|
1
|
Deane KD and Holers VM: The natural
history of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther. 41:1256–1269. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Burmester GR and Pope JE: Novel treatment
strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 389:2338–2348. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ridgley LA, Anderson AE and Pratt AG: What
are the dominant cytokines in early rheumatoid arthritis? Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 30:207–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Noack M and Miossec P: Selected cytokine
pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 39:365–383.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kang S, Tanaka T, Narazaki M and Kishimoto
T: Targeting interleukin-6 signaling in clinic. Immunity.
50:1007–1023. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siouti E and Andreakos E: The many facets
of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Pharmacol.
165:152–169. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yasuda K, Takeuchi Y and Hirota K: The
pathogenicity of Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Semin
Immunopathol. 41:283–297. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arleevskaya MI, Larionova RV, Brooks WH,
Bettacchioli E and Renaudineau Y: Toll-like receptors, infections,
and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. May
29–2019.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
9
|
Alam J, Jantan I and Bukhari SNA:
Rheumatoid arthritis: Recent advances on its etiology, role of
cytokines and pharmacotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 92:615–633.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Silvagni E, Di Battista M, Bonifacio AF,
Zucchi D, Governato G and Scirè CA: One year in review 2019:
Novelties in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 37:519–534. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Conigliaro P, Triggianese P, De Martino E,
Fonti GL, Chimenti MS, Sunzini F, Viola A, Canofari C and Perricone
R: Challenges in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun
Rev. 18:706–713. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cecchi I, Arias de la Rosa I, Menegatti E,
Roccatello D, Collantes-Estevez E, Lopez-Pedrera C and Barbarroja
N: Neutrophils: Novel key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Current
and future therapeutic targets. Autoimmun Rev. 17:1138–1149. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheung TT and McInnes IB: Future
therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis? Semin Immunopathol.
39:487–500. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
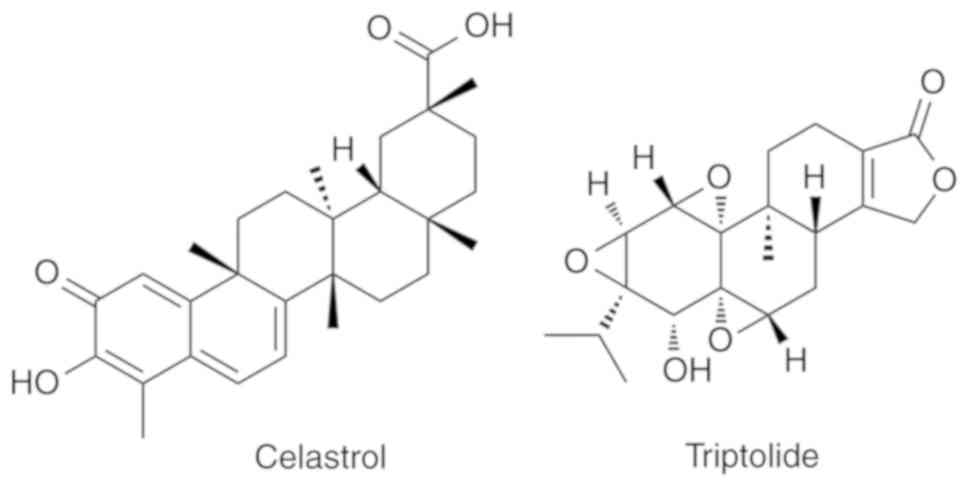
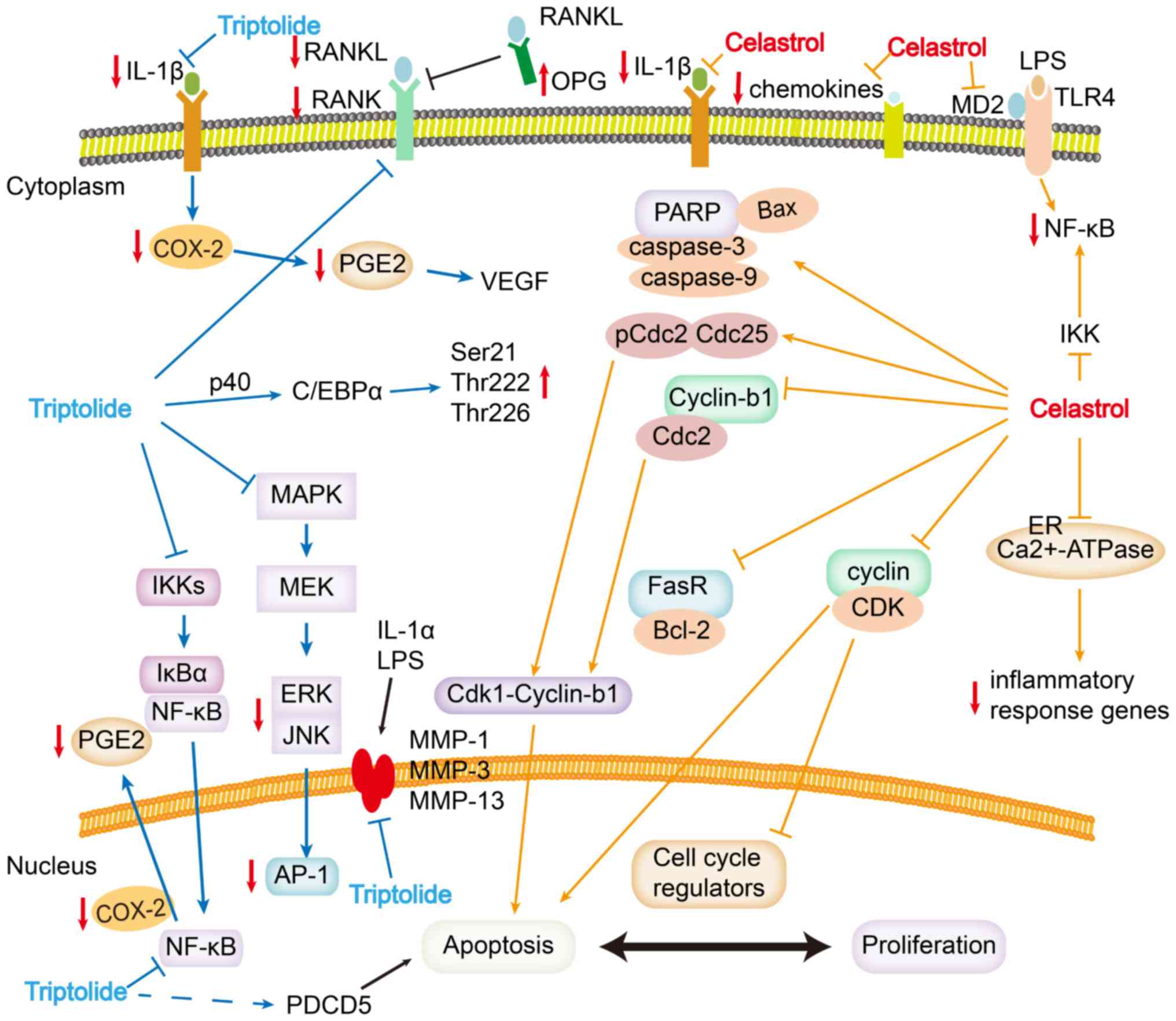
Hou W, Liu B and Xu H: Triptolide:
Medicinal chemistry, chemical biology and clinical progress. Eur J
Med Chem. 176:378–392. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dong Y, Chen H, Gao J, Liu Y, Li J and
Wang J: Bioactive ingredients in Chinese herbal medicines that
target non-coding RNAs: Promising new choices for disease
treatment. Front Pharmacol. 10:5152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang Y, Ma S, Wang Y, Yan R, Wang S, Liu
N, Chen B, Chen J and Liu L: The role of traditional Chinese herbal
medicines and bioactive ingredients on ion channels: A brief review
and prospect. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 18:257–265. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong Y, Wang P, Feng X, Li B, Wang Z and
Li H: The role of Chinese herbal medicines and bioactive
ingredients targeting myocardial KCa and KATP Channels in
cardiovascular diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 23:1070–1076. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lv H, Jiang L, Zhu M, Li Y, Luo M, Jiang
P, Tong S, Zhang H and Yan J: The genus Tripterygium: A
phytochemistry and pharmacological review. Fitoterapia.
137:1041902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Venkatesha SH, Dudics S, Astry B and
Moudgil KD: Control of autoimmune inflammation by celastrol, a
natural triterpenoid. Pathog Dis. 74(pii): ftw0592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tu L, Su P, Zhang Z, Gao L, Wang J, Hu T,
Zhou J, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, et al: Genome of Tripterygium
wilfordii and identification of cytochrome P450 involved in
triptolide biosynthesis. Nat Commun. 11:9712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin N, Sato T and Ito A: Triptolide, a
novel diterpenoid triepoxide from Tripterygium wilfordii
Hook. f., suppresses the production and gene expression of
pro-matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 3 and augments those of tissue
inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 and 2 in human synovial
fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 44:2193–2200. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Astry B, Venkatesha SH, Laurence A,
Christensen-Quick A, Garzino-Demo A, Frieman MB, O'Shea JJ and
Moudgil KD: Celastrol, a Chinese herbal compound, controls
autoimmune inflammation by altering the balance of pathogenic and
regulatory T cells in the target organ. Clin Immunol. 157:228–238.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Di YM, Zhou ZW, Guang Li C and Zhou SF:
Current and future therapeutic targets of rheumatoid arthritis.
Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 10:92–120. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu J, Zhou X, Chen XY and Zhong DF:
Excretion of [3H]triptolide and its metabolites in rats after oral
administration. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:549–554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Q: Triptolide and its expanding
multiple pharmacological functions. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:377–383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li XJ, Jiang ZZ and Zhang LY: Triptolide:
Progress on research in pharmacodynamics and toxicology. J
Ethnopharmacol. 155:67–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng Y, Chen G, Wang L, Kong J, Pan J, Xi
Y, Shen F and Huang Z: Triptolide-induced mitochondrial damage
dysregulates fatty acid metabolism in mouse sertoli cells. Toxicol
Lett. 292:136–150. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xi C, Peng S, Wu Z, Zhou Q and Zhou J:
Toxicity of triptolide and the molecular mechanisms involved.
Biomed Pharmacother. 90:531–541. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song J, Shi F, Zhang Z, Zhu F, Xue J, Tan
X, Zhang L and Jia X: Formulation and evaluation of
celastrol-loaded liposomes. Molecules. 16:7880–7892. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qi J, Lu Y and Wu W: Absorption,
disposition and pharmacokinetics of solid lipid nanoparticles. Curr
Drug Metab. 13:418–428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peng X, Wang J, Song H, Cui D, Li L, Li J,
Lin L, Zhou J and Liu Y: Optimized preparation of celastrol-loaded
polymeric nanomicelles using rotatable central composite design and
response surface methodology. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 8:491–499.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cascao R, Fonseca JE and Moita LF:
Celastrol: A spectrum of treatment opportunities in chronic
diseases. Front Med (Lausanne). 4:692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Venkatesha SH and Moudgil KD: Celastrol
and its role in controlling chronic diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol.
928:267–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shen YF, Zhang X, Wang Y, Cao FF, Uzan G,
Peng B and Zhang DH: Celastrol targets IRAKs to block Toll-like
receptor 4-mediated nuclear factor-κB activation. J Integr Med.
14:203–208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee JH, Koo TH, Yoon H, Jung HS, Jin HZ,
Lee K, Hong YS and Lee JJ: Inhibition of NF-κB activation through
targeting I kappa B kinase by celastrol, a quinone methide
triterpenoid. Biochem Pharmacol. 72:1311–1321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mercurio F, Zhu H, Murray BW, Shevchenko
A, Bennett BL, Li J, Young DB, Barbosa M, Mann M, Manning A and Rao
A: IKK-1 and IKK-2: Cytokine-activated IkappaB kinases essential
for NF-kappaB activation. Science. 278:860–866. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Salminen A, Lehtonen M, Paimela T and
Kaarniranta K: Celastrol: Molecular targets of thunder God vine.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:439–442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rigoglou S and Papavassiliou AG: The NF-κB
signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:2580–2584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Samarpita S, Kim JY, Rasool MK and Kim KS:
Investigation of toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 inhibitor TAK-242 as a
new potential anti-rheumatoid arthritis drug. Arthritis Res Ther.
22:162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Berridge MJ: Calcium signalling
remodelling and disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:297–309. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Clapham DE: Calcium signaling. Cell.
131:1047–1058. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wong VKW, Qiu C, Xu SW, Law BYK, Zeng W,
Wang H, Michelangeli F, Dias IRSR, Qu YQ, Chan TW, et al:
Ca2+ signalling plays a role in celastrol-mediated
suppression of synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis
patients and experimental arthritis in rats. Br J Pharmacol.
176:2922–2944. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoo SA, Park BH, Park GS, Koh HS, Lee MS,
Ryu SH, Miyazawa K, Park SH, Cho CS and Kim WU: Calcineurin is
expressed and plays a critical role in inflammatory arthritis. J
Immunol. 177:2681–2690. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Villalobo A, Ishida H, Vogel HJ and
Berchtold MW: Calmodulin as a protein linker and a regulator of
adaptor/scaffold proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.
1865:507–521. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xu Z, Wu G, Wei X, Chen X, Wang Y and Chen
L: Celastrol induced DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis
in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synovial cells. Am J Chin Med.
41:615–628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fan XX, Li N, Wu JL, Zhou YL, He JX, Liu L
and Leung EL: Celastrol induces apoptosis in gefitinib-resistant
non-small cell lung cancer cells via caspases-dependent pathways
and Hsp90 client protein degradation. Molecules. 19:3508–3522.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu LM, Zheng YJ, Wang Y, Yang Y, Cao FF,
Peng B, Xu XF, An HZ, Zheng AX, Zhang DH, et al: Celastrol inhibits
lung infiltration in differential syndrome animal models by
reducing TNF-α and ICAM-1 levels while preserving differentiation
in ATRA-induced acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. PLoS One.
9:e1051312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fang Z, He D, Yu B, Liu F, Zuo J, Li Y,
Lin Q, Zhou X and Wang Q: High-throughput study of the effects of
celastrol on activated fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients
with rheumatoid arthritis. Genes (Basel). 8(pii): E2212017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mukherjee S, Huda S and Sinha Babu SP:
Toll-like receptor polymorphism in host immune response to
infectious diseases: A review. Scand J Immunol. 90:e127712019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang X, Wang Y, Ge HY, Gu YJ, Cao FF,
Yang CX, Uzan G, Peng B and Zhang DH: Celastrol reverses palmitic
acid (PA)-caused TLR4-MD2 activation-dependent insulin resistance
via disrupting MD2-related cellular binding to PA. J Cell Physiol.
233:6814–6824. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Khan MA, Khurana N, Ahmed RS, Umar S, Md G
Sarwar AH, Alam Q, Kamal MA and Ashraf GM: Chemokines: A potential
therapeutic target to suppress autoimmune arthritis. Curr Pharm
Des. 25:2937–2946. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Eustace AD, McNaughton EF, King S, Kehoe
O, Kungl A, Mattey D, Nobbs AH, Williams N and Middleton J: Soluble
syndecan-3 binds chemokines, reduces leukocyte migration in vitro
and ameliorates disease severity in models of rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 21:1722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bahlas S, Damiati L, Dandachi N, Sait H,
Alsefri M and Pushparaj PN: Rapid immunoprofiling of cytokines,
chemokines and growth factors in patients with active rheumatoid
arthritis using luminex multiple analyte profiling technology for
precision medicine. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 37:112–119. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lee JY, Lee BH, Kim ND and Lee JY:
Celastrol blocks binding of lipopolysaccharides to a Toll-like
receptor4/myeloid differentiation factor2 complex in a
thiol-dependent manner. J Ethnopharmacol. 172:254–260. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li G, Liu D, Zhang Y, Qian Y, Zhang H, Guo
S, Sunagawa M, Hisamitsu T and Liu Y: Celastrol inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rheumatoid fibroblast-like
synoviocyte invasion through suppression of TLR4/NF-κB-mediated
matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. PLoS One. 8:e689052013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Venkatesha SH, Astry B, Nanjundaiah SM, Yu
H and Moudgil KD: Suppression of autoimmune arthritis by
celastrus-derived celastrol through modulation of pro-inflammatory
chemokines. Bioorg Med Chem. 20:5229–5234. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li GQ, Liu D, Zhang Y, Qian YY, Zhu YD,
Guo SY, Sunagawa M, Hisamitsu T and Liu YQ: Anti-invasive effects
of celastrol in hypoxia-induced fibroblast-like synoviocyte through
suppressing of HIF-1α/CXCR4 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
17:1028–1036. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Park B, Sung B, Yadav VR, Chaturvedi MM
and Aggarwal BB: Triptolide, histone acetyltransferase inhibitor,
suppresses growth and chemosensitizes leukemic cells through
inhibition of gene expression regulated by
TNF-TNFR1-TRADD-TRAF2-NIK-TAK1-IKK pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
82:1134–1144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang Y, Ye Y, Qiu Q, Xiao Y, Huang M, Shi
M, Liang L, Yang X and Xu H: Triptolide inhibits the migration and
invasion of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes by blocking the
activation of the JNK MAPK pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 41:8–16.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Fan D, He X, Bian Y, Guo Q, Zheng K, Zhao
Y, Lu C, Liu B, Xu X, Zhang G and Lu A: Triptolide modulates TREM-1
signal pathway to inhibit the inflammatory response in rheumatoid
arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 17:4982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ho LJ, Chang WL, Chen A, Chao P and Lai
JH: Differential immunomodulatory effects by Tripterygium
wilfordii Hook f-derived refined extract PG27 and its purified
component PG490 (triptolide) in human peripheral blood T cells:
Potential therapeutics for arthritis and possible mechanisms
explaining in part Chinese herbal theory ‘Junn-Chenn-Zuou-SS’. J
Transl Med. 11:2942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ruland J: Return to homeostasis:
Downregulation of NF-κB responses. Nat Immunol. 12:709–714. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kanarek N and Ben-Neriah Y: Regulation of
NF-κB by ubiquitination and degradation of the IκBs. Immunol Rev.
246:77–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Criswell LA: Gene discovery in rheumatoid
arthritis highlights the CD40/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in
disease pathogenesis. Immunol Rev. 233:55–61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Schonthaler HB, Guinea-Viniegra J and
Wagner EF: Targeting inflammation by modulating the Jun/AP-1
pathway. Ann Rheum Dis. 70 (Suppl 1):i109–i112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Xiao C, Zhou J, He Y, Jia H, Zhao L, Zhao
N and Lu A: Effects of triptolide from radix Tripterygium
wilfordii (Leigongteng) on cartilage cytokines and
transcription factor NF-kappaB: A study on induced arthritis in
rats. Chin Med. 4:132009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bezerra MC, Carvalho JF, Prokopowitsch AS
and Pereira RM: RANK, RANKL and osteoprotegerin in arthritic bone
loss. Braz J Med Biol Res. 38:161–170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ho TY, Santora K, Chen JC, Frankshun AL
and Bagnell CA: Effects of relaxin and estrogens on bone remodeling
markers, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) and
osteoprotegerin (OPG), in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Bone.
48:1346–1353. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Geusens P: The role of RANK
ligand/osteoprotegerin in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv
Musculoskelet Dis. 4:225–233. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu Q, Chen T, Chen G, Shu X, Sun A, Ma P,
Lu L and Cao X: Triptolide impairs dendritic cell migration by
inhibiting CCR7 and COX-2 expression through PI3-K/Akt and
NF-kappaB pathways. Mol Immunol. 44:2686–2696. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu C, Zhang Y, Kong X, Zhu L, Pang J, Xu
Y, Chen W, Zhan H, Lu A and Lin N: Triptolide prevents bone
destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model of rheumatoid
arthritis by targeting RANKL/RANK/OPG signal pathway. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:6260382013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Brinker AM, Ma J, Lipsky PE and Raskin I:
Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology of genus Tripterygium
(Celastraceae). Phytochemistry. 68:732–766. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xue M, McKelvey K, Shen K, Minhas N, March
L, Park SY and Jackson CJ: Endogenous MMP-9 and not MMP-2 promotes
rheumatoid synovial fibroblast survival, inflammation and cartilage
degradation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 53:2270–2279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Geng Y, Blanco FJ, Cornelisson M and Lotz
M: Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in normal human
articular chondrocytes. J Immunol. 155:796–801. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Maekawa K, Yoshikawa N, Du J, Nishida S,
Kitasato H, Okamoto K, Tanaka H, Mizushima Y and Kawai S: The
molecular mechanism of inhibition of interleukin-1beta-induced
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human synovial cells by
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F extract. Inflamm Res.
48:575–581. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Flower RJ: The development of COX2
inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2:179–191. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Geng Y, Fang M, Wang J, Yu H, Hu Z, Yew DT
and Chen W: Triptolide down-regulates COX-2 expression and PGE2
release by suppressing the activity of NF-κB and MAP kinases in
lipopolysaccharide-treated PC12 cells. Phytother Res. 26:337–343.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ma J, Dey M, Yang H, Poulev A, Pouleva R,
Dorn R, Lipsky PE, Kennelly EJ and Raskin I: Anti-inflammatory and
immunosuppressive compounds from Tripterygium wilfordii.
Phytochemistry. 68:1172–1178. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liacini A, Sylvester J and Zafarullah M:
Triptolide suppresses proinflammatory cytokine-induced matrix
metalloproteinase and aggrecanase-1 gene expression in
chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 327:320–327. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lin N, Liu C, Xiao C, Jia H, Imada K, Wu H
and Ito A: Triptolide, a diterpenoid triepoxide, suppresses
inflammation and cartilage destruction in collagen-induced
arthritis mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 73:136–146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang Y and Ma X: Triptolide inhibits
IL-12/IL-23 expression in APCs via CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein
alpha. J Immunol. 184:3866–3877. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jiang J, Wang N, Guan Z and Houshan LV:
Programmed cell death 5 factor enhances triptolide-induced
fibroblast-like synoviocyte apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 38:38–42. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tasneem S, Liu B, Li B, Choudhary MI and
Wang W: Molecular pharmacology of inflammation: Medicinal plants as
anti-inflammatory agents. Pharmacol Res. 139:126–140. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ziaei S and Halaby R: Immunosuppressive,
anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties of triptolide: A mini
review. Avicenna J Phytomed. 6:149–164. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kong X, Zhang Y, Liu C, Guo W, Li X, Su X,
Wan H, Sun Y and Lin N: Anti-angiogenic effect of triptolide in
rheumatoid arthritis by targeting angiogenic cascade. PLoS One.
8:e775132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zhang W, Li F and Gao W: Tripterygium
wilfordii inhibiting angiogenesis for rheumatoid arthritis
treatment. J Natl Med Assoc. 109:142–148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ramgolam V, Ang SG, Lai YH, Loh CS and Yap
HK: Traditional Chinese medicines as immunosuppressive agents. Ann
Acad Med Singapore. 29:11–16. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cameron M, Gagnier JJ and Chrubasik S:
Herbal therapy for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database
Syst Rev. CD0029482011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Lipsky PE and Tao XL: A potential new
treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: Thunder god vine. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 26:713–723. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lv QW, Zhang W, Shi Q, Zheng WJ, Li X,
Chen H, Wu QJ, Jiang WL, Li HB, Gong L, et al: Comparison of
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F with methotrexate in the
treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (TRIFRA): A randomised,
controlled clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 74:1078–1086. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Tao X, Younger J, Fan FZ, Wang B and
Lipsky PE: Benefit of an extract of Tripterygium Wilfordii
Hook F in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 46:1735–1743. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhao Q, Liu F, Cheng Y, Xiao XR, Hu DD,
Tang YM, Bao WM, Yang JH, Jiang T, Hu JP, et al: Celastrol protects
from cholestatic liver injury through modulation of SIRT1-FXR
signaling. Mol Cell Proteomics. 18:520–533. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang Y, Jiang Z, Xue M, Zhang S, Wang Y
and Zhang L: Toxicogenomic analysis of the gene expression changes
in rat liver after a 28-day oral Tripterygium wilfordii
multiglycoside exposure. J Ethnopharmacol. 141:170–177. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Freag MS, Saleh WM and Abdallah OY:
Self-assembled phospholipid-based phytosomal nanocarriers as
promising platforms for improving oral bioavailability of the
anticancer celastrol. Int J Pharm. 535:18–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Xu H and Liu B: Triptolide-targeted
delivery methods. Eur J Med Chem. 164:342–351. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|