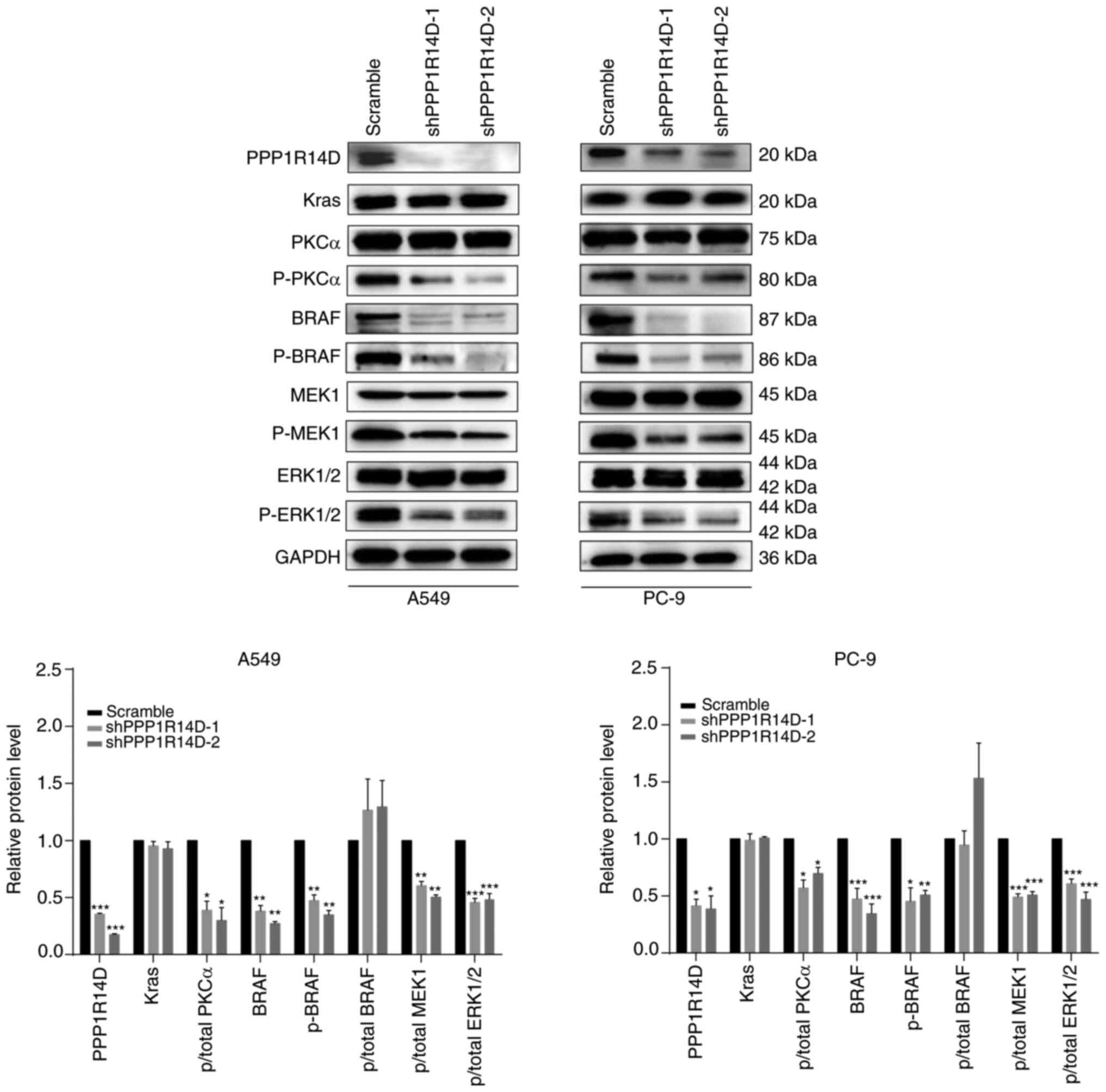
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kleczko EK, Kwak JW, Schenk EL and
Nemenoff RA: Targeting the complement pathway as a therapeutic
strategy in lung cancer. Front Immunol. 10:9542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu T, Yang X, Huang Y, Zhao M, Li M, Ma K,
Yin J, Zhan C and Wang Q: Trends in the incidence, treatment, and
survival of patients with lung cancer in the last four decades.
Cancer Manag Res. 11:943–953. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL,
Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL and Paz-Ares L: Lung cancer: Current
therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 389:299–311. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Duffy MJ and Crown J: Biomarkers for
predicting response to immunotherapy with immune checkpoint
inhibitors in cancer patients. Clin Chem. 65:1228–1238. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng Q, Min S and Zhou Q: Identification
of potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for LUAD based on
TCGA and GEO databases. Biosci Rep. 41:BSR202043702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Denisenko TV, Budkevich IN and Zhivotovsky
B: Cell death-based treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death
Dis. 9:1172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu WJ, Du Y, Wen R, Yang M and Xu J: Drug
resistance to targeted therapeutic strategies in non-small cell
lung cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 206:1074382020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang J, Sun B, Ruan X, Hou X, Zhi J, Meng
X, Zheng X and Gao M: Oncoprotein HBXIP promotes tumorigenesis
through MAPK/ERK pathway activation in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Biol Med. 18:105–119. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dasgupta P, Kulkarni P, Bhat NS, Majid S,
Shiina M, Shahryari V, Yamamura S, Tanaka Y, Gupta RK, Dahiya R and
Hashimoto Y: Activation of the Erk/MAPK signaling pathway is a
driver for cadmium induced prostate cancer. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
401:1151022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang G, Luo X, Wang Z, Xu J, Zhang W,
Chen E, Meng Q, Wang D, Huang X, Zhou W and Song Z: TIMP-2
regulates 5-Fu resistance via the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway in
colorectal cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 14:297–315. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Samatar AA and Poulikakos PI: Targeting
RAS-ERK signalling in cancer: Promises and challenges. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 13:928–942. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mahapatra L, Andruska N, Mao C, Gruber SB,
Johnson TM, Fullen DR, Raskin L and Shapiro DJ: Protein kinase C-α
is upregulated by IMP1 in melanoma and is linked to poor survival.
Melanoma Res. 29:539–543. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Lin R, Bao X, Wang H, Zhu S, Liu Z, Chen
Q, Ai K and Shi B: TRPM2 promotes pancreatic cancer by PKC/MAPK
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 12:5852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Awad MM, Liu S, Rybkin II, Arbour KC,
Dilly J, Zhu VW, Johnson ML, Heist RS, Patil T, Riely GJ, et al:
Acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibition in cancer. N
Engl J Med. 384:2382–2393. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu QR, Zhang PW, Lin Z, Li QF, Woods AS,
Troncoso J and Uhl GR: GBPI, a novel gastrointestinal- and
brain-specific PP1-inhibitory protein, is activated by PKC and
inactivated by PKA. Biochem J. 377:171–181. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Aggen JB, Nairn AC and Chamberlin R:
Regulation of protein phosphatase-1. Chem Biol. 7:R13–R23. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang W, Shang S, Yang Y, Lu P, Wang T,
Cui X and Tang X: Identification of DNA methylation-driven genes by
integrative analysis of DNA methylation and transcriptome data in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 19:2963–2972.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dang M, Armbruster N, Miller MA, Cermeno
E, Hartmann M, Bell GW, Root DE, Lauffenburger DA, Lodish HF and
Herrlich A: Regulated ADAM17-dependent EGF family ligand release by
substrate-selecting signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:9776–9781. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eto M: Regulation of cellular protein
phosphatase-1 (PP1) by phosphorylation of the CPI-17 family,
C-kinase-activated PP1 inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 284:35273–35277.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin H, Sperka T, Herrlich P and Morrison
H: Tumorigenic transformation by CPI-17 through inhibition of a
merlin phosphatase. Nature. 442:576–579. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao M, Shao Y, Xu J, Zhang B, Li C and
Gong J: LINC00466 impacts cell proliferation, metastasis and
sensitivity to temozolomide of glioma by sponging miR-137 to
regulate PPP1R14B expression. Onco Targets Ther. 14:1147–1159.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jian Y, Kong L, Xu H, Shi Y, Huang X,
Zhong W, Huang S, Li Y, Shi D, Xiao Y, et al: Protein phosphatase 1
regulatory inhibitor subunit 14C promotes triple-negative breast
cancer progression via sustaining inactive glycogen synthase kinase
3 beta. Clin Transl Med. 12:e7252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grey J, Jones D, Wilson L, Nakjang S,
Clayton J, Temperley R, Clark E, Gaughan L and Robson C:
Differential regulation of the androgen receptor by protein
phosphatase regulatory subunits. Oncotarget. 9:3922–3935. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dang F, Nie L and Wei W: Ubiquitin
signaling in cell cycle control and tumorigenesis. Cell Death
Differ. 28:427–438. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Yang S, Zhang JJ and Huang XY: Orai1 and
STIM1 are critical for breast tumor cell migration and metastasis.
Cancer Cell. 15:124–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salvi N: Intrinsically disordered
proteins: Dynamics, binding, and function. Elsevier; 2019
|
|
28
|
Xu C and Zheng J: siRNA against TSG101
reduces proliferation and induces G0/G1 arrest in renal cell
carcinoma-involvement of c-myc, cyclin E1, and CDK2. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 24:72019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Santoni-Rugiu E, Falck J, Mailand N,
Bartek J and Lukas J: Involvement of Myc activity in a
G(1)/S-promoting mechanism parallel to the pRb/E2F pathway. Mol
Cell Biol. 20:3497–3509. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Berns K, Hijmans EM and Bernards R:
Repression of c-Myc responsive genes in cycling cells causes G1
arrest through reduction of cyclin E/CDK2 kinase activity.
Oncogene. 15:1347–1356. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Geng X, Chen C, Huang Y and Hou J: The
prognostic value and potential mechanism of matrix
metalloproteinases among prostate cancer. Int J Med Sci.
17:1550–1560. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Andersson P, Yang Y, Hosaka K, Zhang Y,
Fischer C, Braun H, Liu S, Yu G, Liu S, Beyaert R, et al: Molecular
mechanisms of IL-33-mediated stromal interactions in cancer
metastasis. JCI Insight. 3:e1223752018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jiang H and Li H: Prognostic values of
tumoral MMP2 and MMP9 overexpression in breast cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 21:1492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Buttacavoli M, Di Cara G, Roz E,
Pucci-Minafra I, Feo S and Cancemi P: Integrated multi-omics
investigations of metalloproteinases in colon cancer: Focus on MMP2
and MMP9. Int J Mol Sci. 22:123892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schaedel L, Lorenz C, Schepers AV, Klumpp
S and Köster S: Vimentin intermediate filaments stabilize dynamic
microtubules by direct interactions. Nat Commun. 12:37992021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kidd ME, Shumaker DK and Ridge KM: The
role of vimentin intermediate filaments in the progression of lung
cancer. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:1–6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Havel LS, Kline ER, Salgueiro AM and
Marcus AI: Vimentin regulates lung cancer cell adhesion through a
VAV2-Rac1 pathway to control focal adhesion kinase activity.
Oncogene. 34:1979–1990. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Morrison DK and Davis RJ: Regulation of
MAP kinase signaling modules by scaffold proteins in mammals. Annu
Rev Cell Dev Biol. 19:91–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meyer N and Penn LZ: Reflecting on 25
years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:976–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Albihn A, Johnsen JI and Henriksson MA:
MYC in oncogenesis and as a target for cancer therapies. Adv Cancer
Res. 107:163–224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chu J, Li Y, Deng Z, Zhang Z, Xie Q, Zhang
H, Zhong W and Pan B: IGHG1 regulates prostate cancer growth via
the MEK/ERK/c-Myc pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2019:72015622019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Yang S, Zhang S and Wu X:
Oxymatrine inhibits proliferation and migration of vulvar squamous
cell carcinoma cells via attenuation of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK
pathway. Cancer Manag Res. 12:2057–2067. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin F, Chengyao X, Qingchang L, Qianze D,
Enhua W and Yan W: CRKL promotes lung cancer cell invasion through
ERK-MMP9 pathway. Mol Carcinog. 54(Suppl 1): E35–E44. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Qin H, Liu X, Li F, Miao L, Li T, Xu B, An
X, Muth A, Thompson PR and Zhang X: PAD1 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in triple-negative
breast cancer cells by regulating MEK1-ERK1/2MMP2 signaling. Cancer
lett. 409:30–41. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang H, Shen B, Swinarska JT, Li W, Xiao
K and He P: 9-Hydroxypheophorbide α-mediated photodynamic therapy
induces matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9
down-regulation in Hep-2 cells via ROS-mediated suppression of the
ERK pathway. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 11:55–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Isakov N: Protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms
in cancer, tumor promotion and tumor suppression. Semin Cancer
Biol. 48:36–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ricciarelli R and Azzi A: Regulation of
recombinant PKC alpha activity by protein phosphatase 1 and protein
phosphatase 2A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 355:197–200. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Luo W, Xu C, Ayello J, Dela Cruz F,
Rosenblum JM, Lessnick SL and Cairo MS: Protein phosphatase 1
regulatory subunit 1A in ewing sarcoma tumorigenesis and
metastasis. Oncogene. 37:798–809. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|