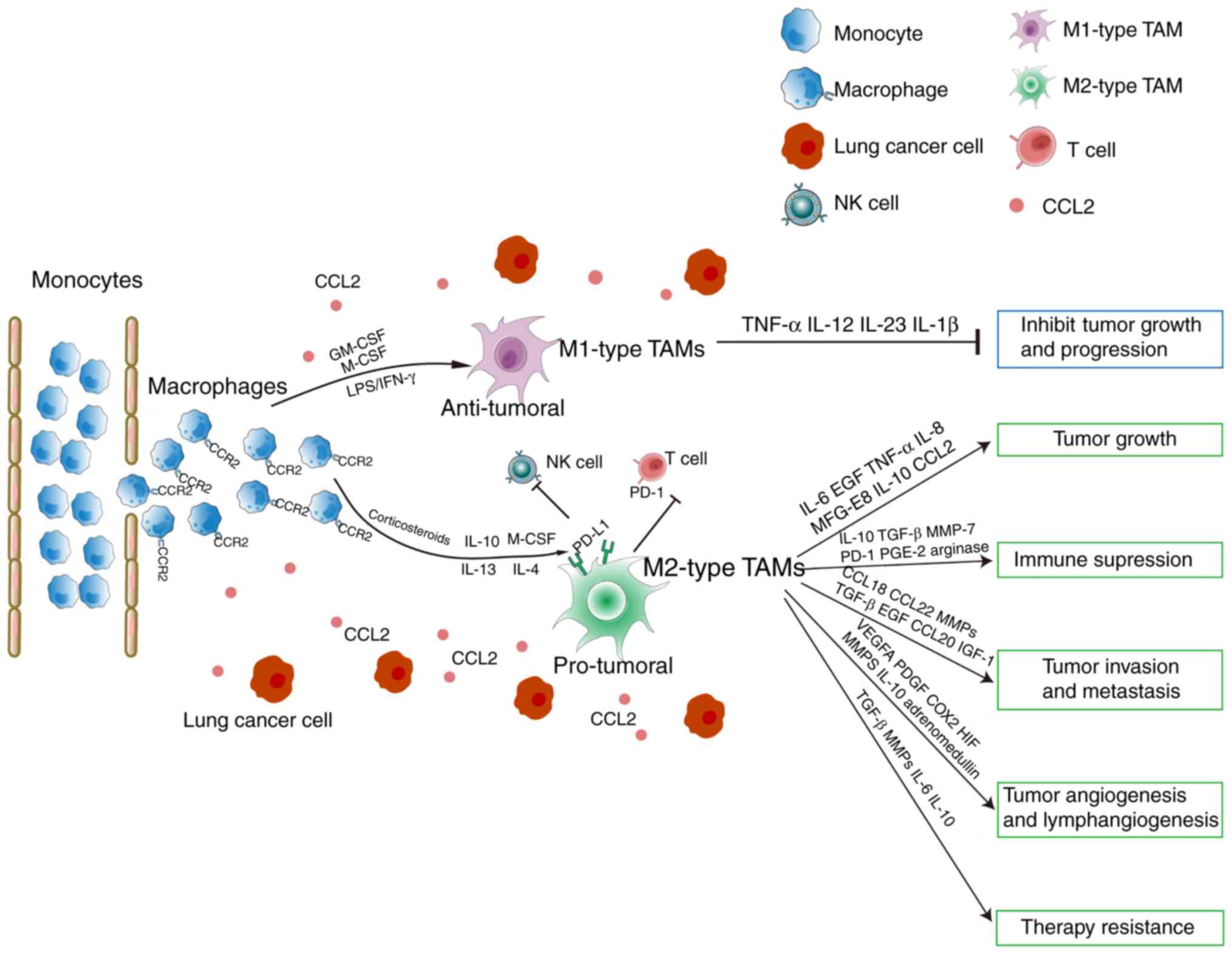
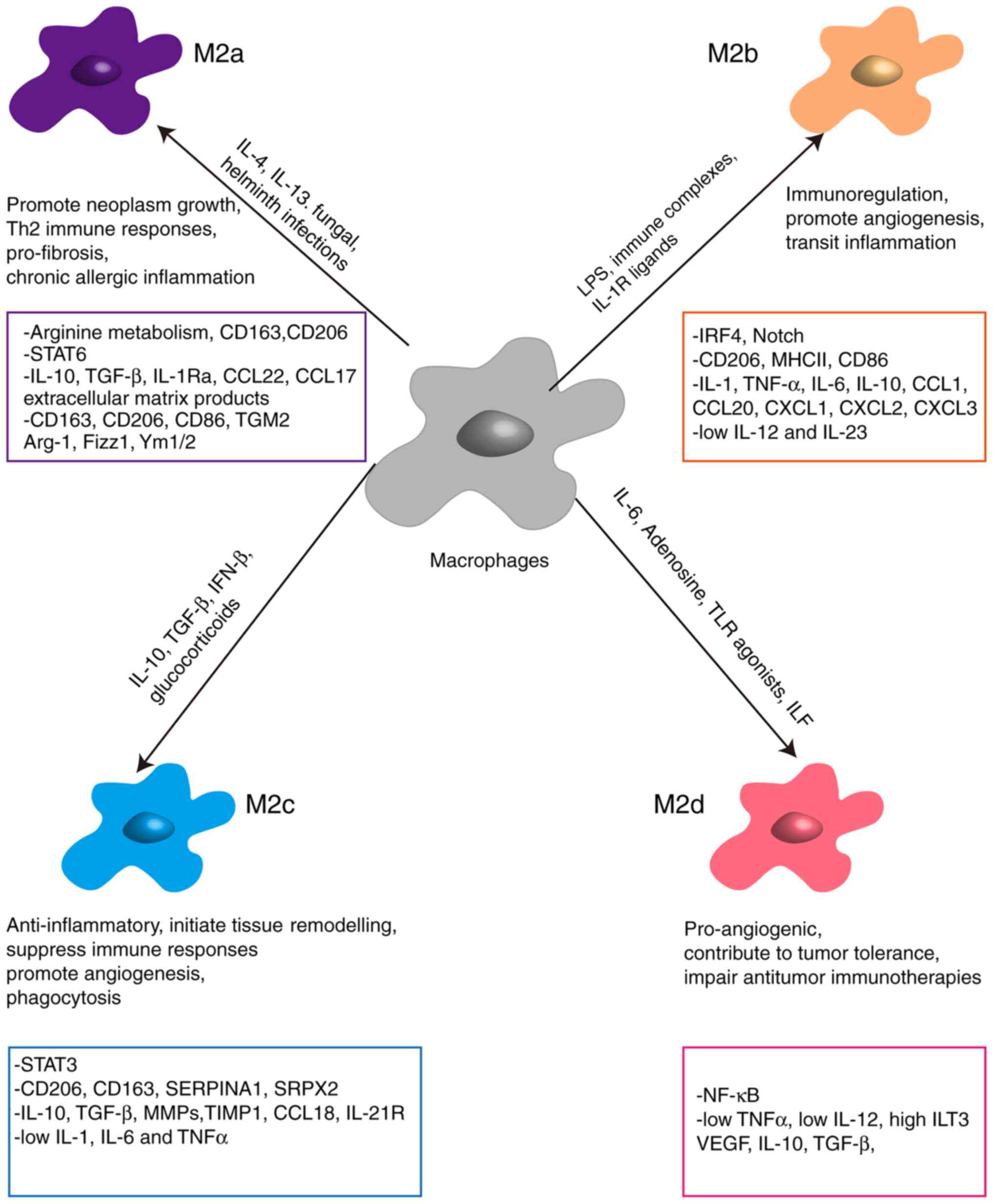
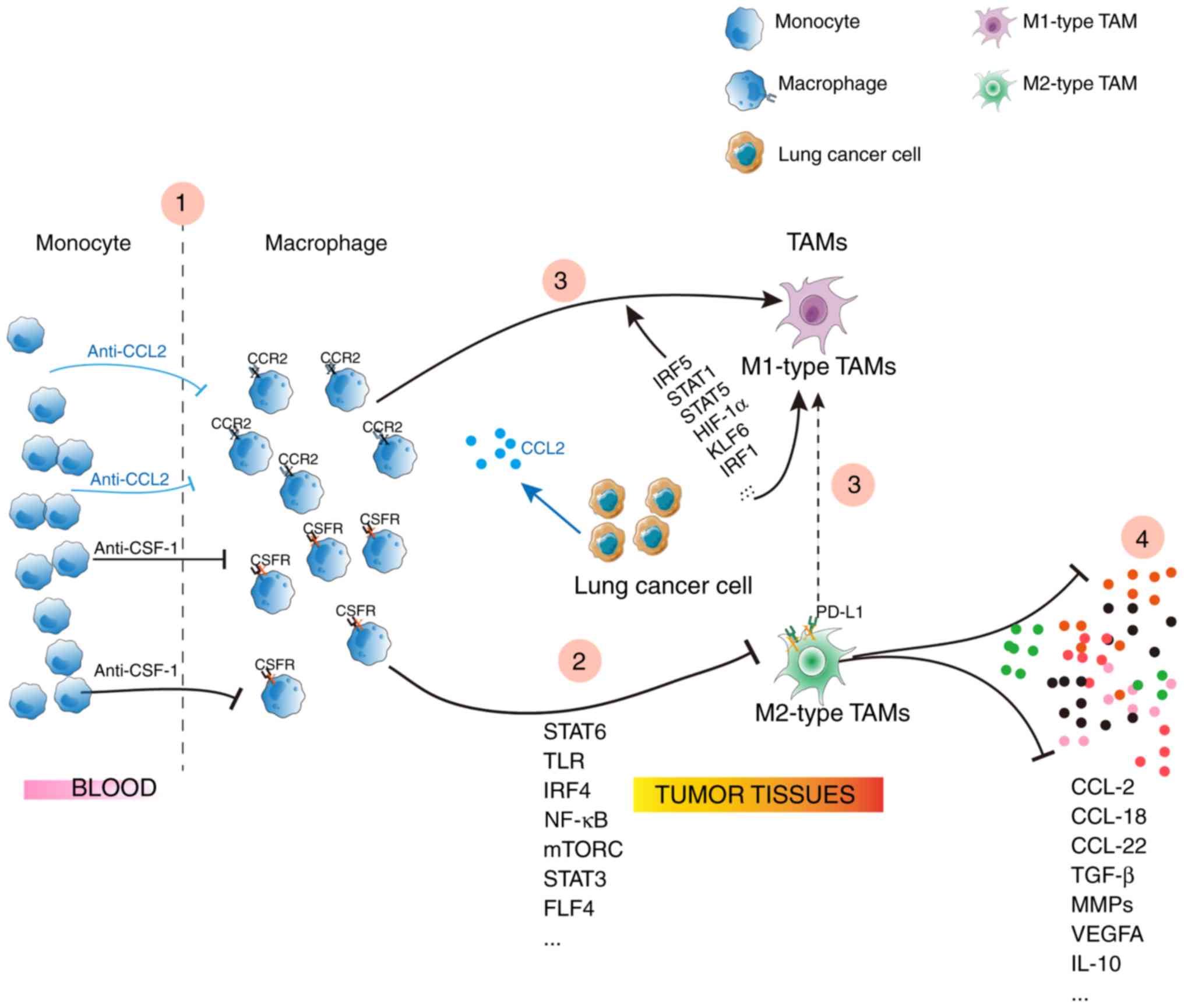
|
1
|
Brenman JE and Temple BR: Opinion:
Alternative views of AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 47:321–331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gridelli C, Perrone F and Monfardini S:
Lung cancer in the elderly. Eur J Cancer. 33:2313–2314. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goswami KK, Ghosh T, Ghosh S, Sarkar M,
Bose A and Baral R: Tumor promoting role of anti-tumor macrophages
in tumor microenvironment. Cell Immunol. 316:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sumitomo R, Hirai T, Fujita M, Murakami H,
Otake Y and Huang CL: PD-L1 expression on tumor-infiltrating immune
cells is highly associated with M2 TAM and aggressive malignant
potential in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 136:136–144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruffell B and Coussens LM: Macrophages and
therapeutic resistance in cancer. Cancer Cell. 27:462–472. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao L, Che X, Qiu X, Li Z, Yang B, Wang S,
Hou K, Fan Y, Qu X and Liu Y: M2 macrophage infiltration into tumor
islets leads to poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cancer Manag Res. 11:6125–6138. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sumitomo R, Hirai T, Fujita M, Murakami H,
Otake Y and Huang CL: M2 tumor-associated macrophages promote tumor
progression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med.
18:4490–4498. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou Z, Peng Y, Wu X, Meng S, Yu W, Zhao
J, Zhang H, Wang J and Li W: CCL18 secreted from M2 macrophages
promotes migration and invasion via the PI3K/Akt pathway in
gallbladder cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 42:81–92. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yeung OW, Lo CM, Ling CC, Qi X, Geng W, Li
CX, Ng KT, Forbes SJ, Guan XY, Poon RT, et al: Alternatively
activated (M2) macrophages promote tumour growth and invasiveness
in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 62:607–616. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sarode P, Zheng X, Giotopoulou GA, Weigert
A, Kuenne C, Günther S, Friedrich A, Gattenlöhner S, Stiewe T,
Brüne B, et al: Reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages by
targeting β-catenin/FOSL2/ARID5A signaling: A potential treatment
of lung cancer. SCI ADV. 6:eaaz61052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kimura Y, Sumiyoshi M and Baba K:
Antitumor and antimetastatic activity of synthetic hydroxystilbenes
through inhibition of lymphangiogenesis and M2 macrophage
differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages. Anticancer Res.
36:137–148. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hughes R, Qian BZ, Rowan C, Muthana M,
Keklikoglou I, Olson OC, Tazzyman S, Danson S, Addison C, Clemons
M, et al: Perivascular M2 macrophages stimulate tumor relapse after
chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 75:3479–3491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Flaherty DM, Monick MM and Hinde SL: Human
alveolar macrophages are deficient in PTEN. The role of endogenous
oxidants. J Biol Chem. 281:5058–5064. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Biswas SK and Mantovani A: Macrophage
plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: Cancer as a
paradigm. Nat Immunol. 11:889–896. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Biswas SK, Gangi L, Paul S, Schioppa T,
Saccani A, Sironi M, Bottazzi B, Doni A, Vincenzo B, Pasqualini F,
et al: A distinct and unique transcriptional program expressed by
tumor-associated macrophages (defective NF-kappaB and enhanced
IRF-3/STAT1 activation). Blood. 107:2112–2122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Klimp AH, Hollema H, Kempinga C, van der
Zee AG, de Vries EG and Daemen T: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2
and inducible nitric oxide synthase in human ovarian tumors and
tumor-associated macrophages. Cancer Res. 61:7305–7309.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nam S and Lim J: Essential role of
interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in immune cell development.
Arch Pharm Res. 39:1548–1555. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gong M, Zhuo X and Ma A: STAT6
Upregulation promotes M2 macrophage polarization to suppress
atherosclerosis. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 23:240–249. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vergadi E, Ieronymaki E, Lyroni K,
Vaporidi K and Tsatsanis C: Akt signaling pathway in macrophage
activation and M1/M2 polarization. J Immunol. 198:1006–1014. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xue J, Schmidt SV, Sander J, Draffehn A,
Krebs W, Quester I, De Nardo D, Gohel TD, Emde M, Schmidleithner L,
et al: Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum
model of human macrophage activation. Immunity. 40:274–288. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nelson MP, Christmann BS, Dunaway CW,
Morris A and Steele C: Experimental Pneumocystis lung infection
promotes M2a alveolar macrophage-derived MMP12 production. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 303:L469–L475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang W, Xu W and Xiong S: Blockade of
Notch1 signaling alleviates murine lupus via blunting macrophage
activation and M2b polarization. J Immunol. 184:6465–6478. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Koscsó B, Csóka B, Kókai E, Németh ZH,
Pacher P, Virág L, Leibovich SJ and Haskó G: Adenosine augments
IL-10-induced STAT3 signaling in M2c macrophages. J Leukoc Biol.
94:1309–1315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Olmes G, Büttner-Herold M, Ferrazzi F,
Distel L, Amann K and Daniel C: CD163+ M2c-like macrophages
predominate in renal biopsies from patients with lupus nephritis.
Arthritis Res Ther. 18:902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Q, Ni H, Lan L, Wei X, Xiang R and
Wang Y: Fra-1 protooncogene regulates IL-6 expression in
macrophages and promotes the generation of M2d macrophages. Cell
Res. 20:701–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Watkins SK, Egilmez NK, Suttles J and
Stout RD: IL-12 rapidly alters the functional profile of
tumor-associated and tumor-infiltrating macrophages in vitro and in
vivo. J Immunol. 178:1357–1362. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schoppmann SF, Birner P, Stöckl J, Kalt R,
Ullrich R, Caucig C, Kriehuber E, Nagy K, Alitalo K and Kerjaschki
D: Tumor-associated macrophages express lymphatic endothelial
growth factors and are related to peritumoral lymphangiogenesis. Am
J Pathol. 161:947–956. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hotchkiss KA, Ashton AW, Klein RS, Lenzi
ML, Zhu GH and Schwartz EL: Mechanisms by which tumor cells and
monocytes expressing the angiogenic factor thymidine phosphorylase
mediate human endothelial cell migration. Cancer Res. 63:527–533.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena
P and Sica A: Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages
as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends
Immunol. 23:549–555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ohri CM, Shikotra A, Green RH, Waller DA
and Bradding P: Macrophages within NSCLC tumour islets are
predominantly of a cytotoxic M1 phenotype associated with extended
survival. Eur Respir J. 33:118–126. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Helm O, Held-Feindt J, Grage-Griebenow E,
Reiling N, Ungefroren H, Vogel I, Krüger U, Becker T, Ebsen M,
Röcken C, et al: Tumor-associated macrophages exhibit pro- and
anti-inflammatory properties by which they impact on pancreatic
tumorigenesis. Int J Cancer. 135:843–861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Che D, Zhang S, Jing Z, Shang L, Jin S,
Liu F, Shen J, Li Y, Hu J, Meng Q and Yu Y: Macrophages induce EMT
to promote invasion of lung cancer cells through the IL-6-mediated
COX-2/PGE(2)/β-catenin signalling pathway. Mol Immunol. 90:197–210.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dehai C, Bo P, Qiang T, Lihua S, Fang L,
Shi J, Jingyan C, Yan Y, Guangbin W and Zhenjun Y: Enhanced
invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells after co-culture with
THP-1-derived macrophages via the induction of EMT by IL-6. Immunol
Lett. 160:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang L, Dong Y, Li Y, Wang D, Liu S, Wang
D, Gao Q, Ji S, Chen X, Lei Q, et al: IL-10 derived from M2
macrophage promotes cancer stemness via JAK1/STAT1/NF-κB/Notch1
pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 145:1099–1110.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Cao J, Ma S, Dong R, Meng W, Ying
M, Weng Q, Chen Z, Ma J, Fang Q, et al: Tumor hypoxia enhances
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer metastasis by selectively promoting
macrophage M2 polarization through the activation of ERK signaling.
Oncotarget. 5:9664–9677. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Laoui D, Van Overmeire E, Di Conza G,
Aldeni C, Keirsse J, Morias Y, Movahedi K, Houbracken I, Schouppe
E, Elkrim Y, et al: Tumor hypoxia does not drive differentiation of
tumor-associated macrophages but rather fine-tunes the M2-like
macrophage population. Cancer Res. 74:24–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang R, Lu M, Zhang J, Chen S, Luo X, Qin
Y and Chen H: Increased IL-10 mRNA expression in tumor-associated
macrophage correlated with late stage of lung cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 30:622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fu XL, Duan W, Su CY, Mao FY, Lv YP, Teng
YS, Yu PW, Zhuang Y and Zhao YL: Interleukin 6 induces M2
macrophage differentiation by STAT3 activation that correlates with
gastric cancer progression. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
66:1597–1608. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang X, Yang X, Tsai Y, Yang L, Chuang KH,
Keng PC, Lee SO and Chen Y: IL-6 mediates macrophage infiltration
after irradiation via up-regulation of CCL2/CCL5 in non-small cell
lung cancer. Radiat Res. 187:50–59. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Cortie K, Russell NS, Coppes RP,
Stewart FA and Scharpfenecker M: Bone marrow-derived macrophages
incorporate into the endothelium and influence vascular and renal
function after irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 90:769–777. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Russell NS, Floot B, van Werkhoven E,
Schriemer M, de Jong-Korlaar R, Woerdeman LA, Stewart FA and
Scharpfenecker M: Blood and lymphatic microvessel damage in
irradiated human skin: The role of TGF-β, endoglin and macrophages.
Radiother Oncol. 116:455–461. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Maeda H, Kuwahara H, Ichimura Y, Ohtsuki
M, Kurakata S and Shiraishi A: TGF-beta enhances macrophage ability
to produce IL-10 in normal and tumor-bearing mice. J immunol.
155:4926–4932. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang S, Che D, Yang F, Chi C, Meng H,
Shen J, Qi L, Liu F, Lv L, Li Y, et al: Tumor-associated
macrophages promote tumor metastasis via the TGF-β/SOX9 axis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 8:99801–99815. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee HJ, Park MK, Lee EJ and Lee CH:
Resolvin D1 inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial mesenchymal
transition of A549 lung cancer cells via lipoxin A4 receptor/formyl
peptide receptor 2 and GPR32. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:2801–2807. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang R, Zhang J, Chen S, Lu M, Luo X, Yao
S, Liu S, Qin Y and Chen H: Tumor-associated macrophages provide a
suitable microenvironment for non-small lung cancer invasion and
progression. Lung Cancer. 74:188–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cardoso AP, Pinto ML, Pinto AT, Pinto MT,
Monteiro C, Oliveira MI, Santos SG, Relvas JB, Seruca R, Mantovani
A, et al: Matrix metalloproteases as maestros for the dual role of
LPS- and IL-10-stimulated macrophages in cancer cell behaviour. BMC
Cancer. 15:4562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim YH, Kwon HJ and Kim DS: Matrix
metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9)-dependent processing of βig-h3 protein
regulates cell migration, invasion, and adhesion. J Biol Chem.
287:38957–38969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang B, Shi L, Sun X, Wang L, Wang X and
Chen C: Production of CCL20 from lung cancer cells induces the cell
migration and proliferation through PI3K pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
20:920–929. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shi L, Zhang B, Sun X, Zhang X, Lv S, Li
H, Wang X, Zhao C, Zhang H, Xie X, et al: CC chemokine ligand
18(CCL18) promotes migration and invasion of lung cancer cells by
binding to Nir1 through Nir1-ELMO1/DOC180 signaling pathway. Mol
Carcinog. 55:2051–2062. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huang R, Wang S, Wang N, Zheng Y, Zhou J,
Yang B, Wang X, Zhang J, Guo L, Wang S, et al: CCL5 derived from
tumor-associated macrophages promotes prostate cancer stem cells
and metastasis via activating β-catenin/STAT3 signaling. Cell Death
Dis. 11:2342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nakanishi T, Imaizumi K, Hasegawa Y,
Kawabe T, Hashimoto N, Okamoto M and Shimokata K: Expression of
macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC)/CCL22 in human lung cancer.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 55:1320–1329. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nakamura ES, Koizumi K, Kobayashi M,
Saitoh Y, Arita Y, Nakayama T, Sakurai H, Yoshie O and Saiki I:
RANKL-induced CCL22/macrophage-derived chemokine produced from
osteoclasts potentially promotes the bone metastasis of lung cancer
expressing its receptor CCR4. Clin Exp Metastasis. 23:9–18. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li W, Zhang X, Wu F, Zhou Y, Bao Z, Li H,
Zheng P and Zhao S: Gastric cancer-derived mesenchymal stromal
cells trigger M2 macrophage polarization that promotes metastasis
and EMT in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 10:9182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cao H, Huang Y, Wang L, Wang H, Pang X, Li
K, Dang W, Tang H, Wei L, Su M, et al: Leptin promotes migration
and invasion of breast cancer cells by stimulating IL-8 production
in M2 macrophages. Oncotarget. 7:65441–65453. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu Q, Li A, Yu S, Qin S, Han N, Pestell
RG, Han X and Wu K: DACH1 antagonizes CXCL8 to repress
tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma and improve prognosis. J
Hematol Oncol. 11:532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tataroğlu C, Kargi A, Ozkal S, Eşrefoğlu N
and Akkoçlu A: Association of macrophages, mast cells and
eosinophil leukocytes with angiogenesis and tumor stage in
non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 43:47–54.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen JJ, Yao PL, Yuan A, Hong TM, Shun CT,
Kuo ML, Lee YC and Yang PC: Up-regulation of tumor interleukin-8
expression by infiltrating macrophages: Its correlation with tumor
angiogenesis and patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:729–737. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lewis JS, Landers RJ, Underwood JC, Harris
AL and Lewis CE: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
by macrophages is up-regulated in poorly vascularized areas of
breast carcinomas. J Pathol. 192:150–158. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Leek RD and Harris AL: Tumor-associated
macrophages in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
7:177–189. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis
E, Turley H, Talks K, Pezzella F, Gatter KC and Harris AL: Relation
of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and 2 alpha in operable
non-small cell lung cancer to angiogenic/molecular profile of
tumours and survival. Br J Cancer. 85:881–890. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gordon SR, Maute RL, Dulken BW, Hutter G,
George BM, McCracken MN, Gupta R, Tsai JM, Sinha R, Corey D, et al:
PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits
phagocytosis and tumour immunity. Nature. 545:495–499. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Peranzoni E, Lemoine J, Vimeux L, Feuillet
V, Barrin S, Kantari-Mimoun C, Bercovici N, Guerin M, Biton J,
Ouakrim H, et al: Macrophages impede CD8 T cells from reaching
tumor cells and limit the efficacy of anti-PD-1 treatment. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E4041–E4050. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sharma SK, Chintala NK, Vadrevu SK, Patel
J, Karbowniczek M and Markiewski MM: Pulmonary alveolar macrophages
contribute to the premetastatic niche by suppressing antitumor T
cell responses in the lungs. J Immunol. 194:5529–5538. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Allavena P, Sica A, Vecchi A, Locati M,
Sozzani S and Mantovani A: The chemokine receptor switch paradigm
and dendritic cell migration: Its significance in tumor tissues.
Immunol Rev. 177:141–149. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Qiao J, Liu Z, Dong C, Luan Y, Zhang A,
Moore C, Fu K, Peng J, Wang Y, Ren Z, et al: Targeting tumors with
IL-10 prevents dendritic cell-mediated CD8+ T cell
apoptosis. Cancer Cell. 35:901–915.e4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang D, Yang L, Yue D, Cao L, Li L, Wang
D, Ping Y, Shen Z, Zheng Y, Wang L and Zhang Y: Macrophage-derived
CCL22 promotes an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment via IL-8
in malignant pleural effusion. Cancer Lett. 452:244–253. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Young MR, Endicott RA, Duffie GP and
Wepsic HT: Suppressor alveolar macrophages in mice bearing
metastatic Lewis lung carcinoma tumors. J Leukoc Biol. 42:682–688.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
De Palma M and Lewis CE: Cancer:
Macrophages limit chemotherapy. Nature. 472:303–304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Dijkgraaf EM, Heusinkveld M, Tummers B,
Vogelpoel LT, Goedemans R, Jha V, Nortier JW, Welters MJ, Kroep JR
and van der Burg SH: Chemotherapy alters monocyte differentiation
to favor generation of cancer-supporting M2 macrophages in the
tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 73:2480–2492. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Mitchem JB, Brennan DJ, Knolhoff BL, Belt
BA, Zhu Y, Sanford DE, Belaygorod L, Carpenter D, Collins L,
Piwnica-Worms D, et al: Targeting tumor-infiltrating macrophages
decreases tumor-initiating cells, relieves immunosuppression, and
improves chemotherapeutic responses. Cancer Res. 73:1128–1141.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
DeNardo DG, Brennan DJ, Rexhepaj E,
Ruffell B, Shiao SL, Madden SF, Gallagher WM, Wadhwani N, Keil SD,
Junaid SA, et al: Leukocyte complexity predicts breast cancer
survival and functionally regulates response to chemotherapy.
Cancer Discov. 1:54–67. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhang C, Yu X, Gao L, Zhao Y, Lai J, Lu D,
Bao R, Jia B, Zhong L, Wang F and Liu Z: Noninvasive imaging of
CD206-positive M2 macrophages as an early biomarker for
post-chemotherapy tumor relapse and lymph node metastasis.
Theranostics. 7:4276–4288. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sugimura K, Miyata H, Tanaka K, Takahashi
T, Kurokawa Y, Yamasaki M, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori M and Doki
Y: High infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages is associated
with a poor response to chemotherapy and poor prognosis of patients
undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal cancer. J Surg
Oncol. 111:752–759. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Paulus P, Stanley ER, Schäfer R, Abraham D
and Aharinejad S: Colony-stimulating factor-1 antibody reverses
chemoresistance in human MCF-7 breast cancer xenografts. Cancer
Res. 66:4349–4356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Salvagno C, Ciampricotti M, Tuit S, Hau
CS, van Weverwijk A, Coffelt SB, Kersten K, Vrijland K, Kos K, Ulas
T, et al: Therapeutic targeting of macrophages enhances
chemotherapy efficacy by unleashing type I interferon response. Nat
Cell Biol. 21:511–521. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Dai F, Liu L, Che G, Yu N, Pu Q, Zhang S,
Ma J, Ma L and You Z: The number and microlocalization of
tumor-associated immune cells are associated with patient's
survival time in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
10:2202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Welsh TJ, Green RH, Richardson D, Waller
DA, O'Byrne KJ and Bradding P: Macrophage and mast-cell invasion of
tumor cell islets confers a marked survival advantage in
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:8959–8967. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Pei BX, Sun BS, Zhang ZF, Wang AL and Ren
P: Interstitial tumor-associated macrophages combined with
tumor-derived colony-stimulating factor-1 and interleukin-6, a
novel prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 148:1208–1216.e2. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ma J, Liu L, Che G, Yu N, Dai F and You Z:
The M1 form of tumor-associated macrophages in non-small cell lung
cancer is positively associated with survival time. BMC Cancer.
10:1122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang B, Yao G, Zhang Y and Gao J, Yang B,
Rao Z and Gao J: M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages are
associated with poor prognoses resulting from accelerated
lymphangiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
66:1879–1886. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jung KY, Cho SW, Kim YA, Kim D, Oh BC,
Park DJ and Park YJ: Cancers with higher density of
tumor-associated macrophages were associated with poor survival
rates. J Pathol Transl Med. 49:318–324. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Hirayama S, Ishii G, Nagai K, Ono S,
Kojima M, Yamauchi C, Aokage K, Hishida T, Yoshida J, Suzuki K and
Ochiai A: Prognostic impact of CD204-positive macrophages in lung
squamous cell carcinoma: Possible contribution of Cd204-positive
macrophages to the tumor-promoting microenvironment. J Thorac
Oncol. 7:1790–1797. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Li X, Yao W, Yuan Y, Chen P, Li B, Li J,
Chu R, Song H, Xie D, Jiang X and Wang H: Targeting of
tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a
therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
66:157–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Keklikoglou I and De Palma M: Cancer:
Metastasis risk after anti-macrophage therapy. Nature. 515:46–47.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li Y, Cao F, Li M, Li P, Yu Y, Xiang L, Xu
T, Lei J, Tai YY, Zhu J, et al: Hydroxychloroquine induced lung
cancer suppression by enhancing chemo-sensitization and promoting
the transition of M2-TAMs to M1-like macrophages. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 37:2592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhang Y, Sun Z, Pei J, Luo Q, Zeng X, Li
Q, Yang Z and Quan J: Identification of α-mangostin as an agonist
of human STING. Chemmedchem. 13:2057–2064. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Brandão RD, Veeck J, Van de Vijver KK,
Lindsey P, de Vries B, van Elssen CH, Blok MJ, Keymeulen K, Ayoubi
T, Smeets HJ, et al: A randomised controlled phase II trial of
pre-operative celecoxib treatment reveals anti-tumour
transcriptional response in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res. 15:R292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhu B, Zou L, Cheng X, Lin Z, Duan Y, Wu
Y, Zhou F and Chen Z: Administration of MIP-3alpha gene to the
tumor following radiation therapy boosts anti-tumor immunity in a
murine model of lung carcinoma. Immunol Lett. 103:101–107. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shiri S, Alizadeh AM, Baradaran B,
Farhanghi B, Shanehbandi D, Khodayari S, Khodayari H and Tavassoli
A: Dendrosomal curcumin suppresses metastatic breast cancer in mice
by changing m1/m2 macrophage balance in the tumor microenvironment.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:3917–3922. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Han S, Wang W, Wang S, Wang S, Ju R, Pan
Z, Yang T, Zhang G, Wang H and Wang L: Multifunctional biomimetic
nanoparticles loading baicalin for polarizing tumor-associated
macrophages. Nanoscale. 11:20206–20220. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Cao M, Yan H, Han X, Weng L, Wei Q, Sun X,
Lu W, Wei Q, Ye J, Cai X, et al: Ginseng-derived nanoparticles
alter macrophage polarization to inhibit melanoma growth. J
Immunother Cancer. 7:3262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang J, Song W, Guo J, Zhang J, Sun Z, Li
L, Ding F and Gao M: Cytotoxicity of different sized TiO2
nanoparticles in mouse macrophages. Toxicol Ind Health. 29:523–533.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Park J, Lim DH, Lim HJ, Kwon T, Choi JS,
Jeong S, Choi IH and Cheon J: Size dependent macrophage responses
and toxicological effects of Ag nanoparticles. Chem Commun (Camb).
47:4382–4384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|