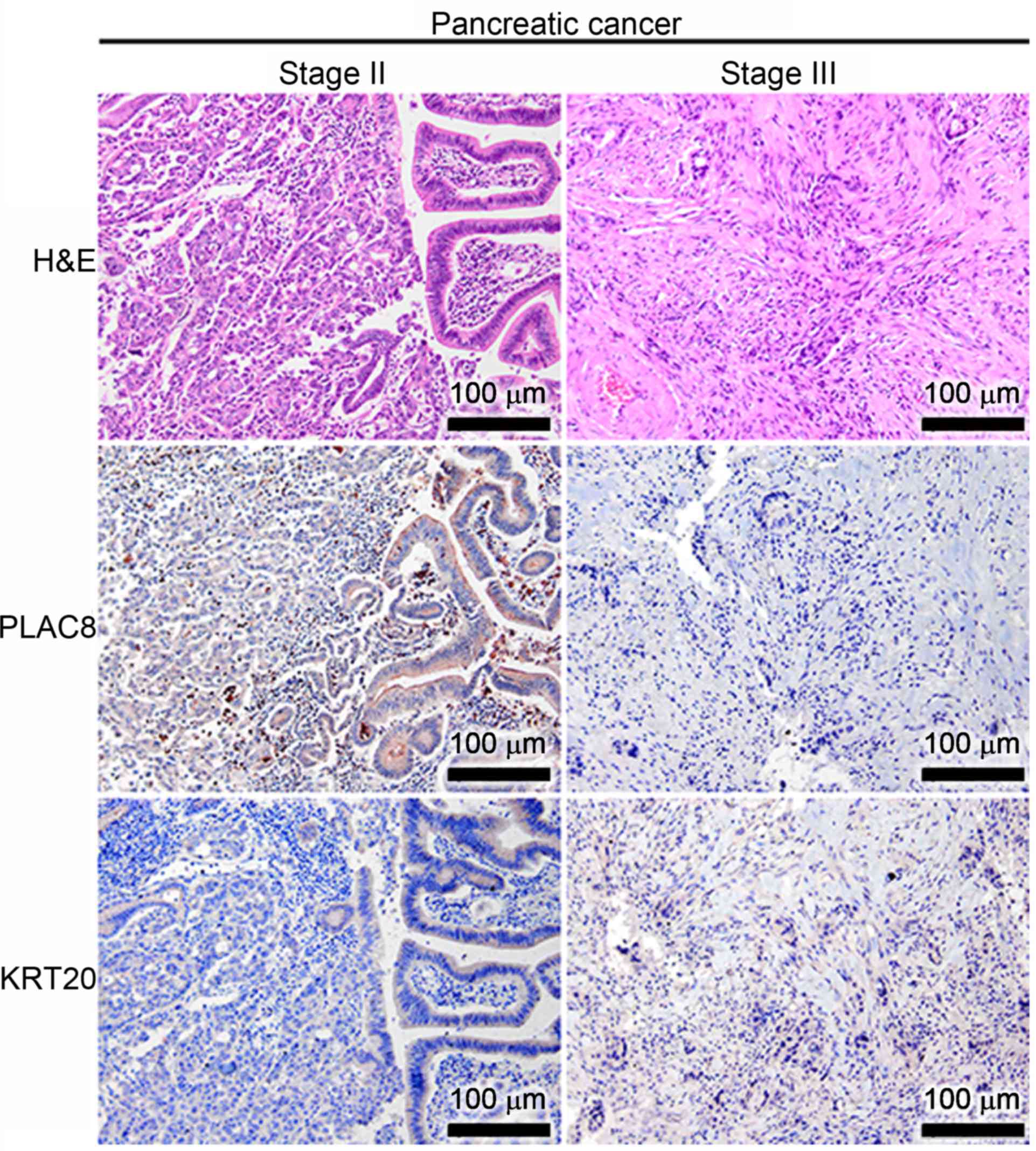
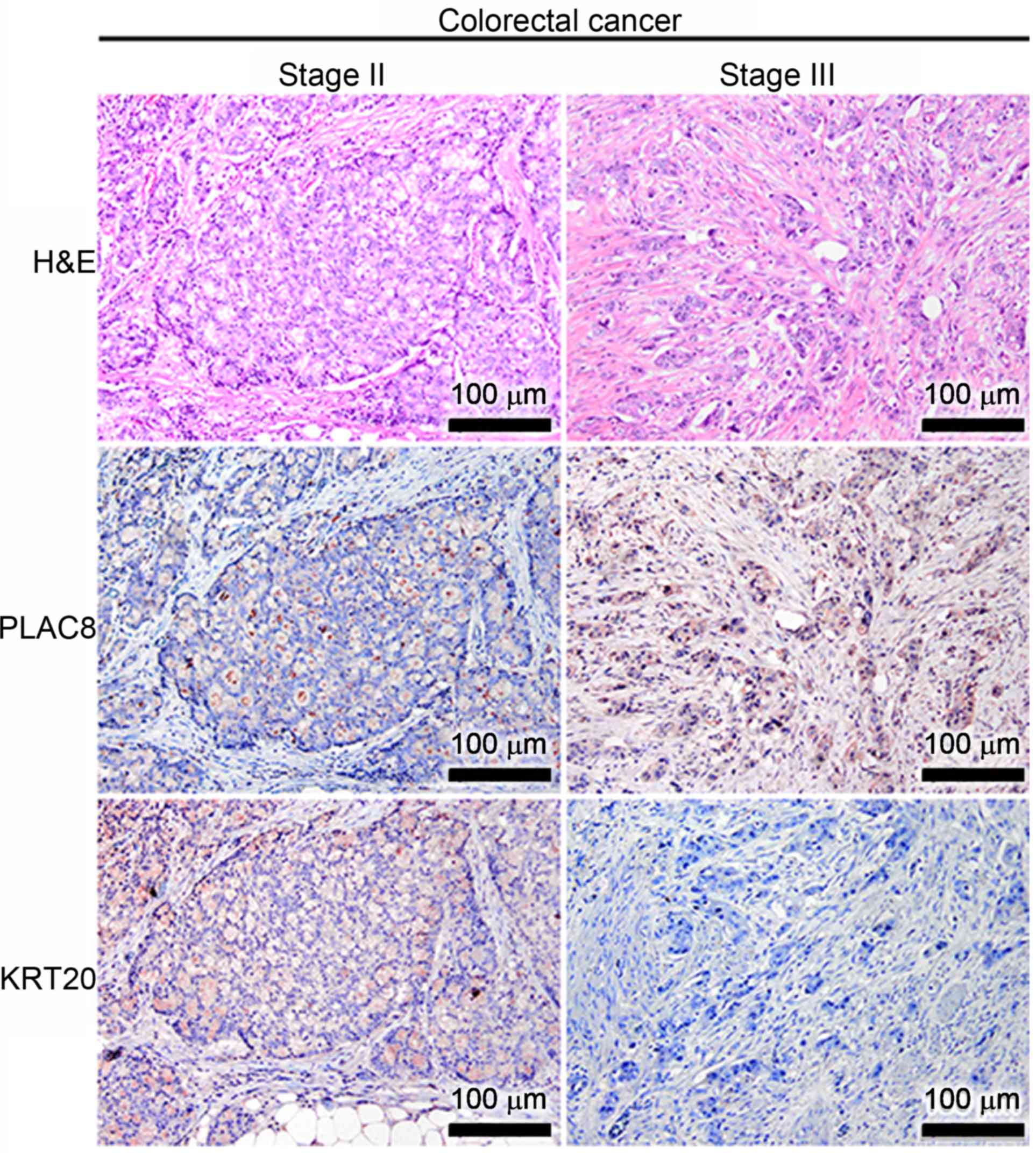
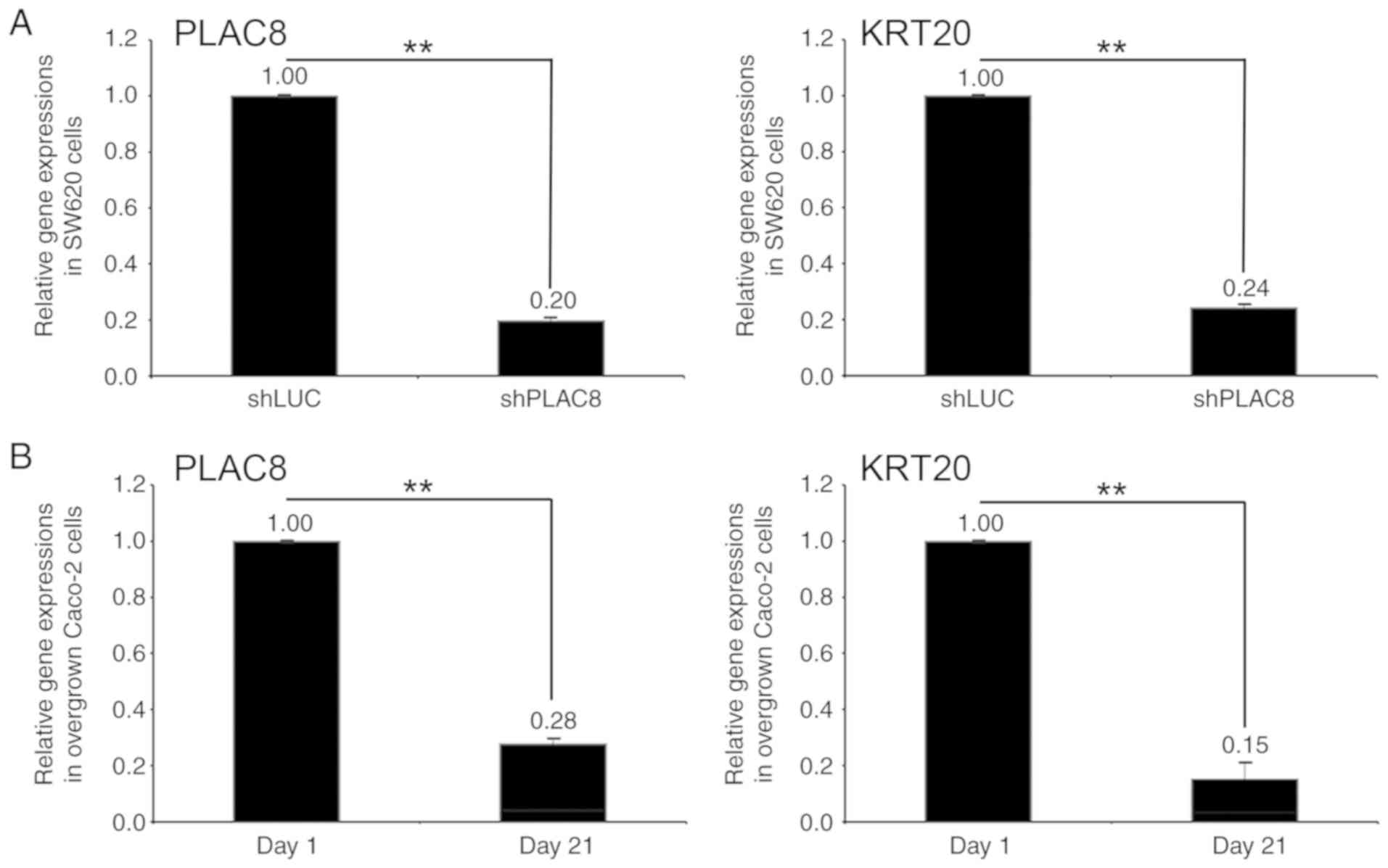
|
1
|
Keighley MR: Gastrointestinal cancers in
europe. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 18:7–30. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Y, Sethi NS, Hinoue T, Schneider BG,
Cherniack AD, Sanchez-Vega F, Seoane JA, Farshidfar F, Bowlby R,
Islam M, et al: Comparative molecular analysis of gastrointestinal
adenocarcinomas. Cancer Cell. 33:721–735. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vedeld HM, Andresen K, Eilertsen IA,
Nesbakken A, Seruca R, Gladhaug IP, Thiis-Evensen E, Rognum TO,
Boberg KM and Lind GE: The novel colorectal cancer biomarkers CDO1,
ZSCAN18 and ZNF331 are frequently methylated across
gastrointestinal cancers. Int J Cancer. 136:844–853. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moll R, Levy R, Czernobilsky B,
Hohlweg-Majert P, Dallenbach-Hellweg G and Franke WW: Cytokeratins
of normal epithelia and some neoplasms of the female genital tract.
Lab Invest. 49:599–610. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim HS, Lee JJ, Do SI, Kim K, Do IG, Kim
DH, Chae SW and Sohn JH: Overexpression of cytokeratin 17 is
associated with the development of papillary thyroid carcinoma and
the presence of lymph node metastasis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:5695–5701. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Osborn M, van Lessen G, Weber K, Kloppel G
and Altmannsberger M: Differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal
carcinomas by using monoclonal antibodies specific for individual
keratin polypeptides. Lab Invest. 55:497–504. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang KD, Kenny L, Perry C, Frazer I and
Punyadeera C: The overexpression of salivary cytokeratins as
potential diagnostic biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. Oncotarget. 8:72272–72280. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tot T: Cytokeratins 20 and 7 as
biomarkers: Usefulness in discriminating primary from metastatic
adenocarcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 38:758–763. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fuchs E: Keratins as biochemical markers
of epithelial differentiation. Trends Genet. 4:277–281. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lipkin M: Biomarkers of increased
susceptibility to gastrointestinal cancer: New application to
studies of cancer prevention in human subjects. Cancer Res.
48:235–245. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mills JC and Sansom OJ: Reserve stem
cells: Differentiated cells reprogram to fuel repair, metaplasia,
and neoplasia in the adult gastrointestinal tract. Sci Signal.
8:re82015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen T, You Y, Jiang H and Wang ZZ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A biological process in
the development, stem cell differentiation, and tumorigenesis. J
Cell Physiol. 232:3261–3272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zou XZ, Liu T, Gong ZC, Hu CP and Zhang Z:
MicroRNAs-Mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in fibrotic
diseases. Eur J Pharmacol. 796:190–206. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Serrano MJ, Ortega FG, Alvarez-Cubero MJ,
Nadal R, Sanchez-Rovira P, Salido M, Rodriguez M, Garcia-Puche JL,
Delgado-Rodriguez M, Sole F, et al: EMT and EGFR in CTCs
cytokeratin negative non-metastatic breast cancer. Oncotarget.
5:7486–7497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hinz S, Hendricks A, Wittig A, Schafmayer
C, Tepel J, Kalthoff H, Becker T and Roder C: Detection of
circulating tumor cells with CK20 RT-PCR is an independent negative
prognostic marker in colon cancer patients-a prospective study. BMC
Cancer. 17:532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang WL, Liu YW, Dang YL, Jiang XX, Xu H,
Huang X, Wang YL, Wang H, Zhu C, Xue LQ, et al: PLAC8, a new marker
for human interstitial extravillous trophoblast cells, promotes
their invasion and migration. Development. 145:dev1489322018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li C, Ma H, Wang Y, Cao Z, Graves-Deal R,
Powell AE, Starchenko A, Ayers GD, Washington MK, Kamath V, et al:
Excess PLAC8 promotes an unconventional ERK2-dependent EMT in colon
cancer. J Clin Invest. 124:2172–2187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miettinen M: Keratin 20:
Immunohistochemical marker for gastrointestinal, urothelial, and
merkel cell carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 8:384–388. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moll R, Divo M and Langbein L: The human
keratins: Biology and pathology. Histochem Cell Biol. 129:705–733.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rogulski K, Li Y, Rothermund K, Pu L,
Watkins S, Yi F and Prochownik EV: Onzin, a c-Myc-repressed target,
promotes survival and transformation by modulating the Akt-Mdm2-p53
pathway. Oncogene. 24:7524–7541. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jia Y, Ying X, Zhou J, Chen Y, Luo X, Xie
S, Wang QC, Hu W and Wang L: The novel KLF4/PLAC8 signaling pathway
regulates lung cancer growth. Cell Death Dis. 9:6032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC,
Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK, Meyer L, Gress DM, Byrd DR and
Winchester DP: The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual:
Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more
‘personalized’ approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:93–99. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee CL, Huang CJ, Yang SH, Chang CC, Huang
CC, Chien CC and Yang RN: Discovery of genes from feces correlated
with colorectal cancer progression. Oncol Lett. 12:3378–3384. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang CJ, Lee CL, Yang SH, Chien CC, Huang
CC, Yang RN and Chang CC: Upregulation of the growth
arrest-specific-2 in recurrent colorectal cancers, and its
susceptibility to chemotherapy in a model cell system. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1862:1345–1353. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Washington MK, Berlin J, Branton P,
Burgart LJ, Carter DK, Fitzgibbons PL, Halling K, Frankel W, Jessup
J, Kakar S, et al: Protocol for the examination of specimens from
patients with primary carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 133:1539–1551. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Duffy MJ, Lamerz R, Haglund C, Nicolini A,
Kalousova M, Holubec L and Sturgeon C: Tumor markers in colorectal
cancer, gastric cancer and gastrointestinal stromal cancers:
European group on tumor markers 2014 guidelines update. Int J
Cancer. 134:2513–2522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dolscheid-Pommerich RC, Manekeller S,
Walgenbach- Brunagel G, Kalff JC, Hartmann G, Wagner BS and
Holdenrieder S: Clinical performance of CEA, CA19-9, CA15-3, CA125
and AFP in gastrointestinal cancer using LOCI-based assays.
Anticancer Res. 37:353–359. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumar Y, Tapuria N, Kirmani N and Davidson
BR: Tumour M2-pyruvate kinase: A gastrointestinal cancer marker.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:265–276. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Myllykangas S, Bohling T and Knuutila S:
Specificity, selection and significance of gene amplifications in
cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 17:42–55. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Myllykangas S, Himberg J, Bohling T, Nagy
B, Hollmen J and Knuutila S: DNA copy number amplification
profiling of human neoplasms. Oncogene. 25:7324–7332. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lukyanchuk VV, Friess H, Kleeff J, Osinsky
SP, Ayuni E, Candinas D and Roggo A: Detection of circulating tumor
cells by cytokeratin 20 and prostate stem cell antigen RT-PCR in
blood of patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Anticancer Res.
23:2711–2716. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dalerba P, Sahoo D, Paik S, Guo X, Yothers
G, Song N, Wilcox-Fogel N, Forgo E, Rajendran PS, Miranda SP, et
al: CDX2 as a prognostic biomarker in stage II and stage III colon
cancer. N Engl J Med. 374:211–222. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pilati C, Taieb J, Balogoun R, Marisa L,
de Reynies A and Laurent-Puig P: CDX2 prognostic value in stage
II/III resected colon cancer is related to CMS classification. Ann
Oncol. 28:1032–1035. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Singh R, Kapur N, Mir H, Singh N, Lillard
JW Jr and Singh S: CXCR6-CXCL16 axis promotes prostate cancer by
mediating cytoskeleton rearrangement via Ezrin activation and
alphavbeta3 integrin clustering. Oncotarget. 7:7343–7353. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu K, Zhang X, Li F, Xiao D, Hou Y, Zhu S,
Liu D, Ye X, Ye M, Yang J, et al: Frequent alterations in
cytoskeleton remodelling genes in primary and metastatic lung
adenocarcinomas. Nat Commun. 6:101312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen NP, Uddin B, Voit R and Schiebel E:
Human phosphatase CDC14A is recruited to the cell leading edge to
regulate cell migration and adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:990–995. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou H, Zhang Y, Chen Q and Lin Y: AKT and
JNK signaling pathways increase the metastatic potential of
colorectal cancer cells by altering transgelin expression. Dig Dis
Sci. 61:1091–1097. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mills KM, Brocardo MG and Henderson BR:
APC binds the Miro/Milton motor complex to stimulate transport of
mitochondria to the plasma membrane. Mol Biol Cell. 27:466–482.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ivanovska J, Zlobec I, Forster S,
Karamitopoulou E, Dawson H, Koelzer VH, Agaimy A, Garreis F, Soder
S, Laqua W, et al: DAPK loss in colon cancer tumor buds:
Implications for migration capacity of disseminating tumor cells.
Oncotarget. 6:36774–36788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zeng Y, Xie H, Qiao Y, Wang J, Zhu X, He
G, Li Y, Ren X, Wang F, Liang L and Ding Y: Formin-Like2 regulates
Rho/ROCK pathway to promote actin assembly and cell invasion of
colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 106:1385–1393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Asfaha S, Hayakawa Y, Muley A, Stokes S,
Graham TA, Ericksen RE, Westphalen CB, von Burstin J, Mastracci TL,
Worthley DL, et al: Krt19(+)/Lgr5(−) cells are radioresistant
cancer-initiating stem cells in the colon and intestine. Cell Stem
Cell. 16:627–638. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li WX, Xiao HW, Hong XQ and Niu WX:
Predictive value of CK20 in evaluating the efficacy of treatment
and prognosis after surgery for colorectal cancer. Genet Mol Res.
14:5823–5829. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Saad RS, Ismiil N, Dube V, Nofech-Mozes S
and Khalifa MA: CDX-2 expression is a common event in primary
intestinal-type endocervical adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol.
132:531–538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bluemke K, Bilkenroth U, Meye A, Fuessel
S, Lautenschlaeger C, Goebel S, Melchior A, Heynemann H, Fornara P
and Taubert H: Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral
blood of patients with renal cell carcinoma correlates with
prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:2190–2194. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mizuuchi E, Semba S, Kodama Y and Yokozaki
H: Down-modulation of keratin 8 phosphorylation levels by PRL-3
contributes to colorectal carcinoma progression. Int J Cancer.
124:1802–1810. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ding SJ, Li Y, Tan YX, Jiang MR, Tian B,
Liu YK, Shao XX, Ye SL, Wu JR, Zeng R, et al: From proteomic
analysis to clinical significance: Overexpression of cytokeratin 19
correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 3:73–81. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hammoudi A, Song F, Reed KR, Jenkins RE,
Meniel VS, Watson AJ, Pritchard DM, Clarke AR and Jenkins JR:
Proteomic profiling of a mouse model of acute intestinal apc
deletion leads to identification of potential novel biomarkers of
human colorectal cancer (CRC). Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
440:364–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang SH, Huang CJ, Lee CL, Liu CC, Chien
CC and Chen SH: Fecal RNA detection of cytokeratin 19 and ribosomal
protein L19 for colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology.
57:710–715. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang RN, Yang SH, Chang CC, Chien CC, Pan
S and Huang CJ: Upregulation of fecal cytokeratin 19 is associated
with prognosis in older colorectal cancer patients. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 14:703–708. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chang CC, Yang SH, Chien CC, Chen SH, Pan
S, Lee CL, Lin CM, Sun HL, Huang CC, Wu YY, et al: Clinical meaning
of age-related expression of fecal cytokeratin 19 in colorectal
malignancy. BMC Cancer. 9:3762009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kende AI, Carr NJ and Sobin LH: Expression
of cytokeratins 7 and 20 in carcinomas of the gastrointestinal
tract. Histopathology. 42:137–140. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Samija I, Lukac J, Mubrin MK, Kirac I,
Kovacevic D and Kusic Z: Detection of cytokeratin-20-positive cells
in preoperative and postoperative blood samples from colorectal
cancer patients by real-time RT-PCR. Int J Biol Markers.
28:174–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kojima S, Sakamoto T, Nagai Y, Honda M and
Ogawa F: Metachronous rectal metastasis from primary transverse
colon cancer: A case report. Surg Case Rep. 4:902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Reisher SR, Hughes TE, Ordovas JM,
Schaefer EJ and Feinstein SI: Increased expression of
apolipoprotein genes accompanies differentiation in the intestinal
cell line Caco-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:5757–5761. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ferruzza S, Rossi C, Scarino ML and Sambuy
Y: A protocol for differentiation of human intestinal Caco-2 cells
in asymmetric serum-containing medium. Toxicol In Vitro.
26:1252–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Meunier V, Bourrie M, Berger Y and Fabre
G: The human intestinal epithelial cell line Caco-2;
pharmacological and pharmacokinetic applications. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 11:187–194. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Buhrke T, Lengler I and Lampen A: Analysis
of proteomic changes induced upon cellular differentiation of the
human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Dev Growth Differ. 53:411–426.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Allegra C and Sargent D: Molecular
diagnostics: Assays, tissues, progress, and pitfalls. J Clin Oncol.
21:395–396. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bustin SA and Dorudi S: Gene expression
profiling for molecular staging and prognosis prediction in
colorectal cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 4:599–607. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Bardelli A and Velculescu VE: Mutational
analysis of gene families in human cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:5–12. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Rozen P: Cancer of the gastrointestinal
tract: Early detection or early prevention? Eur J Cancer Prev.
13:71–75. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Kern
SE, Preisinger AC, Leppert M, Nakamura Y, White R, Smits AM and Bos
JL: Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl
J Med. 319:525–532. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA and Ward E:
Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:366–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR,
Kemberling H, Eyring AD, Skora AD, Luber BS, Azad NS, Laheru D, et
al: PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl
J Med. 372:2509–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat
D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype
C, et al: Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in
irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
351:337–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W,
Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S,
Holmgren E, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
350:2335–2342. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Imai Y, Yamagishi H, Fukuda K, Okamura T,
Ono Y, Ban S, Inoue T and Ueda Y: Expression of cytokeratin 20
indicates invasive histological phenotype in poorly differentiated
colorectal adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 34:159–167.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Barr T, Sureshchandra S, Ruegger P, Zhang
J, Ma W, Borneman J, Grant K and Messaoudi I: Concurrent gut
transcriptome and microbiota profiling following chronic ethanol
consumption in nonhuman primates. Gut Microbes. 9:338–356.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Turroni S, Vitali B, Candela M, Gionchetti
P, Rizzello F, Campieri M and Brigidi P: Antibiotics and probiotics
in chronic pouchitis: A comparative proteomic approach. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:30–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Singh A, Trivedi P and Jain NK: Advances
in siRNA delivery in cancer therapy. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 46:274–283. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Das M, Musetti S and Huang L: RNA
interference-based cancer drugs: The roadblocks, and the ‘Delivery’
of the promise. Nucleic Acid Ther. 29:61–66. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zheng M, Tao W, Zou Y, Farokhzad OC and
Shi B: Nanotechnology-based strategies for siRNA brain delivery for
disease therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 36:562–575. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bukholm IR, Bondi J, Wiik P, Nesland JM,
Andersen SN, Bakka A and Bukholm G: Presence of isolated tumour
cells in mesenteric lymph nodes predicts poor prognosis in patients
with stage II colon cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 29:862–866. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang Y, Hu Q, Li G, Li L, Liang S, Zhang
Y, Liu J, Fan Z, Li L, Zhou B, et al: ONZIN upregulation by mutant
p53 contributes to osteosarcoma metastasis through the CXCL5-MAPK
signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1099–1111. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|