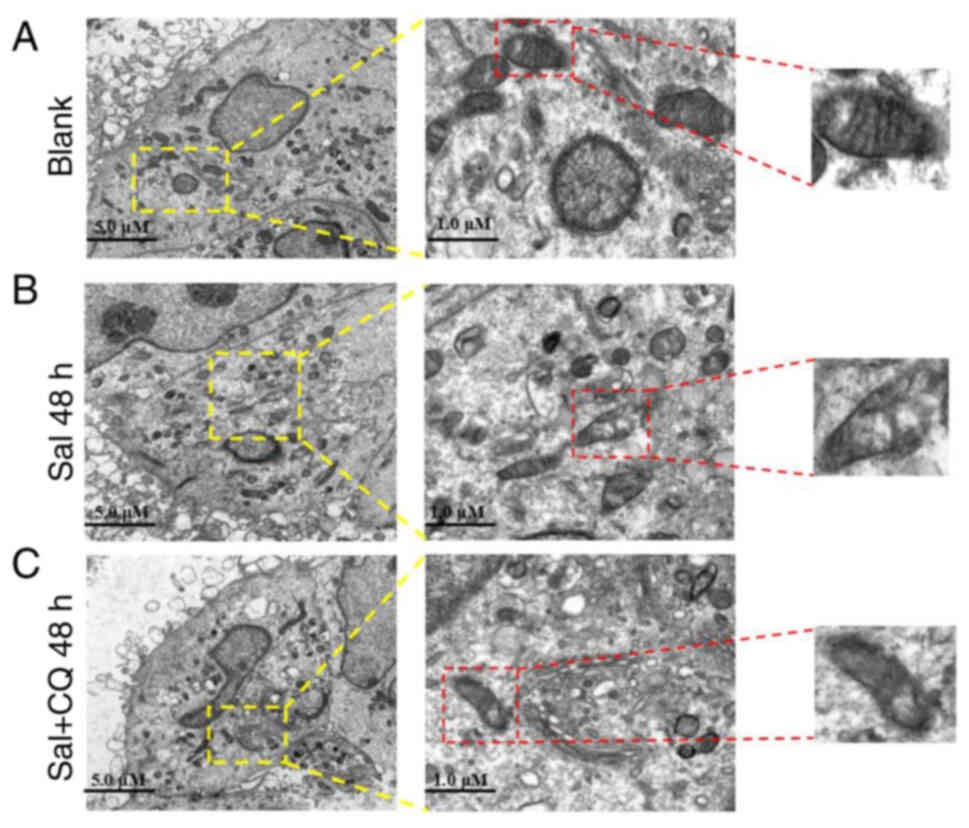
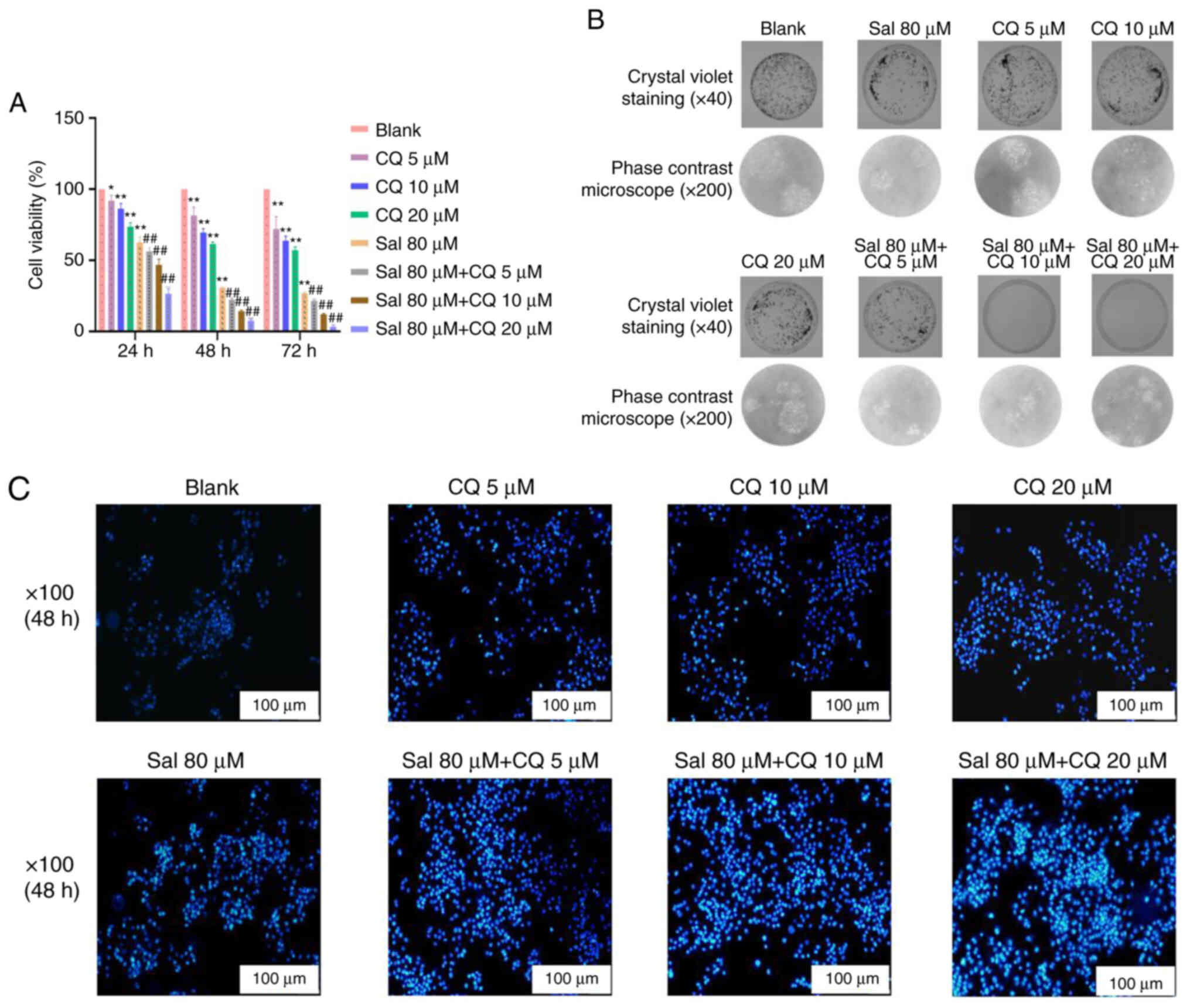
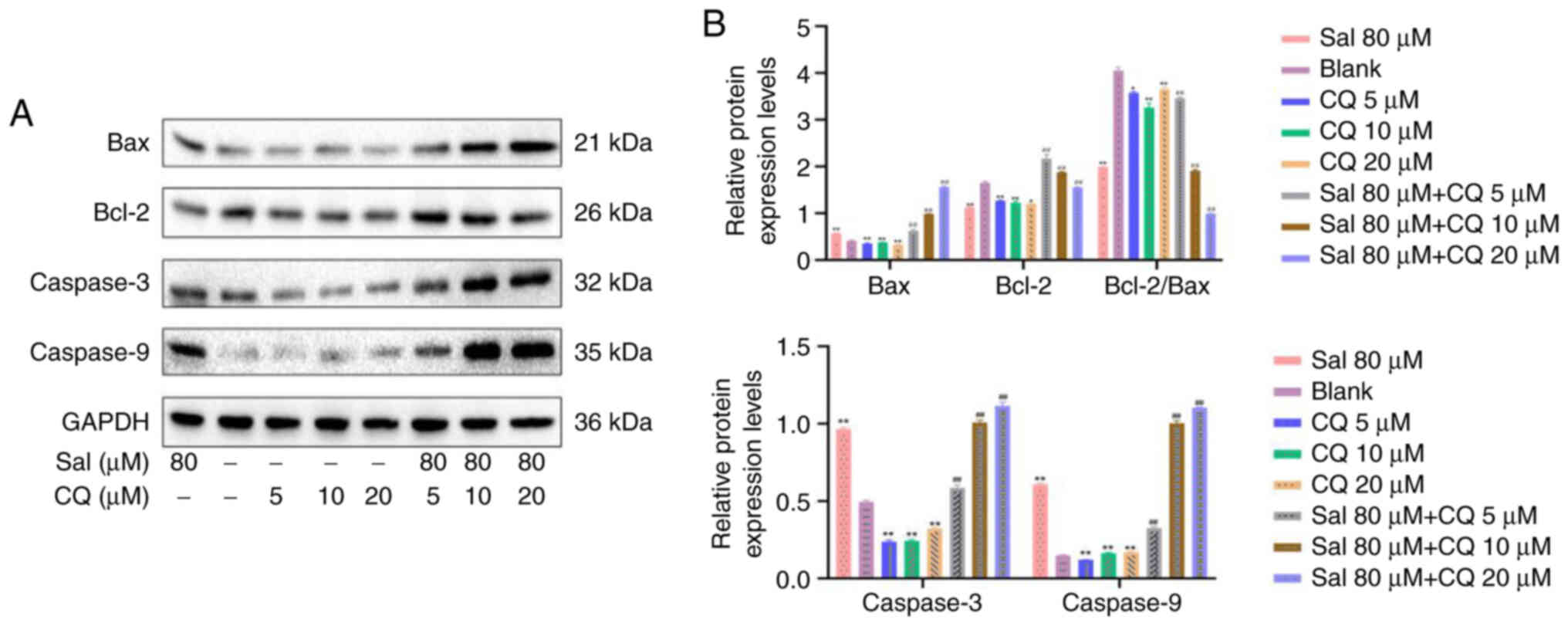
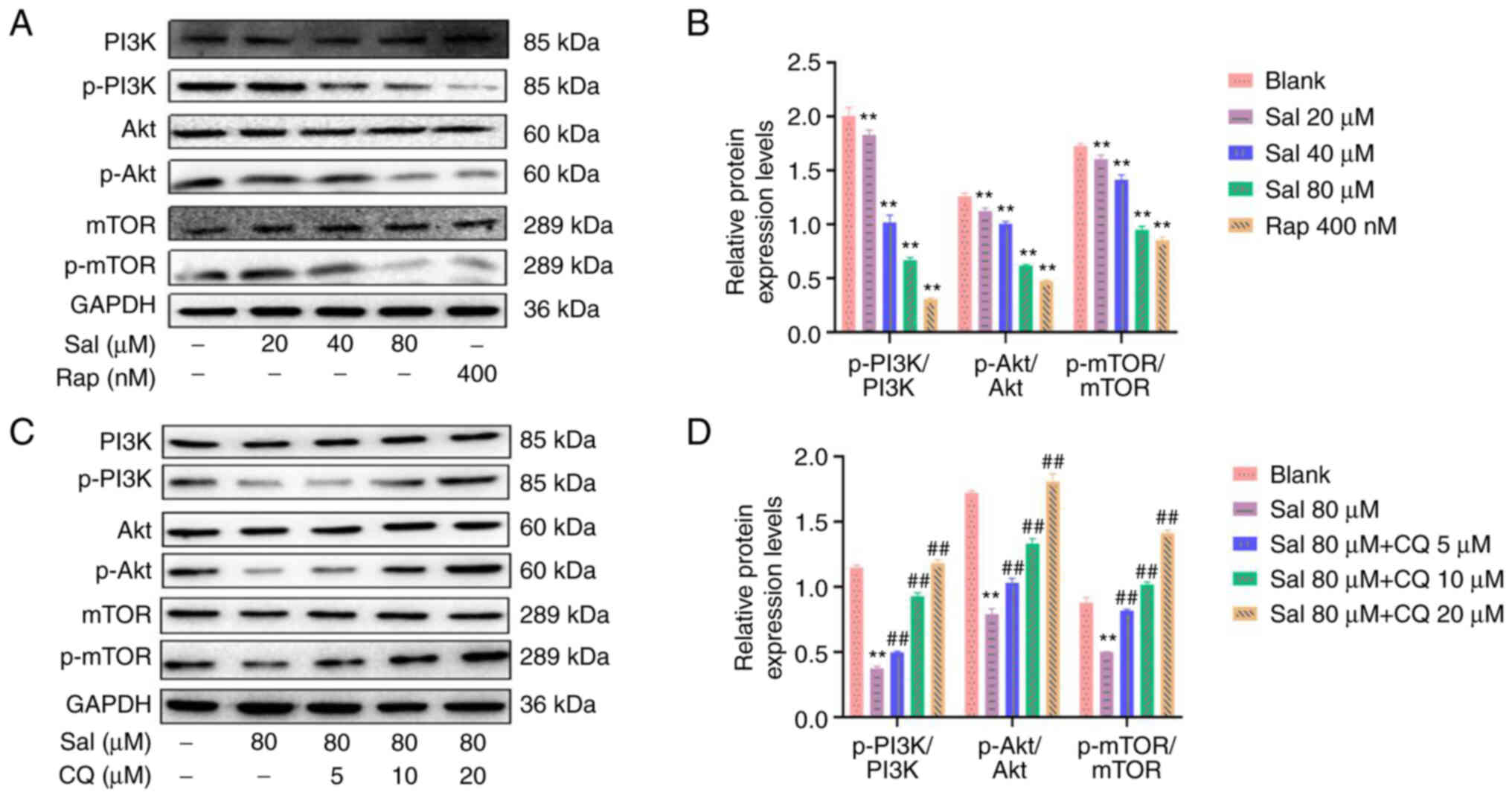
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram L,
Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A and Bray F: Cancer statistics for the
year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer. Apr 5–2021.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Keda M, Morizane C, Ueno M, Okusaka T,
Ishii H and Furuse J: Chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Current status and future perspectives. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
48:103–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kudo M: Targeted and immune therapies for
hepatocellular carcinoma: Predictions for 2019 and beyond. World J
Gastroenterol. 25:789–807. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shin JW and Chung YH: Molecular targeted
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current and future. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:6144–6155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marin JJG, Briz O, Herraez E, Lozano E,
Asensio M, Di Giacomo S, Romero MR, Osorio-Padilla LM,
Santos-Llamas AI, Serrano MA, et al: Molecular bases of the poor
response of liver cancer to chemotherapy. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 42:182–192. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qian KJ: Observation and prevention of
side effects in interventional chemotherapy for liver cancer. J
Clin Med Pract. 4:135–136. 2000.
|
|
7
|
Sun AH, Chen J and Guan HM: Reversal
effect of paeonol on multidrug resistance of liver cancer cell line
HepG2/ADM. Shandong Med J. 56:1–4. 2016.
|
|
8
|
Li W and Huang QN: Advances in studies and
applications on Rhodiola rosea L. J Cap Norm Univ. 3:55–59.
2003.
|
|
9
|
Panossin A, Wikman G and Sarris J:
Rosenroot (Rhodiola rosea): Traditional use, chemical
composition, pharmacology and clinical efficacy. Phytomedicine.
17:481–493. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Booker A, Jalil B, Frommenwiler D, Reich
E, Zhai L, Kulic Z and Heinrich M: The authenticity and quality of
Rhodiola rosea products. Phytomedicine. 23:754–762. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ruhsam M and Hollingsworth PM:
Authentication of Eleutherococcus and Rhodiola herbal supplement
products in the United Kingdom. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 149:403–409.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ming DS, Hillhouse BJ, Guns ES, Eberding
A, Xie S, Vimalanathan S and Towers GH: Bioactive compounds from
Rhodiola rosea (crassulaceae). Phytother Res. 19:740–743.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Buchwald W, Mscisz A and Krajewska-Patan
A: Contents of biologically active compounds in Rhodiola
rosea roots during the vegetation period. Res Gate.
10:1413–1416. 2006.
|
|
14
|
Chen T, Ma Z, Zhu L, Jiang W, Wei T, Zhou
R, Luo F, Zhang K, Fu Q, Ma C and Yan T: Suppressing
receptor-interacting protein 140: A new sight for salidroside to
treat cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol. 53:6240–6250. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen JJ, Yuan LG and Li DD: Research on
the anti-aging role of salidroside in naturally aged mice. Chin Med
Bio. 7:412–417. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Wang S, He H, Chen L, Zhang W, Zhang X and
Chen J: Protective effects of salidroside in the
MPTP/MPP(+)-induced model of Parkinson's disease through
ROS-NO-related mitochondrion pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 51:718–728.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng T, Yang XY, Wu D, Xing S, Bian F, Li
W, Chi J, Bai X, Wu G, Chen X, et al: Salidroside ameliorates
insulin resistance through activation of a mitochondria-associated
AMPK/PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 172:3284–3301. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Parzych KR and Klionsky DJ: An overview of
autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:460–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiang YC, Peng P, Liu XW, Jin X, Shen J,
Zhang T, Zhang L, Wan F, Ren YL, Yu QQ, et al: Paris saponin VII, a
Hippo pathway activator, induces autophagy and exhibits therapeutic
potential against human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
43:1568–1580. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ji YC, Hu WW, Jin Y, Yu H and Fang J:
Liquiritigenin exerts the anti-cancer role in oral cancer via
inducing autophagy-related apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
inhibition in vitro and in vivo. Bioengineered. 12:6070–6082. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bata N and Cosford NDP: Cell survival and
cell death at the intersection of autophagy and apoptosis:
Implications for current and future cancer therapeutics. ACS
Pharmacol Transl Sci. 4:1728–1746. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Liu CY and Wang ZY: Pseudolaric
acid B induced autophagy through DNA damage response to inhibit
apoptosis. Jilin J Chin Med. 37:381–384. 2017.
|
|
24
|
Shi Y, Han JJ, Tennakoon JB, Mehta FF,
Merchant FA, Burns AR, Howe MK, McDonnell DP and Frigo DE:
Androgens promote prostate cancer cell growth through induction of
autophagy. Mol Endocrinol. 27:280–295. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang S, Wang X, Contino G, Liesa M, Sahin
E, Ying H, Bause A, Li Y, Stommel JM, Dell'antonio G, et al:
Pancreatic cancers require autophagy for tumor growth. Genes Dev.
25:717–729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang P, Sun Y and Yao YY: Effects of
resveratrol on female reproductive system malignant tumors. J
Dalian Med Univ. 37:403–407. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Zhan XJ, Xie DZ and Hu YY: Experimental
study on anti-hepatocellular carcinoma and sensitizing effect of
matrine combined with 5-fluorouracil in vitro. Jiangxi J Trad Chin
Med. 47:42–45. 2016.
|
|
28
|
Chang MZ, Zhang SY and Hao YJ: Astragalus
polysaccharide inhibits the proliferation of esophageal cancer
EC109 cells by inducing cell autophagy. Central South Phar.
20:856–862. 2022.
|
|
29
|
Miao H, Yang JL, Zhang SQ and Yan N;
Gynecology Third Treatment Area Jilin Central Hospital, : Effects
of schisandra chinensis polysaccharides on proliferation, autophagy
and endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis of ovarian cancer SKOV3
cells. Systems Med. 6:135–137. 2021.
|
|
30
|
Mai TT, Moon J, Song Y, Viet PQ, Phuc PV,
Lee JM, Yi TH, Cho M and Cho SK: Ginsenoside F2 induces apoptosis
accompanied by protective autophagy in breast cancer stem cells.
Cancer Lett. 321:144–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Bao J, Wang K, Jia X, Zhang C,
Huang B, Chen M, Wan JB, Su H, Wang Y and He C: Pulsatilla saponin
D inhibits autophagic flux and synergistically enhances the
anticancer activity of chemotherapeutic agents against HeLa cells.
Am J Chin Med. 43:1657–1670. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Li JZ, Lu AX, Zhang KF and Li BJ:
Anticancer effect of salidroside on A549 lung cancer cells through
inhibition of oxidative stress and phospho-p38 expression. Oncol
Lett. 7:1159–1164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rong L, Li Z, Leng X, Li H, Ma Y, Chen Y
and Song F: Salidroside induces apoptosis and protective autophagy
in human gastric cancer AGS cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 122:1097262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang B, Yang T and Feng LF: Salidroside
induces the autophagy of 97H cells. Gansu Med J. 41:193–197.
2022.
|
|
35
|
Lu L, Liu S, Dong Q and Xin Y: Salidroside
suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inhibiting the activation of the Notch1 signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 19:4964–4972. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pan WY, Zhu XD, Zhao W, Qu S, Li L, Su F
and Li XY: The effects of chloroquine diphosphate and rapamycin at
different concentration on autophagy of CNE-2 cells. Chin J Oncol
Prev Treat. 3:280–283. 2011.
|
|
37
|
Zhang XY, Zhang YJ and Zhong Y: Research
progress of mitochondrial dynamics disorder in cancer. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 28:1219–1223. 2022.
|
|
38
|
DeVorkin L and Gorski SM: A
mitochondrial-associated link between an effector caspase and
autophagic flux. Autophagy. 10:1866–1867. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kroemer G and Levine B: Autophagic cell
death: The story of a misnomer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:1004–1010.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mariño G, Niso-Santano M, Baehrecke EH and
Kroemer G: Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and
apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:81–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fimia GM and Piacentini M: Regulation of
autophagy in mammals and its interplay with apoptosis. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 67:1581–1588. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Subramani R, Gonzalez E, Arumugam A, Nandy
S, Gonzalez V, Medel J, Camacho F, Ortega A, Bonkoungou S, Narayan
M, et al: Nimbolide inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and
metastasis through ROS-mediated apoptosis and inhibition of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Sci Rep. 6:198192016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang PD, Zhao YL, Deng XQ, Mao YQ, Shi W,
Tang QQ, Li ZG, Zheng YZ, Yang SY and Wei YQ: Antitumor and
antimetastatic activities of chloroquine diphosphate in a murine
model of breast cancer. Biomed Phaemacother. 64:609–614. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sasaki K, Tsuno N, Sunami E, Tsurita G,
Okaji Y, Nishikawa T, Syuno Y, Hongo K, Kitayama J, Takahashi K and
Nagawa H: Abstract #383: Potentiation of pro-apoptotic effect of
5-fluorouracil on HT29 colon cancer cells by inhibition of
autophagy. Cancer Res. 69 (Suppl 9):S3832009.
|
|
45
|
Fan C, Wang W, Zhao B, Zhang S and Miao J:
Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549
lung cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 14:3218–3222. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hao X and Li W: Chloroquine diphosphate
suppresses liver cancer via inducing apoptosis in Wistar rats using
interventional therapy. Oncol Lett. 21:2332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou KJ, Wang C and Xie MY: Effect of
chloroquine on tumor growth in mice with hepatic carcinoma and its
mechanism. Anhui Med J. 39:1167–1170. 2018.
|
|
48
|
Wang ZB, Wang J and Wang L:
Ultrastructural analysis of autophagosome. J Nanjing Med Uni (Nat
Sci). 36:426–429. 2016.
|
|
49
|
Zhang BN, Ye DY and Zhang DG: Application
of laser confocal scanning microscope in observing autophagy. J
Shantou Uni (Nat Sci Edi). 36:76–81. 2021.
|
|
50
|
Cui QZ, Liu BY and Li YY: Hydroxysafflor
yellow A represses Ang II-induced migration through activation of
autophagy in VAFs. Chin Phar Bull. 37:1680–1687. 2021.
|
|
51
|
Wang YW and Hou JS: Function of autophagy
gene Beclin 1 in tumor and its relationship with oral cancer. Chin
J Pra Stom. 4:374–376. 2011.
|
|
52
|
Li BX, Li CY and Peng R: Expression of
beclin-1, an autophagy-related protein, in stage IIIB colon cancer
and its relationship with prognosis. Chin J Clin Onc. 36:146–149.
2009.
|
|
53
|
Zhang Q, Su H, Ranek MJ and Wang X:
Autophagy and p62 in cardiac proteinopathy. Circ Res. 109:296–308.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li XY, Zhao WD and Zhou Y: Expression of
autophagy marker protein p62 in cervical squamous cell cancer and
its clinical significance. Chin J Clin Exp Path. 30:38–41.
2014.
|
|
55
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yamamoto A,
Oshitani-Okamoto S, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, GABARAP and
GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II
formation. J Cell Sci. 117:2805–2812. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shen Y, Liang LZ, Hong MH, Xiong Y, Wei M
and Zhu XF: Expression and clinical significance of
microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) and Beclin1 in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Ai Zheng. 27:595–599. 2008.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Fan XJ, Wang Y, Wang L and Zhu M:
Salidroside induces apoptosis and autophagy in human colorectal
cancer cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol
Rep. 36:3559–3567. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ding SY, Wang MT, Dai DF, Peng JL and Wu
WL: Salidroside induces apoptosis and triggers endoplasmic
reticulum stress in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 527:1057–1063. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Esteban-Martínez L and Boya P: Autophagic
flux determination in vivo and ex vivo. Methods. 75:79–86. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zamzami N and Kroemer G: The mitochondrion
in apoptosis: How Pandora's box opens? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:67–71. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen AWG, Tseng YS, Lin CC, His YT, Lo YS,
Chuang YC, Lin SH, Yu CY, Hsieh MJ and Chen MK: Norcantharidin
induce apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma through caspase
and mitochondrial pathway. Environ Toxicol. 33:343–350. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Snigdha S, Smith ED, Prieto GA and Cotman
CW: Caspase-3 activation as a bifurcation point between plasticity
and cell death. Neurosci Bull. 28:14–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS and Liang J:
Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 37:719–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Noorolyai S, Shajari N, Baghbani E,
Sadreddini S and Baradaran B: The relation between PI3K/AKT
signalling pathway and cancer. Gene. 698:120–128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xu C, Sun G, Yuan G, Wang R and Sun X:
Effects of platycodin D on proliferation, apoptosis and PI3K/Akt
signal pathway of human glioma U251 cells. Molecules.
19:21411–21423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen LY and Liu Y: Quercitrin promotes
apoptosis of gastric cancer cell line SGC7901 by inhibiting
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Chin J Pathophysiol. 34:1976–1980.
2018.
|
|
67
|
Fu WW, Ou YY and Huang CY: Research
progress in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases based on mTOR
regulating autophagy. J Hainan Med Univ. 27:635–640. 2021.
|
|
68
|
Kim KY, Park KI, Kim SH, Yu SN, Park SG,
Kim YW, Seo YK, Ma JY and Ahn SC: Inhibition of autophagy promotes
salinomycin-induced apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mediated
PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK/p38 MAPK-dependent signaling in human
prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:10882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|