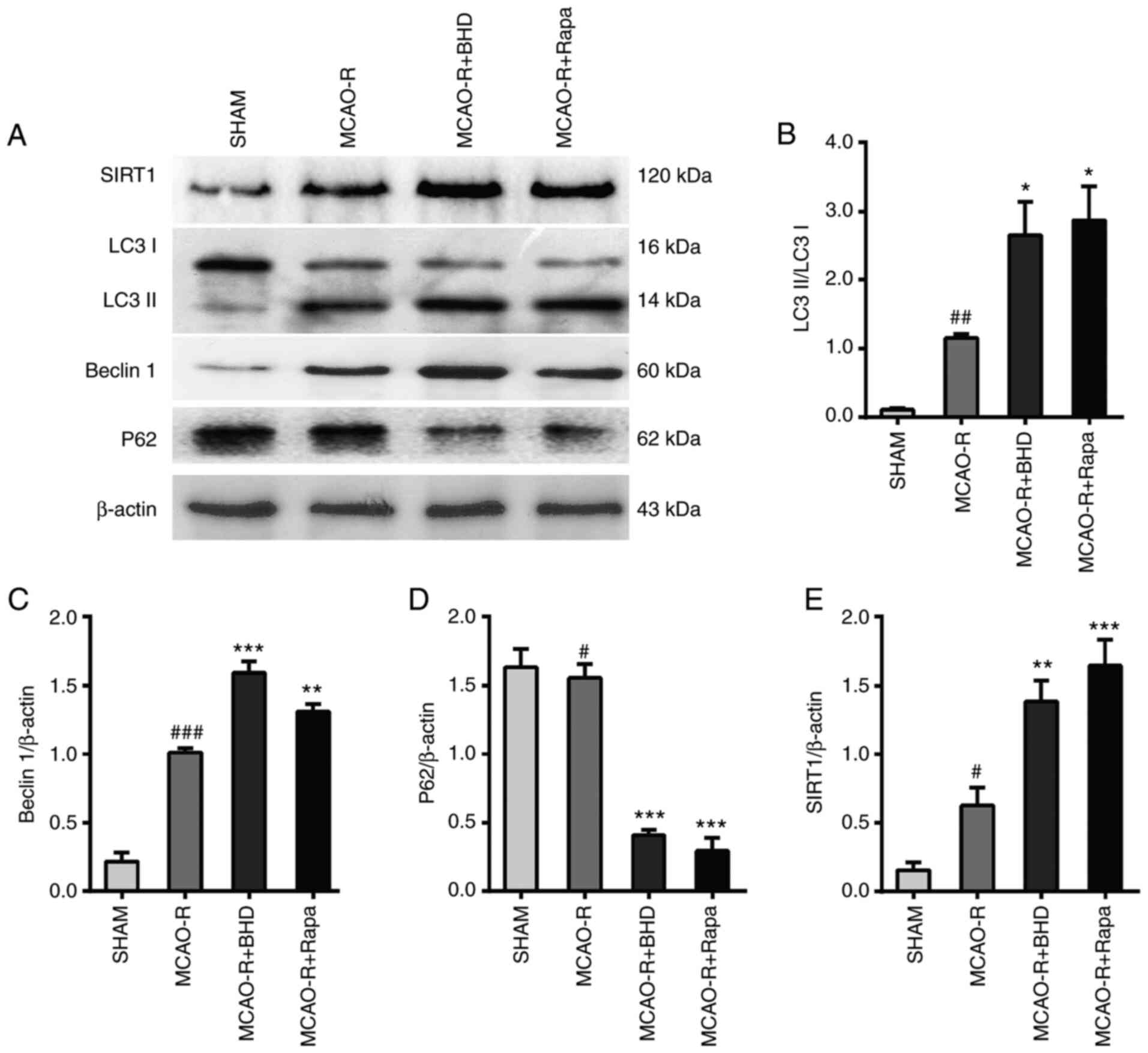
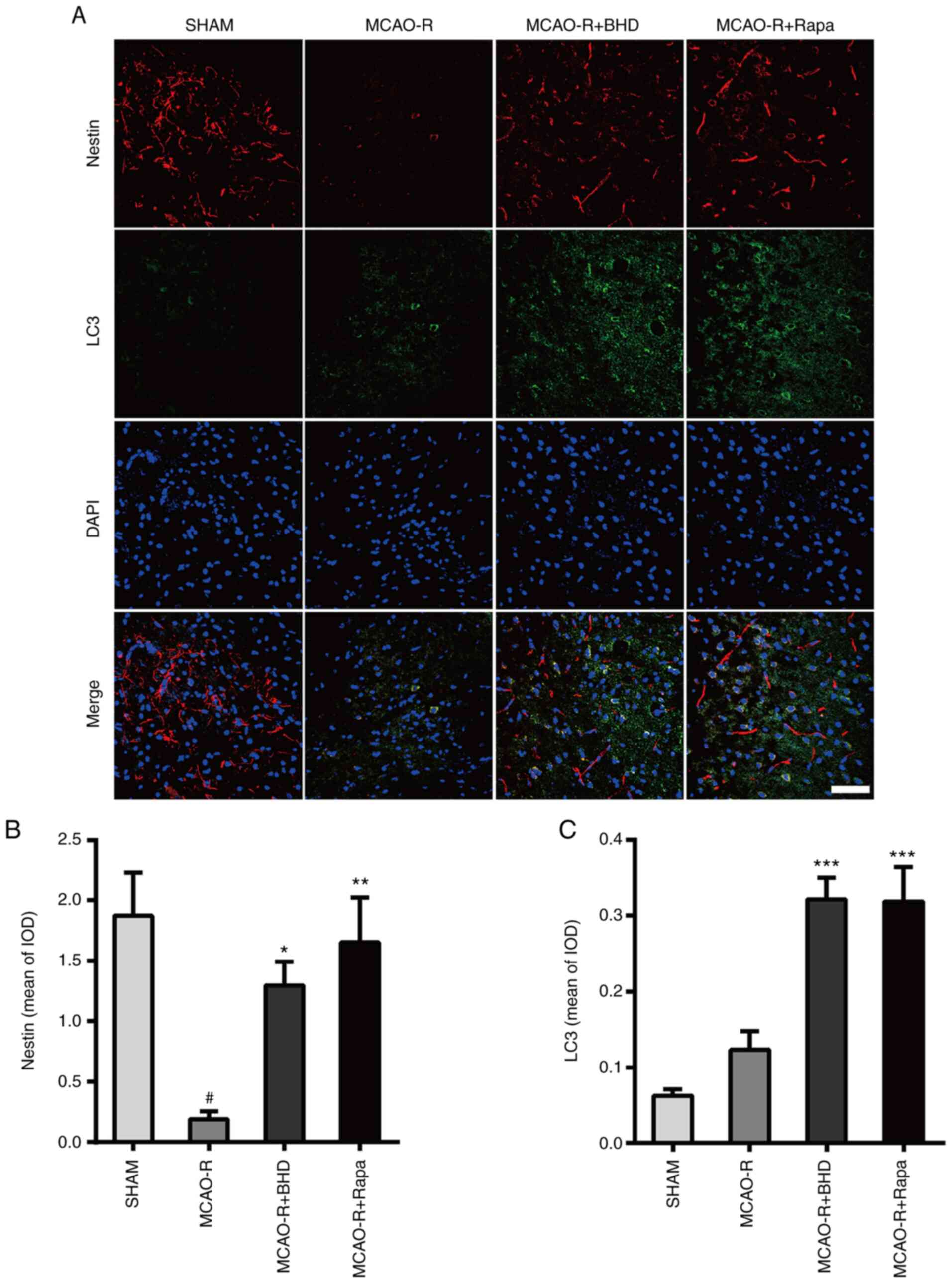
|
1
|
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW,
Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling
FN, Deo R, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update:
A report from the American heart association. Circulation.
137:e67–e492. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou M, Wang H, Zhu J, Chen W, Wang L, Liu
S, Li Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Yin P, et al: Cause-specific mortality for
240 causes in China during 1990–2013: A systematic subnational
analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet.
387:251–272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
GBD 2016 Lifetime Risk of Stroke
Collaborators, ; Feigin VL, Nguyen G, Cercy K, Johnson CO, Alam T,
Parmar PG, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abd-Allah F, et al: Global,
regional, and country-specific lifetime risks of stroke, 1990 and
2016. N Engl J Med. 379:2429–2437. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dai W, Liu X, Zhang Z, Chen J, Guo R,
Zheng H, Jin X, Wen S, Gao Y, Li T, et al: A two-level model for
the analysis of syndrome of acute ischemic stroke: From diagnostic
model to molecular mechanism. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:2930102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Han CH, Kim M, Cho SY, Jung WS, Moon SK,
Park JM, Ko CN, Cho KH and Kwon S: Adjunctive herbal medicine
treatment for patients with acute ischemic stroke: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 33:124–137.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hodges H: Graft-induced recovery of
cognitive function after diffuse and focal brain damage:
Implications for neural transplantation in man. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat
Im I P Pavlova. 45:29–58. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hossmann KA: Pathophysiology and therapy
of experimental stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 26:1057–1083. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patel RAG and McMullen PW: Neuroprotection
in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Prog Cardiovasc Dis.
59:542–548. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
George PM and Steinberg GK: Novel stroke
therapeutics: Unraveling stroke pathophysiology and its impact on
clinical treatments. Neuron. 87:297–309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Prabhakaran S, Ruff I and Bernstein RA:
Acute stroke intervention: A systematic review. JAMA.
313:1451–1462. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang S, Boyd J, Delaney K and Murphy TH:
Rapid reversible changes in dendritic spine structure in vivo gated
by the degree of ischemia. J Neurosci. 25:5333–5338. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakagiri A, Sunamoto M and Murakami M:
NADPH oxidase is involved in ischaemia/reperfusion-induced damage
in rat gastric mucosa via ROS production-role of NADPH oxidase in
rat stomachs. Inflammopharmacology. 15:278–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gage FH: Adult neurogenesis in mammals.
Science. 364:827–828. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cavallucci V, Fidaleo M and Pani G:
Nutrients and neurogenesis: The emerging role of autophagy and gut
microbiota. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 50:46–52. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duan X, Chen B, Cui Y, Zhou L, Wu C, Yang
Z, Wen Y, Miao X, Li Q, Xiong L and He J: Ready player one?
Autophagy shapes resistance to photodynamic therapy in cancers.
Apoptosis. 23:587–606. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang K, Zhu L, Tan J, Shi W, He Q and Yu
B: Identification of autophagy signaling network that contributes
to stroke in the ischemic rodent brain via gene expression.
Neurosci Bull. 31:480–490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Liu XQ, Gao B
and Qin ZH: Autophagy activation is associated with neuroprotection
in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemic preconditioning.
Autophagy. 6:482–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Su J, Zhang T, Wang K, Zhu T and Li X:
Autophagy activation contributes to the neuroprotection of remote
ischemic perconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats.
Neurochem Res. 39:2068–2077. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao L, Jiang T, Guo J, Liu Y, Cui G, Gu L,
Su L and Zhang Y: Inhibition of autophagy contributes to ischemic
postconditioning-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. PLoS One. 7:e460922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vázquez P, Arroba AI, Cecconi F, de la
Rosa EJ, Boya P and de Pablo F: Atg5 and Ambra1 differentially
modulate neurogenesis in neural stem cells. Autophagy. 8:187–199.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lv X, Jiang H, Li B, Liang Q, Wang S, Zhao
Q and Jiao J: The crucial role of Atg5 in cortical neurogenesis
during early brain development. Sci Rep. 4:60102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Pan Z, Fang Z, Lin W, Wu S, Yang
F, Li Y, Fu H, Gao H and Li S: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid
attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced neuronal apoptosis by
inducing autophagy through the upregulation of SIRT1-mediated
deacetylation of Beclin-1. J Neuroinflammation. 15:3102018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang Q, Len Q, Liu Z and Wang W:
Overexpression of miR-22 attenuates oxidative stress injury in
diabetic cardiomyopathy via Sirt 1. Cardiovasc Ther. 36:2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Carloni S, Albertini MC, Galluzzi L,
Buonocore G, Proietti F and Balduini W: Melatonin reduces
endoplasmic reticulum stress and preserves sirtuin 1 expression in
neuronal cells of newborn rats after hypoxia-ischemia. J Pineal
Res. 57:192–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Q, Liu M, Liu WW, Hao WB, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: In vivo recovery effect of silibinin
treatment on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice is associated
with the modulations of Sirt-1 expression and autophagy in
pancreatic β-cell. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 14:413–423. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo Q, Zhong M, Xu H, Mao X, Zhang Y and
Lin N: A systems biology perspective on the molecular mechanisms
underlying the therapeutic effects of buyang huanwu decoction on
ischemic stroke. Rejuvenation Res. 18:313–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hao CZ, Wu F, Shen J, Lu L, Fu DL, Liao WJ
and Zheng GQ: Clinical efficacy and safety of buyang huanwu
decoction for acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of 19 randomized controlled trials. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:6301242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng XW, Shan CS, Xu QQ, Wang Y, Shi YH,
Wang Y and Zheng GQ: Buyang huanwu decoction targets SIRT1/VEGF
pathway to promote angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Front Neurosci. 12:9112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu B, Cai G, Yi J and Chen X: Buyang
huanwu decoction regulates neural stem cell behavior in ischemic
brain. Neural Regen Res. 8:2336–2342. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luo L, Deng S, Yi J, Zhou S, She Y and Liu
B: Buyang huanwu decoction ameliorates poststroke depression via
promoting neurotrophic pathway mediated neuroprotection and
neurogenesis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017:40726582017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Liu X, Hu T, Li X, Chen Y, Xiao G,
Huang J, Chang Y, Zhu Y, Zhang H and Wang Y: Astragalus saponins
improves stroke by promoting the proliferation of neural stem cells
through phosphorylation of Akt. J Ethnopharmacol. 277:1142242021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li JH, Liu AJ, Li HQ, Wang Y, Shang HC and
Zheng GQ: Buyang huanwu decoction for healthcare: Evidence-based
theoretical interpretations of treating different diseases with the
same method and target of vascularity. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2014:5067832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang ZQ, Song JY, Jia YQ and Zhang YK:
Buyanghuanwu decoction promotes angiogenesis after cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury: Mechanisms of brain tissue repair.
Neural Regen Res. 11:435–440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang WW, Xu F, Wang D, Ye J and Cai SQ:
Buyang huanwu decoction ameliorates ischemic stroke by modulating
multiple targets with multiple components: In vitro evidences. Chin
J Nat Med. 16:194–202. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo C, Ouyang MW, Fang YY, Li SJ, Zhou Q,
Fan J, Qin ZS and Tao T: Dexmedetomidine protects mouse brain from
ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting neuronal autophagy
through Up-Regulating HIF-1α. Front Cell Neurosci. 11:1972017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen J, Zhu Y, Huang K, Jiang H, Shi C,
Xiong X, Zhan R and Pan J: Buyang Huanwu Decoction attenuates
H2O2-induced apoptosis by inhibiting reactive oxygen
species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway in human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. BMC Complement Altern Med.
16:1542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang YT, Chen YY, Lai YH, Cheng CC, Lin
TC, Su YS, Liu CH and Lai PC: Resveratrol alleviates the
cytotoxicity induced by the radiocontrast agent, ioxitalamate, by
reducing the production of reactive oxygen species in HK-2 human
renal proximal tubule epithelial cells in vitro. Int J Mol Med.
37:83–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Zhang L, Wang S and
Maiese K: Mammalian target of rapamycin: Hitting the bull's-eye for
neurological disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:374–391. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xia D, Zhang Z and Zhao Y: Acteoside
attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis in rats with
focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biol Pharm Bull.
41:1645–1651. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang J, Yan H, Li S and Zhang M: Berberine
ameliorates MCAO induced Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion injury via
activation of the BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem
Res. 43:702–710. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li YQ, Hui ZR, Tao T, Shao KY, Liu Z, Li M
and Gu LL: Protective effect of hypoxia inducible factor-1α gene
therapy using recombinant adenovirus in cerebral
ischaemia-reperfusion injuries in rats. Pharm Biol. 58:438–446.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Song M, Mohamad O, Gu X, Wei L and Yu SP:
Restoration of intracortical and thalamocortical circuits after
transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into the
ischemic brain of mice. Cell Transplant. 22:2001–2015. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee JH, Yu WH, Kumar A, Lee S, Mohan PS,
Peterhoff CM, Wolfe DM, Martinez-Vicente M, Massey AC, Sovak G, et
al: Lysosomal proteolysis and autophagy require presenilin 1 and
are disrupted by Alzheimer-related PS1 mutations. Cell.
141:1146–1158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hou K, Xu D, Li F, Chen S and Li Y: The
progress of neuronal autophagy in cerebral ischemia stroke:
Mechanisms, roles and research methods. J Neurol Sci. 400:72–82.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Carloni S, Girelli S, Scopa C, Buonocore
G, Longini M and Balduini W: Activation of autophagy and Akt/CREB
signaling play an equivalent role in the neuroprotective effect of
rapamycin in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Autophagy. 6:366–377. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Cao Y and Liu C: Autophagy and
ischemic stroke. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1207:111–134. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim KJ and Namgung U: Facilitating effects
of Buyang Huanwu decoction on axonal regeneration after peripheral
nerve transection. J Ethnopharmacol. 213:56–64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang M, Chai Y, Liu T, Xu N and Yang C:
Synergistic effects of Buyang Huanwu decoction and embryonic neural
stem cell transplantation on the recovery of neurological function
in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med. 9:1141–1148.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Min L, Ling W, Hua R, Qi H, Chen S, Wang
H, Tang L and Shangguan W: Anti-angiogenic therapy for
normalization of tumor vasculature: A potential effect of Buyang
Huanwu decoction on nude mice bearing human hepatocellular
carcinoma xenografts with high metastatic potential. Mol Med Rep.
13:2518–2526. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wu L, Zhang W, Li H, Chen BY, Zhang GM,
Tang YH, He FY and Deng CQ: Inhibition of aortic intimal
hyperplasia and cell cycle protein and extracellular matrix protein
expressions by BuYang HuanWu Decoction. J Ethnopharmacol.
125:423–435. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rodrigo R, Fernández-Gajardo R, Gutiérrez
R, Matamala JM, Carrasco R, Miranda-Merchak A and Feuerhake W:
Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: Novel
therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
12:698–714. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Orellana-Urzúa S, Rojas I, Líbano L and
Rodrigo R: Pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: Role of oxidative
stress. Curr Pharm Des. 26:4246–4260. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, Tsai AP, Cheng
YL, Cheng PW, Li CY and Li CJ: Current mechanistic concepts in
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1650–1667. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Filomeni G, De Zio D and Cecconi F:
Oxidative stress and autophagy: The clash between damage and
metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ. 22:377–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yamashita T and Abe K: Recent progress in
therapeutic strategies for ischemic stroke. Cell Transplant.
25:893–898. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kalogeris T, Bao Y and Korthuis RJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: A double edged sword in
ischemia/reperfusion vs preconditioning. Redox Biol. 2:702–714.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ and Thompson CB:
Autophagy in metazoans: Cell survival in the land of plenty. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:439–448. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kroemer G and Jäättelä M: Lysosomes and
autophagy in cell death control. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:886–897. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Björk-Eriksson
T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA and Gage FH: Neurogenesis in
the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 4:1313–1317. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang RL, Zhang ZG, Zhang L and Chopp M:
Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells in the cortex
and the subventricular zone in the adult rat after focal cerebral
ischemia. Neuroscience. 105:33–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jin K, Minami M, Lan JQ, Mao XO, Batteur
S, Simon RP and Greenberg DA: Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular
zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia
in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:4710–4715. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Doetsch F, Caillé I, Lim DA,
García-Verdugo JM and Alvarez-Buylla A: Subventricular zone
astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain.
Cell. 97:703–716. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Palmer TD, Takahashi J and Gage FH: The
adult rat hippocampus contains primordial neural stem cells. Mol
Cell Neurosci. 8:389–404. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Boya P, Codogno P and Rodriguez-Muela N:
Autophagy in stem cells: Repair, remodelling and metabolic
reprogramming. Development. 145:dev1465062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Dhaliwal J, Xi Y, Bruel-Jungerman E,
Germain J, Francis F and Lagace DC: Doublecortin (DCX) is not
essential for survival and differentiation of Newborn Neurons in
the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Front Neurosci. 9:4942015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fasemore TM, Patzke N, Kaswera-Kyamakya C,
Gilissen E, Manger PR and Ihunwo AO: The Distribution of Ki-67 and
doublecortin-immunopositive cells in the brains of three
strepsirrhine primates: Galago demidoff, perodicticus potto, and
Lemur catta. Neuroscience. 372:46–57. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shahsavani M, Pronk RJ, Falk R, Lam M,
Moslem M, Linker SB, Salma J, Day K, Schuster J, Anderlid BM, et
al: An in vitro model of lissencephaly: Expanding the role of DCX
during neurogenesis. Mol Psychiatry. 23:1674–1684. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bojnordi MN, Azizi H, Skutella T,
Movahedin M, Pourabdolhossein F, Shojaei A and Hamidabadi HG:
Differentiation of spermatogonia stem cells into functional mature
neurons characterized with differential gene expression. Mol
Neurobiol. 54:5676–5682. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chen X, Chen H, He Y, Fu S, Liu H, Wang Q
and Shen J: Proteomics-guided study on buyang huanwu decoction for
its neuroprotective and neurogenic mechanisms for transient
ischemic stroke: Involvements of EGFR/PI3K/Akt/Bad/14-3-3 and
Jak2/Stat3/Cyclin D1 signaling cascades. Mol Neurobiol.
57:4305–4321. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lapierre LR, Kumsta C, Sandri M, Ballabio
A and Hansen M: Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of
autophagy in aging. Autophagy. 11:867–880. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang JF, Zhang YL and Wu YC: The role of
sirt1 in ischemic stroke: Pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies.
Front Neurosci. 12:8332018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wang P, Guan YF, Du H, Zhai QW, Su DF and
Miao CY: Induction of autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection
of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in cerebral ischemia.
Autophagy. 8:77–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|