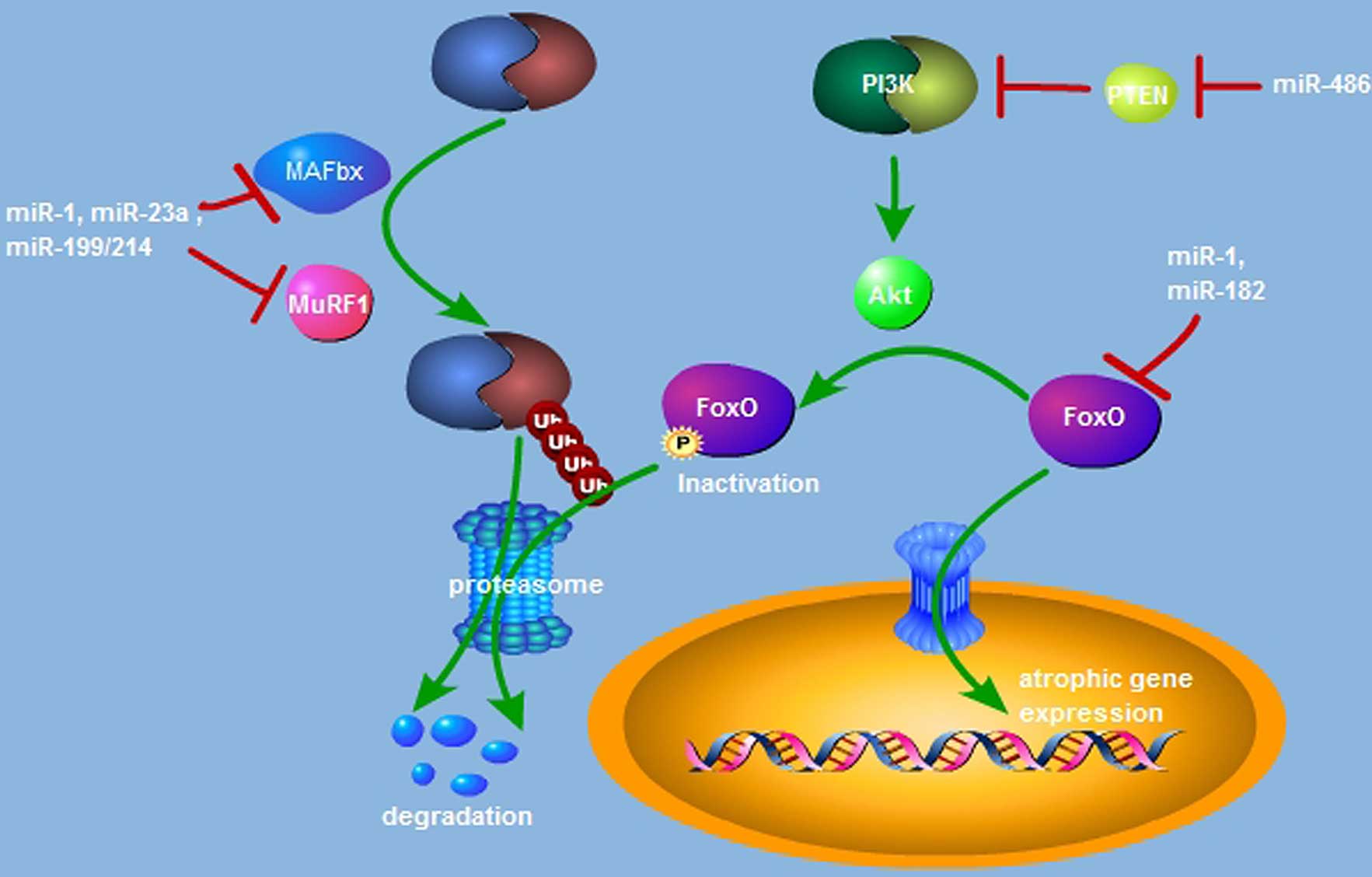
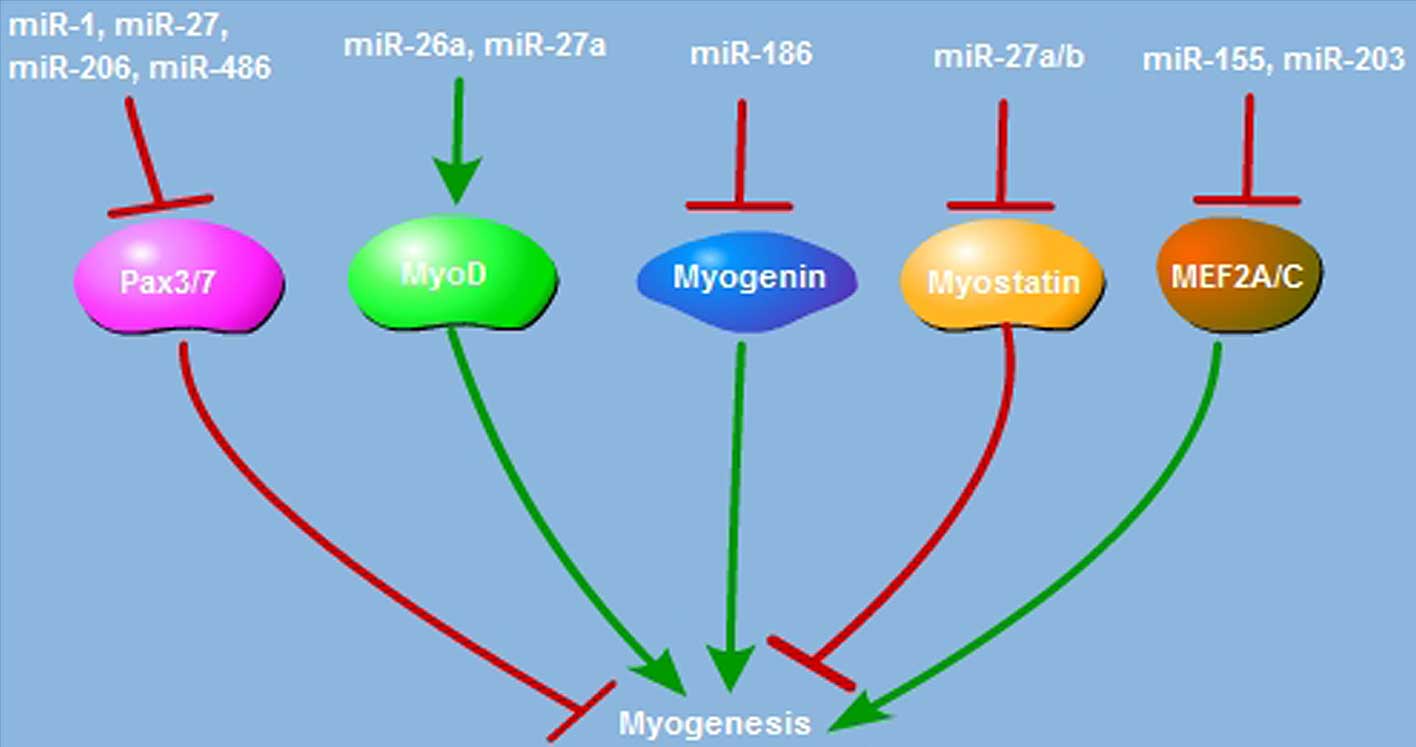
|
1
|
Hitachi K and Tsuchida K: Role of
microRNAs in skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Front Physiol. 4:4082014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paul PK, Bhatnagar S, Mishra V, Srivastava
S, Darnay BG, Choi Y and Kumar A: The E3 Kubiquitin ligase TRAF6
intercedes in starvation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy through
multiple mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 32:1248–1259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McGregor RA, Poppitt SD and Cameron-Smith
D: Role of microRNAs in the age-related changes in skeletal muscle
and diet or exercise interventions to promote healthy aging in
humans. Ageing Res Rev. 17:25–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nystrom G, Pruznak A, Huber D, Frost RA
and Lang CH: Local insulin-like growth factor I prevents
sepsis-induced muscle atrophy. Metabolism. 58:787–797. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang H, Lai YJ, Chan YL, Li TL and Wu CJ:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate effectively attenuates skeletal muscle
atrophy caused by cancer cachexia. Cancer Lett. 305:40–49. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bertsch S, Lang CH and Vary TC: Inhibition
of glycogen synthase kinase 3[beta] activity with lithium in vitro
attenuates sepsis-induced changes in muscle protein turnover.
Shock. 35:266–274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hart DW, Wolf SE, Chinkes DL, Gore DC,
Mlcak RP, Beauford RB, Obeng MK, Lal S, Gold WF, Wolfe RR and
Herndon DN: Determinants of skeletal muscle catabolism after severe
burn. Ann Surg. 232:455–465. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu J, Li R, Workeneh B, Dong Y, Wang X and
Hu Z: Transcription factor FoxO1, the dominant mediator of muscle
wasting in chronic kidney disease, is inhibited by microRNA-486.
Kidney Int. 82:401–411. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Metter EJ, Talbot LA, Schrager M and
Conwit R: Skeletal muscle strength as a predictor of all-cause
mortality in healthy men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
57:B359–B365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chai J, Wu Y and Sheng ZZ: Role of
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in skeletal muscle wasting in rats
with endotoxemia. Crit Care Med. 31:1802–1807. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Attaix D, Combaret L, Bechet D and
Taillandier D: Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in muscle
atrophy in cachexia. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2:262–266.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sishi B, Loos B, Ellis B, Smith W, du Toit
EF and Engelbrecht AM: Diet-induced obesity alters signalling
pathways and induces atrophy and apoptosis in skeletal muscle in a
prediabetic rat model. Exp Physiol. 96:179–193. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Engelbrecht AM, Smith C, Neethling I,
Thomas M, Ellis B, Mattheyse M and Myburgh KH: Daily brief
restraint stress alters signaling pathways and induces atrophy and
apoptosis in rat skeletal muscle. Stress. 13:132–141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dupont-Versteegden EE: Apoptosis in
skeletal muscle and its relevance to atrophy. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:7463–7466. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sayed D and Abdellatif M: MicroRNAs in
development and disease. Physiol Rev. 91:827–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Didiano D and Hobert O: Molecular
architecture of a miRNA-regulated 3′ UTR. RNA. 14:1297–1317. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Travaglini L, Vian L, Billi M, Grignani F
and Nervi C: Epigenetic reprogramming of breast cancer cells by
valproic acid occurs regardless of estrogen receptor status. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:225–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Taulli R, Bersani F, Foglizzo V, Linari A,
Vigna E, Ladanyi M, Tuschl T and Ponzetto C: The muscle-specific
microRNA miR-206 blocks human rhabdomyosarcoma growth in
xeno-transplanted mice by promoting myogenic differentiation. J
Clin Invest. 119:2366–2378. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Melton DW, Gelfond JA, McManus LM
and Shireman PK: MiR-351 transiently increases during muscle
regeneration and promotes progenitor cell proliferation and
survival upon differentiation. Physiol Genomics. 44:1042–1051.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Motohashi N, Alexander MS,
Shimizu-Motohashi Y, Myers JA, Kawahara G and Kunkel LM: Regulation
of IRS1/Akt insulin signaling by microRNA-128a during myogenesis. J
Cell Sci. 126:2678–2691. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hartmann-Petersen R and Gordon C: Proteins
interacting with the 26S proteasome. Cell Mol Life Sci.
61:1589–1595. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK,
Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K,
et al: Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal
muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Eddins MJ, Marblestone JG, Suresh Kumar
KG, Leach CA, Sterner DE, Mattern MR and Nicholson B: Targeting the
ubiquitin E3 ligase MuRF1 to inhibit muscle atrophy. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 60:113–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Clavel S, Coldefy AS, Kurkdjian E, Salles
J, Margaritis I and Derijard B: Atrophy-related ubiquitin ligases,
atrogin-1 and MuRF1 are up-regulated in aged rat Tibialis Anterior
muscle. Mech Ageing Dev. 127:794–801. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wada S, Kato Y, Okutsu M, Miyaki S, Suzuki
K, Yan Z, Schiaffino S, Asahara H, Ushida T and Akimoto T:
Translational suppression of atrophic regulators by microRNA-23a
integrates resistance to skeletal muscle atrophy. J Biol Chem.
286:38456–38465. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kukreti H, Amuthavalli K, Harikumar A,
Sathiyamoorthy S, Feng PZ, Anantharaj R, Tan SL, Lokireddy S,
Bonala S, Sriram S, et al: Muscle-specific microRNA1 (miR1) targets
heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) during dexamethasone-mediated
atrophy. J Biol Chem. 288:6663–6678. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baumgarten A, Bang C, Tschirner A,
Engelmann A, Adams V, von Haehling S, Doehner W, Pregla R, Anker
MS, Blecharz K, et al: TWIST1 regulates the activity of ubiquitin
proteasome system via the miR-199/214 cluster in human end-stage
dilated cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 168:1447–1452. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Penna F, Costamagna D, Fanzani A, Bonelli
G, Baccino FM and Costelli P: Muscle wasting and impaired
myogenesis in tumor bearing mice are prevented by ERK inhibition.
PLoS One. 5:e136042010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Verhees KJ, Pansters NA, Baarsma HA,
Remels AH, Haegens A, de Theije CC, Schols AM, Gosens R and Langen
RC: Pharmacological inhibition of GSK-3 in a guinea pig model of
LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation: II. Effects on skeletal muscle
atrophy. Respir Res. 14:1172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi H, Verma M, Zhang L, Dong C, Flavell
RA and Bennett AM: Improved regenerative myogenesis and muscular
dystrophy in mice lacking Mkp5. J Clin Invest. 123:2064–2077. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Malena A, Pennuto M, Tezze C, Querin G,
D'Ascenzo C, Silani V, Cenacchi G, Scaramozza A, Romito S, Morandi
L, et al: Androgen-dependent impairment of myogenesis in spinal and
bulbar muscular atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 126:109–121. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sacco A, Doyonnas R, Kraft P, Vitorovic S
and Blau HM: Self-renewal and expansion of single transplanted
muscle stem cells. Nature. 456:502–506. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dachs E, Hereu M, Piedrafita L, Casanovas
A, Calderó J and Esquerda JE: Defective neuromuscular junction
organization and postnatal myogenesis in mice with severe spinal
muscular atrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 70:444–461. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang XH: MicroRNA in myogenesis and muscle
atrophy. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 16:258–266. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen JF, Tao Y, Li J, Deng Z, Yan Z, Xiao
X and Wang DZ: microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle
satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing
Pax7. J Cell Biol. 190:867–879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dey BK, Gagan J and Dutta A: miR-206 and
-486 induce myoblast differentiation by downregulating Pax7. Mol
Cell Biol. 31:203–214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Liu N, Williams AH, Maxeiner JM,
Bezprozvannaya S, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R and
Olson EN: microRNA-206 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration and
delays progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice. J Clin
Invest. 122:2054–2065. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goljanek-Whysall K, Sweetman D, Abu-Elmagd
M, Chapnik E, Dalmay T, Hornstein E and Münsterberg A: MicroRNA
regulation of the paired-box transcription factor Pax3 confers
robustness to developmental timing of myogenesis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:11936–11941. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Crist CG, Montarras D, Pallafacchina G,
Cumano A, Conway SJ and Buckingham M: Muscle stem cell behavior is
modified by microRNA-27 regulation of Pax3 expression. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:13383–13387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen X, Huang Z, Chen D, Yang T and Liu G:
Role of microRNA-27a in myoblast differentiation. Cell Biol Int.
38:266–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wong CF and Tellam RL: MicroRNA-26a
targets the histone methyltransferase Enhancer of Zeste homolog 2
during myogenesis. J Biol Chem. 283:9836–9843. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dey BK, Gagan J, Yan Z and Dutta A:
miR-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and
regeneration in mice. Genes Dev. 26:2180–2191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Antoniou A, Mastroyiannopoulos NP, Uney JB
and Phylactou LA: miR-186 inhibits muscle cell differentiation
through myogenin regulation. J Biol Chem. 289:3923–3935. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang Z, Chen X, Yu B, He J and Chen D:
MicroRNA-27a promotes myoblast proliferation by targeting
myostatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:265–269. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
McFarlane C, Vajjala A, Arigela H,
Lokireddy S, Ge X, Bonala S, Manickam R, Kambadur R and Sharma M:
Negative auto-regulation of myostatin expression is mediated by
Smad3 and microRNA-27. PLoS One. 9:e876872014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yang T, Chen XL, Huang ZQ, Wen WX, Xu M,
Chen DW, Yu B, He J, Luo JQ, Yu J, et al: MicroRNA-27a promotes
porcine myoblast proliferation by downregulating myostatin
expression. Animal. 8:1867–1872. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ge Y, Sun Y and Chen J: IGF-II is
regulated by microRNA-125b in skeletal myogenesis. J Cell Biol.
192:69–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang MB, Xu H, Xie SJ, Zhou H and Qu LH:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor is regulated by microRNA-133
during skeletal myogenesis. PLoS One. 6:e291732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jia L, Li YF, Wu GF, Song ZY, Lu HZ, Song
CC, Zhang QL, Zhu JY, Yang GS and Shi XE: MiRNA-199a-3p regulates
C2C12 myoblast differentiation through IGF-1/AKT/mTOR signal
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 15:296–308. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Luo W, Wu H, Ye Y, Li Z, Hao S, Kong L,
Zheng X, Lin S, Nie Q and Zhang X: The transient expression of
miR-203 and its inhibiting effects on skeletal muscle cell
proliferation and differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 5:e13472014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Seok HY, Tatsuguchi M, Callis TE, He A, Pu
WT and Wang DZ: miR-155 inhibits expression of the MEF2A protein to
repress skeletal muscle differentiation. J Biol Chem.
286:35339–35346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wei W, He HB, Zhang WY, Zhang HX, Bai JB,
Liu HZ, Cao JH, Chang KC, Li XY and Zhao SH: miR-29 targets Akt3 to
reduce proliferation and facilitate differentiation of myoblasts in
skeletal muscle development. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou L, Wang L, Lu L, Jiang P, Sun H and
Wang H: A novel target of microRNA-29, Ring1 and YY1-binding
protein (Rybp), negatively regulates skeletal myogenesis. J Biol
Chem. 287:25255–25265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dupont-Versteegden EE: Apoptosis in muscle
atrophy: Relevance to sarcopenia. Exp Gerontol. 40:473–481. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Dirks AJ and Leeuwenburgh C: The role of
apoptosis in age-related skeletal muscle atrophy. Sports Med.
35:473–483. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lee HY, Kaneki M, Andreas J, Tompkins RG
and Martyn JA: Novel mitochondria-targeted antioxidant peptide
ameliorates burn-induced apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress
in the skeletal muscle of mice. Shock. 36:580–585. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fanzani A, Conraads VM, Penna F and
Martinet W: Molecular and cellular mechanisms of skeletal muscle
atrophy: An update. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 3:163–179. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Libera LD, Zennaro R, Sandri M, Ambrosio
GB and Vescovo G: Apoptosis and atrophy in rat slow skeletal
muscles in chronic heart failure. Am J Physiol. 277:C982–C986.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yasuhara S, Perez ME, Kanakubo E, Yasuhara
Y, Shin YS, Kaneki M, Fujita T and Martyn JA: Skeletal muscle
apoptosis after burns is associated with activation of proapoptotic
signals. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 279:E1114–E1121.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Marzetti E, Lawler JM, Hiona A, Manini T,
Seo AY and Leeuwenburgh C: Modulation of age-induced apoptotic
signaling and cellular remodeling by exercise and calorie
restriction in skeletal muscle. Free Radic Biol Med. 44:160–168.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Callis TE, Chen JF and Wang DZ: MicroRNAs
in skeletal and cardiac muscle development. DNA Cell Biol.
26:219–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Idris NM, Ashraf M, Ahmed RP, Shujia J and
Haider KH: Activation of IL-11/STAT3 pathway in preconditioned
human skeletal myoblasts blocks apoptotic cascade under oxidant
stress. Regen Med. 7:47–57. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Haider KH, Idris NM, Kim HW, Ahmed RP,
Shujia J and Ashraf M: MicroRNA-21 is a key determinant in
IL-11/Stat3 anti-apoptotic signalling pathway in preconditioning of
skeletal myoblasts. Cardiovasc Res. 88:168–178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
He WA, Calore F, Londhe P, Canella A,
Guttridge DC and Croce CM: Microvesicles containing miRNAs promote
muscle cell death in cancer cachexia via TLR7. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:4525–4529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hirai H, Verma M, Watanabe S, Tastad C,
Asakura Y and Asakura A: MyoD regulates apoptosis of myoblasts
through microRNA-mediated down-regulation of Pax3. J Cell Biol.
191:347–365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Stitt TN, Drujan D, Clarke BA, Panaro F,
Timofeyva Y, Kline WO, Gonzalez M, Yancopoulos GD and Glass DJ: The
IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle
atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription
factors. Mol Cell. 14:395–403. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Sugita H, Kaneki M, Sugita M, Yasukawa T,
Yasuhara S and Martyn JA: Burn injury impairs insulin-stimulated
Akt/PKB activation in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 288:E585–E591. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Du K, Yu Y, Zhang D, Luo W, Huang H, Chen
J, Gao J and Huang C: NFkappaB1 (p50) suppresses SOD2 expression by
inhibiting FoxO3a transactivation in a miR190/PHLPP1/Akt-dependent
axis. Mol Biol Cell. 24:3577–3583. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, Skurk C,
Calabria E, Picard A, Walsh K, Schiaffino S, Lecker SH and Goldberg
AL: Foxo transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin
ligase atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell.
117:399–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sheriff S, Kadeer N, Joshi R, Friend LA,
James JH and Balasubramaniam A: Des-acyl ghrelin exhibits
pro-anabolic and anti-catabolic effects on C2C12 myotubes exposed
to cytokines and reduces burn-induced muscle proteolysis in rats.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 351:286–295. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Alexander MS, Casar JC, Motohashi N, Myers
JA, Eisenberg I, Gonzalez RT, Estrella EA, Kang PB, Kawahara G and
Kunkel LM: Regulation of DMD pathology by an ankyrin-encoded miRNA.
Skelet Muscle. 1:272011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chen D, Goswami CP, Burnett RM, Anjanappa
M, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Muller W and Nakshatri H: Cancer affects
microRNA expression, release and function in cardiac and skeletal
muscle. Cancer Res. 74:4270–4281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hitachi K, Nakatani M and Tsuchida K:
Myostatin signaling regulates Akt activity via the regulation of
miR-486 expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 47:93–103. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Hudson MB, Rahnert JA, Zheng B,
Woodworth-Hobbs ME, Franch HA and Price SR: miR-182 attenuates
atrophy-related gene expression by targeting FoxO3 in skeletal
muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 307:C314–C319. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|