-AS with the prognosis and prediction
of 1st-line tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Sci Rep.
8:96572018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
68
|
Garcia-Vazquez R, Ruiz-García E, Meneses
García A, Astudillo-de la Vega H, Lara-Medina F, Alvarado-Miranda
A, Mal donado-Martínez H, Gonzalez-Barrios JA, Campos-Parra AD,
Rodríguez Cuevas S, et al: A microRNA signature associated with
pathological complete response to novel neoadjuvant therapy regimen
in triple-negative breast cancer. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177028992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Unger FT, Klasen HA, Tchartchian G, de
Wilde RL and Witte I: DNA damage induced by cis- and carboplatin as
indicator for in vitro sensitivity of ovarian carcinoma cells. BMC
Cancer. 9:3592009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Su WC, Chang SL, Chen TY, Chen JS and Tsao
CJ: Comparison of in vitro growth-inhibitory activity of
carboplatin and cisplatin on leukemic cells and hematopoietic
progenitors: The myelosuppressive activity of carboplatin may be
greater than its antileukemic effect. Jpn. J Clin Oncol.
30:562–567. 2000.
|
|
71
|
Kuittinen T, Rovio P, Staff S, Luukkaala
T, Kallioniemi A, Grénman S, Laurila M and Maenpaa J: Paclitaxel,
carboplatin and 1,25D3 inhibit proliferation of endometrial cancer
cells in vitro. Anticancer Res. 37:6575–6581. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
He Q, Liang CH and Lippard SJ: Steroid
hormones induce HMG1 overexpression and sensitize breast cancer
cells to cisplatin and carboplatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:5768–5772. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Diehl JA, Zindy F and Sherr CJ: Inhibition
of cyclin D1 phosphorylation on threonine-286 prevents its rapid
degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev.
11:957–972. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Luo H, Zhang J, Dastvan F, Yanagawa B,
Reidy MA, Zhang HM, Yang D, Wilson JE and McManus BM:
Ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of cyclin D1 is associated with
coxsackievirus-induced cell growth arrest. J Virol. 77:1–9. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
75
|
Fuller-Pace FV: DEAD box RNA helicase
functions in cancer. RNA Biol. 10:121–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Mazurek A, Luo W, Krasnitz A, Hicks J,
Powers RS and Stillman B: DDX5 regulates DNA replication and is
required for cell proliferation in a subset of breast cancer cells.
Cancer Discov. 2:812–825. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang D, Huang J and Hu Z: RNA helicase
DDX5 regulates microRNA expression and contributes to cytoskeletal
reorganization in basal breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Proteomics.
11:M111.0119322012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
78
|
Bates GJ, Nicol SM, Wilson BJ, Jacobs AM,
Bourdon JC, Wardrop J, Gregory DJ, Lane DP, Perkins ND and
Fuller-Pace FV: The DEAD box protein p68: A novel transcriptional
coactivator of the p53 tumour suppressor. EMBO J. 24:543–553. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wortham NC, Ahamed E, Nicol SM, Thomas RS,
Periyasamy M, Jiang J, Ochocka AM, Shousha S, Huson L, Bray SE, et
al: The DEAD-box protein p72 regulates ERalpha-/oestrogen-dependent
transcription and cell growth, and is associated with improved
survival in ERalpha-positive breast cancer. Oncogene. 28:4053–4064.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shin S, Rossow KL, Grande JP and Janknecht
R: Involvement of RNA helicases p68 and p72 in colon cancer. Cancer
Res. 67:7572–7578. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jalal C, Uhlmann-Schiffler H and Stahl H:
Redundant role of DEAD box proteins p68 (Ddx5) and p72/p82 (Ddx17)
in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Nucleic Acids Res.
35:3590–3601. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Concepcion CP, Bonetti C and Ventura A:
The microRNA-17-92family of microRNA clusters in development and
disease. Cancer J. 18:262–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Mogilyansky E and Rigoutsos I: The
miR-17/92 cluster: A comprehensive update on its genomics,
genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles
in health and disease. Cell Death Differ. 20:1603–1614. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Farazi TA, Horlings HM, Ten Hoeve JJ,
Mihailovic A, Halfwerk H, Morozov P, Brown M, Hafner M, Reyal F,
van Kouwenhove M, et al: MicroRNA sequence and expression analysis
in breast tumors by deep sequencing. Cancer Res. 71:4443–4453.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Calvano Filho CM, Calvano-Mendes DC,
Carvalho KC, Maciel GA, Ricci MD, Torres AP, Filassi JR and Baracat
EC: Triple-negative and luminal A breast tumors: Differential
expression of miR-18a-5p, and miR-17-5p, and miR-20a-5p. Tumour
Biol. 35:7733–7741. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hashim A, Rizzo F, Marchese G, Ravo M,
Tarallo R, Nassa G, Giurato G, Santamaria G, Cordella A, Cantarella
C and Weisz A: RNA sequencing identifies specific PIWI-interacting
small non-coding RNA expression patterns in breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 5:9901–9910. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Liu B, Su F, Chen M, Li Y, Qi X, Xiao J,
Li X, Liu X, Liang W, Zhang Y and Zhang J: Serum miR-21 and
miR-125b as markers predicting neoadjuvant chemotherapy response
and prognosis in stage II/III breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 64:44–52.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gu X, Xue JQ, Han SJ, Qian SY and Zhang
WH: Circulating microRNA-451 as a predictor of resistance to
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Biomark.
16:395–403. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Al-Khanbashi M, Caramuta S, Alajmi AM,
Al-Haddabi I, Al-Riyami M, Lui WO and Al-Moundhri MS: Tissue and
Serum miRNA profile in locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) in
response to Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) treatment. PLoS One.
11:e01520322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Edgar JR: Q&A: What are exosomes,
exactly? BMC Biol. 14:462016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
91
|
Ben-Dov IZ, Whalen VM, Goilav B, Max KE
and Tuschl T: Cell and microvesicle urine microRNA deep sequencing
profiles from healthy individuals: Observations with potential
impact on biomarker studies. PLoS One. 11:e01472492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Shirjang S,
Baghbani E and Baradaran B: Micro RNA 34a and Let-7a expression in
human breast cancers is associated with apoptotic expression genes.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:1887–1890. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Liu K, Zhang C, Li T, Ding Y, Tu T, Zhou
F, Qi W, Chen H and Sun X: Let-7a inhibits growth and migration of
breast cancer cells by targeting HMGA1. Int J Oncol. 46:2526–2534.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Marques MM, Evangelista AF, Macedo T,
Vieira RADC, Scapulatempo-Neto C, Reis RM, Carvalho AL and Silva
IDCGD: Expression of tumor suppressors miR-195 and let-7a as
potential biomarkers of invasive breast cancer. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 73:e1842018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
95
|
Huang SK, Luo Q, Peng H, Li J, Zhao M,
Wang J, Gu YY, Li Y, Yuan P, Zhao GH and Huang CZ: A Panel of serum
noncoding RNAs for the diagnosis and monitoring of response to
therapy in patients with breast cancer. Med Sci Monit.
24:2476–2488. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Khalighfard S, Alizadeh AM, Irani S and
Omranipour R: Plasma miR-21, miR-155, miR-10b, and Let-7a as the
potential biomarkers for the monitoring of breast cancer patients.
Sci Rep. 8:179812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Mi Y, Liu F, Liang X, Liu S, Huang X, Sang
M and Geng C: Tumor suppressor let-7a inhibits breast cancer cell
proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting MAGE-A1.
Neoplasma. 66:54–62. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Guo Q, Wen R, Shao B, Li Y, Jin X, Deng H,
Wu J, Su F and Yu F: Combined Let-7a and H19 signature: A
prognostic index of progression-free survival in primary breast
cancer patients. J Breast Cancer. 21:142–149. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Lehmann TP, Korski K, Gryczka R, Ibbs M,
Thieleman A, Grodecka-Gazdecka S and Jagodzinski PP: Relative
levels of let-7a, miR-17, miR-27b, miR-125a, miR-125b and miR-206
as potential molecular markers to evaluate grade, receptor status
and molecular type in breast cancer. Mol Med Rep. 12:4692–4702.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Thakur S, Grover RK, Gupta S, Yadav AK and
Das BC: Identification of Specific miRNA signature in paired sera
and tissue samples of Indian Women with Triple Negative breast
cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01589462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ahram M, Mustafa E, Zaza R, Abu Hammad S,
Alhudhud M, Bawadi R and Zihlif M: Differential expression and
androgen regulation of microRNAs and metalloprotease 13 in breast
cancer cells. Cell Biol Int. 41:1345–1355. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yu CC, Chen YW, Chiou GY, Tsai LL, Huang
PI, Chang CY, Tseng LM, Chiou SH, Yen SH, Chou MY, et al: MicroRNA
let-7a represses chemoresistance and tumourigenicity in head and
neck cancer via stem-like properties ablation. Oral Oncol.
47:202–210. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Qiu L, Zhang GF, Yu L, Wang HY, Jia XJ and
Wang TJ: Novel oncogenic and chemoresistance-inducing functions of
resistin in ovarian cancer cells require miRNAs-mediated induction
of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Sci Rep. 8:125222018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Xiao G, Wang X and Yu Y: CXCR4/Let-7a Axis
regulates metastasis and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells
through targeting HMGA2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:840–851. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Serguienko A, Grad I, Wennerstrpm AB,
Meza-Zepeda LA, Thiede B, Stratford EW, Myklebost O and Munthe E:
Metabolic reprogramming of metastatic breast cancer and melanoma by
let-7a microRNA. Oncotarget. 6:2451–2465. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Tsang WP and Kwok TT: Let-7a microRNA
suppresses therapeutics-induced cancer cell death by targeting
caspase-3. Apoptosis. 13:1215–1222. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Wu J, Li S, Jia W, Deng H, Chen K, Zhu L,
Yu F and Su F: Reduced let-7a is associated with chemoresistance in
primary breast cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01336432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Bhutia YD, Hung SW, Krentz M, Patel D,
Lovin D, Manoharan R, Thomson JM and Govindarajan R: Differential
processing of let-7a precursors influences RRM2 expression and
chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer: Role of LIN-28 and SET
oncoprotein. PLoS One. 8:e534362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Lu L, Schwartz P, Scarampi L, Rutherford
T, Canuto EM, Yu H and Katsaros D: MicroRNA let-7a: A potential
marker for selection of paclitaxel in ovarian cancer management.
Gynecol Oncol. 122:366–371. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Lv K, Liu L, Wang L, Yu J, Liu X, Cheng Y,
Dong M, Teng R, Wu L, Fu P, et al: Lin28 mediates paclitaxel
resistance by modulating p21, Rb and Let-7a miRNA in breast cancer
cells. PLoS One. 7:e400082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yin PT, Pongkulapa T, Cho HY, Han J,
Pasquale NJ, Rabie H, Kim JH, Choi JW and Lee KB: Overcoming
chemoresistance in cancer via combined MicroRNA therapeutics with
anticancer drugs using multifunctional magnetic Core-shell
nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 10:26954–26963. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Farré PL, Scalise GD, Duca RB, Dalton GN,
Massillo C, Porretti J, Grana K, Gardner K, De Luca P and De Siervi
A: CTBP1 and metabolic syndrome induce an mRNA and miRNA expression
profile critical for breast cancer progression and metastasis.
Oncotarget. 9:13848–13858. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Aure MR, Leivonen SK, Fleischer T, Zhu Q,
Overgaard J, Alsner J, Tramm T, Louhimo R, Alnaes GI, Perala M, et
al: Individual and combined effects of DNA methylation and copy
number alterations on miRNA expression in breast tumors. Genome
Biol. 14:R1262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lv J, Xia K, Xu P, Sun E, Ma J, Gao S,
Zhou Q, Zhang M, Wang F, Chen F, et al: miRNA expression patterns
in chemoresistant breast cancer tissues. Biomed Pharmacother.
68:935–942. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Oztemur Islakoglu Y, Noyan S, Aydos A and
Gur Dedeoglu B: Meta-microRNA biomarker signatures to classify
breast cancer subtypes. OMICS. 22:709–716. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Shan Y, Liu Y, Zhao L, Liu B, Li Y and Jia
L: MicroRNA-33a and let-7e inhibit human colorectal cancer
progression by targeting ST8SIA1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
90:48–58. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Svoboda M, Sana J, Fabian P, Kocakova I,
Gombosova J, Nekvindova J, Radova L, Vyzula R and Slaby O: MicroRNA
expression profile associated with response to neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer patients.
Radiat Oncol. 7:1952012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Cai J, Yang C, Yang Q, Ding H, Jia J, Guo
J, Wang J and Wang Z: Deregulation of let-7e in epithelial ovarian
cancer promotes the development of resistance to cisplatin.
Oncogenesis. 2:e752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle
C, Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 111:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Xiao M, Cai J, Cai L, Jia J, Xie L, Zhu Y,
Huang B, Jin D and Wang Z: Let-7e sensitizes epithelial ovarian
cancer to cisplatin through repressing DNA double strand break
repair. J Ovarian Res. 10:242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Block I, Burton M, Sprensen KP, Andersen
L, Larsen MJ, Bak M, Cold S, Thomassen M, Tan Q and Kruse TA:
Association of miR-548c-5p, miR-7-5p, miR-210-3p, miR-128-3p with
recurrence in systemically untreated breast cancer. Oncotarget.
9:9030–9042. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M, Look MP,
de Weerd V, Boersma AW, Klijn JG, Wiemer EA and Martens JW: Four
miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative,
estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13021–13026. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Gong C, Tan W, Chen K, You N, Zhu S, Liang
G, Xie X, Li Q, Zeng Y, Ouyang N, et al: Prognostic value of a
BCSC-associated MicroRNA signature in hormone receptor-positive
HER2-negative breast cancer. EBioMedicine. 11:199–209. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Raychaudhuri M, Bronger H, Buchner T,
Kiechle M, Weichert W and Avril S: MicroRNAs miR-7 and miR-340
predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 162:511–521. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Shi Y, Ye P and Long X: Differential
expression profiles of the transcriptome in breast cancer cell
lines revealed by next generation sequencing. Cell Physiol Biochem.
44:804–816. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Cui YX, Bradbury R, Flamini V, Wu B,
Jordan N and Jiang WG: MicroRNA-7 suppresses the homing and
migration potential of human endothelial cells to highly metastatic
human breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 117:89–101. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Vera-Puente O, Rodriguez-Antolin C,
Salgado-Figueroa A, Michalska P, Pernia O, Reid BM, Rosas R,
Garcia-Guede A, SacristAn S, Jimenez J, et al: MAFG is a potential
therapeutic target to restore chemosensitivity in
cisplatin-resistant cancer cells by increasing reactive oxygen
species. Transl Res. 200:1–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Filipits M, Nielsen TO, Rudas M, Greil R,
Stoger H, Jakesz R, Bago-Horvath Z, Dietze O, Regitnig P and
Gruber-Rossipal C: et al The PAM50 risk-of-recurrence score
predicts risk for late distant recurrence after endocrine therapy
in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast
cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 20:1298–1305. 2014.
|
|
129
|
Blume CJ, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Hüllein J,
Sellner L, Jethwa A, Stolz T, Slabicki M, Lee K, Sharathchandra A,
Benner A, et al: p53-dependent non-coding RNA networks in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 29:2015–2023. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Liu DZ, Chang B, Li XD, Zhang QH and Zou
YH: MicroRNA-9 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion
of breast cancer cells via down-regulating FOXO1. Clin Transl
Oncol. 19:1133–1140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh
P, Muth D, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reinhardt F, Onder TT, Valastyan S,
et al: miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin
and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 12:247–256. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Sporn JC, Katsuta E, Yan L and Takabe K:
Expression of MicroRNA-9 is associated with overall survival in
breast cancer patients. J Surg Res. 233:426–435. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Orangi E and Motovali-Bashi M: Evaluation
of miRNA-9 and miRNA-34a as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of
breast cancer in Iranian women. Gene. 687:272–279. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Naorem LD, Muthaiyan M and Venkatesan A:
Identification of dysregulated miRNAs in triple negative breast
cancer: A meta-analysis approach. J Cell Physiol. 234:11768–11779.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Kia V, Paryan M, Mortazavi Y, Biglari A
and Mohammadi-Yeganeh S: Evaluation of exosomal miR-9 and miR-155
targeting PTEN and DUSP14 in highly metastatic breast cancer and
their effect on low metastatic cells. J Cell Biochem.
120:5666–5676. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Jang MH, Kim HJ, Gwak JM, Chung YR and
Park SY: Prognostic value of microRNA-9 and microRNA-155 expression
in triple-negative breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 68:69–78. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Cheng CW, Yu JC, Hsieh YH, Liao WL, Shieh
JC, Yao CC, Lee HJ, Chen PM, Wu PE and Shen CY: Increased cellular
levels of MicroRNA-9 and MicroRNA-221 correlate with cancer
stemness and predict poor outcome in human breast cancer. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 48:2205–2218. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
D'Ippolito E, Plantamura I, Bongiovanni L,
Casalini P, Baroni S, Piovan C, Orlandi R, Gualeni AV, Gloghini A,
Rossini A, et al: miR-9 and miR-200 Regulate PDGFRp-mediated
endothelial differentiation of tumor cells in Triple-negative
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 76:5562–5572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Li X, Pan Q, Wan X, Mao Y, Lu W, Xie X and
Cheng X: Methylation-associated Has-miR-9 deregulation in pacli-
taxel-resistant epithelial ovarian carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
15:5092015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Pezuk JA, Miller TLA, Bevilacqua JLB, de
Barros ACSD, de Andrade FEM, E Macedo LFA, Aguilar V, Claro ANM,
Camargo AA, Galante PAF and Reis LFL: Measuring plasma levels of
three microRNAs can improve the accuracy for identification of
malignant breast lesions in women with BI-RADS 4 mammography.
Oncotarget. 8:83940–83948. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Kodahl AR, Lyng MB, Binder H, Cold S,
Gravgaard K, Knoop AS and Ditzel HJ: Novel circulating microRNA
signature as a potential non-invasive multi-marker test in
ER-positive early-stage breast cancer: A case control study. Mol
Oncol. 8:874–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Yang L, Zhao W, Wei P, Zuo W and Zhu S:
Tumor suppressor p53 induces miR-15a processing to inhibit neuronal
apoptosis inhibitory protein (NAIP) in the apoptotic response DNA
damage in breast cancer cell. Am J Transl Res. 9:683–691.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Patel N, Garikapati KR, Ramaiah MJ,
Polavarapu KK, Bhadra U and Bhadra MP: miR-15a/miR-16 induces
mitochondrial dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cells by
suppressing oncogene BMI1. Life Sci. 164:60–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Hamdi K, Blancato J, Goerlitz D, Islam M,
Neili B, Abidi A, Gat A, Ayed FB, Chivi S, Loffredo C, et al:
Circulating Cell-free miRNA expression and its association with
clinicopathologic features in inflammatory and non-inflammatory
breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:1801–1810. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Shinden Y, Akiyoshi S, Ueo H, Nambara S,
Saito T, Komatsu H, Ueda M, Hirata H, Sakimura S, Uchi R, et al:
Diminished expression of MiR-15a is an independent prognostic
marker for breast cancer cases. Anticancer Res. 35:123–127.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Li F, Xu Y, Deng S, Li Z, Zou D, Yi S, Sui
W, Hao M and Qiu L: MicroRNA-15a/161 cluster located at chromosome
13q14 is down-regulated but displays different expression pattern
and prognostic significance in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget.
6:38270–38282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Patel N, Garikapati KR, Makani VKK, Nair
AD, Vangara N, Bhadra U and Pal Bhadra M: Regulating BMI1
expression via miRNAs promote Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transition
(MET) and sensitizes breast cancer cell to chemotherapeutic drug.
PLoS One. 13:e01902452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Monroig PDC, Redis RS,
Bayraktar E, Almeida MI, Ivan C, Fuentes-Mattei E, Rashed MH,
Chavez-Reyes A, Ozpolat B, et al: Regulation of hnRNPA1 by
microRNAs controls the miR-18a-K-RAS axis in chemotherapy-resistant
ovarian cancer. Cell Discov. 3:170292017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Wang L, Zhang X, Sheng L, Qiu C and Luo R:
LINC00473 promotes the Taxol resistance via miR-15a in colorectal
cancer. Biosci Rep. 38:pii: BSR20180790. 2018.
|
|
150
|
Chu J, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Sun L, Lv X, Wu Y, Hu
P, Su F, Gong C, Song E, et al: E2F7 overexpression leads to
tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells by competing with E2F1
at miR-15a/16 promoter. Oncotarget. 6:31944–31957. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Jurkovicova D, Smolkova B, Magyerkova M,
Sestakova Z, Kajabova VH, Kulcsar L, Zmetakova I, Kalinkova L,
Krivulcik T, Karaba M, et al: Down-regulation of traditional
oncomiRs in plasma of breast cancer patients. Oncotarget.
8:77369–77384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Zhang N, Zhang H, Liu Y, Su P, Zhang J,
Wang X, Sun M, Chen B, Zhao W, Wang L, et al: SREBP1, targeted by
miR-18a-5p, modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast
cancer via forming a co-repressor complex with Snail and HDAC1/2.
Cell Death Differ. 26:843–859. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Yang F, Li Y, Xu L, Zhu Y, Gao H, Zhen L
and Fang L: miR-17 as a diagnostic biomarker regulates cell
proliferation in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 10:543–550.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Wang Y, Li J, Dai L, Zheng J, Yi Z and
Chen L: MiR-17-5p may serve as a novel predictor for breast cancer
recurrence. Cancer Biomark. 22:721–726. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Sueta A, Yamamoto Y, Tomiguchi M,
Takeshita T, Yamamoto-Ibusuki M and Iwase H: Differential
expression of exosomal miRNAs between breast cancer patients with
and without recurrence. Oncotarget. 8:69934–69944. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Hesari A, Azizian M, Darabi H, Nesaei A,
Hosseini SA, Salarinia R, Motaghi AA and Ghasemi F: Expression of
circulating miR-17, miR-25, and miR-133 in breast cancer patients.
J Cell Biochem. Nov 28–2018. View Article : Google Scholar : Epub ahead of
print.
|
|
157
|
Li H, Liu J, Chen J, Wang H, Yang L, Chen
F, Fan S, Wang J, Shao B, Yin D, et al: A serum microRNA signature
predicts trastuzumab benefit in HER2-positive metastatic breast
cancer patients. Nat Commun. 9:16142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Braicu C, Raduly L, Morar-Bolba G,
Cojocneanu R, Jurj A, Pop LA, Pileczki V, Ciocan C, Moldovan A,
Irimie A, et al: Aberrant miRNAs expressed in HER-2 negative breast
cancers patient. J Exp Cli. Cancer Res. 37:2572018.
|
|
159
|
Li J, Lai Y, Ma J, Liu Y, Bi J, Zhang L,
Chen L, Yao C, Lv W, Chang G, et al: miR-17-5p suppresses cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting ETV1 in triple-negative
breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 17:7452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Li X, Wu B, Chen L, Ju Y, Li C and Meng S:
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor inhibits apoptosis in
triple-negative breast cancer through miR-17/20a suppression of
death receptors 4 and 5. Oncotarget. 8:88645–88657. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Cui YH, Kim H, Lee M, Yi JM, Kim RK, Uddin
N, Yoo KC, Kang JH, Choi MY, Cha HJ, et al: FBXL14 abolishes breast
cancer progression by targeting CDCP1 for proteasomal degradation.
Oncogene. 37:5794–5809. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Wang ST, Liu LB, Li XM, Wang YF, Xie PJ,
Li Q, Wang R, Wei Q, Kang YH, Meng R, et al: Circ-ITCH regulates
triple-negative breast cancer progression through the Wnt/p-catenin
pathway. Neoplasma. 66:232–239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Jia J, Zhan D, Li J, Li Z, Li H and Qian
J: The contrary functions of lncRNA HOTAIR/miR-17-5p/PTEN axis and
Shenqifuzheng injection on chemosensitivity of gastric cancer
cells. J Cell Mol Med. 23:656–669. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Wu DM, Hong XW, Wang LL, Cui XF, Lu J,
Chen GQ and Zheng YL: MicroRNA-17 inhibition overcomes
chemoresistance and suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through a DEDD-dependent mechanism in gastric cancer. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 102:59–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Fan B, Shen C, Wu M, Zhao J, Guo Q and Luo
Y: miR-17-92 cluster is connected with disease progression and
oxaliplatin/capecitabine chemotherapy efficacy in advanced gastric
cancer patients: A preliminary study. Medicine (Baltimore).
97:e120072018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Huang FX, Chen HJ, Zheng FX, Gao ZY, Sun
PF, Peng Q, Liu Y, Deng X, Huang YH, Zhao C and Miao LJ: LncRNA
BLACAT1 is involved in chemoresistance of nonsmall cell lung cancer
cells by regulating autophagy. Int J Oncol. 54:339–347. 2019.
|
|
167
|
Gu J, Wang D, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Li Y, Chen
H, Shi M, Wang X, Shen B, Deng X, et al: GFRa2 prompts cell growth
and chemo- resistance through down-regulating tumor suppressor gene
PTEN via Mir-17-5p in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 380:434–441.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Cioffi M, Trabulo SM, Sanchez-Ripoll Y,
Miranda-Lorenzo I, Lonardo E, Dorado J, Reis Vieira C, Ramirez JC,
Hidalgo M, Aicher A, et al: The miR-17-92 cluster counteracts
quiescence and chemoresistance in a distinct subpopulation of
pancreatic cancer stem cells. Gut. 64:1936–1948. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Yan HJ, Liu WS, Sun WH, Wu J, Ji M, Wang
Q, Zheng X, Jiang JT and Wu CP: miR-17-5p inhibitor enhances chemo-
sensitivity to gemcitabine via upregulating Bim expression in
pancreatic cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci. 57:3160–3167. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Ao X: Decreased expression of microRNA-17
and microRNA-20b promotes breast cancer resistance to taxol therapy
by upregula- tion of NCOA3. Cell Death Dis. 7:e24632016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Liao XH, Xiang Y, Yu CX, Li JP, Li H and
Nie Q: STAT3 is required for MiR-17-5p-mediated sensitization to
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:15763–15774. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Zhu H, Yang SY, Wang J, Wang L and Han SY:
Evidence for miR-s17-92 and miR-134 gene cluster regulation of
ovarian cancer drug resistance. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:2526–2531. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Fang Y, Xu C and Fu Y: MicroRNA-17-5p
induces drug resistance and invasion of ovarian carcinoma cells by
targeting PTEN signaling. J Biol Res (Thessalon). 22:122015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay D and
Chakrabarti G: miR-17-5p downregulation contributes to paclitaxel
resistance of lung cancer cells through altering beclin1
expression. PLoS One. 9:e957162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Krutilina R, Sun W, Sethuraman A, Brown M,
Seagroves TN, Pfeffer LM, Ignatova T and Fan M: MicroRNA-18a
inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor 1a activity and lung metastasis
in basal breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 16:R782014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Godfrey AC, Xu Z, Weinberg CR, Getts RC,
Wade PA, DeRoo LA, Sandler DP and Taylor JA: Serum microRNA
expression as an early marker for breast cancer risk in
prospectively collected samples from the Sister Study cohort.
Breast Cancer Res. 15:R422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Shidfar A, Costa FF, Scholtens D, Bischof
JM, Sullivan ME, Ivancic DZ, Vanin EF, Soares MB, Wang J and Khan
SA: Expression of miR-18a and miR-210 in normal breast tissue as
candidate biomarkers of breast cancer risk. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 10:89–97. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Sha LY, Zhang Y, Wang W, Sui X, Liu SK,
Wang T and Zhang H: MiR-18a upregulation decreases Dicer expression
and confers paclitaxel resistance in triple negative breast cancer.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2201–2208. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Xiao H, Liu Y, Liang P, Wang B, Tan H,
Zhang Y, Gao X and Gao J: TP53TG1 enhances cisplatin sensitivity of
non-small cell lung cancer cells through regulating miR-18a/PTEN
axis. Cell Biosci. 8:232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Hummel R, Sie C, Watson DI, Wang T, Ansar
A, Michael MZ, Van der Hoek M, Haier J and Hussey DJ: MicroRNA
signatures in chemotherapy resistant esophageal cancer cell lines.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:14904–14912. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Fan YX, Dai YZ, Wang XL, Ren YQ, Han JJ
and Zhang H: MiR-18a upregulation enhances autophagy in triple
negative cancer cells via inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2194–2200. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Zhu HY, Bai WD, Ye XM, Yang AG and Jia LT:
Long non-coding RNA UCA1 desensitizes breast cancer cells to
trastuzumab by impeding miR-18a repression of Yes-associated
protein 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 496:1308–1313. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Li M, Zhou Y, Xia T, Zhou X, Huang Z,
Zhang H, Zhu W, Ding Q and Wang S: Circulating microRNAs from the
miR-106a-363 cluster on chromosome X as novel diagnostic biomarkers
for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 170:257–270. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Li C, Zhang J, Ma Z, Zhang F and Yu W:
miR-19b serves as a prognostic biomarker of breast cancer and
promotes tumor progression through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Onco
Targets Ther. 11:4087–4095. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Zhao L, Zhao Y, He Y and Mao Y: miR-19b
promotes breast cancer metastasis through targeting MYLIP and its
related cell adhesion molecules. Oncotarget. 8:64330–64343.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Liu M, Yang R, Urrehman U, Ye C, Yan X,
Cui S, Hong Y, Gu Y, Liu Y, Zhao C, et al: MiR-19b suppresses PTPRG
to promote breast tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 7:64100–64108.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Maleki E, Ghaedi K, Shahanipoor K and
Karimi Kurdistani Z: Down-regulation of microRNA-19b in hormone
receptor-posi- tive/HER2-negative breast cancer. APMI. S.
126:303–308. 2018.
|
|
188
|
Wu Q, Guo L, Jiang F, Li L, Li Z and Chen
F: Analysis of the miRNA-mRNA-lncRNA networks in ER+ and ER-breast
cancer cell lines. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2874–2887. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Kurokawa K, Tanahashi T, Iima T, Yamamoto
Y, Akaike Y, Nishida K, Masuda K, Kuwano Y, Murakami Y, Fukushima M
and Rokutan K: Role of miR-19b and its target mRNAs in 5-fluo -
rouracil resistance in colon cancer cells. J Gastroenterol.
47:883–895. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Thorne JL, Battaglia S, Baxter DE, Hayes
JL, Hutchinson SA, Jana S, Millican-Slater RA, Smith L, Teske MC,
Wastall LM and Hughes TA: MiR-19b non-canonical binding is directed
by HuR and confers chemosensitivity through regulation of
P-glycoprotein in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul
Mech. 1861:996–1006. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Jiang T, Ye L, Han Z, Liu Y, Yang Y, Peng
Z and Fan J: miR-19b-3p promotes colon cancer proliferation and
oxalipl- atin-based chemoresistance by targeting SMAD4: Validation
by bioinformatics and experimental analyses. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:1312017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
192
|
Jin J, Sun Z, Yang F, Tang L, Chen W and
Guan X: miR-19b-3p inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation and
reverses saraca- tinib-resistance by regulating PI3K/Akt pathway.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 645:54–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Tsai HP, Huang SF, Li CF, Chien HT and
Chen SC: Differential microRNA expression in breast cancer with
different onset age. PLoS One. 13:e01911952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Chernyy V, Pustylnyak V, Kozlov V and
Gulyaeva L: Increased expression of miR-155 and miR-222 is
associated with lymph node positive status. J Cancer. 9:135–140.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Xiong DD, Lv J, Wei KL, Feng ZB, Chen JT,
Liu KC, Chen G and Luo DZ: A nine-miRNA signature as a potential
diagnostic marker for breast carcinoma: An integrated study of
1,110 cases. Oncol Rep. 37:3297–3304. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Bahrami A, Aledavood A, Anvari K,
Hassanian SM, Maftouh M, Yaghobzade A, Salarzaee O, ShahidSales S
and Avan A: The prognostic and therapeutic application of microRNAs
in breast cancer: Tissue and circulating microRNAs. J Cell Physiol.
233:774–786. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
197
|
Zhu M, Wang X, Gu Y, Wang F, Li L and Qiu
X: MEG3 overexpression inhibits the tumorigenesis of breast cancer
by downregulating miR-21 through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 661:22–30. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
198
|
Wang W, Yuan X, Xu A, Zhu X, Zhan Y, Wang
S and Liu M: Human cancer cells suppress behaviors of endothelial
progenitor cells through miR-21 targeting IL6R. Microvasc Res.
120:21–28. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Han JG, Jiang YD, Zhang CH, Yang YM, Pang
D, Song YN and Zhang GQ: A novel panel of serum
miR-21/miR-155/miR-365 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for
breast cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res. 92:55–66. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Yu X, Liang J, Xu J, Li X, Xing S, Li H,
Liu W, Liu D, Xu J, Huang L and Du H: Identification and validation
of circulating MicroRNA signatures for breast cancer early
detection based on large scale tissue-derived data. J Breast
Cancer. 21:363–370. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Hu X, Fan J, Duan B, Zhang H, He Y, Duan P
and Li X: Single-molecule catalytic hairpin assembly for rapid and
direct quantification of circulating miRNA biomarkers. Anal Chim.
Acta. 1042:109–115. 2018.
|
|
202
|
Fan T, Mao Y, Sun Q, Liu F, Lin JS, Liu Y,
Cui J and Jiang Y: Branched rolling circle amplification method for
measuring serum circulating microRNA levels for early breast cancer
detection. Cancer Sci. 109:2897–2906. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Hannafon BN, Trigoso YD, Calloway CL, Zhao
YD, Lum DH, Welm AL, Zhao ZJ, Blick KE, Dooley WC and Ding WQ:
Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 18:902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Wang M, Ji S, Shao G, Zhang J, Zhao K,
Wang Z and Wu A: Effect of exosome biomarkers for diagnosis and
prognosis of breast cancer patients. Clin Transl Oncol. 20:906–911.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
205
|
Adhami M, Haghdoost AA, Sadeghi B and
Malekpour Afshar R: Candidate miRNAs in human breast cancer biomark
ers: A systematic review. Breast Cancer. 25:198–205. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
206
|
Petrovic N, Sami A, Martinovic J, Zaric M,
Nakashidze I, Lukic S and Jovanovic-Cupic S: TIMP-3 mRNA expression
levels positively correlates with levels of miR-21 in in situ BC
and negatively in PR positive invasive BC. Pathol Res Pract.
213:1264–1270. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Jinling W, Sijing S, Jie Z and Guinian W:
Prognostic value of circulating microRNA-21 for breast cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 45:1–6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Papadaki C, Stratigos M, Markakis G,
Spiliotaki M, Mastrostamatis G, Nikolaou C, Mavroudis D and Agelaki
S: Circulating microRNAs in the early prediction of disease
recurrence in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 20:722018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Huo D, Clayton WM, Yoshimatsu TF, Chen J
and Olopade OI: Identification of a circulating microRNA signature
to distinguish recurrence in breast cancer patients. Oncotarget.
7:55231–55248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Shin VY, Siu JM, Cheuk I, Ng EK and Kwong
A: Circulating cell-free miRNAs as biomarker for triple-negative
breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:1751–1759. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Fang H, Xie J, Zhang M, Zhao Z, Wan Y and
Yao Y: miRNA-21 promotes proliferation and invasion of
triple-negative breast cancer cells through targeting PTEN. Am J
Transl Res. 9:953–961. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Dong G, Liang X, Wang D, Gao H, Wang L,
Wang L, Liu J and Du Z: High expression of miR-21 in
triple-negative breast cancers was correlated with a poor prognosis
and promoted tumor cell in vitro proliferation. Med Oncol.
31:572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Kawaguchi T,
Miyamae M, Okajima W, Ohashi T, Imamura T, Kiuchi J, Konishi H,
Shiozaki A, et al: Circulating miR-21 as an independent predictive
biomarker for chemoresistance in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 6:1511–1523. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Campayo M, Navarro A, Benitez JC,
Santasusagna S, Ferrer C, Monzo M and Cirera L: miR-21, miR-99b and
miR-375 combination as predictive response signature for
preoperative chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. PLoS One.
13:e02065422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Gaudelot K, Gibier JB, Pottier N, Hemon B,
Van Seuningen I, Glowacki F, Leroy X, Cauffiez C, Gnemmi V, Aubert
S and Perrais M: Targeting miR-21 decreases expression of
multi-drug resistant genes and promotes chemosensitivity of renal
carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177073722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Lin L, Tu HB, Wu L, Liu M and Jiang GN:
MicroRNA-21 regulates non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion and
chemo-sensitivity through SMAD7. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:2152–2162. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Szejniuk WM, Robles AI, McCulloch T,
Falkmer UGI and Roe OD: Epigenetic predictive biomarkers for
response or outcome to platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small
cell lung cancer, current state-of-art. Pharmacogenomics J.
19:5–14. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
218
|
Feng Y, Zou W, Hu C, Li G, Zhou S, He Y,
Ma F, Deng C and Sun L: Modulation of CASC2/miR-21/PTEN pathway
sensitizes cervical cancer to cisplatin. Arch Biochem Biophys.
623-624:20–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Chan JK, Blansit K, Kiet T, Sherman A,
Wong G, Earle C and Bourguignon LY: The inhibition of miR-21
promotes apoptosis and chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 132:739–744. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Pink RC, Samuel P, Massa D, Caley DP,
Brooks SA and Carter DR: The passenger strand, miR-21-3p, plays a
role in mediating cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 137:143–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Dai X, Fang M, Li S, Yan Y, Zhong Y and Du
B: miR-21 is involved in transforming growth factor |31-induced
chemoresis- tance and invasion by targeting PTEN in breast cancer.
Oncol Lett. 14:6929–6936. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Bose RJC, Uday Kumar S, Zeng Y, Afjei R,
Robinson E, Lau K, Bermudez A, Habte F, Pitteri SJ, Sinclair R, et
al: Tumor cell-derived extracellular vesicle-coated nanocarriers:
An efficient theranostic platform for the cancer-specific delivery
of Anti-miR-21 and imaging agents. ACS Nano. 12:10817–10832. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Zhou Q, Zeng H, Ye P, Shi Y, Guo J and
Long X: Differential microRNA profiles between
fulvestrant-resistant and tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer
cells. Anticancer Drugs. 29:539–548. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Wu ZH, Tao ZH, Zhang J, Li T, Ni C, Xie J,
Zhang JF and Hu XC: MiRNA-21 induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transition and gemcitabine resistance via the PTEN/AKT pathway in
breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:7245–7254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Dhayat SA, Mardin WA, Seggewifi J, Strose
AJ, Matuszcak C, Hummel R, Senninger N, Mees ST and Haier J:
MicroRNA profiling implies new markers of gemcitabine
chemoresistance in mutant p53 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
PLoS One. 10:e01437552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Dong J, Zhao YP, Zhou L, Zhang TP and Chen
G: Bcl-2 upregu- lation induced by miR-21 via a direct interaction
is associated with apoptosis and chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2
pancreatic cancer cells. Arch Med Res. 42:8–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Kopczynska E: Role of microRNAs in the
resistance of prostate cancer to docetaxel and paclitaxel. Contemp
Oncol (Pozn). 19:423–427. 2015.
|
|
228
|
Haghnavaz N, Asghari F, Komi Ali Elieh D,
Shanehbandi D, Baradaran B and Kazemi T: HER2 positivity may confer
resistance to therapy with paclitaxel in breast cancer cell lines.
Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46:518–523. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
229
|
Du G, Cao D and Meng L: miR-21 inhibitor
suppresses cell proliferation and colony formation through
regulating the PTEN/AKT pathway and improves paclitaxel sensitivity
in cervical cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 15:2713–2719. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Jin B, Liu Y and Wang H: Antagonism of
miRNA-21 sensitizes human gastric cancer cells to paclitaxel. Cell
Biochem Biophys. 72:275–282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
231
|
Mei M, Ren Y, Zhou X, Yuan XB, Han L, Wang
GX, Jia Z, Pu PY, Kang CS and Yao Z: Downregulation of miR-21
enhances chemotherapeutic effect of taxol in breast carcinoma
cells. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 9:77–86. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Naro Y, Ankenbruck N, Thomas M, Tivon Y,
Connelly CM, Gardner L and Deiters A: Small molecule inhibition of
MicroRNA miR-21 rescues chemosensitivity of renal-cell carcinoma to
topotecan. J Med Chem. 61:5900–5909. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Liu Y, Xu J, Choi HH, Han C, Fang Y, Li Y,
Van der Jeught K, Xu H, Zhang L, Frieden M, et al: Targeting 17q23
amplicon to overcome the resistance to anti-HER2 therapy in HER2+
breast cancer. Nat Commun. 9:47182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Decker JT, Hall MS, Blaisdell RB, Schwark
K, Jeruss JS and Shea LD: Dynamic microRNA activity identifies
therapeutic targets in trastuzumab-resistant HER2+
breast cancer. Biotechnol Bioeng. 115:2613–2623. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Bahreyni A, Alibolandi M, Ramezani M,
Sarafan Sadeghi A, Abnous K and Taghdisi SM: A novel MUC1
aptamer-modified PLGA-epirubicin-PpAE-antimir-21 nanocomplex
platform for targeted co-delivery of anticancer agents in vitro and
in vivo. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 175:231–238. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
236
|
Vandghanooni S, Eskandani M, Barar J and
Omidi Y: AS1411 aptamer-decorated cisplatin-loaded
poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles for targeted therapy of
miR-21-inhibited ovarian cancer cells. Nanomedicine (Lond).
13:2729–2758. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
237
|
Wang W, Huang S, Yuan J, Xu X, Li H, Lv Z,
Yu W, Duan S and Hu Y: Reverse multidrug resistance in human
HepG2/ADR by Anti-miR-21 combined with hyperthermia mediated by
functionalized gold nanocages. Mol Pharm. 15:3767–3776. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Luo J, Zhao Q, Zhang W, Zhang Z, Gao J,
Zhang C, Li Y and Tian Y: A novel panel of microRNAs provides a
sensitive and specific tool for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Mol
Med Rep. 10:785–791. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Zhang K, Wang YW, Wang YY, Song Y, Zhu J,
Si PC and Ma R: Identification of microRNA biomarkers in the blood
of breast cancer patients based on microRNA profiling. Gene.
619:10–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Croset M, Pantano F, Kan CWS, Bonnelye E,
Descotes F, Alix-Panabieres C, Lecellier CH, Bachelier R, Allioli
N, Hong SS, et al: MicroRNA-30 family members inhibit breast cancer
invasion, osteomimicry, and bone destruction by directly targeting
multiple bone metastasis-associated genes. Cancer Res.
78:5259–5273. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Ni Q, Stevic I, Pan C, Muller V,
Oliviera-Ferrer L, Pantel K and Schwarzenbach H: Different
signatures of miR-16, miR-30b and miR-93 in exosomes from breast
cancer and DCIS patients. Sci Rep. 8:129742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Xi Z, Si J and Nan J: LncRNA MALAT1
potentiates autophagyassociated cisplatin resistance by regulating
the microRNA30b/autophagyrelated gene 5 axis in gastric cancer. Int
J Oncol. 54:239–248. 2019.
|
|
243
|
Chen JC, Su YH, Chiu CF, Chang YW, Yu YH,
Tseng CF, Chen HA and Su JL: Suppression of Dicer increases
sensitivity to gefitinib in human lung cancer cells. Ann Surg
Oncol. 21(Suppl 4): S555–S563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Tormo E, Adam-Artigues A, Ballester S,
Pineda B, Zazo S, Gonzalez-Alonso P, Albanell J, Rovira A, Rojo F,
Lluch A and Eroles P: The role of miR-26a and miR-30b in HER2+
breast cancer trastuzumab resistance and regulation of the CCNE2
gene. Sci Rep. 7:413092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Gu YF, Zhang H, Su D, Mo ML, Song P, Zhang
F and Zhang SC: miR-30b and miR-30c expression predicted response
to tyrosine kinase inhibitors as first line treatment in non-small
cell lung cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:4435–4439. 2013.
|
|
246
|
Amini S, Abak A, Estiar MA, Montazeri V,
Abhari A and Sakhinia E: Expression Analysis of MicroRNA-222 in
breast cancer. Clin Lab. 64:491–496. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Zong Y, Zhang Y, Sun X, Xu T, Cheng X and
Qin Y: miR-221/222 promote tumor growth and suppress apoptosis by
targeting lncRNA GAS5 in breast cancer. Biosci Rep. 39:pii:
BSR20181859. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
248
|
Hoppe R, Fan P, Buttner F, Winter S, Tyagi
AK, Cunliffe H, Jordan VC and Brauch H: Profiles of miRNAs matched
to biology in aromatase inhibitor resistant breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:71235–71254. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Han SH, Kim HJ, Gwak JM, Kim M, Chung YR
and Park SY: MicroRNA-222 expression as a predictive marker for
tumor progression in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. J
Breast Cancer. 20:35–44. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Kim C, Go EJ and Kim A: Recurrence
prediction using microRNA expression in hormone receptor positive
breast cancer during tamoxifen treatment. Biomarkers. 23:804–811.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Zhu W, Liu M, Fan Y, Ma F, Xu N and Xu B:
Dynamics of circulating microRNAs as a novel indicator of clinical
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Med.
7:4420–4433. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Chen X, Lu P, Wang DD, Yang SJ, Wu Y, Shen
HY, Zhong SL, Zhao JH and Tang JH: The role of miRNAs in drug
resistance and prognosis of breast cancer formalin-fixed
paraffin-embedded tissues. Gene. 595:221–226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Chen J, Chen Z, Huang J, Chen F, Ye W,
Ding G and Wang X: Bioinformatics identification of dysregulated
microRNAs in triple negative breast cancer based on microRNA
expression profiling. Oncol Lett. 15:3017–3023. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Li Y, Liang C, Ma H, Zhao Q, Lu Y, Xiang
Z, Li L, Qin J, Chen Y, Cho WC, et al: miR-221/222 promotes S-phase
entry and cellular migration in control of basal-like breast
cancer. Molecules. 19:7122–7137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Zhao L, Ren Y, Tang H, Wang W, He Q, Sun
J, Zhou X and Wang A: Deregulation of the miR-222-ABCG2 regulatory
module in tongue squamous cell carcinoma contributes to
chemoresistance and enhanced migratory/invasive potential.
Oncotarget. 6:44538–44550. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Shen H, Wang D, Li L, Yang S, Chen X, Zhou
S, Zhong S, Zhao J and Tang J: MiR-222 promotes drug-resistance of
breast cancer cells to adriamycin via modulation of PTEN/Akt/FOXO1
pathway. Gene. 596:110–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
257
|
Wang DD, Yang SJ, Chen X, Shen HY, Luo LJ,
Zhang XH, Zhong SL, Zhao JH and Tang JH: miR-222 induces Adriamycin
resistance in breast cancer through PTEN/Akt/p27(kip1) pathway.
Tumour Biol. 37:15315–15324. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Rao X, Di Leva G, Li M, Fang F, Devlin C,
Hartman-Frey C, Burow ME, Ivan M, Croce CM and Nephew KP: MicroRNA-
221/222 confers breast cancer fulvestrant resistance by regulating
multiple signaling pathways. Oncogene. 30:1082–1097. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
259
|
Wei F, Ma C, Zhou T, Dong X, Luo Q, Geng
L, Ding L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhang L, et al: Exosomes derived from
gemcitabine-resistant cells transfer malignant phenotypic traits
via delivery of miRNA-222-3p. Mol Cancer. 16:1322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Bliss SA, Sinha G, Sandiford OA, Williams
LM, Engelberth DJ, Guiro K, Isenalumhe LL, Greco SJ, Ayer S, Bryan
M, et al: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulate cycling
quiescence and early breast cancer dormancy in bone marrow. Cancer
Res. 76:5832–5844. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Ding J, Xu Z, Zhang Y, Tan C, Hu W, Wang
M, Xu Y and Tang J: Exosome-mediated miR-222 transferring: An
insight into NF-kappaB-mediated breast cancer metastasis. Exp Cell
Res. 369:129–138. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Gan R, Yang Y, Yang X, Zhao L, Lu J and
Meng QH: Downregulation of miR-221/222 enhances sensitivity of
breast cancer cells to tamoxifen through upregulation of TIMP3.
Cancer Gene Ther. 21:290–296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Vishnubalaji R, Hamam R, Yue S, Al-Obeed
O, Kassem M, Liu FF, Aldahmash A and Alajez NM: MicroRNA-320
suppresses colorectal cancer by targeting SOX4, FOXM1, and FOXQ1.
Oncotarget. 7:35789–35802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Iwagami Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Akita H,
Hama N, Wada H, Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Tomokuni A, Tomimaru Y, et
al: miR-320c regulates gemcitabine-resistance in pancreatic cancer
via SMARCC1. Br J Cancer. 109:502–511. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Li M, Zeringer E, Barta T, Schageman J,
Cheng A and Vlassov AV: Analysis of the RNA content of the exosomes
derived from blood serum and urine and its potential as biomarkers.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 369:pii: 201305022014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|