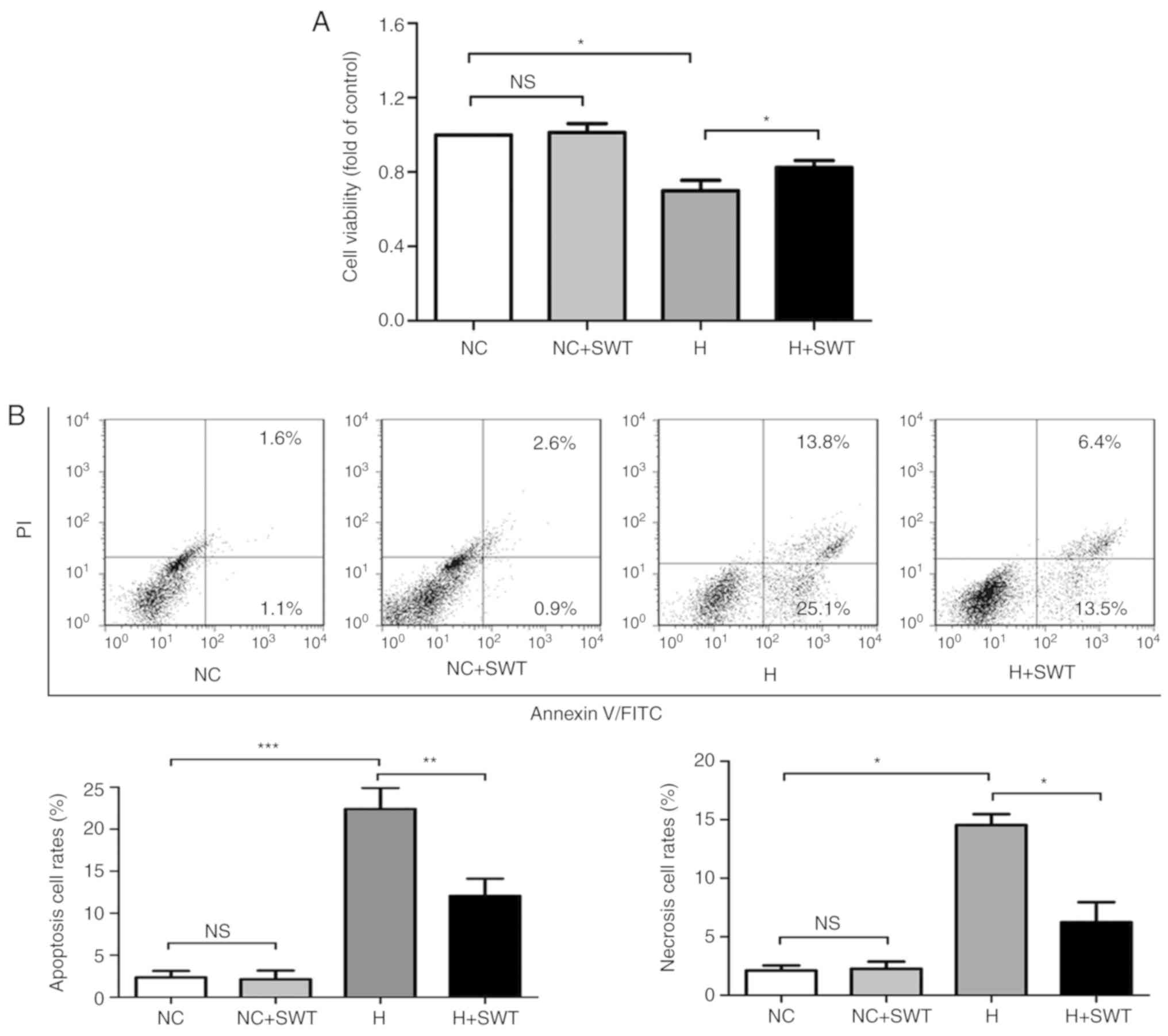
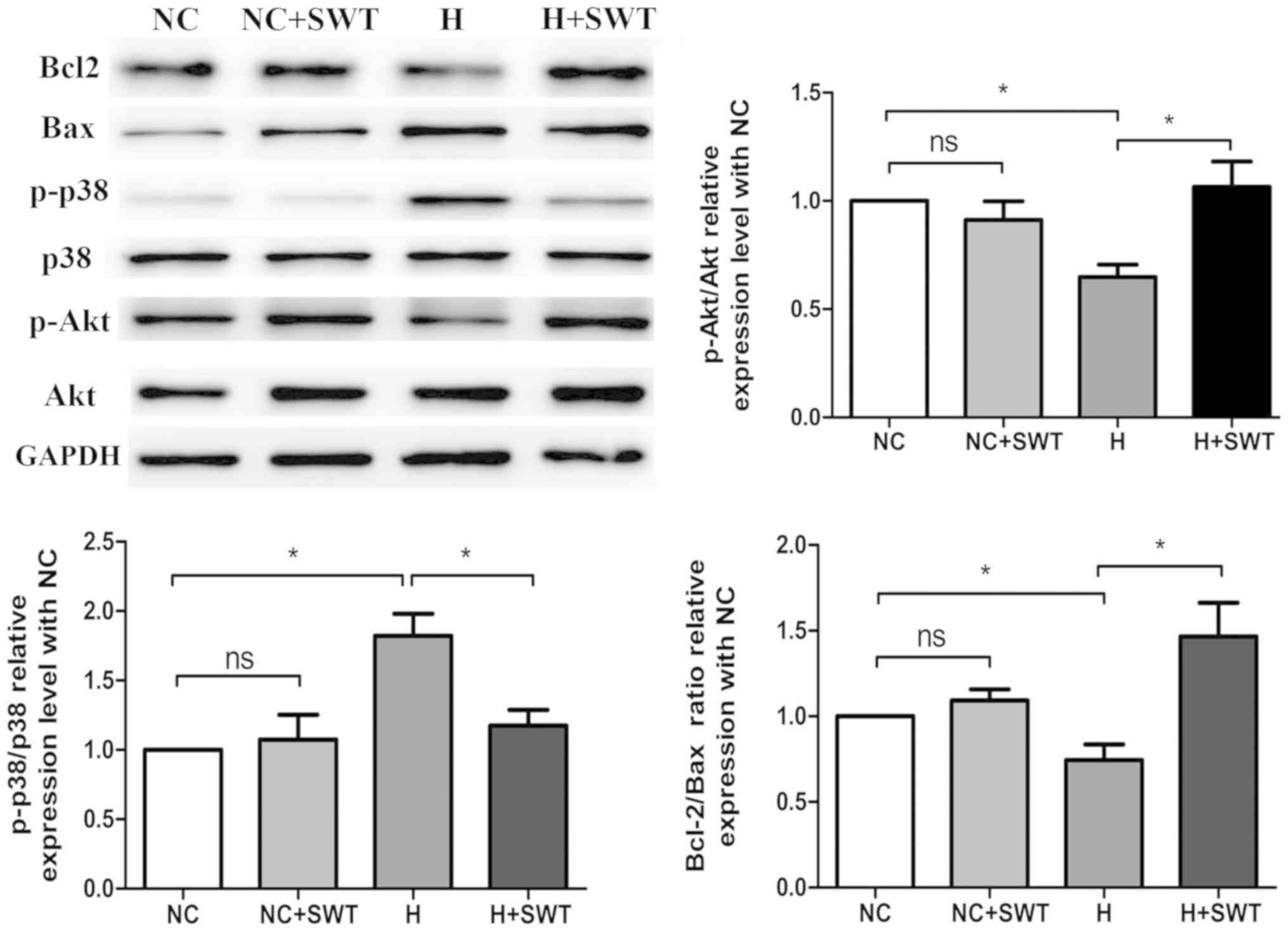
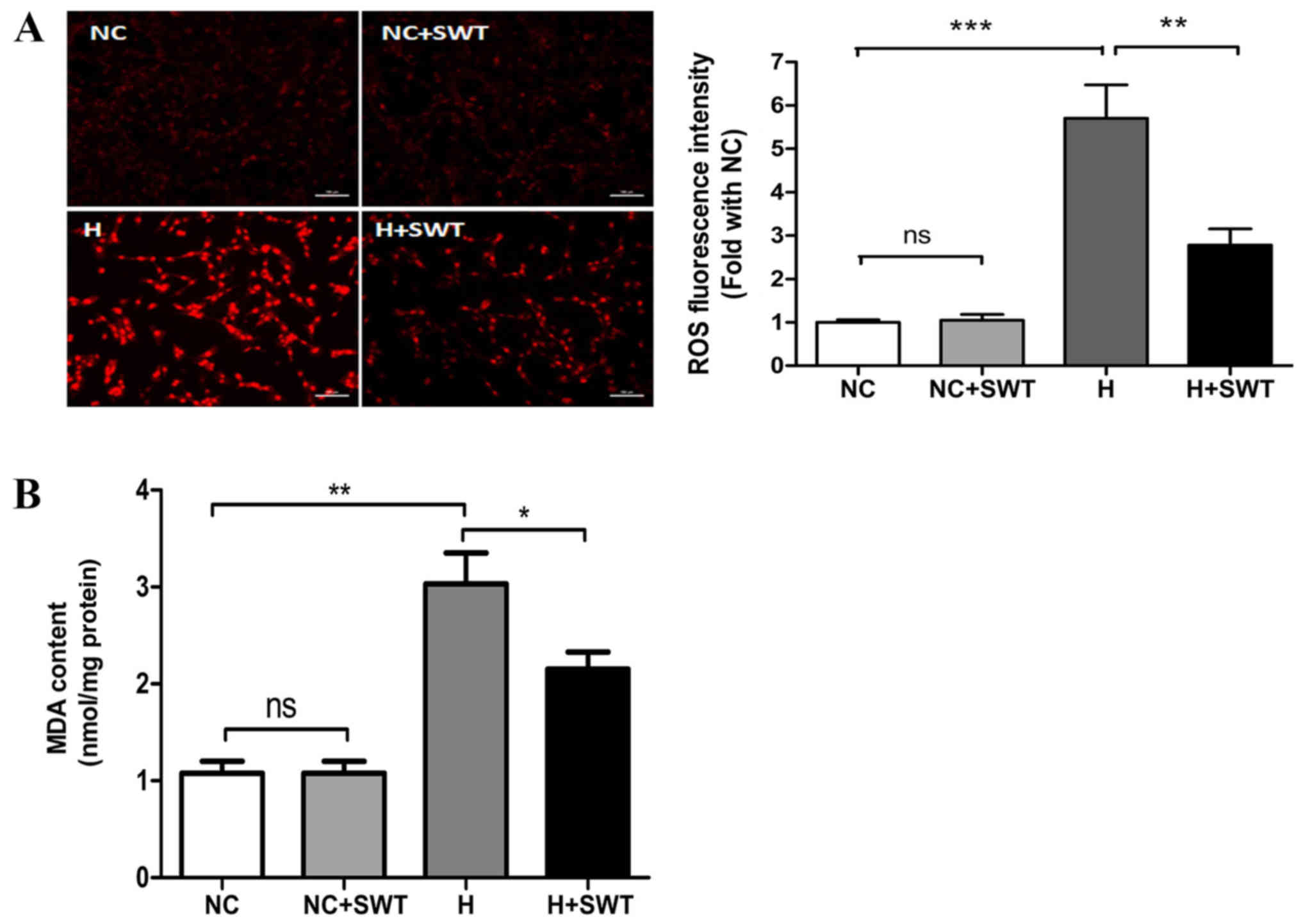
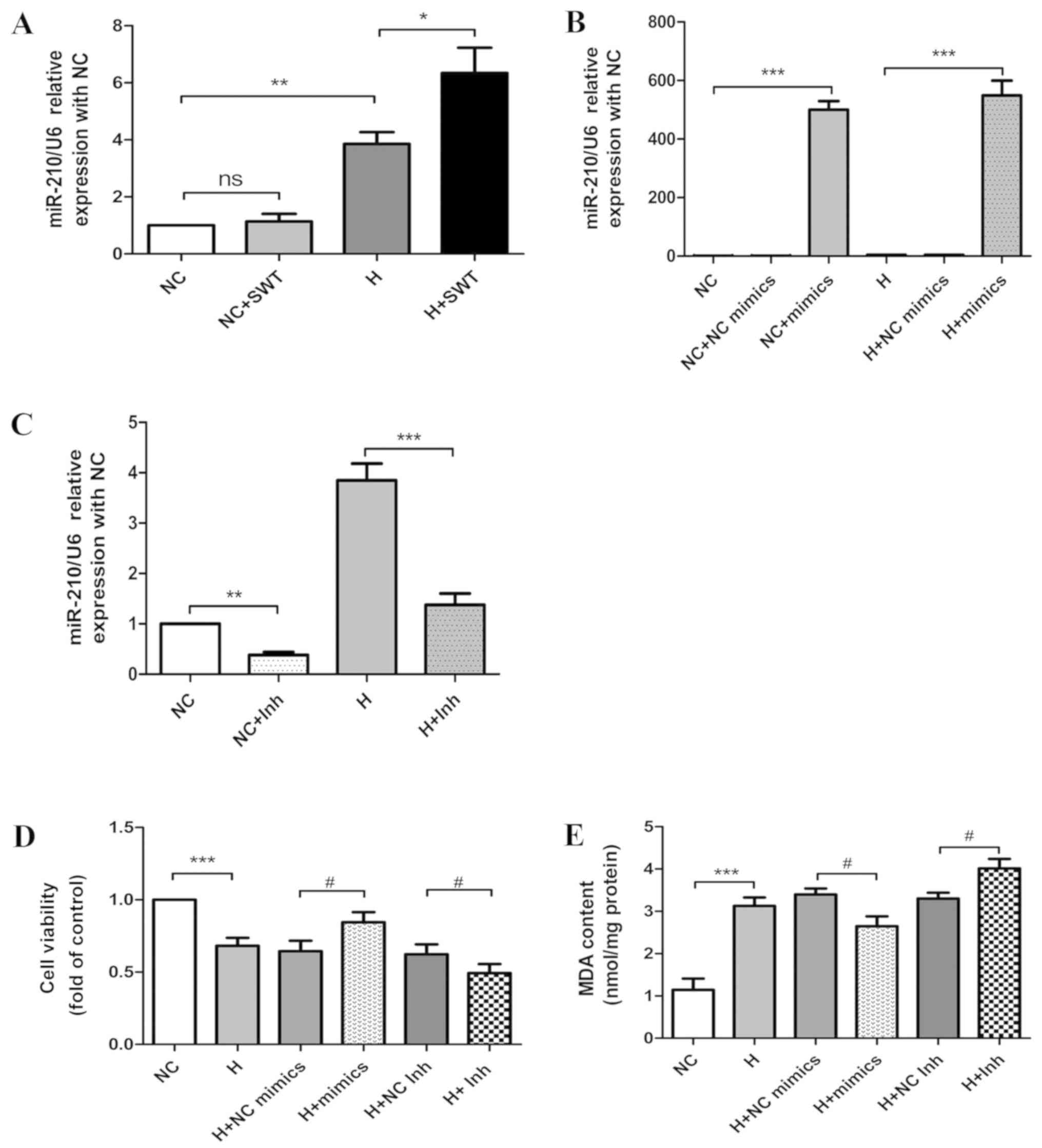
|
1
|
Ibanez B, Heusch G, Ovize M and Van de
Werf F: Evolving therapies for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 65:1454–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shepard D, VanderZanden A, Moran A,
Naghavi M, Murray C and Roth G: Ischemic heart disease worldwide,
1990 to 2013: Estimates from the global burden of disease study
2013. Circulation. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 8:455–456. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:5092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang Y, Zheng J, Sun Y, Wu Z, Liu Z and
Huang G: MicroRNA-1 regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting
Bcl-2. Int Heart J. 50:377–387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sayed D, He M, Hong C, Gao S, Rane S, Yang
Z and Abdellatif M: MicroRNA-21 is a downstream effector of AKT
that mediates its antiapoptotic effects via suppression of Fas
ligand. J Biol Chem. 285:20281–20290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ren XP, Wu J, Wang X, Sartor MA, Jones K,
Qian J, Nicolaou P, Pritchard TJ and Fan GC: MicroRNA-320 is
involved in the regulation of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury
by targeting heat-shock protein 20. Circulation. 119:2357–2366.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang JX, Zhang XJ, Li Q, Wang K, Wang Y,
Jiao JQ, Feng C, Teng S, Zhou LY, Gong Y, et al: MicroRNA-103/107
regulate programmed necrosis and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury through targeting FADD. Circ Res. 117:352–363. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE,
Garzon R, Alder H, Agosto-Perez FJ, Davuluri R, Liu CG, Croce CM,
Negrini M, et al: A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol.
27:1859–1867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim HW, Haider HK, Jiang S and Ashraf M:
Ischemic preconditioning augments survival of stem cells via
miR-210 expression by targeting caspase-8-associated protein 2. J
Biol Chem. 284:33161–33168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mutharasan RK, Nagpal V, Ichikawa Y and
Ardehali H: microRNA-210 is upregulated in hypoxic cardiomyocytes
through Akt- and p53-dependent pathways and exerts cytoprotective
effects. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H1519–H1530. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim HW, Jiang S, Ashraf M and Haider KH:
Stem cell-based delivery of Hypoxamir-210 to the infarcted heart:
Implications on stem cell survival and preservation of infarcted
heart function. J Mol Med (Berl). 90:997–1010. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fasanaro P, D'Alessandra Y, Di Stefano V,
Melchionna R, Romani S, Pompilio G, Capogrossi MC and Martelli F:
MicroRNA-210 modulates endothelial cell response to hypoxia and
inhibits the receptor tyrosine kinase ligand Ephrin-A3. J Biol
Chem. 283:15878–15883. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nishida T, Shimokawa H, Oi K, Tatewaki H,
Uwatoku T, Abe K, Matsumoto Y, Kajihara N, Eto M, Matsuda T, et al:
Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy markedly ameliorates
ischemia-induced myocardial dysfunction in pigs in vivo.
Circulation. 110:3055–3061. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fukumoto Y, Ito A, Uwatoku T, Matoba T,
Kishi T, Tanaka H, Takeshita A, Sunagawa K and Shimokawa H:
Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy ameliorates myocardial
ischemia in patients with severe coronary artery disease. Coron
Artery Dis. 17:63–70. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cassar A, Prasad M, Rodriguez-Porcel M,
Reeder GS, Karia D, DeMaria AN and Lerman A: Safety and efficacy of
extracorporeal shock wave myocardial revascularization therapy for
refractory angina pectoris. Mayo Clin Proc. 89:346–354. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khattab AA, Brodersen B,
Schuermann-Kuchenbrandt D, Beurich H, Tölg R, Geist V, Schäfer T
and Richardt G: Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave therapy: First
experience in the everyday practice for treatment of chronic
refractory angina pectoris. Int J Cardiol. 121:84–85. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu W, Shen T, Liu B, Wang S, Li J, Dai D,
Cai J and He Q: Cardiac shock wave therapy attenuates H9c2 myoblast
apoptosis by activating the AKT signal pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 33:1293–1303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Shen T, Liu B, Dai D, Cai J, Zhao
C, Du L, Jia N and He Q: Cardiac shock wave therapy attenuates
cardiomyocyte apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction in rats.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:1734–1746. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR and Gottlieb
RA: Enhancing macroautophagy protects against ischemia/reperfusion
injury in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 281:29776–29787. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Du L, Shen T, Liu B, Zhang Y, Zhao C, Jia
N, Wang Q and He Q: Shock wave therapy promotes cardiomyocyte
autophagy and survival during hypoxia. Cell Physiol Biochem.
42:673–684. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. 25:402–408. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
White SM, Constantin PE and Claycomb WC:
Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: Use of cultured HL-1
cardiomyocytes for studies of cardiac muscle cell structure and
function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 286:H823–H829. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Levraut J, Iwase H, Shao ZH, Hoek TLV and
Schumacker PT: Cell death during ischemia: Relationship to
mitochondrial depolarization and ROS generation. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 284:H549–H558. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pryor WA and Stanley JP: Suggested
mechanism for the production of malonaldehyde during the
autoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nonenzymic production
of prostaglandin endoperoxides during autoxidation. J Org Chem.
40:3615–3617. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan SY and Loscalzo J: MicroRNA-210: A
unique and pleiotropic hypoxamir. Cell Cycle. 9:1072–1083. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang Peter M, Haunstetter A, Aoki H,
Usheva A and Izumo S: Morphological and molecular characterization
of adult cardiomyocyte apoptosis during hypoxia and reoxygenation.
Circ Res. 87:118–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Buja LM: Myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Pathol. 14:170–175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Misao J, Hayakawa Y, Ohno M, Kato S,
Fujiwara T and Fujiwara H: Expression of bcl-2 protein, an
inhibitor of apoptosis, and Bax, an accelerator of apoptosis, in
ventricular myocytes of human hearts with myocardial infarction.
Circulation. 94:1506–1512. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Olivetti G, Quaini F, Sala R, Lagrasta C,
Corradi D, Bonacina E, Gambert SR, Cigola E and Anversa P: Acute
myocardial infarction in humans is associated with activation of
programmed myocyte cell death in the surviving portion of the
heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 28:2005–2016. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang BC, Zander DS and Mehta JL:
Hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cultured adult rat
myocytes and the protective effect of platelets and transforming
growth factor-beta(1). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 291:733–738.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
See F, Thomas W, Way K, Tzanidis A, Kompa
A, Lewis D, Itescu S and Krum H: p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase inhibition improves cardiac function and attenuates left
ventricular remodeling following myocardial infarction in the rat.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 44:1679–1689. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lima J, Batty JA, Sinclair H and Kunadian
V: MicroRNAs in ischemic heart disease: From pathophysiology to
potential clinical applications. Cardiol Rev. 25:117–125. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Boon RA and Dimmeler S: MicroRNAs in
myocardial infarction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 12:135–142. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu S, Huang M, Li Z, Jia F, Ghosh Z,
Lijkwan MA, Fasanaro P, Sun N, Wang X, Martelli F, et al:
MicroRNA-210 as a novel therapy for treatment of ischemic heart
disease. Circulation. 122 (11 Suppl):S124–S131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arif M, Pandey R, Alam P, Jiang S,
Sadayappan S, Paul A and Ahmed RPH: MicroRNA-210-mediated
proliferation, survival, and angiogenesis promote cardiac repair
post myocardial infarction in rodents. J Mol Med (Berl).
95:1369–1385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li T, Song X, Zhang J, Zhao L, Shi Y, Li
Z, Liu J, Liu N, Yan Y, Xiao Y, et al: Protection of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells against oxidative stress by
MicroRNA-210. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:35656132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Diao H, Liu B, Shi Y, Song C, Guo Z, Liu
N, Song X, Lu Y, Lin X and Li Z: MicroRNA-210 alleviates oxidative
stress-associated cardiomyocyte apoptosis by regulating BNIP3.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 81:1712–1720. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen Z, Li Y, Zhang H, Huang P and Luthra
R: Hypoxia-regulated microRNA-210 modulates mitochondrial function
and decreases ISCU and COX10 expression. Oncogene. 29:4362–4368.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim HW, Mallick F, Durrani S, Ashraf M,
Jiang S and Haider KH: Concomitant activation of miR-107/PDCD10 and
hypoxamir-210/Casp8ap2 and their role in cytoprotection during
ischemic preconditioning of stem cells. Antioxid Redox Signal.
17:1053–1065. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Imai Y, Kimura T, Murakami A, Yajima N,
Sakamaki K and Yonehara S: The CED-4-homologous protein FLASH is
involved in Fas-mediated activation of caspase-8 during apoptosis.
Nature. 398:777–785. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xie Q, Lin T, Zhang Y, Zheng J and Bonanno
JA: Molecular cloning and characterization of a human AIF-like gene
with ability to induce apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 280:19673–19681.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|