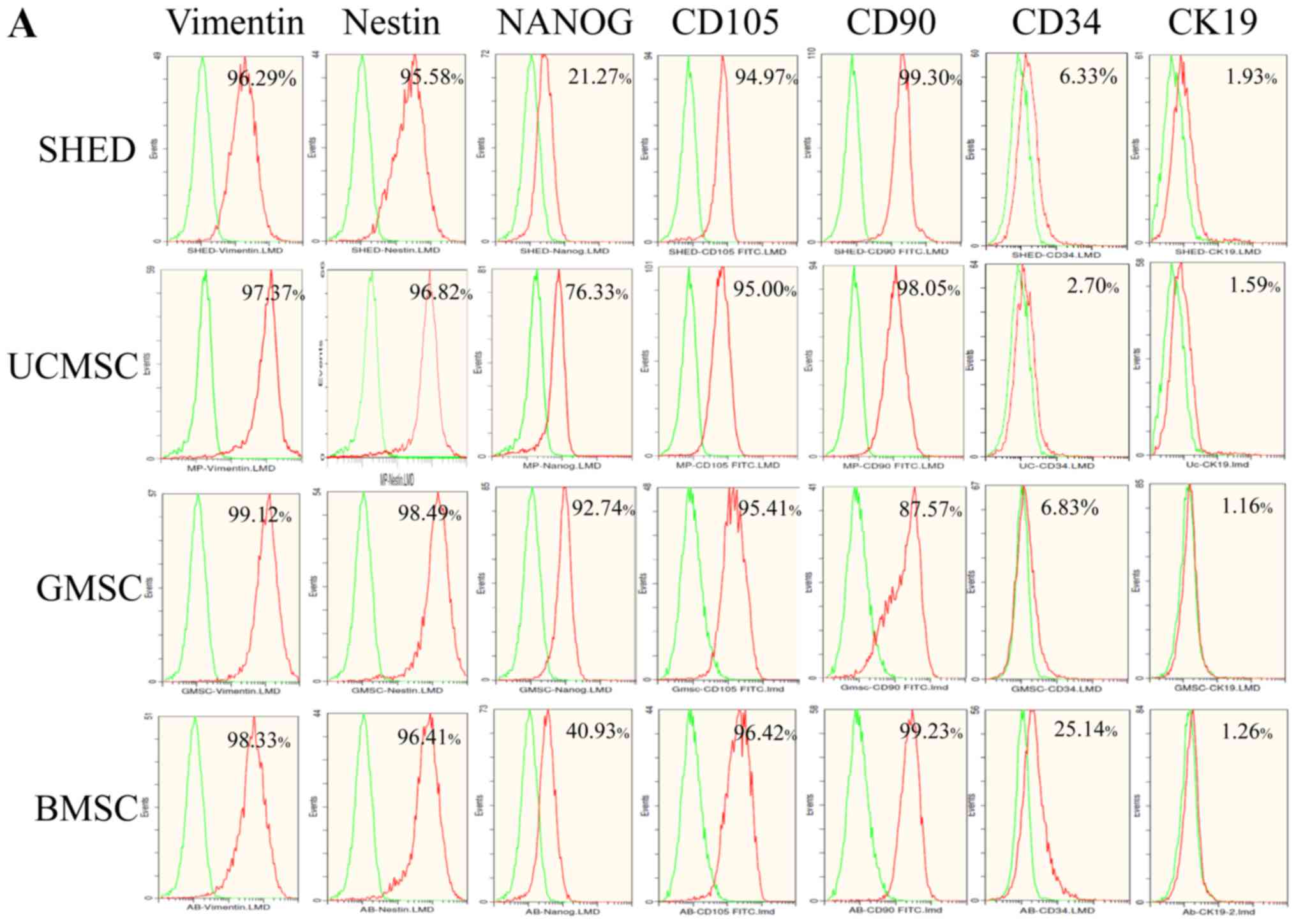
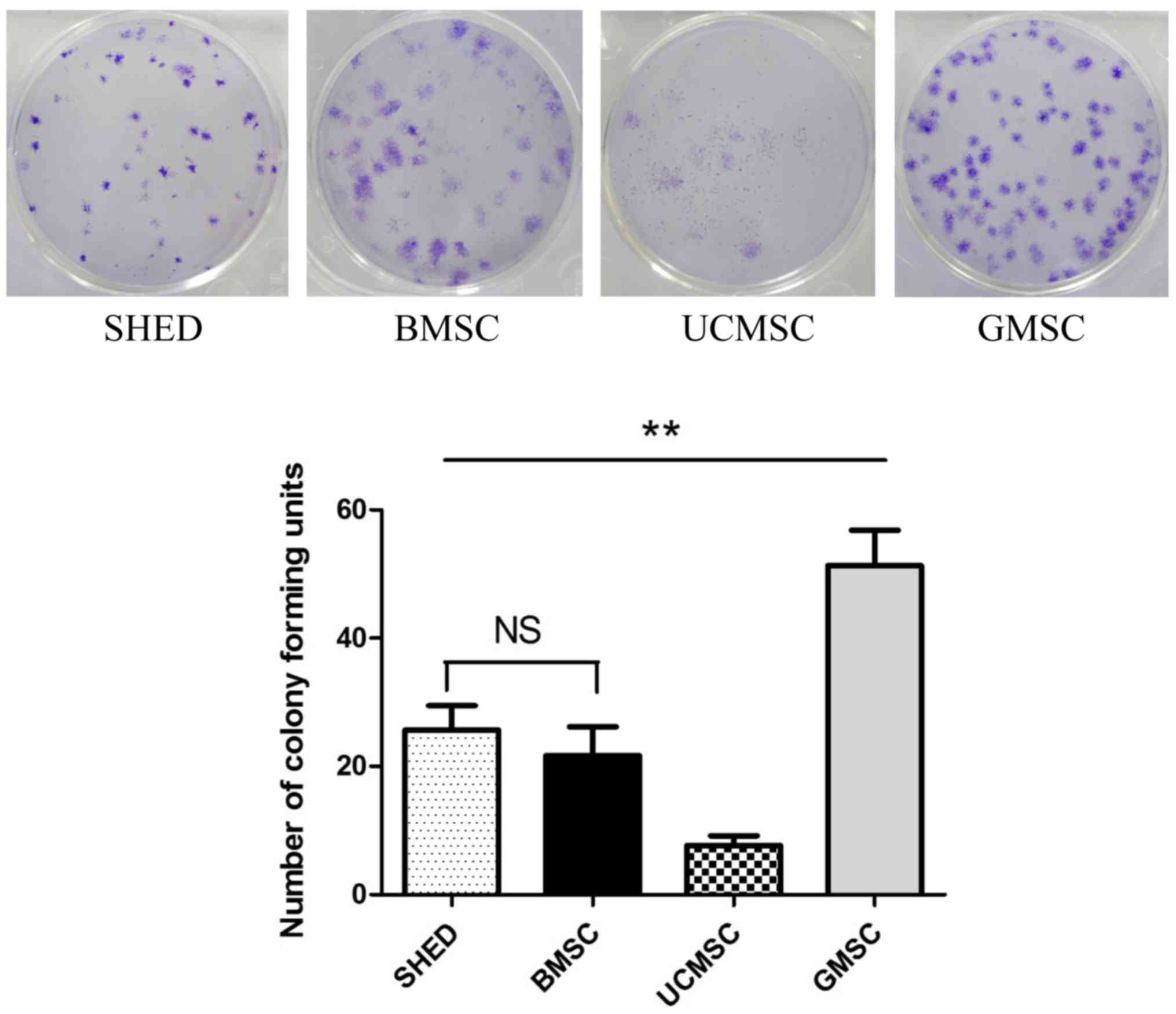
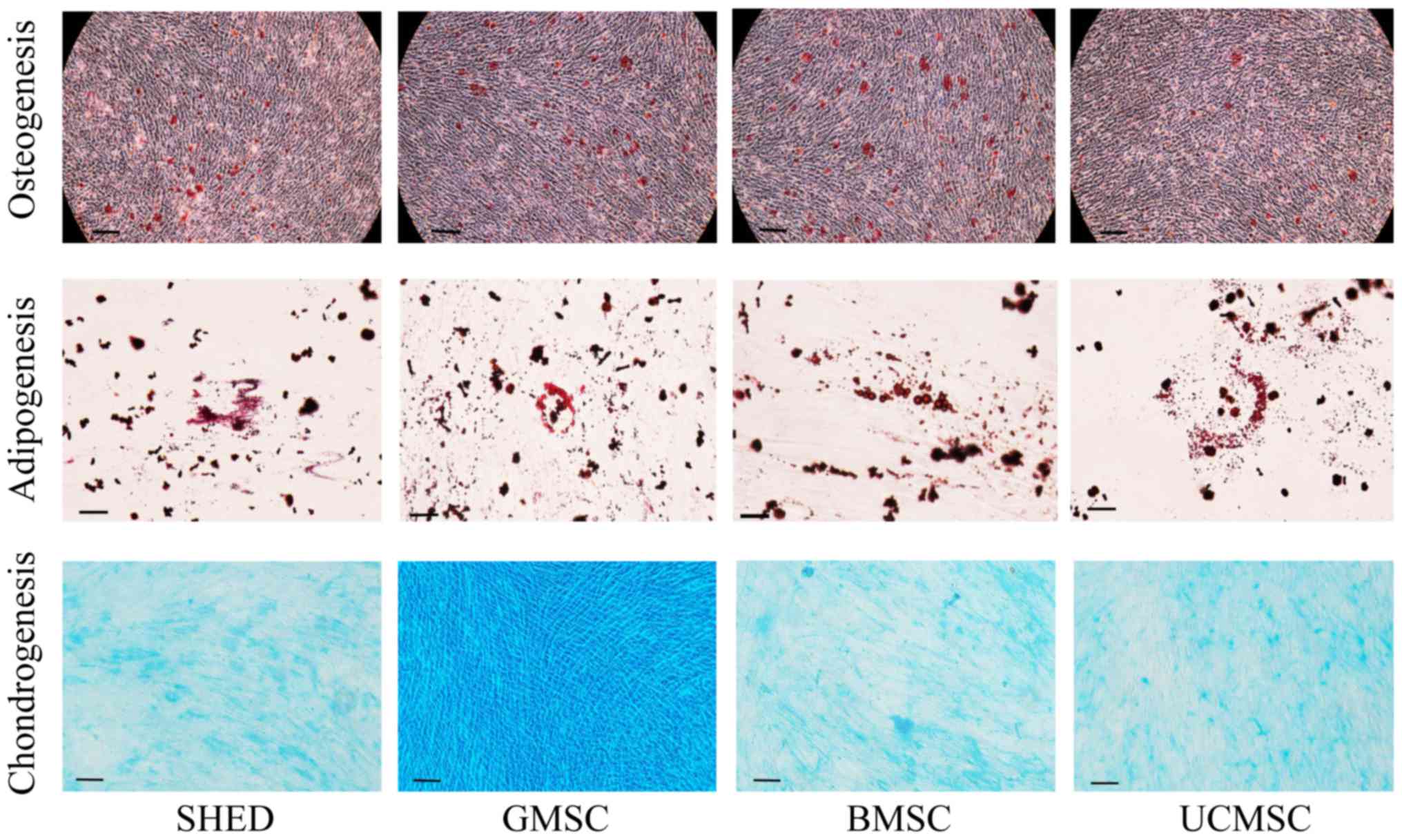
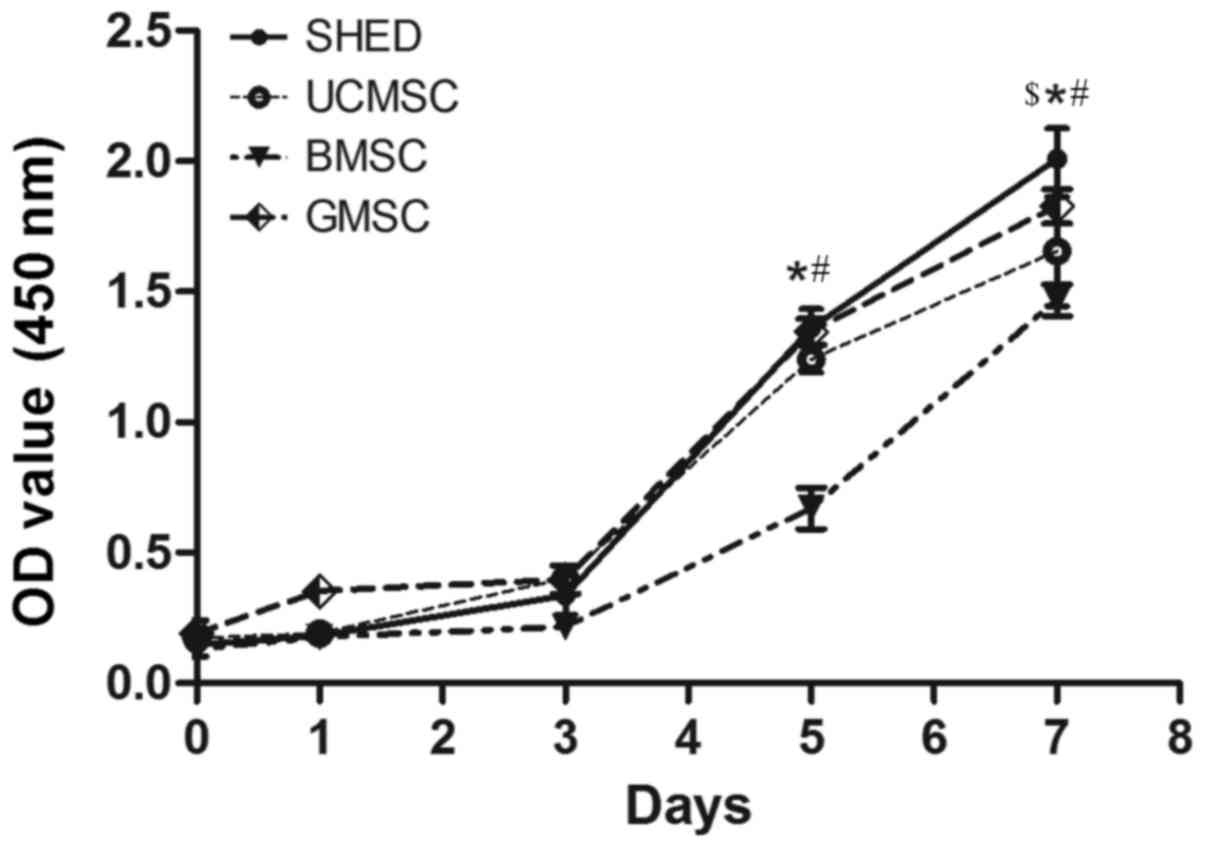
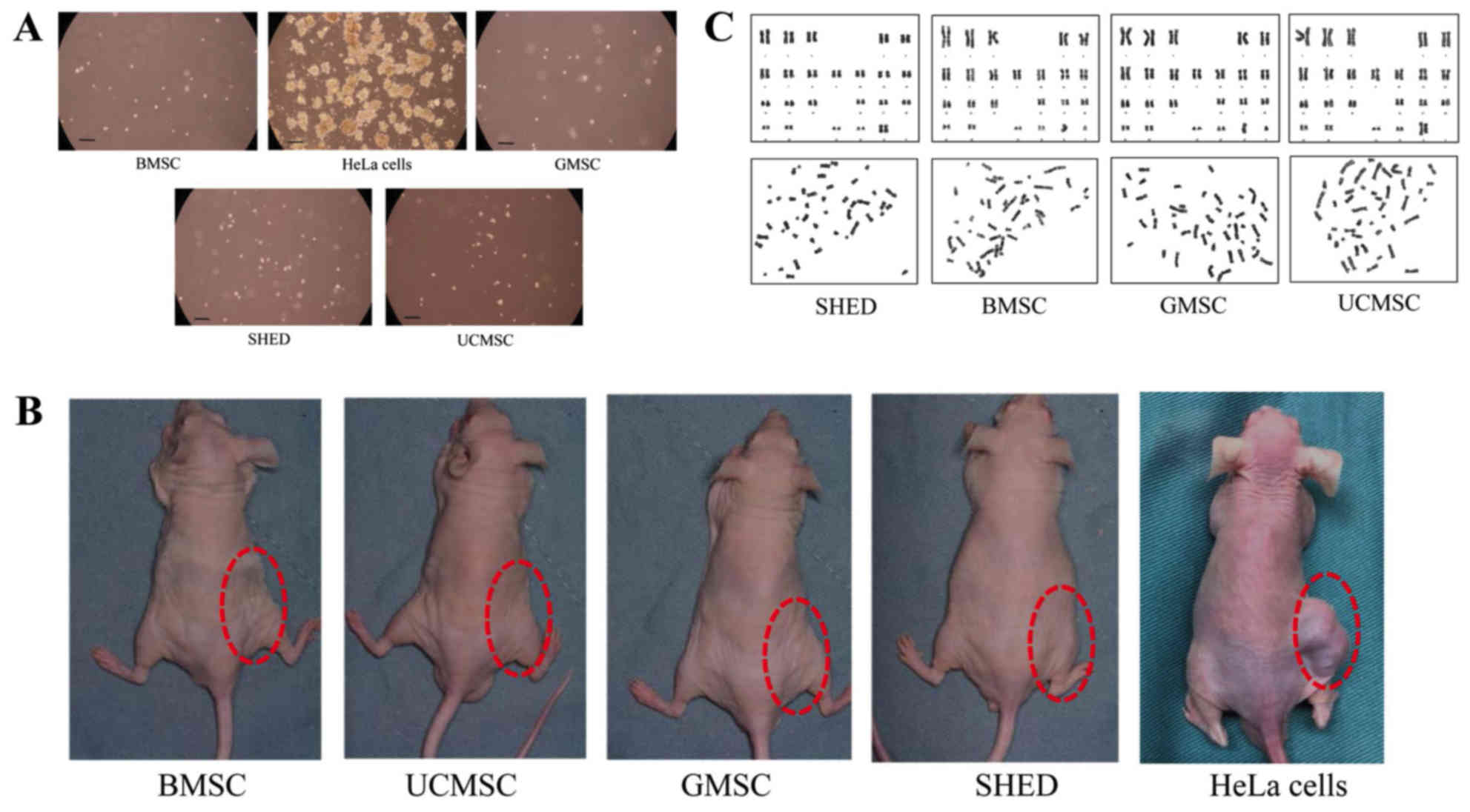
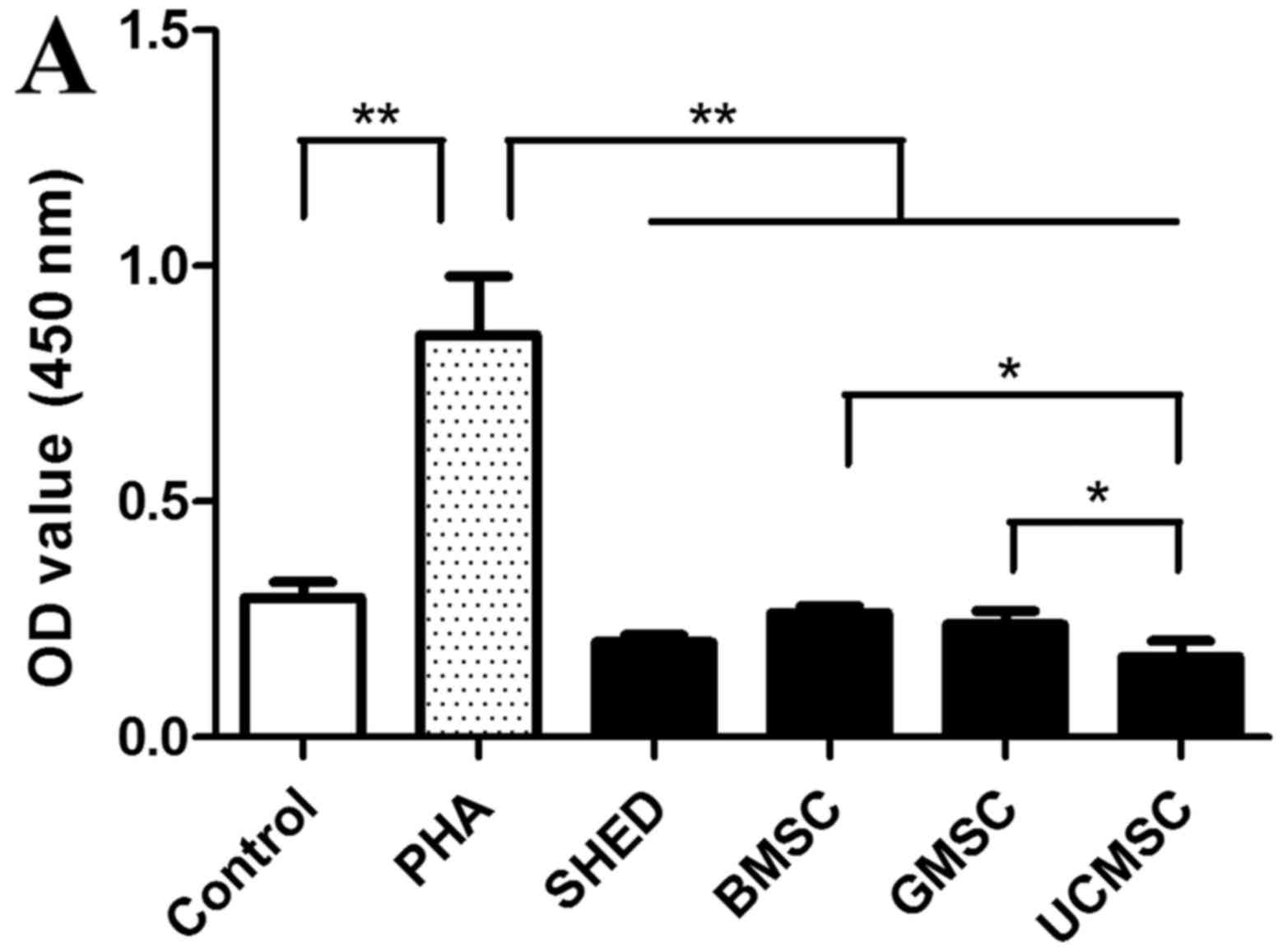
|
1
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cels as stem
cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 276:71–74. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pittenger MF and Martin BJ: Mesenchymal
stem cells and their potential as cardiac therapeutics. Circ Res.
95:9–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Satake K, Lou J and Lenke LG: Migration of
mesenchymal stem cells through cerebrospinal fluid into injured
spinal cord tissue. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 29:1971–1979. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Satija NK, Singh VK, Verma YK, Gupta P,
Sharma S, Afrin F, Sharma M, Sharma P, Tripathi RP and Gurudutta
GU: Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: A new paradigm in
regenerative medicine. J Cell Mol Med. 13:4385–4402. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Taran R, Mamidi MK, Singh G, Dutta S,
Parhar IS, John JP, Bhonde R, Pal R and Das AK: In vitro and in
vivo neurogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from
different sources. J Biosci. 39:157–169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma J, Both SK, Yang F, Cui FZ, Pan J,
Meijer GJ, Jansen JA and van den Beucken JJ: Concise review:
Cell-based strategies in bone tissue engineering and regenerative
medicine. Stem Cells Transl Med. 3:98–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shang Q, Wang Z, Liu W, Shi Y, Cui L and
Cao Y: Tissue-engineered bone repair of sheep cranial defects with
autologous bone marrow stromal cells. J Craniofac Surg. 12:586–595.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ferrari G, Cusella-De Angelis G, Coletta
M, Paolucci E, Stornaiuolo A, Cossu G and Mavilio F: Muscle
regeneration by bone marrow-derived myogenic progenitors. Science.
279:1528–1530. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shintani S, Murohara T, Ikeda H, Ueno T,
Honma T, Katoh A, Sasaki K, Shimada T, Oike Y and Imaizumi T:
Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with acute
myocardial infarction. Circulation. 103:2776–2779. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ringdén O, Uzunel M, Rasmusson I,
Remberger M, Sundberg B, Lönnies H, Marschall HU, Dlugosz A, Szakos
A, Hassan Z, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of
therapy-resistant graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation.
81:1390–1397. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Angelopoulou M, Novelli E, Grove JE,
Rinder HM, Civin C, Cheng L and Krause DS: Cotransplantation of
human mesenchymal stem cells enhances human myelopoiesis and
megakaryocytopoiesis in NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol. 31:413–420.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miura M, Gronthos S, Zhao M, Lu B, Fisher
LW, Robey PG and Shi S: SHED: Stem cells from human exfoliated
deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:5807–5812. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ren H, Sang Y, Zhang F, Liu Z, Qi N and
Chen Y: Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from
umbilical cord, dental pulp, and menstrual blood as sources for
cell therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016:35165742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren HY, Zhao QJ, Xing W, Yang SG, Lu SH,
Ren Q, Zhang L and Han ZC: Differentiation of human umbilical cord
derived mesenchymal stem cells into low immunogenic and functional
hepatocyte-like cells in vitro. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue
Bao. 32:190–194. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Q, Shi S, Liu Y, Uyanne J, Shi Y,
Shi S and Le AD: Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human gingiva
are capable of immunomodulatory functions and ameliorate
inflammation-related tissue destruction in experimental colitis. J
Immunol. 183:7787–7798. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tomar GB, Srivastava RK, Gupta N,
Barhanpurkar AP, Pote ST, Jhaveri HM, Mishra GC and Wani MR: Human
gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells are superior to bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for cell therapy in
regenerative medicine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 393:377–383.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang F, Yu M, Yan X, Wen Y, Zeng Q, Yue W,
Yang P and Pei X: Gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cell-mediated
therapeutic approach for bone tissue regeneration. Stem Cells Dev.
20:2093–2102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jacobs SA, Roobrouck VD, Verfaillie CM and
Van Gool SW: Immunological characteristics of human mesenchymal
stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells. Immunol Cell
Biol. 91:32–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Deans RJ and Moseley AB: Mesenchymal stem
cells: Biology and potential clinical uses. Exp Hematol.
28:875–884. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Inoue S, Popp FC, Koehl GE, Piso P,
Schlitt HJ, Geissler EK and Dahlke MH: Immunomodulatory effects of
mesenchymal stem cells in a rat organ transplant model.
Transplantation. 81:1589–1595. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamaza T, Kentaro A, Chen C, Liu Y, Shi Y,
Gronthos S, Wang S and Shi S: Immunomodulatory properties of stem
cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Stem Cell Res Ther.
1:52010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li P, Zhao Y and Ge L: Therapeutic effects
of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stromal cells on murine
contact hypersensitivity via prostaglandin E2-EP3 signaling. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 7:1032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu X, Chen Y, Xie FN, Dong P, Liu WB, Cao
Y, Zhang WJ and Xiao R: Comparison of immunological characteristics
of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human embryonic stem cells
and bone marrow. Tissue Eng Part A. 21:616–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang M, Yang Y, Yang D, Luo F, Liang W,
Guo S and Xu J: The immunomodulatory activity of human umbilical
cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Immunology.
126:220–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
de Witte SFH, Lambert EE, Merino A, Strini
T, Douben HJCW, O'Flynn L, Elliman SJ, de Klein AJEMM, Newsome PN,
Baan CC and Hoogduijn MJ: Aging of bone marrow- and umbilical
cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells during expansion.
Cytotherapy. 19:798–807. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo W, Li S, Peng B, Ye Y, Deng X and Yao
K: Embryonic stem cells markers SOX2, OCT4 and Nanog expression and
their correlations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e563242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Isobe Y, Koyama N, Nakao K, Osawa K, Ikeno
M, Yamanaka S, Okubo Y, Fujimura K and Bessho K: Comparison of
human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovial
fluid, adult dental pulp, and exfoliated deciduous tooth pulp. Int
J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 45:124–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakashima M, Iohara K, Murakami M,
Nakamura H, Sato Y, Ariji Y and Matsushita K: Pulp regeneration by
transplantation of dental pulp stem cells in pulpitis: A pilot
clinical study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M,
Ferrer K, McIntosh K, Patil S, Hardy W, Devine S, Ucker D, Deans R,
et al: Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in
vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol.
30:42–48. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B,
Götherström C, Hassan M, Uzunel M and Ringdén O: Treatment of
severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party
haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 363:1439–1441. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun L, Akiyama K, Zhang H, Yamaza T, Hou
Y, Zhao S, Xu T, Le A and Shi S: Mesenchymal stem cell
transplantation reverses multiorgan dysfunction in systemic lupus
erythematosus mice and humans. Stem Cells. 27:1421–1432. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sheng H, Wang Y, Jin Y, Zhang Q, Zhang Y,
Wang L, Shen B, Yin S, Liu W, Cui L and Li N: A critical role of
IFNgamma in priming MSC-mediated suppression of T cell
proliferation through up-regulation of B7-H1. Cell Res. 18:846–857.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ryan JM, Barry FP, Murphy JM and Mahon BP:
Mesenchymal stem cells avoid allogeneic rejection. J Inflamm
(Lond). 2:82005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bocelli-Tyndall C, Zajac P, Di Maggio N,
Trella E, Benvenuto F, Iezzi G, Scherberich A, Barbero A, Schaeren
S, Pistoia V, et al: Fibroblast growth factor 2 and
platelet-derived growth factor, but not platelet lysate, induce
proliferation-dependent, functional class II major
histocompatibility complex antigen in human mesenchymal stem cells.
Arthritis Rheum. 62:3815–3825. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|