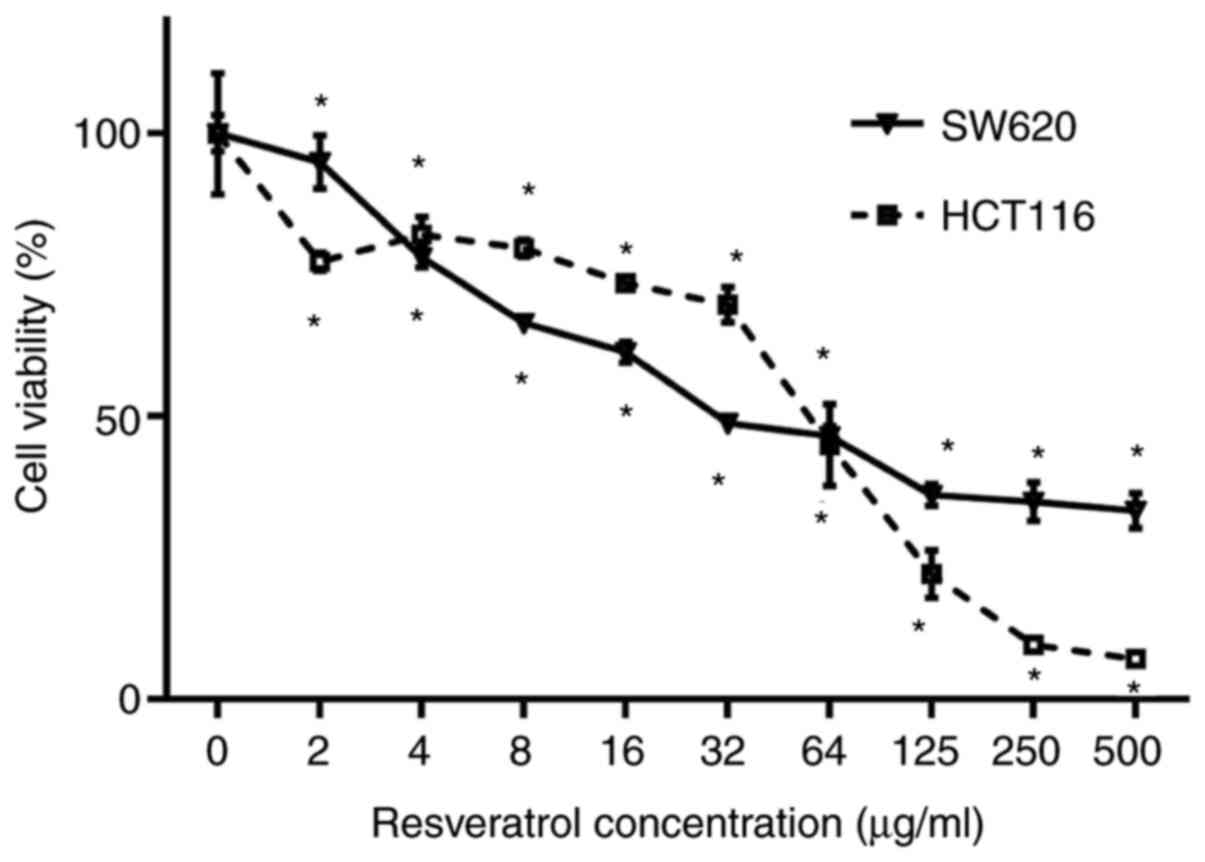
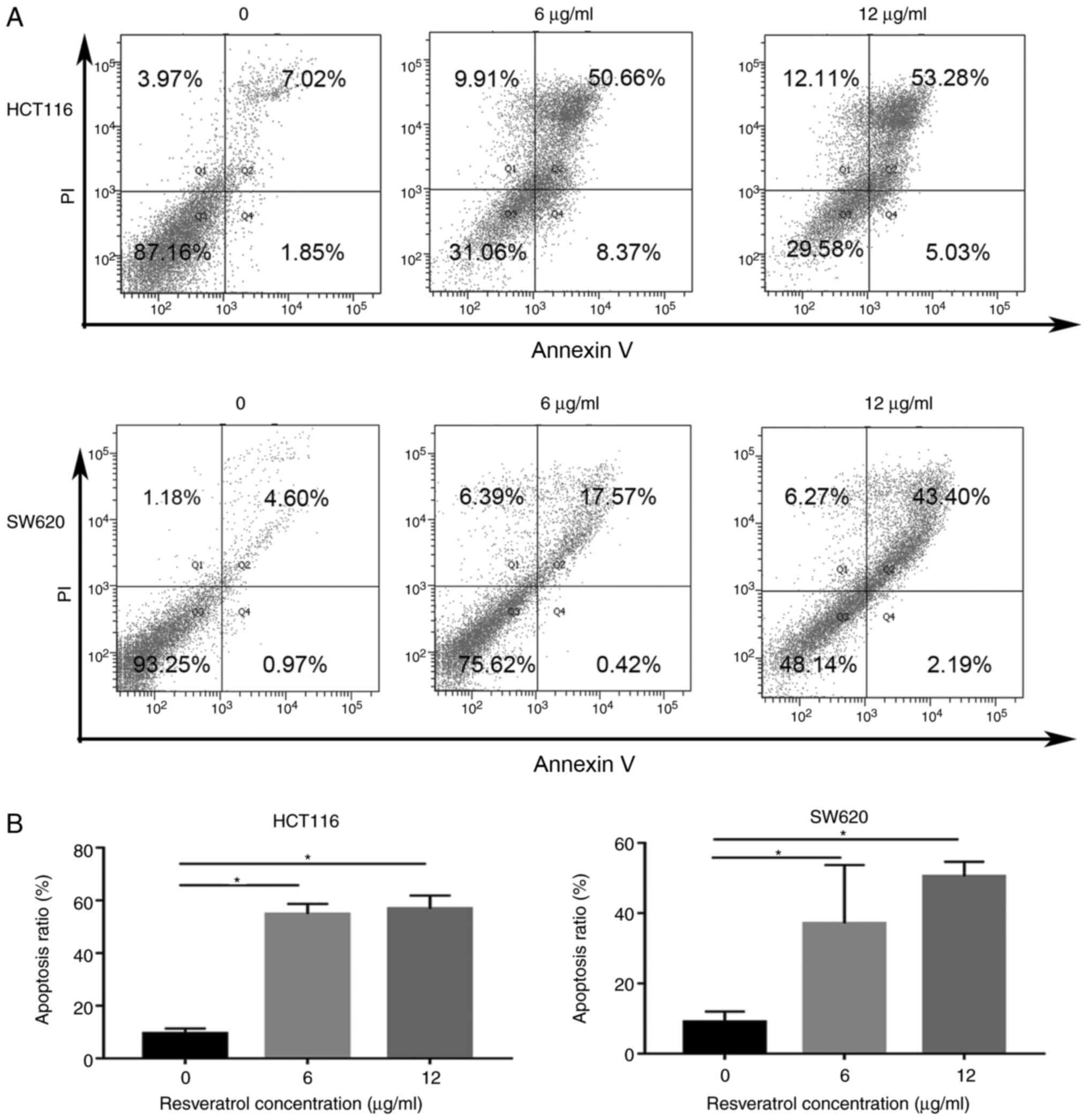
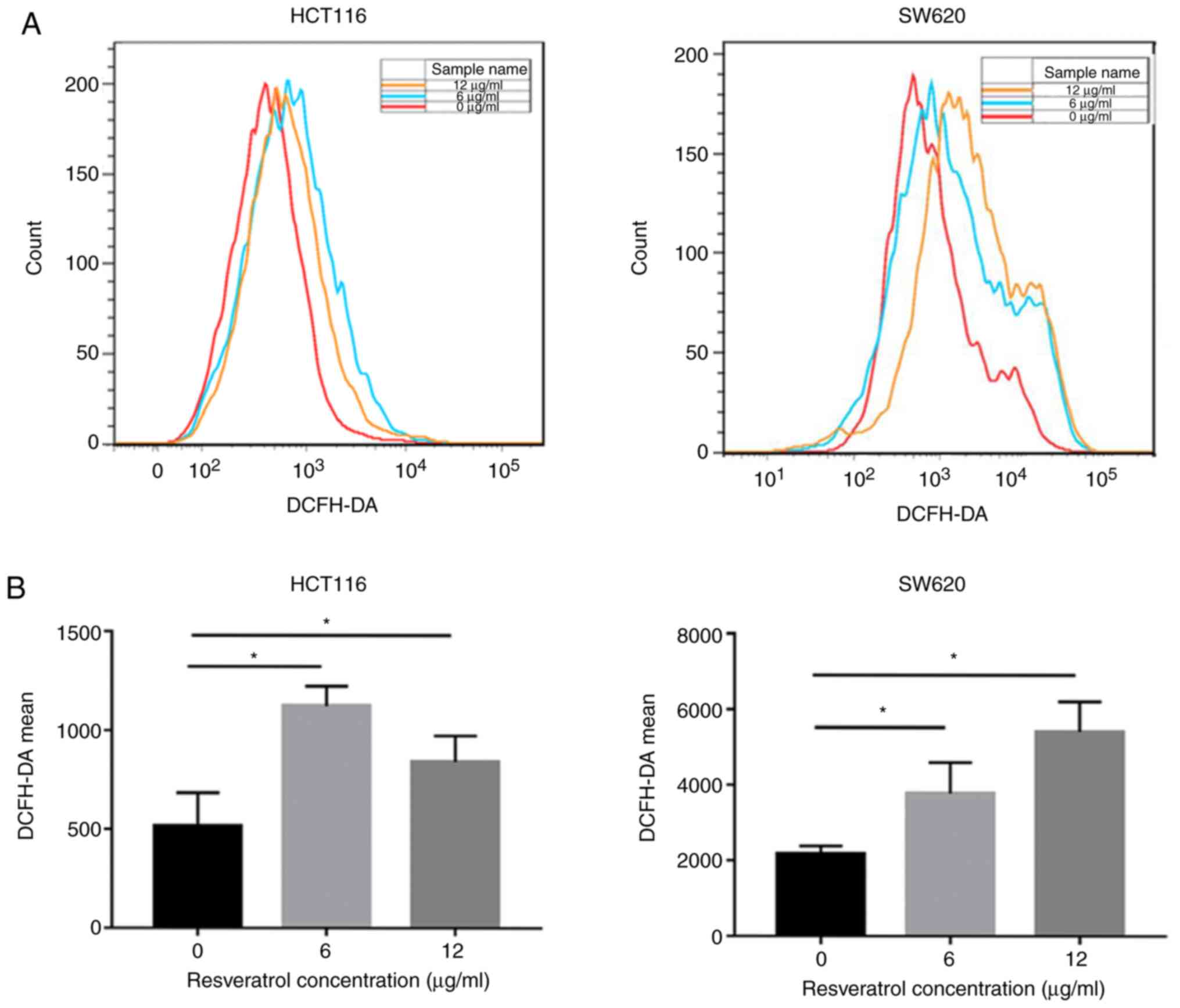
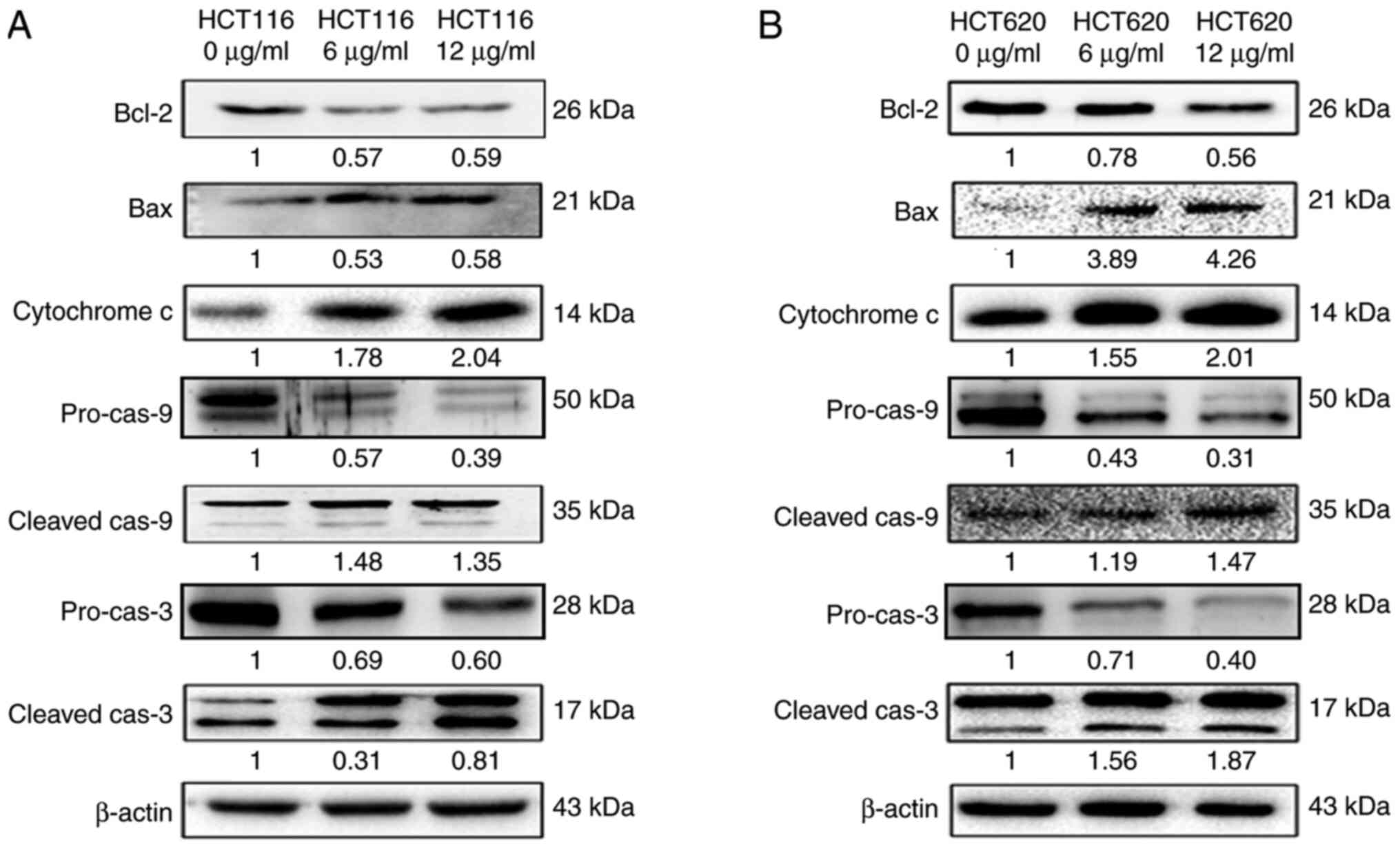
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RGS, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van der Stok EP, Spaander MCW, Grünhagen
DJ, Verhoef C and Kuipers EJ: Surveillance after curative treatment
for colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:297–315. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loree JM and Kopetz S: Recent developments
in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Ther Adv Med
Oncol. 9:551–564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huminiecki L and Horbańczuk J: The
functional genomic studies of resveratrol in respect to its
anti-cancer effects. Biotechnol Adv. 36:1699–1708. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Panaro MA, Carofiglio V, Acquafredda A,
Cavallo P and Cianciulli A: Anti-inflammatory effects of
resveratrol occur via inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced
NF-κB activation in Caco-2 and SW480 human colon cancer cells. Br J
Nutr. 108:1623–1632. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Garvin S, Ollinger K and Dabrosin C:
Resveratrol induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in human
breast cancer xenografts in vivo. Cancer Lett. 231:113–122. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu J, Liu D, Niu H, Zhu G, Xu Y, Ye D, Li
J and Zhang Q: Resveratrol reverses doxorubicin resistance by
inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through
modulating PTEN/Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 36:192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV,
Thomas CF, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Farnsworth NR, Kinghorn AD, Mehta
RG, et al: Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a
natural product derived from grapes. Science. 275:218–220. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson
HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K,
et al: Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a
high-calorie diet. Nature. 444:337–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sung MM, Hamza SM and Dyck JR: Myocardial
metabolism in diabetic cardiomyopathy: Potential therapeutic
targets. Antioxid Redox Signal. 22:1606–1630. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Athar M, Back JH, Tang X, Kim KH,
Kopelovich L, Bickers DR and Kim AL: Resveratrol: A review of
preclinical studies for human cancer prevention. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 224:274–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Buhrmann C, Yazdi M, Popper B, Shayan P,
Goel A, Aggarwal BB and Shakibaei M: Resveratrol Chemosensitizes
TNF-β-Induced Survival of 5-FU-Treated Colorectal Cancer Cells.
Nutrients. 10:102018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kaminski BM, Weigert A, Scherzberg MC, Ley
S, Gilbert B, Brecht K, Brüne B, Steinhilber D, Stein J and
Ulrich-Rückert S: Resveratrol-induced potentiation of the antitumor
effects of oxaliplatin is accompanied by an altered cytokine
profile of human monocyte-derived macrophages. Apoptosis.
19:1136–1147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Crowell JA, Korytko PJ, Morrissey RL,
Booth TD and Levine BS: Resveratrol-associated renal toxicity.
Toxicol Sci. 82:614–619. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Farghali H, Kgalalelo Kemelo M, Wojnarová
L and Kutinová Canová N: In vitro and in vivo experimental
hepatotoxic models in liver research: Applications to the
assessment of potential hepatoprotective drugs. Physiol Res. 65
(Suppl 4):S417–S425. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Perše M: Oxidative stress in the
pathogenesis of colorectal cancer: Cause or consequence? BioMed Res
Int. 2013:7257102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sabharwal SS and Schumacker PT:
Mitochondrial ROS in cancer: Initiators, amplifiers or an Achilles'
heel? Nat Rev Cancer. 14:709–721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
NavaneethaKrishnan S, Rosales JL and Lee
KY: Loss of Cdk5 in breast cancer cells promotes ROS-mediated cell
death through dysregulation of the mitochondrial permeability
transition pore. Oncogene. 37:1788–1804. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumar S, Stokes J III, Singh UP,
Scissum-Gunn K, Singh R, Manne U and Mishra MK: Prolonged exposure
of resveratrol induces reactive superoxide species-independent
apoptosis in murine prostate cells. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177150392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng X, Jia B, Tian XT, Song X, Wu ML,
Kong QY, Li H and Liu J: Correlation of reactive oxygen species
levels with resveratrol sensitivities of anaplastic thyroid cancer
cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:62354172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Santandreu FM, Valle A, Oliver J and Roca
P: Resveratrol potentiates the cytotoxic oxidative stress induced
by chemotherapy in human colon cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem.
28:219–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng L, Yan B, Chen K, Jiang Z, Zhou C,
Cao J, Qian W, Li J, Sun L, Ma J, et al: Resveratrol-induced
downregulation of NAF-1 enhances the sensitivity of pancreatic
cancer cells to gemcitabine via the ROS/Nrf2 signaling pathways.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:94820182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ashkenazi A, Fairbrother WJ, Leverson JD
and Souers AJ: From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced
selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:273–284.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weng CJ and Yen GC: Chemopreventive
effects of dietary phytochemicals against cancer invasion and
metastasis: Phenolic acids, monophenol, polyphenol, and their
derivatives. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:76–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sliva D: Suppression of cancer
invasiveness by dietary compounds. Mini Rev Med Chem. 8:677–688.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan X, Zhao Y, Cheng T, Zheng A, Ge A,
Zang L, Xu K and Tang B: Monitoring NAD(P)H by an ultrasensitive
fluorescent probe to reveal reductive stress induced by natural
antioxidants in HepG2 cells under hypoxia. Chem Sci (Camb).
10:8179–8186. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wu H, Chen L, Zhu F, Han X, Sun L and Chen
K: The cytotoxicity effect of resveratrol: cell cycle arrest and
induced apoptosis of breast cancer 4T1 cells. Toxins (Basel).
11:112019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Khusbu FY, Zhou X, Roy M, Chen FZ, Cao Q
and Chen HC: Resveratrol induces depletion of TRAF6 and suppresses
prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 118:1056442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ashkenazi A: Directing cancer cells to
self-destruct with pro-apoptotic receptor agonists. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 7:1001–1012. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghobrial IM, Witzig TE and Adjei AA:
Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J Clin.
55:178–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schellenberg B, Wang P, Keeble JA,
Rodriguez-Enriquez R, Walker S, Owens TW, Foster F, Tanianis-Hughes
J, Brennan K, Streuli CH, et al: Bax exists in a dynamic
equilibrium between the cytosol and mitochondria to control
apoptotic priming. Mol Cell. 49:959–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li J and Yuan J: Caspases in apoptosis and
beyond. Oncogene. 27:6194–6206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri
ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry
WS, Fulda S, et al: Molecular definitions of cell death
subroutines: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell
Death 2012. Cell Death Differ. 19:107–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reed JC: Bcl-2 and the regulation of
programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 124:1–6. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mahajan NP, Linder K, Berry G, Gordon GW,
Heim R and Herman B: Bcl-2 and Bax interactions in mitochondria
probed with green fluorescent protein and fluorescence resonance
energy transfer. Nat Biotechnol. 16:547–552. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hussain AR, Uddin S, Bu R, Khan OS, Ahmed
SO, Ahmed M and Al-Kuraya KS: Resveratrol suppresses constitutive
activation of AKT via generation of ROS and induces apoptosis in
diffuse large B cell lymphoma cell lines. PLoS One. 6:e247032011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Z, Li W, Meng X and Jia B:
Resveratrol induces gastric cancer cell apoptosis via reactive
oxygen species, but independent of sirtuin1. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 39:227–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu S, Sun Z, Chu P, Li H, Ahsan A, Zhou
Z, Zhang Z, Sun B, Wu J, Xi Y, et al: EGCG protects against
homocysteine-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells
apoptosis by modulating mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic signaling
and PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathways. Apoptosis. 22:672–680. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu L, Trimarchi JR, Smith PJ and Keefe
DL: Mitochondrial dysfunction leads to telomere attrition and
genomic instability. Aging Cell. 1:40–46. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|