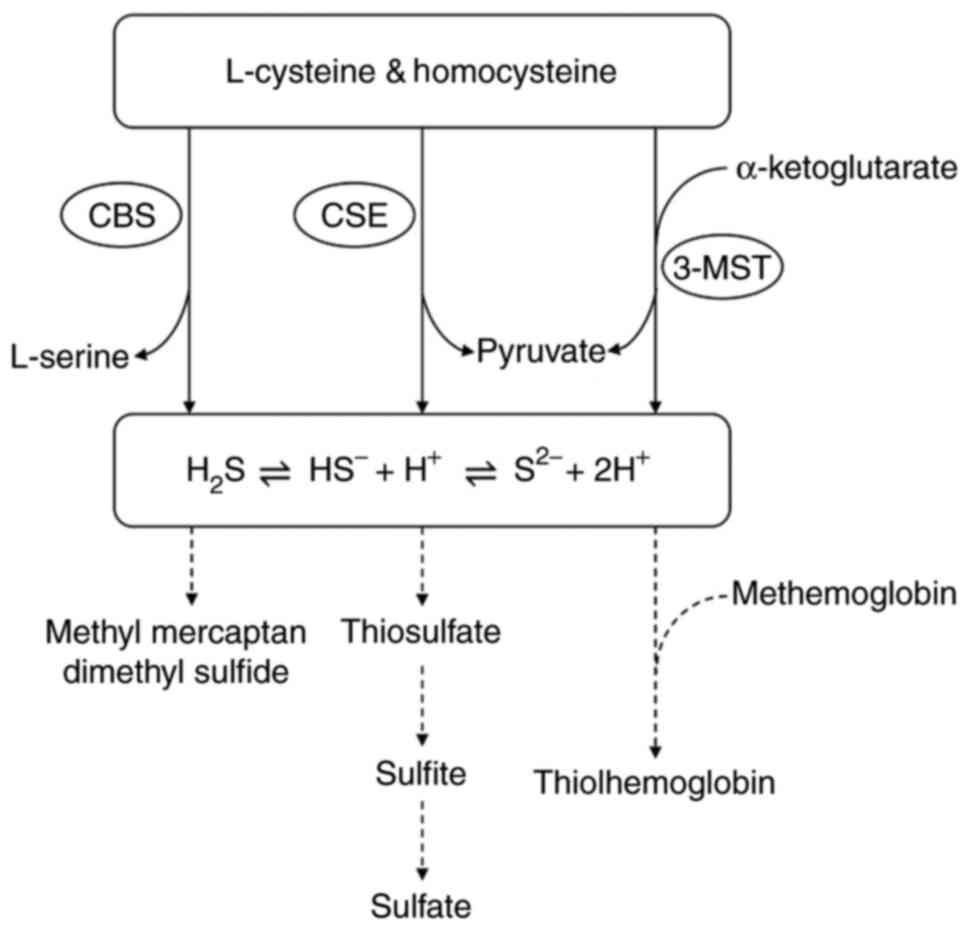
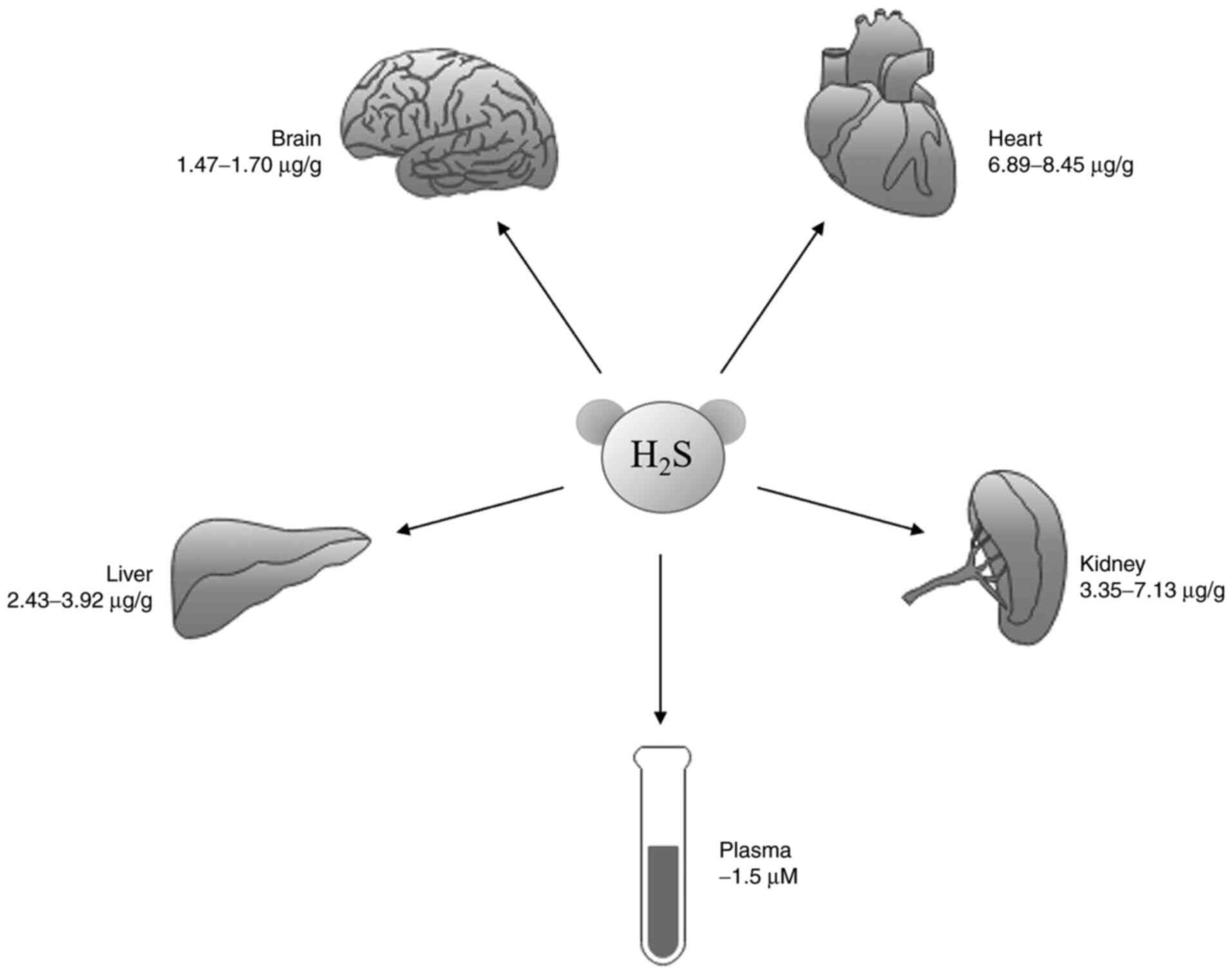
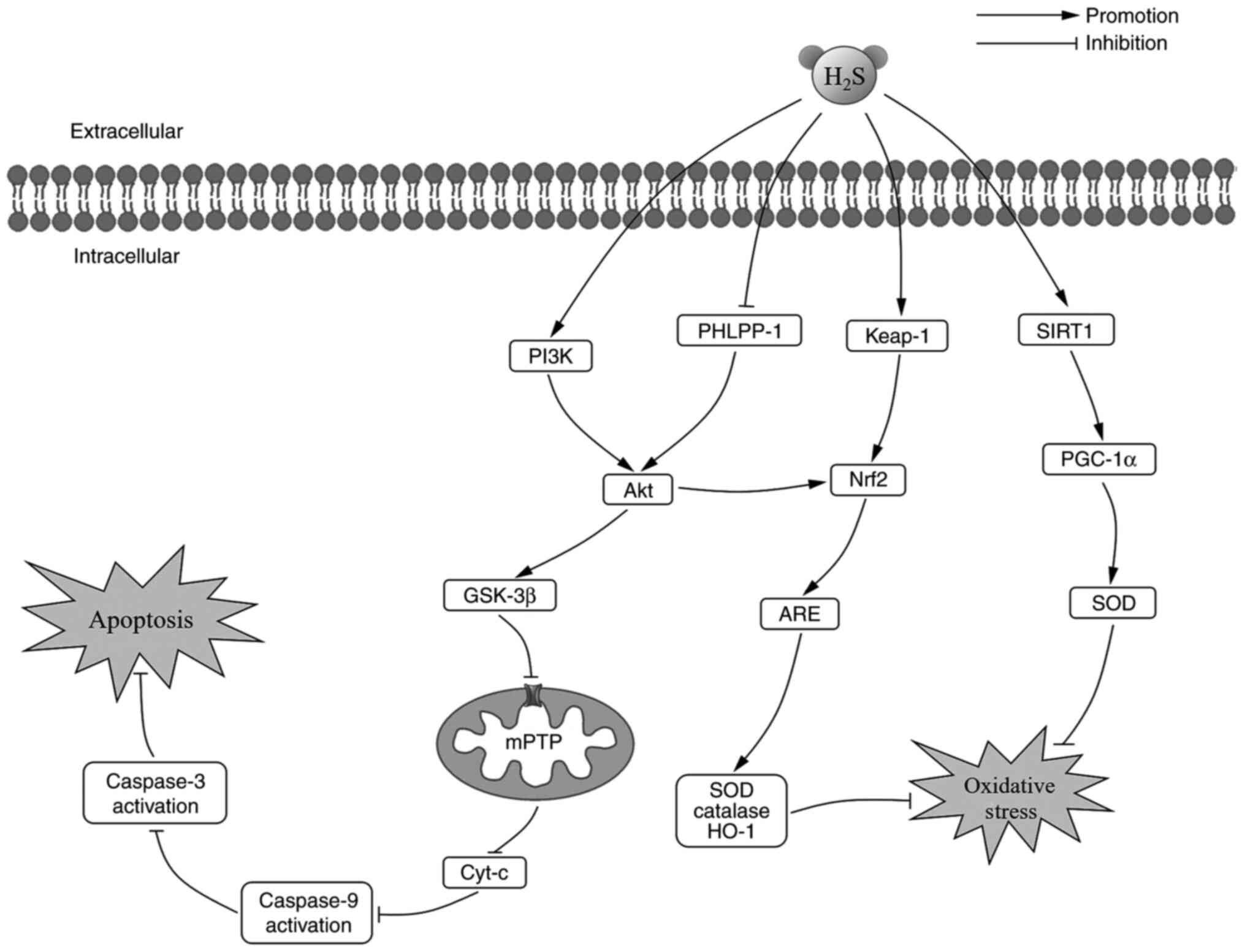
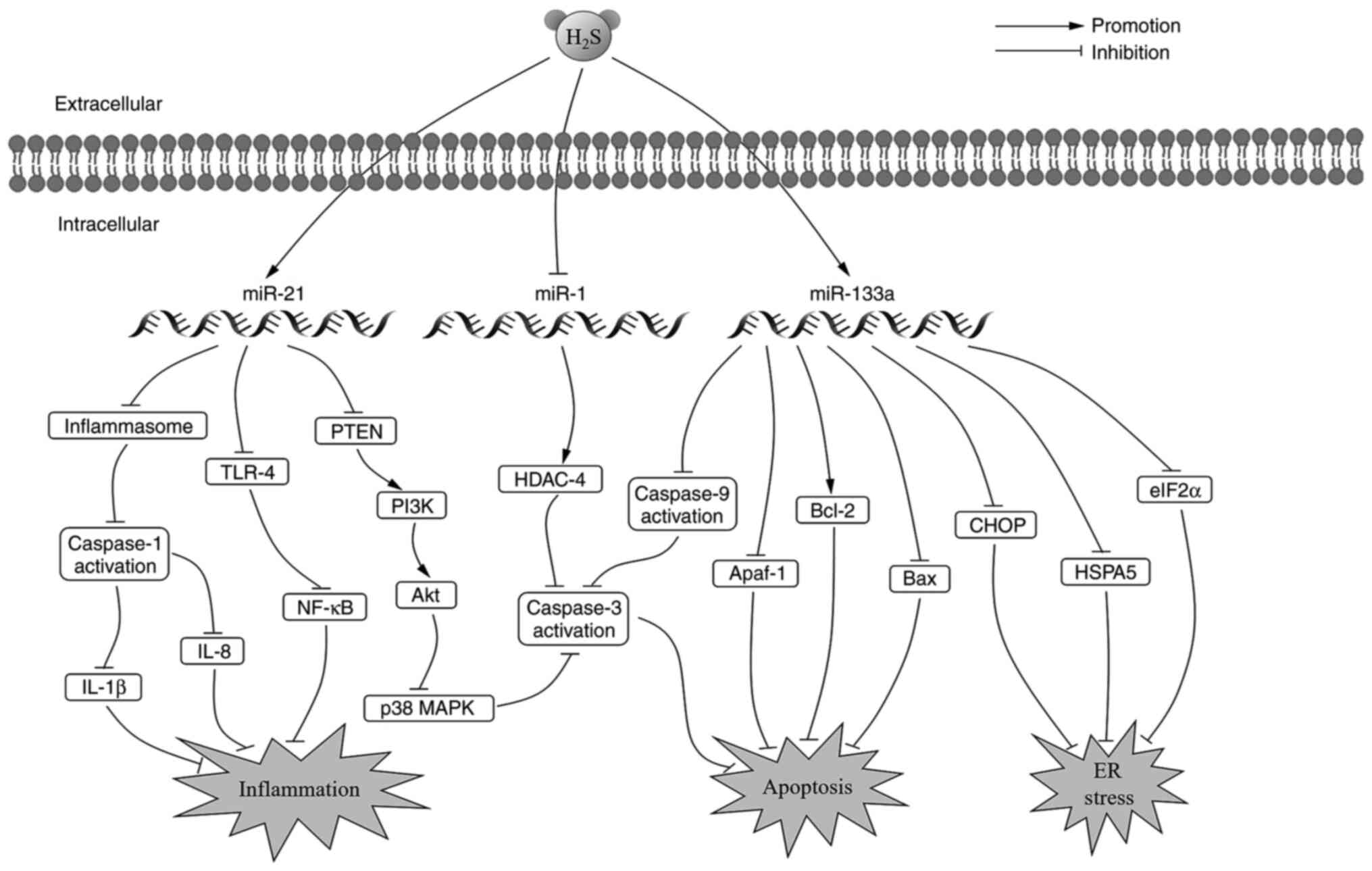
|
1
|
Townsend N, Wilson L, Bhatnagar P,
Wickramasinghe K, Rayner M and Nichols M: Cardiovascular disease in
Europe: Epidemiological update 2016. Eur Heart J. 37:3232–3245.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato
G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, Barengo NC, Beaton AZ, Benjamin EJ,
Benziger CP, et al: Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and
risk factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 76:2982–3021. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, Tsai AP, Cheng
YL, Cheng PW, Li CY and Li CJ: Current mechanistic concepts in
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1650–1667. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ibáñez B, Heusch G, Ovize M and Van de
Werf F: Evolving therapies for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 65:1454–1471. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gorini F, Bustaffa E, Chatzianagnostou K,
Bianchi F and Vassalle C: Hydrogen sulfide and cardiovascular
disease: Doubts, clues, and interpretation difficulties from
studies in geothermal areas. Sci Total Environ. 743:1408182020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu D, Hu Q, Tan B, Rose P, Zhu D and Zhu
YZ: Amelioration of mitochondrial dysfunction in heart failure
through S-sulfhydration of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent
protein kinase II. Redox Biol. 19:250–262. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang ZJ, Wu J, Guo W and Zhu YZ:
Atherosclerosis and the hydrogen sulfide signaling
pathway-therapeutic approaches to disease prevention. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:859–875. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Donnarumma E, Trivedi RK and Lefer DJ:
Protective actions of H2S in acute myocardial infarction and heart
failure. Compr Physiol. 7:583–602. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu T, Ding W, Ji X, Ao X, Liu Y, Yu W and
Wang J: Oxidative stress in cell death and cardiovascular diseases.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:90305632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS
release. Physiol Rev. 94:909–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bai YD, Yang YR, Mu XP, Lin G, Wang YP,
Jin S, Chen Y, Wang MJ and Zhu YC: Hydrogen sulfide alleviates
acute myocardial ischemia injury by modulating autophagy and
inflammation response under oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:34028092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsutsui H, Kinugawa S and Matsushima S:
Oxidative stress and heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 301:H2181–H2190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van der Pol A, van Gilst WH, Voors AA and
van der Meer P: Treating oxidative stress in heart failure: Past,
present and future. Eur J Heart Fail. 21:425–435. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li X, Fang P, Mai J, Choi ET, Wang H and
Yang XF: Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel
therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. J Hematol Oncol.
6:192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Briston T, Selwood DL, Szabadkai G and
Duchen MR: Mitochondrial permeability transition: A molecular
lesion with multiple drug targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 40:50–70.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bauer TM and Murphy E: Role of
mitochondrial calcium and the permeability transition pore in
regulating cell death. Circ Res. 126:280–293. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kwong JQ and Molkentin JD: Physiological
and pathological roles of the mitochondrial permeability transition
pore in the heart. Cell Metab. 21:206–214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li HW and Xiao FY: Effect of hydrogen
sulfide on cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats with myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via the JNK signaling pathway. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:2054–2061. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ong S, Samangouei P, Kalkhoran SB and
Hausenloy DJ: The mitochondrial permeability transition pore and
its role in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 78:23–34. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M,
Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B and Sadoshima J: Distinct roles of
autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: Roles of
AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy.
Circ Res. 100:914–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Loos B, Genade S, Ellis B, Lochner A and
Engelbrecht AM: At the core of survival: Autophagy delays the onset
of both apoptotic and necrotic cell death in a model of ischemic
cell injury. Exp Cell Res. 317:1437–1453. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: New directions
for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury:
Targeting the Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinase (RISK)-pathway.
Cardiovasc Res. 61:448–460. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Reperfusion
injury salvage kinase signalling: Taking a RISK for
cardioprotection. Heart Fail Rev. 12:217–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peake BF, Nicholson CK, Lambert JP, Hood
RL, Amin H, Amin S and Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide preconditions
the db/db diabetic mouse heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury
by activating Nrf2 signaling in an Erk-dependent manner. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H1215–H1224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao X, Ding L, Xie ZZ, Yang Y, Whiteman M,
Moore PK and Bian JS: A review of hydrogen sulfide synthesis,
metabolism, and measurement: Is modulation of hydrogen sulfide a
novel therapeutic for cancer? Antioxid Redox Signal. 31:1–38. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bełtowski J and Jamroz-Wiśniewska A:
Hydrogen sulfide and endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation.
Molecules. 19:21183–21199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Panthi S, Chung HJ, Jung J and Jeong NY:
Physiological importance of hydrogen sulfide: Emerging potent
neuroprotector and neuromodulator. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:90497822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wilinski B, Wilinski J, Somogyi E,
Goralska M and Piotrowska J: Paracetamol (acetaminophen) decreases
hydrogen sulfide tissue concentration in brain but increases it in
the heart, liver and kidney in mice. Folia Biol (Krakow). 59:41–44.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wilinski B, Wilinski J, Somogyi E,
Goralska M and Piotrowska J: Ramipril affects hydrogen sulfide
generation in mouse liver and kidney. Folia Biol (Krakow).
58:177–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wilinski J, Wilinski B, Somogyi E,
Piotrowska J, Kameczura T and Zygmunt M: Nicotine affects hydrogen
sulfide concentrations in mouse kidney and heart but not in brain
and liver tissues. Folia Med Cracov. 57:55–64. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tan B, Jin S, Sun J, Gu Z, Sun X, Zhu Y,
Huo K, Cao Z, Yang P, Xin X, et al: New method for quantification
of gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide in biological matrices by
LC-MS/MS. Sci Rep. 7:462782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu D, Hu Q and Zhu YZ; Therapeutic
application of hydrogen sulfide donors, : The potential and
challenges. Front Med. 10:18–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pei J, Wang F, Pei S, Bai R, Cong X, Nie Y
and Chen X: Hydrogen sulfide promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation
and heart regeneration via ROS scavenging. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020:14126962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng A, Ling C, Xin-duo L, Bing W, San-Wu
W, Yu Z, Yu-Lan H and You-En Z: Hydrogen sulfide protects human
cardiac fibroblasts against H2O2-induced
injury through regulating autophagy-related proteins. Cell
Transplant. 27:1222–1234. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang Z, Dong X, Zhuang X, Hu X, Wang L
and Liao X: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against high
glucose-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity in H9c2 cardiac
cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:4911–4917. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan C, Hou HT, Chen HX, Wang J, Wang ZQ,
Chen TN, Novakovic A, Marinko M, Yang Q, Liu ZG, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide-mediated endothelial function and the interaction with eNOS
and PDE5A activity in human internal mammary arteries. J Int Med
Res. 47:3778–3791. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang GG and Li W: Hydrogen sulfide
improves vessel formation of the ischemic adductor muscle and wound
healing in diabetic db/db mice. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 22:1192–1197.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang CN, Liu YJ, Duan GL, Zhao W, Li XH,
Zhu XY and Ni X: CBS and CSE are critical for maintenance of
mitochondrial function and glucocorticoid production in adrenal
cortex. Antioxid Redox Signal. 21:2192–2207. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li L, Whiteman M, Guan YY, Neo KL, Cheng
Y, Lee SW, Zhao Y, Baskar R, Tan CH and Moore PK: Characterization
of a novel, water-soluble hydrogen sulfide-releasing molecule
(GYY4137): New insights into the biology of hydrogen sulfide.
Circulation. 117:2351–2360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Castelblanco M, Lugrin J, Ehirchiou D,
Nasi S, Ishii I, So A, Martinon F and Busso N: Hydrogen sulfide
inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and reduces cytokine
production both in vitro and in a mouse model of inflammation. J
Biol Chem. 293:2546–2557. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qiu Y, Wu Y, Meng M, Luo M, Zhao H, Sun H
and Gao S: GYY4137 protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury via activation of the PHLPP-1/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway in
diabetic mice. J Surg Res. 225:29–39. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang H, Mao Y, Tan B, Luo S and Zhu Y: The
protective effects of endogenous hydrogen sulfide modulator,
S-propargyl-cysteine, on high glucose-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes: A novel mechanism mediated by the activation of
Nrf2. Eur J Pharmacol. 761:135–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qian X, Li X, Ma F, Luo S, Ge R and Zhu Y:
Novel hydrogen sulfide-releasing compound, S-propargyl-cysteine,
prevents STZ-induced diabetic nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 473:931–938. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kan J, Guo W, Huang C, Bao G, Zhu Y and
Zhu YZ: S-propargyl-cysteine, a novel water-soluble modulator of
endogenous hydrogen sulfide, promotes angiogenesis through
activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:2303–2316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao FL, Fang F, Qiao PF, Yan N, Gao D and
Yan Y: AP39, a mitochondria-targeted hydrogen sulfide donor,
supports cellular bioenergetics and protects against Alzheimer's
disease by preserving mitochondrial function in APP/PS1 mice and
neurons. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:83607382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Szczesny B, Módis K, Yanagi K, Coletta C,
Le Trionnaire S, Perry A, Wood ME, Whiteman M and Szabo C: AP39, a
novel mitochondria-targeted hydrogen sulfide donor, stimulates
cellular bioenergetics, exerts cytoprotective effects and protects
against the loss of mitochondrial DNA integrity in oxidatively
stressed endothelial cells in vitro. Nitric Oxide. 41:120–130.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chao C, Zatarain JR, Ding Y, Coletta C,
Mrazek AA, Druzhyna N, Johnson P, Chen H, Hellmich JL,
Asimakopoulou A, et al: Cystathionine-beta-synthase inhibition for
colon cancer: Enhancement of the efficacy of aminooxyacetic acid
via the prodrug approach. Mol Med. 22:361–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lilyanna S, Peh MT, Liew OW, Wang P, Moore
PK, Richards AM and Martinez EC: GYY4137 attenuates remodeling,
preserves cardiac function and modulates the natriuretic peptide
response to ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 87:27–37. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhou X, Tang S, Hu K, Zhang Z, Liu P, Luo
Y, Kang J and Xu L: DL-Propargylglycine protects against myocardial
injury induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia through inhibition
of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Sleep Breath. 22:853–863. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Szabo C, Ransy C, Modis K, Andriamihaja M,
Murghes B, Coletta C, Olah G, Yanagi K and Bouillaud F: Regulation
of mitochondrial bioenergetic function by hydrogen sulfide. Part I.
Biochemical and physiological mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol.
171:2099–2122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xie L, Gu Y, Wen M, Zhao S, Wang W, Ma Y,
Meng G, Han Y, Wang Y, Liu G, et al: Hydrogen sulfide induces Keap1
S-sulfhydration and suppresses diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis
via Nrf2 activation. Diabetes. 65:3171–3184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Meng G, Liu J, Liu S, Song Q, Liu L, Xie
L, Han Y and Ji Y: Hydrogen sulfide pretreatment improves
mitochondrial function in myocardial hypertrophy via a
SIRT3-dependent manner. Br J Pharmacol. 175:1126–1145. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sun Y, Lu F, Yu X, Wang B, Chen J, Lu F,
Peng S, Sun X, Yu M, Chen H, et al: Exogenous H2S
promoted USP8 sulfhydration to regulate mitophagy in the hearts of
db/db mice. Aging Dis. 11:269–285. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yu M, Du H, Wang B, Chen J, Lu F, Peng S,
Sun Y, Liu N, Sun X, Shiyun D, et al: Exogenous H2S
induces Hrd1 S-sulfhydration and prevents CD36 translocation via
VAMP3 ubiquitylation in diabetic hearts. Aging Dis. 11:286–300.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kar S, Shahshahan HR, Hackfort BT, Yadav
SK, Yadav R, Kambis TN, Lefer DJ and Mishra PK: Exercise training
promotes cardiac hydrogen sulfide biosynthesis and mitigates
pyroptosis to prevent high-fat diet-induced diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Antioxidants. 8:6382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shimizu Y, Polavarapu R, Eskla KL,
Nicholson CK, Koczor CA, Wang R, Lewis W, Shiva S, Lefer DJ and
Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide regulates cardiac mitochondrial
biogenesis via the activation of AMPK. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
116:29–40. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wu T, Li H, Wu B, Zhang L, Wu SW, Wang JN
and Zhang YE: Hydrogen sulfide reduces recruitment of
CD11b+Gr-1+ cells in mice with myocardial
infarction. Cell Transplant. 26:753–764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ye P, Gu Y, Zhu YR, Chao YL, Kong XQ, Luo
J, Ren XM, Zuo GF, Zhang DM and Chen SL: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide
attenuates the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy via the FoxO1
pathway. J Cell Physiol. 233:9786–9798. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ellmers LJ, Templeton EM, Pilbrow AP,
Frampton C, Ishii I, Moore PK, Bhatia M, Richards AM and Cameron
VA: Hydrogen sulfide treatment improves post-infarct remodeling and
long-term cardiac function in CSE knockout and wild-type mice. Int
J Mol Sci. 21:42842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sun X, Zhao D, Lu F, Peng S, Yu M, Liu N,
Sun Y, Du H, Wang B, Chen J, et al: Hydrogen sulfide regulates
muscle RING finger-1 protein S-sulfhydration at Cys44 to
prevent cardiac structural damage in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Br J
Pharmacol. 177:836–856. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Meng G, Xiao Y, Ma Y, Tang X, Xie L, Liu
J, Gu Y, Yu Y, Park CM, Xian M, et al: Hydrogen sulfide regulates
krüppel-like factor 5 transcription activity via specificity
protein 1 s-sulfhydration at Cys664 to prevent myocardial
hypertrophy. J Am Heart Assoc. 5:e0041602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yu W, Liao Y, Huang Y, Chen SY, Sun Y, Sun
C, Wu Y, Tang C, Du J and Jin H: Endogenous hydrogen sulfide
enhances carotid sinus baroreceptor sensitivity by activating the
transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V Member 1
(TRPV1) Channel. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:e0049712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jin S, Teng X, Xiao L, Xue H, Guo Q, Duan
X, Chen Y and Wu Y: Hydrogen sulfide ameliorated L-NAME-induced
hypertensive heart disease by the Akt/eNOS/NO pathway. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 242:1831–1841. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Meng G, Zhu J, Xiao Y, Huang Z, Zhang Y,
Tang X, Xie L, Chen Y, Shao Y, Ferro A, et al: Hydrogen sulfide
donor GYY4137 protects against myocardial fibrosis. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015:6910702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Huang C, Kan J, Liu X, Ma F, Tran BH, Zou
Y, Wang S and Zhu YZ: Cardioprotective effects of a novel hydrogen
sulfide agent-controlled release formulation of
S-propargyl-cysteine on heart failure rats and molecular
mechanisms. PLoS One. 8:e692052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhong X, Wang L, Wang Y, Dong S, Leng X,
Jia J, Zhao Y, Li H, Zhang X, Xu C, et al: Exogenous hydrogen
sulfide attenuates diabetic myocardial injury through cardiac
mitochondrial protection. Mol Cell Biochem. 371:187–198. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sodha NR, Clements RT, Feng J, Liu Y,
Bianchi C, Horvath EM, Szabo C, Stahl GL and Sellke FW: Hydrogen
sulfide therapy attenuates the inflammatory response in a porcine
model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 138:977–984. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Meng G, Wang J, Xiao Y, Bai W, Xie L, Shan
L, Moore PK and Ji Y: GYY4137 protects against myocardial ischemia
and reperfusion injury by attenuating oxidative stress and
apoptosis in rats. J Biomed Res. 29:203–213. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
King AL, Polhemus DJ, Bhushan S, Otsuka H,
Kondo K, Nicholson CK, Bradley JM, Islam KN, Calvert JW, Tao YX, et
al: Hydrogen sulfide cytoprotective signaling is endothelial nitric
oxide synthase-nitric oxide dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:3182–3187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Karwi QG, Bice JS and Baxter GF: Pre- and
postconditioning the heart with hydrogen sulfide (H2S)
against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Basic Res Cardiol. 113:62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Xiong Q, Wang Z, Yu Y, Wen Y, Suguro R,
Mao Y and Zhu YZ: Hydrogen sulfide stabilizes atherosclerotic
plaques in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Pharmacol Res.
144:90–98. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sun X, Wang W, Dai J, Jin S, Huang J, Guo
C, Wang C, Pang L and Wang Y: A Long-term and slow-releasing
hydrogen sulfide donor protects against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci Rep. 7:35412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hu MZ, Zhou B, Mao HY, Sheng Q, Du B, Chen
JL, Pang QF and Ji Y: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide postconditioning
protects isolated rat hearts from ischemia/reperfusion injury
through Sirt1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Int Heart J. 57:477–482.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Karwi QG, Bornbaum J, Boengler K,
Torregrossa R, Whiteman M, Wood ME, Schulz R and Baxter GF: AP39, a
mitochondria-targeting hydrogen sulfide (H2 S) donor, protects
against myocardial reperfusion injury independently of salvage
kinase signalling. Br J Pharmacol. 174:287–301. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nandi S, Ravindran S and Kurian GA: Role
of endogenous hydrogen sulfide in cardiac mitochondrial
preservation during ischemia reperfusion injury. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:271–279. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, Doeller
JE, Kraus DW, Tao L, Jiao X, Scalia R, Kiss L, Szabo C, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:15560–15565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ji Y, Pang Q, Xu G, Wang L, Wang J and
Zeng Y: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide postconditioning protects
isolated rat hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur J
Pharmacol. 587:1–7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Testai L, Marino A, Piano I, et al: The
novel H2S-donor 4-carboxyphenyl isothiocyanate promotes
cardioprotective effects against ischemia/reperfusion injury
through activation of mitoKATP channels and reduction of oxidative
stress. Pharmacol Res. 113:290–299. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yao LL, Huang XW, Wang YG, Cao YX, Zhang
CC and Zhu YC: Hydrogen sulfide protects cardiomyocytes from
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis by preventing
GSK-3beta-dependent opening of mPTP. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 298:H1310–H1319. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lambert JP, Nicholson CK, Amin H, Amin S
and Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide provides cardioprotection against
myocardial/ischemia reperfusion injury in the diabetic state
through the activation of the RISK pathway. Med Gas Res. 4:202014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Meng W, Pei Z, Feng Y, Zhao J, Chen Y, Shi
W, Xu Q, Lin F, Sun M and Xiao K: Neglected role of hydrogen
sulfide in sulfur mustard poisoning: Keap1 S-sulfhydration and
subsequent Nrf2 pathway activation. Sci Rep. 7:94332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Calvert JW, Jha S, Gundewar S, Elrod JW,
Ramachandran A, Pattillo CB, Kevil CG and Lefer DJ: hydrogen
sulfide mediates cardioprotection through Nrf2 signaling. Circ Res.
105:365–374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tu W, Wang H, Li S, Liu Q and Sha H: The
anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE
signaling pathway in chronic diseases. Aging Dis. 10:637–651. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Gao T, Furnari F and Newton AC: PHLPP: A
phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates Akt, promotes apoptosis,
and suppresses tumor growth. Mol Cell. 18:13–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Miyamoto S, Purcell NH, Smith JM, Gao T,
Whittaker R, Huang K, Castillo R, Glembotski CC, Sussman MA, Newton
AC and Brown JH: PHLPP-1 negatively regulates Akt activity and
survival in the heart. Circ Res. 107:476–484. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ji K, Xue L, Cheng J and Bai Y:
Preconditioning of H2S inhalation protects against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury by induction of HSP70 through
PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Brain Res Bull. 121:68–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kang B, Li W, Xi W, Yi Y, Ciren Y, Shen H,
Zhang Y, Jiang H, Xiao J and Wang Z: Hydrogen sulfide protects
cardiomyocytes against apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion through
MiR-1-regulated histone deacetylase 4 pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 41:10–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Muñoz-Planillo R, Nuñez G, Franchi L and
Eigenbrod T: The inflammasome: A caspase-1-activation platform that
regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat Immunol.
10:241–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Toldo S, Das A, Mezzaroma E, Chau VQ,
Marchetti C, Durrant D, Samidurai A, Van Tassell BW, Yin C, Ockaili
RA, et al: Induction of microRNA-21 with exogenous hydrogen sulfide
attenuates myocardial ischemic and inflammatory injury in mice.
Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 7:311–320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhu WD, Xu J, Zhang M, Zhu TM, Zhang YH
and Sun K: MicroRNA-21 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury by targeting nuclear factor-κB. Exp Ther Med.
16:4616–4622. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yan X, Liu Y, Kong X, Ji J, Zhu H, Zhang
Z, Fu T, Yang J, Zhang Z, Liu F and Gu Z: MicroRNA-21-5p are
involved in apoptosis and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes
through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signal. Cytotechnology. 71:317–328. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Huang W, Tian SS, Hang PZ, Sun C, Guo J
and Du ZM: Combination of microRNA-21 and microRNA-146a attenuates
cardiac dysfunction and apoptosis during acute myocardial
infarction in mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 5:e2962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Karaskov E, Scott C, Zhang L, Teodoro T,
Ravazzola M and Volchuk A: Chronic palmitate but not oleate
exposure induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, which may contribute
to INS-1 pancreatic beta-Cell apoptosis. Endocrinology.
147:3398–3407. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ren L, Wang Q, Chen Y, Ma Y and Wang D:
Involvement of MicroRNA-133a in the protective effect of hydrogen
sulfide against ischemia/reperfusion-induced endoplasmic reticulum
stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Pharmacology. 103:1–9. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
He B, Xiao J, Ren AJ, Zhang YF, Zhang H,
Chen M, Xie B, Gao XG and Wang YW: Role of miR-1 and miR-133a in
myocardial ischemic postconditioning. J Biomed Sci. 18:222011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Dakhlallah D, Zhang J, Yu L, Marsh CB,
Angelos MG and Khan M: MicroRNA-133a engineered mesenchymal stem
cells augment cardiac function and cell survival in the infarct
heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 65:241–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Predmore BL, Kondo K, Bhushan S,
Zlatopolsky MA, King AL, Aragon JP, Grinsfelder DB, Condit ME and
Lefer DJ: The polysulfide diallyl trisulfide protects the ischemic
myocardium by preservation of endogenous hydrogen sulfide and
increasing nitric oxide bioavailability. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 302:H2410–H2418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Minamishima S, Bougaki M, Sips PY, Yu JD,
Minamishima YA, Elrod JW, Lefer DJ, Bloch KD and Ichinose F:
Hydrogen sulfide improves survival after cardiac arrest and
cardiopulmonary resuscitation via a nitric oxide synthase
3-dependent mechanism in mice. Circulation. 120:888–896. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Bibli SI, Hu J, Looso M, Weigert A, Ratiu
C, Wittig J, Drekolia MK, Tombor L, Randriamboavonjy V, Leisegang
MS, et al: Mapping the endothelial Cell S-sulfhydrome highlights
the crucial role of integrin sulfhydration in vascular function.
Circulation. 143:935–948. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Sun J, Aponte AM, Menazza S, Gucek M,
Steenbergen C and Murphy E: Additive cardioprotection by
pharmacological postconditioning with hydrogen sulfide and nitric
oxide donors in mouse heart: S-sulfhydration vs. S-nitrosylation.
Cardiovasc Res. 110:96–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|