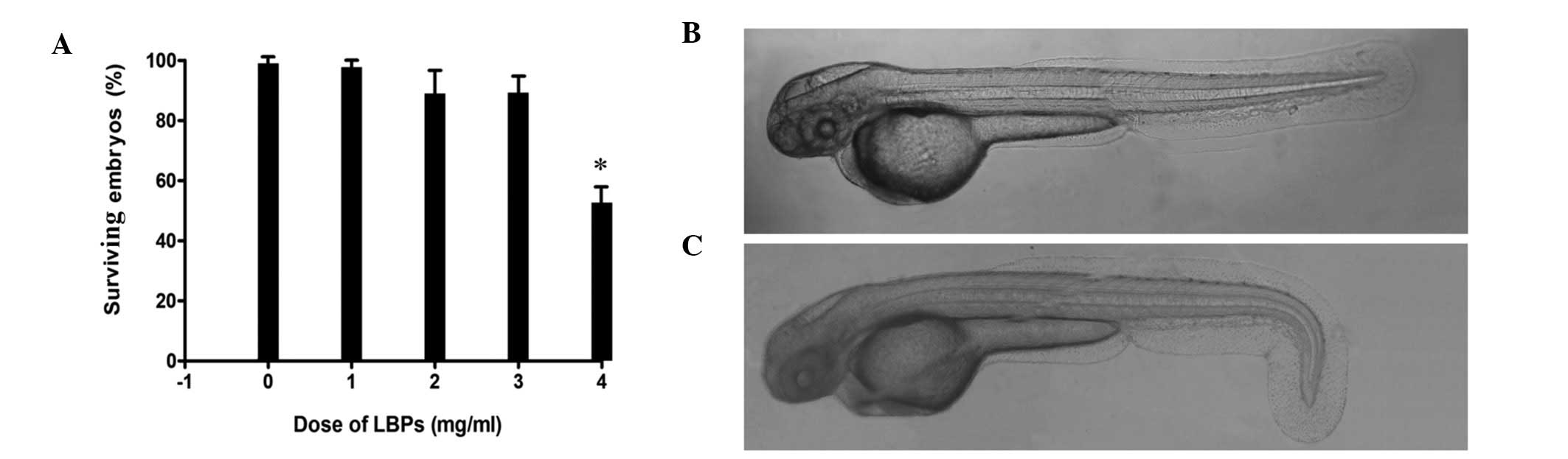
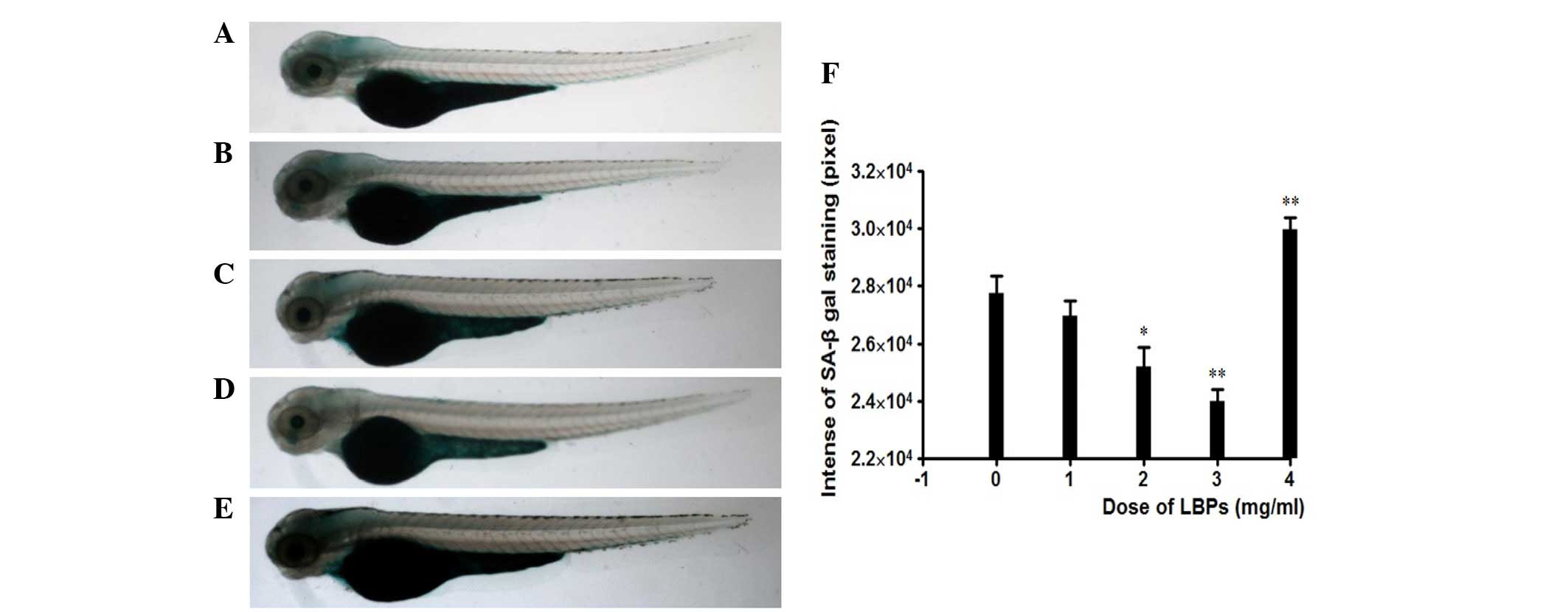
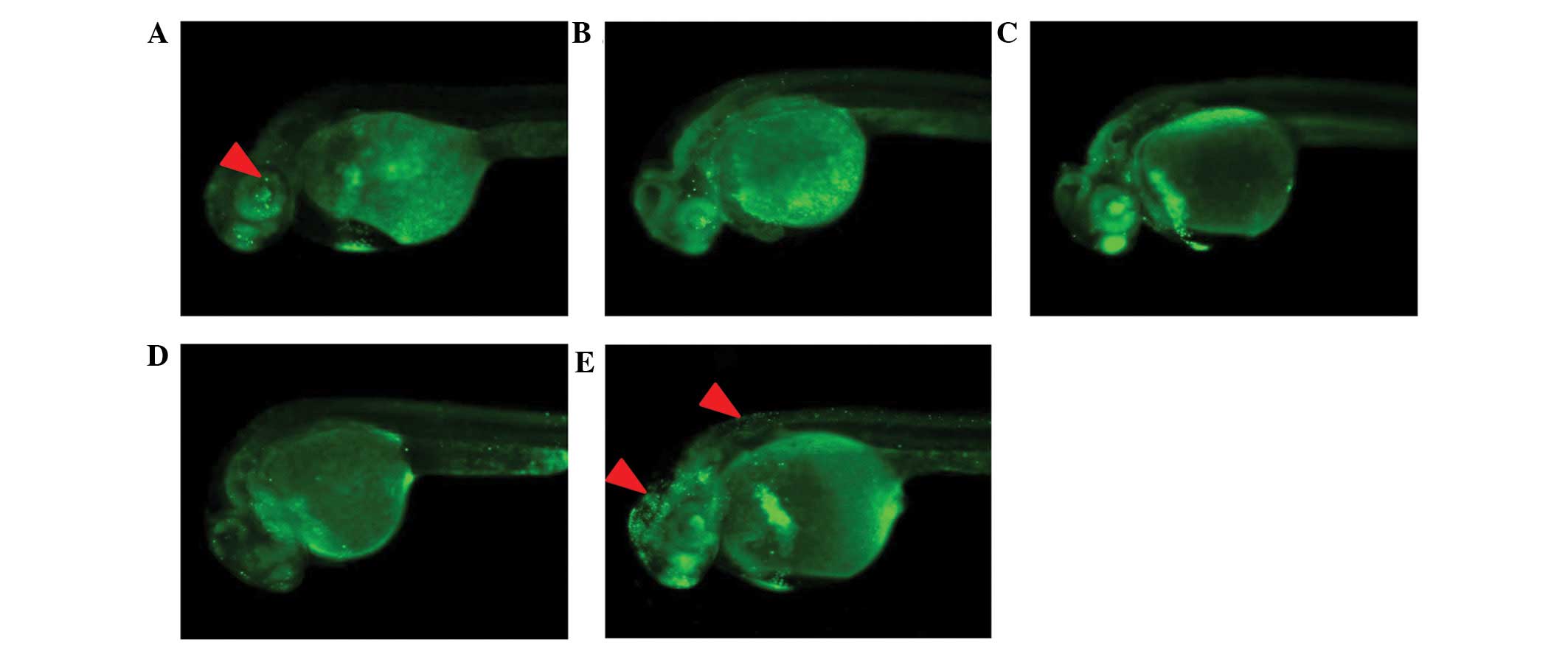
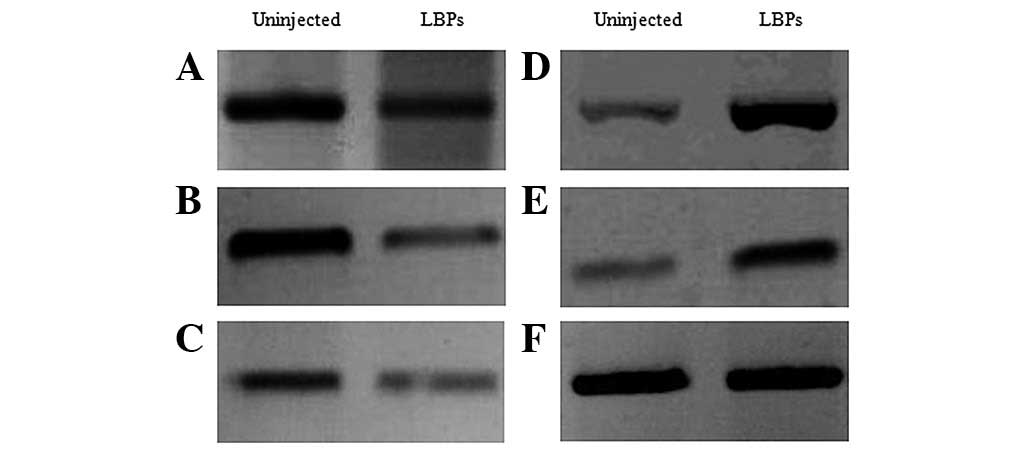
|
1
|
Harman D: The free radical theory of
aging. Antioxid Redox Signal. 5:557–561. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Greer EL and Brunet A: Signaling networks
in aging. J Cell Sci. 121:407–412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bastianetto S and Quirion R: Natural
extracts as possible protective agents of brain aging. Neurobiol
Aging. 23:891–897. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang IM: Anti-aging and health-promoting
constituents derived from traditional oriental herbal remedies:
information retrieval using the TradiMed 2000 DB. Ann NY Acad Sci.
928:281–286. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gan L, Zhang SH, Liu Q and Xu HB: A
polysaccharide-protein complex from Lycium barbarum
upregulates cytokine expression in human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 471:217–222. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li XM, Ma YL and Liu XJ: Effect of the
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on age-related oxidative
stress in aged mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 111:504–511. 2007.
|
|
7
|
Zhang M, Chen H, Huang J, Li Z, Zhu C and
Zhang S: Effect of lycium barbarum polysaccharide on human
hepatoma QGY7703 cells: inhibition of proliferation and induction
of apoptosis. Life Sci. 76:2115–2124. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Du G, Liu L and Fang J: Experimental study
on the enhancement of murine splenic lymphocyte proliferation by
Lycium barbarum glycopeptide. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog
Med Sci. 24:518–520. 5272004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vidal K, Benyacoub J, Sanchez-Garcia J, et
al: Intake of a milk-based wolfberry formulation enhances the
immune response of young-adult and aged mice. Rejuvenation Res.
13:47–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu MS, Lai CS, Ho YS, et al:
Characterization of the effects of anti-aging medicine Fructus
lycii on beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Med.
20:261–268. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu MS, Leung SK, Lai SW, et al:
Neuroprotective effects of anti-aging oriental medicine Lycium
barbarum against beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Exp
Gerontol. 40:716–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li SY, Yang D, Yeung CM, et al: Lycium
barbarum polysaccharides reduce neuronal damage, blood-retinal
barrier disruption and oxidative stress in retinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 6:e163802011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jin M, Huang Q, Zhao K and Shang P:
Biological activities and potential health benefit effects of
polysaccharides isolated from Lycium barbarum L. Int J Biol
Macromol. 54:16–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
May P and May E: Twenty years of p53
research: structural and functional aspects of the p53 protein.
Oncogene. 18:7621–7636. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen L and Du G: Lycium barbarum
polysaccharide stimulates proliferation of MCF-7 cells by the ERK
pathway. Life Sci. 91:353–357. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Keller ET and Murtha JM: The use of mature
zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model for human aging and
disease. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 138:335–341.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsai SB, Tucci V, Uchiyama J, et al:
Differential effects of genotoxic stress on both concurrent body
growth and gradual senescence in the adult zebrafish. Aging Cell.
6:209–224. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Parng C, Seng WL, Semino C and McGrath P:
Zebrafish: a preclinical model for drug screening. Assay Drug Dev
Technol. 1:41–48. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gerhard GS, Kauffman EJ, Wang X, et al:
Life spans and senescent phenotypes in two strains of zebrafish
(Danio rerio). Exp Gerontol. 37:1055–1068. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Herrera M and Jagadeeswaran P: Annual fish
as a genetic model for aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
59:101–107. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Granato M and Nusslein-Volhard C: Fishing
for genes controlling development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 6:461–468.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Luo Q, Cai Y, Yan J, Sun M and Corke H:
Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects and antioxidant activity of
fruit extracts from Lycium barbarum. Life Sci. 76:137–149.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kishi S, Bayliss PE, Uchiyama J, et al:
The identification of zebrafish mutants showing alterations in
senescence-associated biomarkers. PLoS Genet. 4:e10001522008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Robu ME, Larson JD, Nasevicius A, et al:
p53 activation by knockdown technologies. PLoS Genet. 3:e782007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, et al: A
biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in
aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9363–9367. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cao L, Li W, Kim S, Brodie SG and Deng CX:
Senescence, aging, and malignant transformation mediated by p53 in
mice lacking the Brca1 full-length isoform. Genes Dev. 17:201–213.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Keyes WM, Wu Y, Vogel H, Guo X, Lowe SW
and Mills AA: p63 deficiency activates a program of cellular
senescence and leads to accelerated aging. Genes Dev. 19:1986–1999.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ikegami R, Zhang J, Rivera-Bennetts AK and
Yager TD: Activation of the metaphase checkpoint and an apoptosis
programme in the early zebrafish embryo, by treatment with the
spindle-destabilising agent nocodazole. Zygote. 5:329–350. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ben-Porath I and Weinberg RA: When cells
get stressed: an integrative view of cellular senescence. J Clin
Invest. 113:8–13. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Concetti F, Lucarini N, Carpi FM, et al:
The functional VNTR MNS16A of the TERT gene is associated with
human longevity in a population of Central Italy. Exp Gerontol.
48:587–592. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jaskelioff M, Muller FL, Paik JH, et al:
Telomerase reactivation reverses tissue degeneration in aged
telomerase-deficient mice. Nature. 469:102–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wyllie FS, Jones CJ, Skinner JW, et al:
Telomerase prevents the accelerated cell ageing of Werner syndrome
fibroblasts. Nat Genet. 24:16–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chang RC and So KF: Use of anti-aging
herbal medicine, Lycium barbarum, against aging-associated
diseases. What do we know so far? Cell Mol Neurobiol. 28:643–652.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Potterat O: Goji (Lycium barbarum
and L. chinense): Phytochemistry, pharmacology and safety in
the perspective of traditional uses and recent popularity. Planta
Med. 76:7–19. 2010.
|
|
35
|
Yang D, Li SY, Yeung CM, et al: Lycium
barbarum extracts protect the brain from blood-brain barrier
disruption and cerebral edema in experimental stroke. PLoS One.
7:e335962012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Koivusalo R, Krausz E, Ruotsalainen P,
Helenius H and Hietanen S: Chemoradiation of cervical cancer cells:
targeting human papillomavirus E6 and p53 leads to either augmented
or attenuated apoptosis depending on the platinum carrier ligand.
Cancer Res. 62:7364–7371. 2002.
|
|
37
|
Singh S, Upadhyay AK, Ajay AK and Bhat MK:
p53 regulates ERK activation in carboplatin induced apoptosis in
cervical carcinoma: a novel target of p53 in apoptosis. FEBS Lett.
581:289–295. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gomez-Manzano C, Fueyo J, Kyritsis AP, et
al: Characterization of p53 and p21 functional interactions in
glioma cells en route to apoptosis. J Natl Cancer Inst.
89:1036–1044. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|