|
1
|
Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S,
Yang F, Yan X, Zhang S, Li N and Chen W: Cancer statistics in China
and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin
Med J (Engl). 135:584–590. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
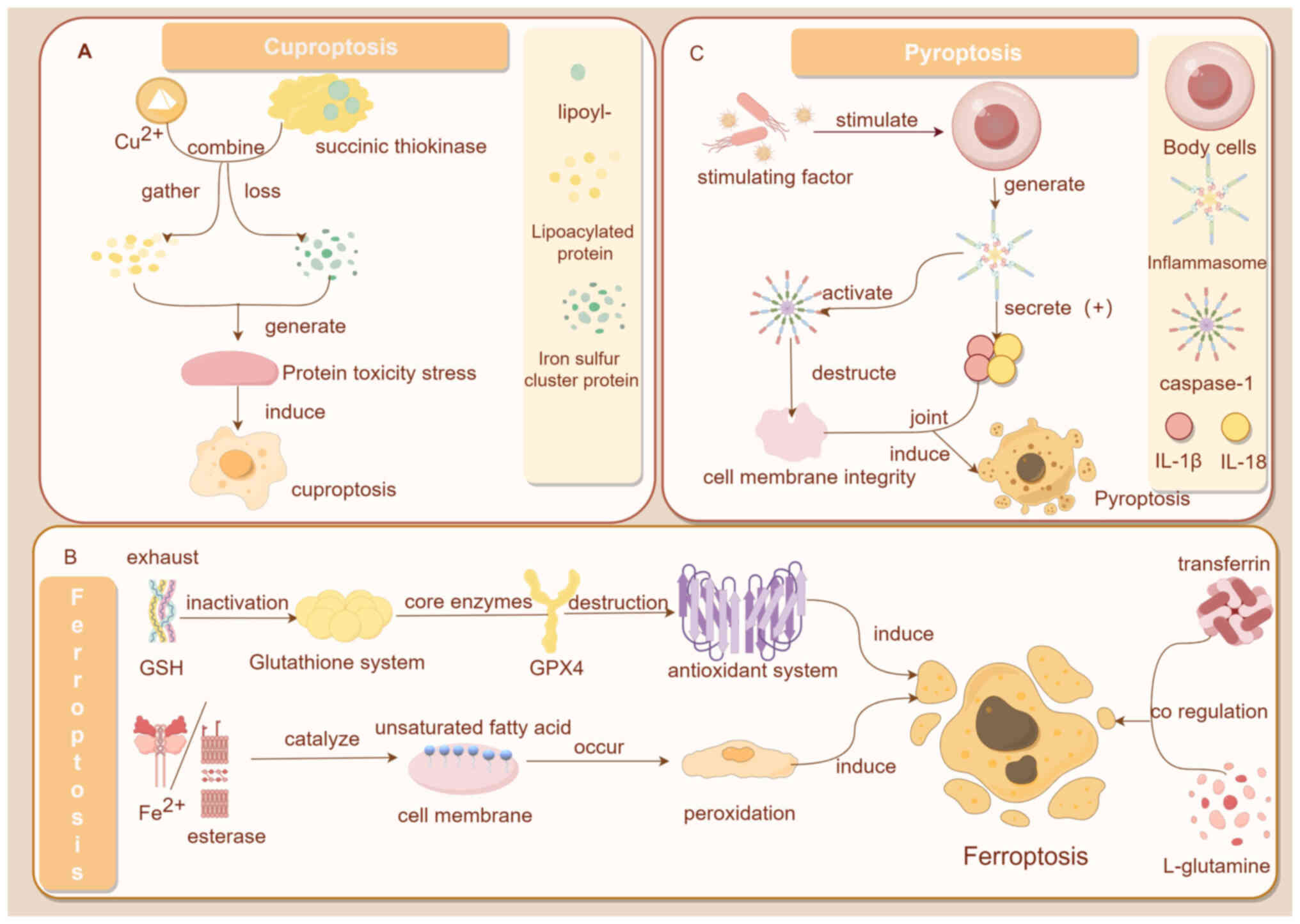
|
|
3
|
Cameron D, Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Gelber RD,
Procter M, Goldhirsch A, de Azambuja E, Castro G Jr, Untch M, Smith
I, Gianni L, et al: 11 years' follow-up of trastuzumab after
adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive early breast cancer: Final
analysis of the HERceptin Adjuvant (HERA) trial. Lancet.
389:1195–1205. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams
JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Amelio I and
Andrews DW: Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of
the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ.
25:486–541. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang D, Kang R, Berghe TV, Vandenabeele P
and Kroemer G: The molecular machinery of regulated cell death.
Cell Res. 29:347–364. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Conradt B: Genetic control of programmed
cell death during animal development. Annu Rev Genet. 43:493–523.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Programmed cell
death in animal development and disease. Cell. 147:742–758. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Kepp O and
Kroemer G: Regulated cell death and adaptive stress responses. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 73:2405–2410. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lutsenko S: Human copper homeostasis: A
network of interconnected pathways. Curr Opin Chem Biol.
14:211–217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gaggelli E, Kozlowski H, Valensin D and
Valensin G: Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders
(Alzheimer's, prion, and Parkinson's diseases and amyotrophic
lateral sclerosis). Chem Rev. 106:1995–2044. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Festa RA and Thiele DJ: Copper: An
essential metal in biology. Curr Biol. 21:R877–R883. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chillappagari S, Seubert A, Trip H,
Kuipers OP, Marahiel MA and Miethke M: Copper stress affects iron
homeostasis by destabilizing iron-sulfur cluster formation in
Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 192:2512–2524. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Macomber L and Imlay JA: The iron-sulfur
clusters of dehydratases are primary intracellular targets of
copper toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:8344–8349. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Zhang L and Zhou F: Cuproptosis: A
new form of programmed cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. 19:867–868.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang D, Chen X and Kroemer G: Cuproptosis:
A coppertriggered modality of mitochondrial cell death. Cell Res.
32:417–418. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon
M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, Rossen J, Joesch-Cohen L, Humeidi R,
Spangler RD, et al: Copper induces cell death by targeting
lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 375:1254–1261. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsvetkov P, Detappe A, Cai K, Keys HR,
Brune Z, Ying W, Thiru P, Reidy M, Kugener G, Rossen J, et al:
Mitochondrial metabolism promotes adaptation to proteotoxic stress.
Nat Chem Biol. 15:681–689. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Skrott Z, Majera D, Gursky J, Buchtova T,
Hajduch M, Mistrik M and Bartek J: Disulfiram's anti-cancer
activity reflects targeting NPL4, not inhibition of aldehyde
dehydrogenase. Oncogene. 38:6711–6722. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pan M, Zheng Q, Yu Y, Ai H, Xie Y, Zeng X,
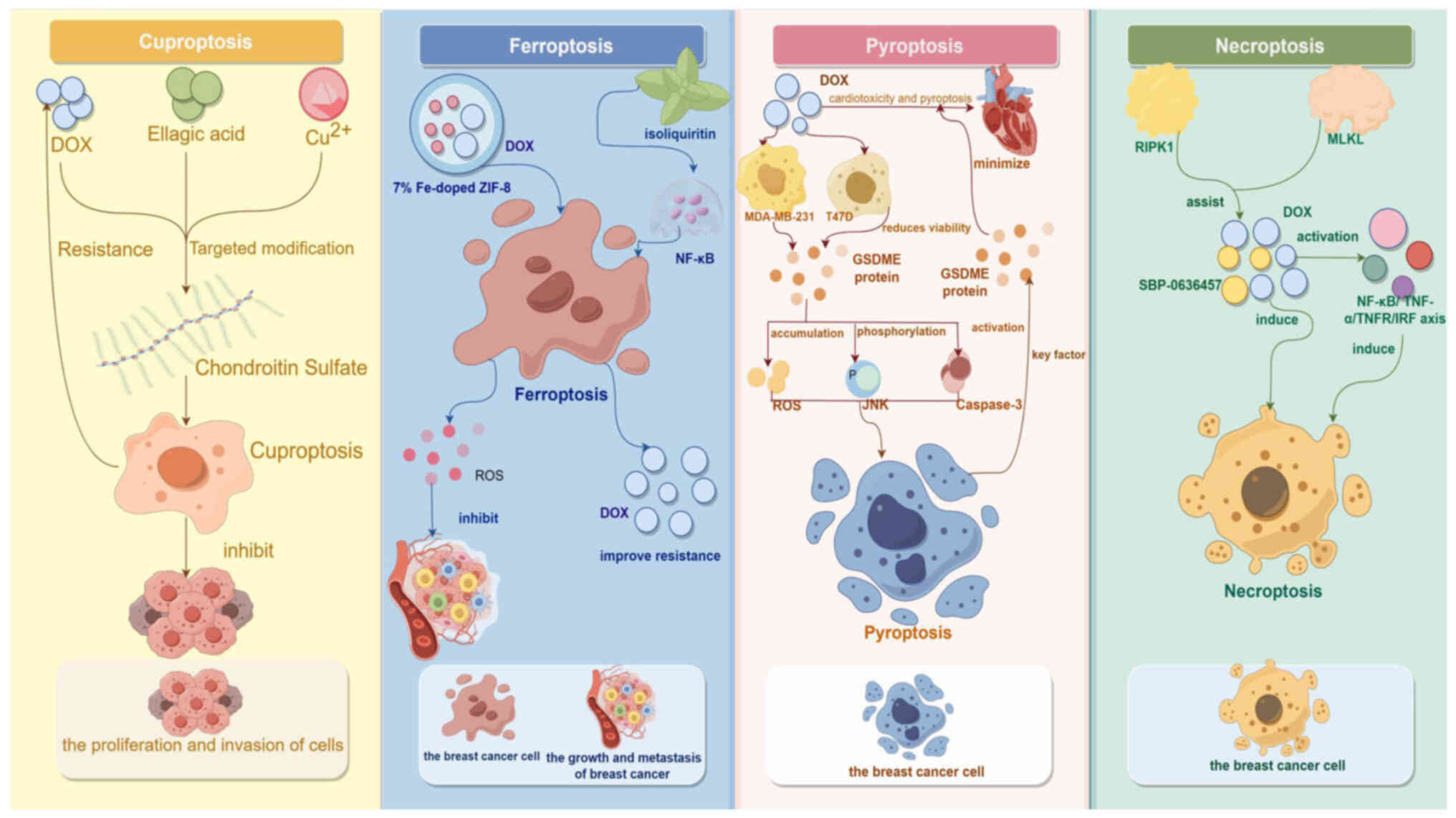
Wang C, Liu L and Zhao M: Seesaw conformations of Npl4 in the human
p97 complex and the inhibitory mechanism of a disulfiram
derivative. Nat Commun. 12:1212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
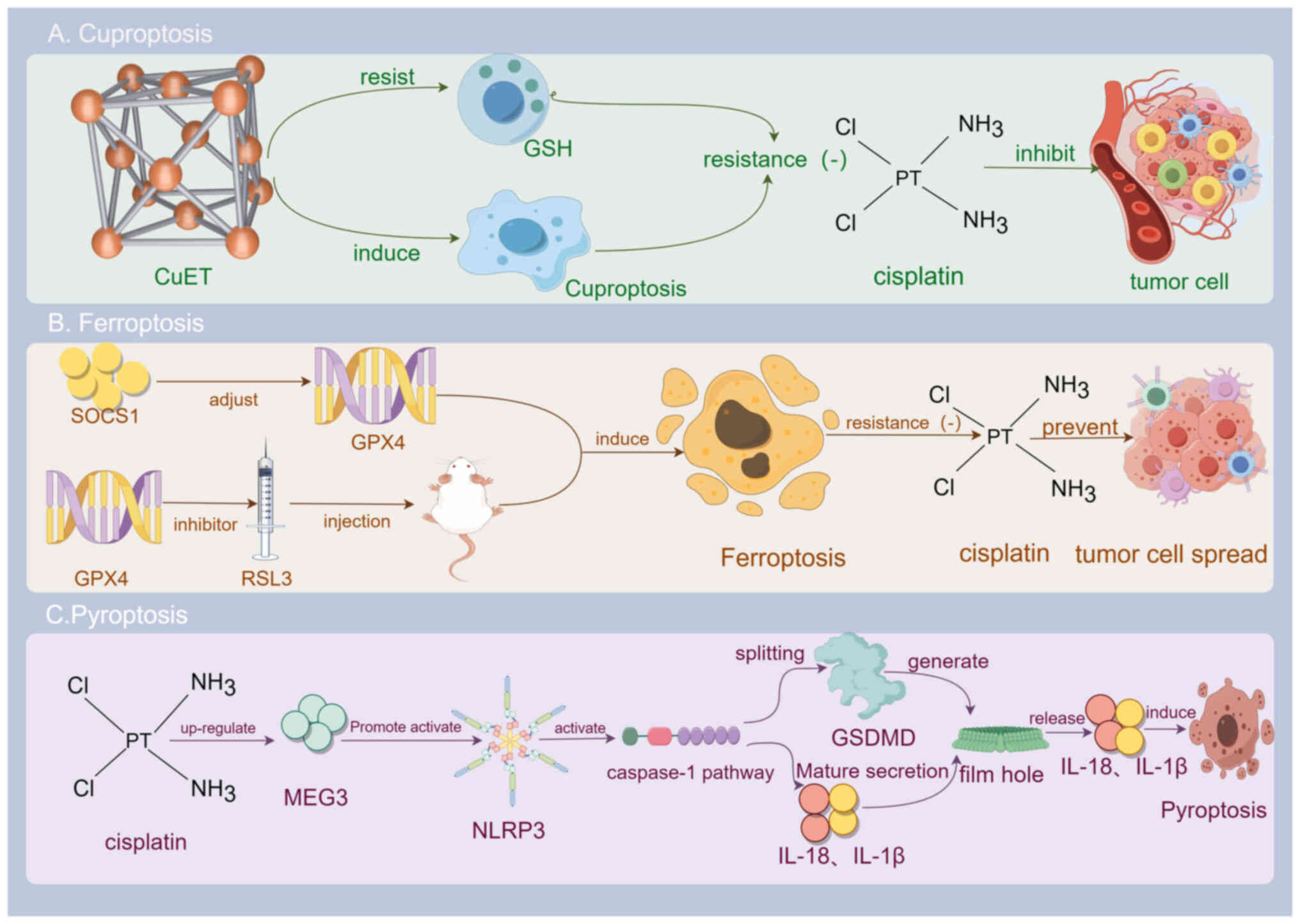
21
|
Tsang T, Posimo JM, Gudiel AA, Cicchini M,
Feldser DM and Brady DC: Copper is an essential regulator of the
autophagic kinases ULK1/2 to drive lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Cell
Biol. 22:412–424. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Davis CI, Gu X, Kiefer RM, Ralle M, Gade
TP and Brady DC: Altered copper homeostasis underlies sensitivity
of hepatocellular carcinoma to copper chelation. Metallomics.
12:1995–2008. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ge EJ, Bush AI, Casini A, Cobine PA, Cross
JR, DeNicola GM, Dou QP, Franz KJ, Gohil VM, Gupta S, et al:
Connecting copper and cancer: From transition metal signalling to
metalloplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 22:102–113. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Hasinoff BB, Yadav AA, Patel D and Wu X:
The cytotoxicity of the anticancer drug elesclomol is due to
oxidative stress indirectly mediated through its complex with
Cu(II). J Inorg Biochem. 137:22–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tardito S, Bassanetti I, Bignardi C,
Elviri L, Tegoni M, Mucchino C, Bussolati O, Franchi-Gazzola R and
Marchiò L: Copper binding agents acting as copper ionophores lead
to caspase inhibition and paraptotic cell death in human cancer
cells. J Am Chem Soc. 133:6235–6242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pavithra V, Sathisha TG, Kasturi K,
Mallika DS, Amos SJ and Ragunatha S: Serum levels of metal ions in
female patients with breast cancer. J Clin Diagn Res. 9:BC25–BC27.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu J, Zhu Y, Luo M and Li L: Comprehensive
analysis of pyroptosis-related genes and tumor microenvironment
infiltration characterization in breast cancer. Front Immunol.
12:7482212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brady DC, Crowe MS, Turski ML, Hobbs GA,
Yao X, Chaikuad A, Knapp S, Xiao K, Campbell SL, Thiele DJ and
Counter CM: Copper is required for oncogenic BRAF signalling and
tumorigenesis. Nature. 509:492–496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cui L, Gouw AM, LaGory EL, Guo S,
Attarwala N, Tang Y, Qi J, Chen YS, Gao Z, Casey KM, et al:
Mitochondrial copper depletion suppresses triple-negative breast
cancer in mice. Nat Biotechnol. 39:357–367. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Blockhuys S, Zhang X and Wittung-Stafshede
P: Single-cell tracking demonstrates copper chaperone Atox1 to be
required for breast cancer cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:2014–2019. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kirshner JR, He S, Balasubramanyam V,
Kepros J, Yang CY, Zhang M, Du Z, Barsoum J and Bertin J:
Elesclomol induces cancer cell apoptosis through oxidative stress.
Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2319–2327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nagai M, Vo NH, Shin Ogawa L, Chimmanamada
D, Inoue T, Chu J, Beaudette-Zlatanova BC, Lu R, Blackman RK,
Barsoum J, et al: The oncology drug elesclomol selectively
transports copper to the mitochondria to induce oxidative stress in
cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:2142–2150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yadav AA, Patel D, Wu X and Hasinoff BB:
Molecular mechanisms of the biological activity of the anticancer
drug elesclomol and its complexes with Cu(II), Ni(II) and Pt(II). J
Inorg Biochem. 126:1–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Renier N, Reinaud O, Jabin I and Valkenier
H: Transmembrane transport of copper(i) by imidazole-functionalised
calix[4] arenes. Chem Commun (Camb). 56:8206–8209. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Min J and Wang F: Copper
homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 7:3782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smirnova J, Kabin E, Järving I, Bragina O,
Tõugu V, Plitz T and Palumaa P: Copper(I)-binding properties of
de-coppering drugs for the treatment of Wilson disease. α-Lipoic
acid as a potential anti-copper agent. Sci Rep. 8:14632018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
He K, Chen Z, Ma Y and Pan Y:
Identification of high-copper-responsive target pathways in Atp7b
knockout mouse liver by GSEA on microarray data sets. Mamm Genome.
22:703–713. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sheftel AD, Stehling O, Pierik AJ,
Elsässer HP, Mühlenhoff U, Webert H, Hobler A, Hannemann F,
Bernhardt R and Lill R: Humans possess two mitochondrial
ferredoxins, Fdx1 and Fdx2, with distinct roles in steroidogenesis,
heme, and Fe/S cluster biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:11775–11780. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Strushkevich N, MacKenzie F, Cherkesova T,
Grabovec I, Usanov S and Park HW: Structural basis for pregnenolone
biosynthesis by the mitochondrial monooxygenase system. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:10139–10143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zalewski A, Ma NS, Legeza B, Renthal N,
Flück CE and Pandey AV: Vitamin D-Dependent rickets type 1 caused
by mutations in CYP27B1 affecting protein interactions with
adrenodoxin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 101:3409–3418. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Moriya M, Ho YH, Grana A, Nguyen L,
Alvarez A, Jamil R, Ackland ML, Michalczyk A, Hamer P, Ramos D, et
al: Copper is taken up efficiently from albumin and
alpha2-macroglobulin by cultured human cells by more than one
mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 295:C708–C721. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xie J, Yang Y, Gao Y and He J:
Cuproptosis: Mechanisms and links with cancers. Mol Cancer.
22:462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lu Z and Hunter T: Metabolic kinases
moonlighting as protein kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 43:301–310.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Li M, Cui Z, Chai D, Guan Y, Chen
C and Wang W: Systematic analysis of the role of SLC52A2 in
multiple human cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 22:82022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Halestrap AP: The SLC16 gene
family-structure, role and regulation in health and disease. Mol
Aspects Med. 34:337–349. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Higuchi K, Sugiyama K, Tomabechi R,
Kishimoto H and Inoue K: Mammalian monocarboxylate transporter 7
(MCT7/Slc16a6) is a novel facilitative taurine transporter. J Biol
Chem. 298:1018002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wright ME, Peters U, Gunter MJ, Moore SC,
Lawson KA, Yeager M, Weinstein SJ, Snyder K, Virtamo J and Albanes
D: Association of variants in two vitamin e transport genes with
circulating vitamin e concentrations and prostate cancer risk.
Cancer Res. 69:1429–1438. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tanaka T, Bai Z, Srinoulprasert Y, Yang
BG, Hayasaka H and Miyasaka M: Chemokines in tumor progression and
metastasis. Cancer Sci. 96:317–322. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
de Marco MC, Martín-Belmonte F, Kremer L,
Albar JP, Correas I, Vaerman JP, Marazuela M, Byrne JA and Alonso
MA: MAL2, a novel raft protein of the MAL family, is an essential
component of the machinery for transcytosis in hepatoma HepG2
cells. J Cell Biol. 159:37–44. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li DD, Yagüe E, Wang LY, Dai LL, Yang ZB,
Zhi S, Zhang N, Zhao XM and Hu YH: Novel copper complexes that
inhibit the proteasome and trigger apoptosis in triple-negative
breast cancer cells. ACS Med Chem Lett. 10:1328–1335. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee ZY, Leong CH, Lim KUL, Wong CCS,
Pongtheerawan P, Arikrishnan SA, Tan KL, Loh JS, Low ML, How CW, et
al: Induction of apoptosis and autophagy by ternary copper complex
towards breast cancer cells. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
22:1159–1170. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Li X, Ma Z and Mei L: Cuproptosis-related
gene SLC31A1 is a potential predictor for diagnosis, prognosis and
therapeutic response of breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res.
12:3561–3580. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li L, Li L and Sun Q: High expression of
cuproptosis-related SLC31A1 gene in relation to unfavorable outcome
and deregulated immune cell infiltration in breast cancer: An
analysis based on public databases. BMC Bioinformatics. 23:3502022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li Z, Zhang H, Wang X, Wang Q, Xue J, Shi
Y, Wang M, Wang G and Zhang J: Identification of
cuproptosis-related subtypes, characterization of tumor
microenvironment infiltration, and development of a prognosis model
in breast cancer. Front Immunol. 13:9968362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sha S, Si L, Wu X, Chen Y, Xiong H, Xu Y,
Liu W, Mei H, Wang T and Li M: Prognostic analysis of
cuproptosis-related gene in triple-negative breast cancer. Front
Immunol. 13:9227802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Guan X, Lu N and Zhang J: Construction of
a prognostic model related to copper dependence in breast cancer by
single-cell sequencing analysis. Front Genet. 13:9498522022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jiang ZR, Yang LH, Jin LZ, Yi LM, Bing PP,
Zhou J and Yang JS: Identification of novel cuproptosis-related
lncRNA signatures to predict the prognosis and immune
microenvironment of breast cancer patients. Front Oncol.
12:9886802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhao Q and Qi T: The implications and
prospect of cuproptosis-related genes and copper transporters in
cancer progression. Front Oncol. 13:11171642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Song S, Zhang M, Xie P, Wang S and Wang Y:
Comprehensive analysis of cuproptosis-related genes and tumor
microenvironment infiltration characterization in breast cancer.
Front Immunol. 13:9789092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ning S, Lyu M, Zhu D, Lam JWY, Huang Q,
Zhang T and Tang BZ: Type-I AIE photosensitizer loaded biomimetic
system boosting cuproptosis to inhibit breast cancer metastasis and
rechallenge. ACS Nano. 17:10206–10217. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lee SY, Seo JH, Kim S, Hwang C, Jeong DI,
Park J, Yang M, Huh JW and Cho HJ: Cuproptosis-Inducible
chemotherapeutic/cascade catalytic reactor system for combating
with breast cancer. Small. 19:e23014022023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xu T, Ding W, Ji X, Ao X, Liu Y, Yu W and
Wang J: Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cancer
therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 23:4900–4912. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R and
Jiang X: Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 59:298–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lu B, Chen XB, Ying MD, He QJ, Cao J and
Yang B: The role of ferroptosis in cancer development and treatment
response. Front Pharmacol. 8:9922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xie Y, Wang B, Zhao Y, Tao Z, Wang Y, Chen
G and Hu X: Mammary adipocytes protect triple-negative breast
cancer cells from ferroptosis. J Hematol Oncol. 15:722022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang YY, Attané C, Milhas D, Dirat B,
Dauvillier S, Guerard A, Gilhodes J, Lazar I, Alet N, Laurent V, et
al: Mammary adipocytes stimulate breast cancer invasion through
metabolic remodeling of tumor cells. JCI Insight. 2:e874892017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang D, Li Y, Xing L, Tan Y, Sun J, Zeng
B, Xiang T, Tan J, Ren G and Wang Y: Utilization of
adipocyte-derived lipids and enhanced intracellular trafficking of
fatty acids contribute to breast cancer progression. Cell Commun
Signal. 16:322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu W, Chakraborty B, Safi R, Kazmin D,
Chang CY and McDonnell DP: Dysregulated cholesterol homeostasis
results in resistance to ferroptosis increasing tumorigenicity and
metastasis in cancer. Nat Commun. 12:51032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Baek AE, Yu YA, He S, Wardell SE, Chang
CY, Kwon S, Pillai RV, McDowell HB, Thompson JW, Dubois LG, et al:
The cholesterol metabolite 27 hydroxycholesterol facilitates breast
cancer metastasis through its actions on immune cells. Nat Commun.
8:8642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Vallianou NG, Kostantinou A, Kougias M and
Kazazis C: Statins and cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
14:706–712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Sha R, Xu Y, Yuan C, Sheng X, Wu Z, Peng
J, Wang Y, Lin Y, Zhou L, Xu S, et al: Predictive and prognostic
impact of ferroptosis-related genes ACSL4 and GPX4 on breast cancer
treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. EBioMedicine. 71:1035602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ding Y, Chen X, Liu C, Ge W, Wang Q, Hao
X, Wang M, Chen Y and Zhang Q: Identification of a small molecule
as inducer of ferroptosis and apoptosis through ubiquitination of
GPX4 in triple negative breast cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol.
14:192021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Zhang K, Ping L, Du T, Liang G, Huang Y,
Li Z, Deng R and Tang J: A Ferroptosis-Related lncRNAs signature
predicts prognosis and immune microenvironment for breast cancer.
Front Mol Biosci. 8:6788772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ping L, Zhang K, Ou X, Qiu X and Xiao X: A
novel pyroptosis-associated long Non-coding RNA signature predicts
prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment of patients with breast
cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7271832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhu Z and Leung GKK: More than a metabolic
enzyme: MTHFD2 as a novel target for anticancer therapy? Front
Oncol. 10:6582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhang H, Zhu S, Zhou H, Li R, Xia X and
Xiong H: Identification of MTHFD2 as a prognostic biomarker and
ferroptosis regulator in triple-negative breast cancer. Front
Oncol. 13:10983572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yadav P, Sharma P, Sundaram S, Venkatraman
G, Bera AK and Karunagaran D: SLC7A11/xCT is a target of miR-5096
and its restoration partially rescues miR-5096-mediated ferroptosis
and anti-tumor effects in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
522:211–224. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Koppula P, Zhuang L and Gan B: Cystine
transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: Ferroptosis, nutrient
dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell. 12:599–620. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
81
|
He J, Wang X, Chen K, Zhang M and Wang J:
The amino acid transporter SLC7A11-mediated crosstalk implicated in
cancer therapy and the tumor microenvironment. Biochem Pharmacol.
205:1152412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang Y, Liang Y, Wang Y, Ye F, Kong X and
Yang Q: A novel ferroptosis-related gene signature for overall
survival prediction and immune infiltration in patients with breast
cancer. Int J Oncol. 61:1482022. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
83
|
Liu Q, Ma JY and Wu G: Identification and
validation of a ferroptosis-related gene signature predictive of
prognosis in breast cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 13:21385–21399.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Xu Y, Du Y, Zheng Q, Zhou T, Ye B, Wu Y,
Xu Q and Meng X: Identification of ferroptosis-related prognostic
signature and subtypes related to the immune microenvironment for
breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Front
Immunol. 13:8951102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yang YF, Lee YC, Wang YY, Wang CH, Hou MF
and Yuan SF: YWHAE promotes proliferation, metastasis, and
chemoresistance in breast cancer cells. Kaohsiung J Med Sci.
35:408–416. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Qiao X, Zhang Y, Sun L, Ma Q, Yang J, Ai
L, Xue J, Chen G, Zhang H, Ji C, et al: Association of human breast
cancer CD44-/CD24-cells with delayed distant metastasis. Elife.
10:e654182021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Gong Z, Li Q, Shi J, Liu ET, Shultz LD and
Ren G: Lipid-laden lung mesenchymal cells foster breast cancer
metastasis via metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells and natural
killer cells. Cell Metab. 34:1960–1976.e9. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li Y, Jin K, van Pelt GW, van Dam H, Yu X,
Mesker WE, Ten Dijke P, Zhou F and Zhang L: c-Myb enhances breast
cancer invasion and metastasis through the Wnt/β-Catenin/Axin2
pathway. Cancer Res. 76:3364–3375. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Li Y, Zhang Y, Liu X, Wang M, Wang P, Yang
J and Zhang S: Lutein inhibits proliferation, invasion and
migration of hypoxic breast cancer cells via downregulation of
HES1. Int J Oncol. 52:2119–2129. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Huo Q, Wang J and Xie N: High HSPB1
expression predicts poor clinical outcomes and correlates with
breast cancer metastasis. BMC Cancer. 23:5012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang H, Ge Z, Wang Z, Gao Y, Wang Y and
Qu X: Circular RNA RHOT1 promotes progression and inhibits
ferroptosis via mir-106a-5p/STAT3 axis in breast cancer. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:8115–8126. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhou Y, Che Y, Fu Z, Zhang H and Wu H:
Triple-Negative breast cancer analysis based on metabolic gene
classification and immunotherapy. Front Public Health.
10:9023782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang J, Yang J, Zuo T, Ma S, Xokrat N, Hu
Z, Wang Z, Xu R, Wei Y and Shen Q: Heparanase-driven sequential
released nanoparticles for ferroptosis and tumor microenvironment
modulations synergism in breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials.
266:1204292021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Nieto C, Vega MA and Martín Del Valle EM:
Tailored-Made polydopamine nanoparticles to induce ferroptosis in
breast cancer cells in combination with chemotherapy. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:31612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhou Z, Liang H, Yang R, Yang Y, Dong J,
Di Y and Sun M: Glutathione depletion-induced activation of
dimersomes for potentiating the ferroptosis and immunotherapy of
'cold' tumor. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 61:e2022028432022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Dattachoudhury S, Sharma R, Kumar A and
Jaganathan BG: Sorafenib inhibits proliferation, migration and
invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncology. 98:478–486. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Yu M, Gai C, Li Z, Ding D, Zheng J, Zhang
W, Lv S and Li W: Targeted exosome-encapsulated erastin induced
ferroptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
110:3173–3182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Yang J, Zhou Y, Xie S, Wang J, Li Z, Chen
L, Mao M, Chen C, Huang A, Chen Y, et al: Metformin induces
Ferroptosis by inhibiting UFMylation of SLC7A11 in breast cancer. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:2062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Ma S, Henson ES, Chen Y and Gibson SB:
Ferroptosis is induced following siramesine and lapatinib treatment
of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ma S, Dielschneider RF, Henson ES, Xiao W,
Choquette TR, Blankstein AR, Chen Y and Gibson SB: Ferroptosis and
autophagy induced cell death occur independently after siramesine
and lapatinib treatment in breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
12:e01829212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Chen Z, Li R, Fang M, Wang Y, Bi A, Yang
L, Song T, Li Y, Li Q, Lin B, et al: Integrated analysis of
FKBP1A/SLC3A2 axis in everolimus inducing ferroptosis of breast
cancer and anti-proliferation of T lymphocyte. Int J Med Sci.
20:1060–1078. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Li H, Liu W, Zhang X, Wu F, Sun D and Wang
Z: Ketamine suppresses proliferation and induces ferroptosis and
apoptosis of breast cancer cells by targeting KAT5/GPX4 axis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 585:111–116. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Song X, Wang X, Liu Z and Yu Z: Role of
GPX4-Mediated ferroptosis in the sensitivity of triple negative
breast cancer cells to gefitinib. Front Oncol. 10:5974342020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Yao X, Xie R, Cao Y, Tang J, Men Y, Peng H
and Yang W: Simvastatin induced ferroptosis for triple-negative
breast cancer therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 19:3112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zhang Z, Lu M, Chen C, Tong X, Li Y, Yang
K, Lv H, Xu J and Qin L: Holo-lactoferrin: the link between
ferroptosis and radiotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer.
Theranostics. 11:3167–3182. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Sun D, Li YC and Zhang XY: Lidocaine
promoted ferroptosis by targeting miR-382-5p/SLC7A11 axis in
ovarian and breast cancer. Front Pharmacol. 12:6812232021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Li R, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Gao Q, Wang R, Fu
Y, Zheng L and Yu H: Transcriptome Investigation and in vitro
verification of curcumin-induced HO-1 as a feature of ferroptosis
in breast cancer cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:34698402020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Zhai FG, Liang QC, Wu YY, Liu JQ and Liu
JW: Red ginseng polysaccharide exhibits anticancer activity through
GPX4 downregulation-induced ferroptosis. Pharm Biol. 60:909–914.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cookson BT and Brennan MA:
Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol.
9:113–114. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Järveläinen HA, Galmiche A and Zychlinsky
A: Caspase-1 activation by Salmonella. Trends Cell Biol.
13:204–209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Martinon F, Burns K and Tschopp J: The
inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of
inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell.
10:417–426. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Feng S, Fox D and Man SM: Mechanisms of
gasdermin family members in inflammasome signaling and cell death.
J Mol Biol. 430(18 Pt B): 3068–3080. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Gao W, Ding J, Li
P, Hu L and Shao F: Inflammatory caspases are innate immune
receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature. 514:187–192. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Xia J, Chu C, Li W, Chen H, Xie W, Cheng
R, Hu K and Li X: Mitochondrial Protein UCP1 inhibits the malignant
behaviors of triple-negative breast cancer through activation of
mitophagy and pyroptosis. Int J Biol Sci. 18:2949–2961. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yu X, Shi M, Wu Q, Wei W, Sun S and Zhu S:
Identification of UCP1 and UCP2 as potential prognostic markers in
breast cancer: A study based on immunohistochemical analysis and
bioinformatics. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:8917312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Xia S, Kong Q, Li S, Liu
X, Junqueira C, Meza-Sosa KF, Mok TMY, Ansara J, et al: Gasdermin E
suppresses tumour growth by activating anti-tumour immunity.
Nature. 579:415–420. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Yi M, Niu M, Xu L, Luo S and Wu K:
Regulation of PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment. J
Hematol Oncol. 14:102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Zhang M, Wu K, Wang M, Bai F and Chen H:
CASP9 as a prognostic biomarker and promising drug target plays a
pivotal role in inflammatory breast cancer. Int J Anal Chem.
2022:10434452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Chu L, Yi Q, Yan Y, Peng J, Li Z, Jiang F,
He Q, Ouyang L, Wu S, Fu C, et al: A prognostic signature
consisting of pyroptosis-related genes and SCAF11 for predicting
immune response in breast cancer. Front Med (Lausanne).
9:8827632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Xu D, Ji Z and Qiang L: Molecular
characteristics, clinical implication, and cancer immunity
interactions of pyroptosis-related genes in breast cancer. Front
Med (Lausanne). 8:7026382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Zhou Y, Zheng J, Bai M, Gao Y and Lin N:
Effect of pyroptosis-related genes on the prognosis of breast
cancer. Front Oncol. 12:9481692022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Jin H and Kim HJ: NLRC4, ASC and Caspase-1
are inflammasome components that are mediated by P2Y2R activation
in breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:33372020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
124
|
Hergueta-Redondo M, Sarrió D,
Molina-Crespo Á, Megias D, Mota A, Rojo-Sebastian A, García-Sanz P,
Morales S, Abril S, Cano A, et al: Gasdermin-B promotes invasion
and metastasis in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e900992014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Song C, Kendi AT, Lowe VJ and Lee S: The
A20/TNFAIP3-CDC20-CASP1 axis promotes inflammation-mediated
metastatic disease in triple-negative breast cancer. Anticancer
Res. 42:681–695. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Velloso FJ, Campos AR, Sogayar MC and
Correa RG: Proteome profiling of triple negative breast cancer
cells overexpressing NOD1 and NOD2 receptors unveils molecular
signatures of malignant cell proliferation. BMC Genomics.
20:1522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Miao H, Wang L, Zhan H, Dai J, Chang Y, Wu
F, Liu T, Liu Z, Gao C, Li L and Song X: A long noncoding RNA
distributed in both nucleus and cytoplasm operates in the
PYCARD-regulated apoptosis by coordinating the epigenetic and
translational regulation. PLoS Genet. 15:e10081442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Faria SS, Costantini S, de Lima VCC, de
Andrade VP, Rialland M, Cedric R, Budillon A and Magalhães KG:
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cytokine production and pyroptosis cell
death in breast cancer. J Biomed Sci. 28:262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Siersbæk R, Scabia V, Nagarajan S,
Chernukhin I, Papachristou EK, Broome R, Johnston SJ, Joosten SEP,
Green AR, Kumar S, et al: IL6/STAT3 signaling hijacks estrogen
receptor α enhancers to drive breast cancer metastasis. Cancer
Cell. 38:412–423.e9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Wei Y, Huang H, Qiu Z, Li H, Tan J, Ren G
and Wang X: NLRP1 overexpression is correlated with the
tumorigenesis and proliferation of human breast tumor. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:49384732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Tan Y, Sun R, Liu L, Yang D, Xiang Q, Li
L, Tang J, Qiu Z, Peng W, Wang Y, et al: Tumor suppressor DRD2
facilitates M1 macrophages and restricts NF-κB signaling to trigger
pyroptosis in breast cancer. Theranostics. 11:5214–5231. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
132
|
Zhang Z, Zhang H, Li D, Zhou X, Qin Q and
Zhang Q: Caspase-3-mediated GSDME induced Pyroptosis in breast
cancer cells through the ROS/JNK signalling pathway. J Cell Mol
Med. 25:8159–8168. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
An H, Heo JS, Kim P, Lian Z, Lee S, Park
J, Hong E, Pang K, Park Y, Ooshima A, et al: Tetraarsenic hexoxide
enhances generation of mitochondrial ROS to promote pyroptosis by
inducing the activation of caspase-3/GSDME in triple-negative
breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 12:1592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Ma JH, Qin L and Li X: Role of STAT3
signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 18:332020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Wu L, Bai S, Huang J, Cui G, Li Q, Wang J,
Du X, Fu W, Li C, Wei W, et al: Nigericin boosts anti-tumor immune
response via inducing pyroptosis in triple-negative breast cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 15:32212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Wang H, Rong X, Zhao G, Zhou Y, Xiao Y, Ma
D, Jin X, Wu Y, Yan Y, Yang H, et al: The microbial metabolite
trimethylamine N-oxide promotes antitumor immunity in
triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Metab. 34:581–594.e8. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Lei S, Li S, Xiao W, Jiang Q, Yan S, Xiao
W, Cai J, Wang J, Zou L, Chen F, et al: Azurocidin 1 inhibits the
aberrant proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer through the
regulation of pyroptosis. Oncol Rep. 50:1882023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Pizato N, Luzete BC, Kiffer LFMV, Corrêa
LH, de Oliveira Santos I, Assumpção JAF, Ito MK and Magalhães KG:
Omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid induces pyroptosis cell death in
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 8:19522018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Chen C, Yuan S, Chen X, Xie J and Wei Z:
Xihuang pill induces pyroptosis and inhibits progression of breast
cancer cells via activating the cAMP/PKA signalling pathway. Am J
Cancer Res. 13:1347–1362. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Li Y, Wang W, Li A, Huang W, Chen S, Han F
and Wang L: Dihydroartemisinin induces pyroptosis by promoting the
AIM2/caspase-3/DFNA5 axis in breast cancer cells. Chem Biol
Interact. 340:1094342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zhong C, Li Y, Li W, Lian S, Li Y, Wu C,
Zhang K, Zhou G, Wang W, Xu H, et al: Ganoderma lucidum extract
promotes tumor cell pyroptosis and inhibits metastasis in breast
cancer. Food Chem Toxicol. 174:1136542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Zhao P, Wang M, Chen M, Chen Z, Peng X,
Zhou F, Song J and Qu J: Programming cell pyroptosis with
biomimetic nanoparticles for solid tumor immunotherapy.
Biomaterials. 254:1201422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Li L, Tian H, Zhang Z, Ding N, He K, Lu S,
Liu R, Wu P, Wang Y, He B, et al: Carrier-Free nanoplatform via
evoking pyroptosis and immune response against breast cancer. ACS
Appl Mater Interfaces. 15:452–468. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Li C, Wang X, Chen T, Li W, Zhou X, Wang L
and Yang Q: Huaier induces immunogenic cell death via
CircCLASP1/PKR/eIF2α signaling pathway in triple negative breast
cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:9138242022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Yamamoto A, Huang Y, Krajina BA, McBirney
M, Doak AE, Qu S, Wang CL, Haffner MC and Cheung KJ: Metastasis
from the tumor interior and necrotic core formation are regulated
by breast cancer-derived angiopoietin-like 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 120:e22148881202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Wen N, Lv Q and Du ZG: MicroRNAs involved
in drug resistance of breast cancer by regulating autophagy. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 21:690–702. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Wu Q and Sharma D: Autophagy and breast
cancer: connected in growth, progression, and therapy. Cells.
12:11562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Tadokoro T, Ikeda M, Ide T, Deguchi H,
Ikeda S, Okabe K, Ishikita A, Matsushima S, Koumura T, Yamada KI,
et al: Mitochondria-dependent ferroptosis plays a pivotal role in
doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. JCI Insight. 8:e1697562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Wang Y, Shi P, Chen Q, Huang Z, Zou D,
Zhang J, Gao X and Lin Z: Mitochondrial ROS promote macrophage
pyroptosis by inducing GSDMD oxidation. J Mol Cell Biol.
11:1069–1082. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Dai S, Chen Y, Fan X, Han J, Zhong L,
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Lin J, Huang W, Su L, et al: Emodin attenuates
cardiomyocyte pyroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by
directly binding to GSDMD. Phytomedicine. 121:1551052023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Lu S, Tian H, Li B, Li L, Jiang H, Gao Y,
Zheng L, Huang C, Zhou Y, Du Z and Xu J: An ellagic acid
coordinated copper-based nanoplatform for efficiently overcoming
cancer chemoresistance by cuproptosis and synergistic inhibition of
cancer cell stemness. Small. Dec 3–2023.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
152
|
Zhong Y, Peng Z, Peng Y, Li B, Pan Y,
Ouyang Q, Sakiyama H, Muddassir M and Liu J: Construction of
Fe-doped ZIF-8/DOX nanocomposites for ferroptosis strategy in the
treatment of breast cancer. J Mater Chem B. 11:6335–6345. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Wang J, Li Y, Zhang J and Luo C:
Isoliquiritin modulates ferroptosis via NF-κB signaling inhibition
and alleviates doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 45:443–454. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Yu R, Wang L, Ji X and Mao C: SBP-0636457,
a novel smac mimetic, cooperates with doxorubicin to induce
necroptosis in breast cancer cells during apoptosis blockage. J
Oncol. 2022:23900782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Wei T, Xiaojun X and Peilong C:
Magnoflorine improves sensitivity to doxorubicin (DOX) of breast
cancer cells via inducing apoptosis and autophagy through AKT/mTOR
and p38 signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 121:1091392020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Lu Y, Pan Q, Gao W, Pu Y and He B:
Reversal of cisplatin chemotherapy resistance by
glutathione-resistant copper-based nanomedicine via cuproptosis. J
Mater Chem B. 10:6296–6306. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Roh JL, Kim EH, Jang HJ, Park JY and Shin
D: Induction of ferroptotic cell death for overcoming cisplatin
resistance of head and neck cancer. Cancer Lett. 381:96–103. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Wang Y, Pang X, Liu Y, Mu G and Wang Q:
SOCS1 acts as a ferroptosis driver to inhibit the progression and
chemotherapy resistance of triple-negative breast cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 44:708–715. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Zhang X, Sui S, Wang L, Li H, Zhang L, Xu
S and Zheng X: Inhibition of tumor propellant glutathione
peroxidase 4 induces ferroptosis in cancer cells and enhances
anticancer effect of cisplatin. J Cell Physiol. 235:3425–3437.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Yan H, Luo B, Wu X, Guan F, Yu X, Zhao L,
Ke X, Wu J and Yuan J: Cisplatin induces pyroptosis via activation
of MEG3/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway in triple-negative breast
cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 17:2606–2621. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Shen M, Duan WM, Wu MY, Wang WJ, Liu L, Xu
MD, Zhu J, Li DM, Gui Q, Lian L, et al: Participation of autophagy
in the cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells by cisplatin. Oncol
Rep. 34:359–367. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Peng F, Liao M, Qin R, Zhu S, Peng C, Fu
L, Chen Y and Han B: Regulated cell death (RCD) in cancer: Key
pathways and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
7:2862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11:882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-Mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Song L, Zeng R, Yang K, Liu W, Xu Z and
Kang F: The biological significance of cuproptosis-key gene MTF1 in
pan-cancer and its inhibitory effects on ROS-mediated cell death of
liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Discov Oncol. 14:1132023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Zheng D, Liu J, Piao H, Zhu Z, Wei R and
Liu K: ROS-triggered endothelial cell death mechanisms: Focus on
pyroptosis, parthanatos, and ferroptosis. Front Immunol.
13:10392412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Abais JM, Xia M, Zhang Y, Boini KM and Li
PL: Redox regulation of NLRP3 inflammasomes: ROS as trigger or
effector? Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:1111–1129. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
168
|
Li C and Zhang Y: Construction and
validation of a cuproptosis-related five-lncRNA signature for
predicting prognosis, immune response and drug sensitivity in
breast cancer. BMC Med Genomics. 16:1582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Xu Z, Wang X, Sun W, Xu F, Kou H, Hu W,
Zhang Y, Jiang Q, Tang J and Xu Y: RelB-activated GPX4 inhibits
ferroptosis and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer.
Redox Biol. 68:1029522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Xu W, Song C, Wang X, Li Y, Bai X, Liang
X, Wu J and Liu J: Downregulation of miR-155-5p enhances the
anti-tumor effect of cetuximab on triple-negative breast cancer
cells via inducing cell apoptosis and pyroptosis. Aging (Albany
NY). 13:228–240. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Shen Y, Li D, Liang Q, Yang M, Pan Y and
Li H: Cross-talk between cuproptosis and ferroptosis regulators
defines the tumor microenvironment for the prediction of prognosis
and therapies in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol.
13:10290922022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Yang X, Deng L, Diao X, Yang S, Zou L,
Yang Q, Li J, Nie J, Zhao L and Jiao B: Targeting cuproptosis by
zinc pyrithione in triple-negative breast cancer. iScience.
26:1082182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Li Y, Li T, Zhai D, Xie C, Kuang X, Lin Y
and Shao N: Quantification of ferroptosis pathway status revealed
heterogeneity in breast cancer patients with distinct immune
microenvironment. Front Oncol. 12:9569992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Wu Y, Lin Z, Tang X, Tong Z, Ji Y, Xu Y,
Zhou Z, Yang J, Li Z and Liu T: Ferroptosis-related gene HIC1 in
the prediction of the prognosis and immunotherapeutic efficacy with
immunological activity. Front Immunol. 14:11820302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Zeng L, Ding S, Cao Y, Li C, Zhao B, Ma Z,
Zhou J, Hu Y, Zhang X, Yang Y, et al: A MOF-Based potent
ferroptosis inducer for enhanced radiotherapy of triple negative
breast cancer. ACS Nano. 17:13195–13210. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Yang X, Weng X, Yang Y and Jiang Z:
Pyroptosis-Related lncRNAs predict the prognosis and immune
response in patients with breast cancer. Front Genet.
12:7921062021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Huang QF, Fang DL, Nong BB and Zeng J:
Focal pyroptosis-related genes AIM2 and ZBP1 are prognostic markers
for triple-negative breast cancer with brain metastases. Transl
Cancer Res. 10:4845–4858. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Ma L, Bian M, Gao H, Zhou Z and Yi W: A
novel 3-acyl isoquinolin-1(2H)-one induces G2 phase arrest,
apoptosis and GSDME-dependent pyroptosis in breast cancer. PLoS
One. 17:e02680602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|