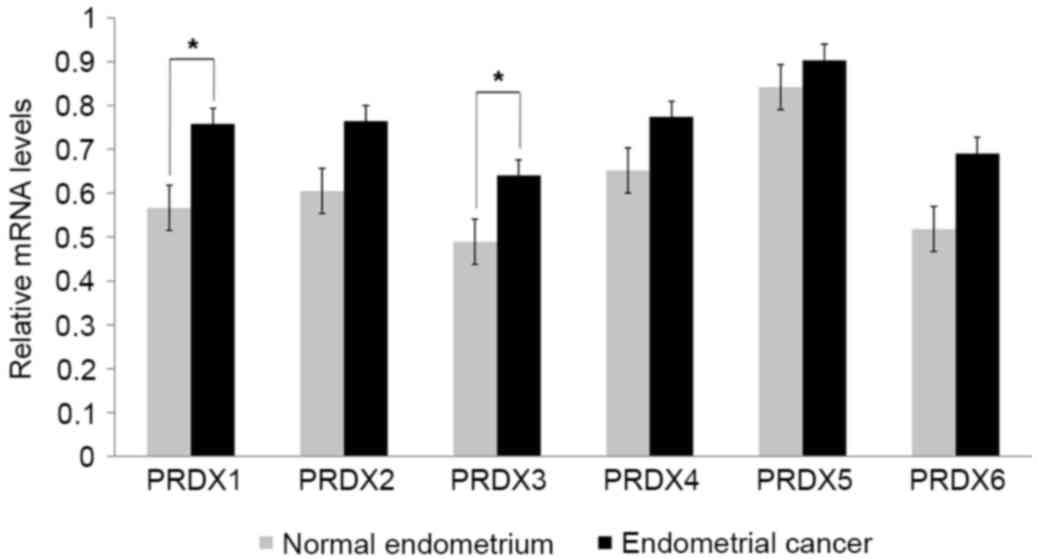
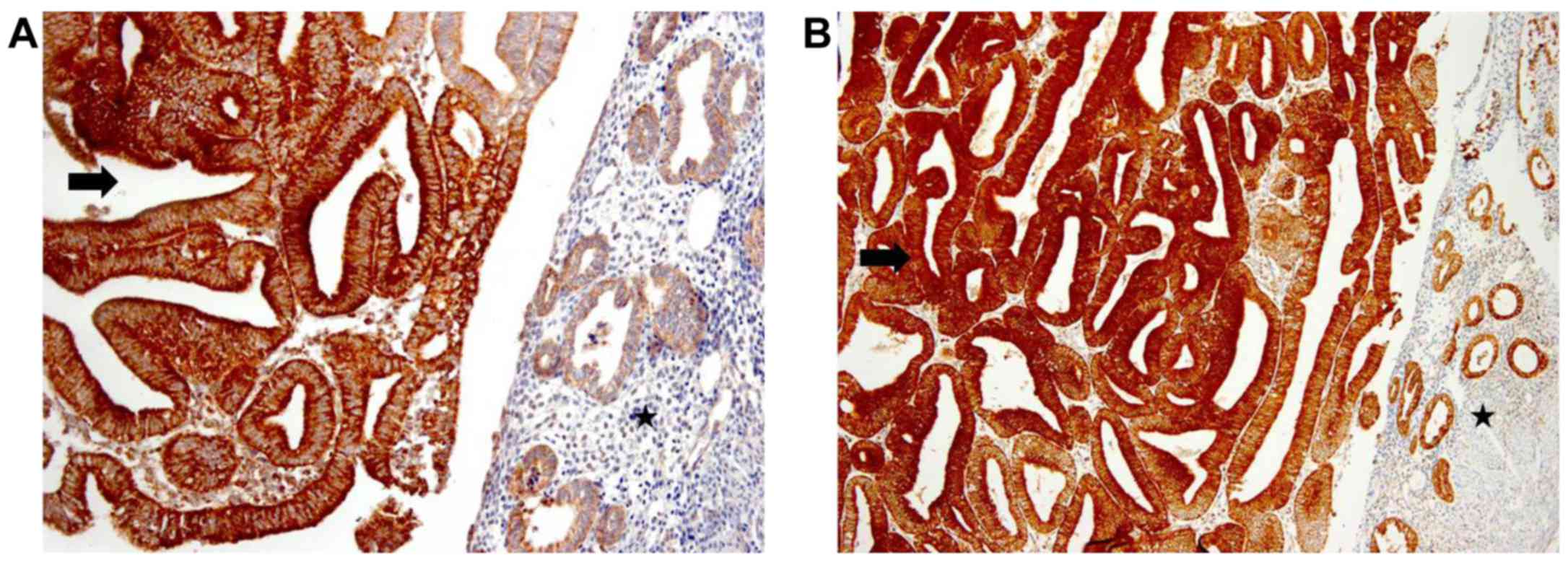
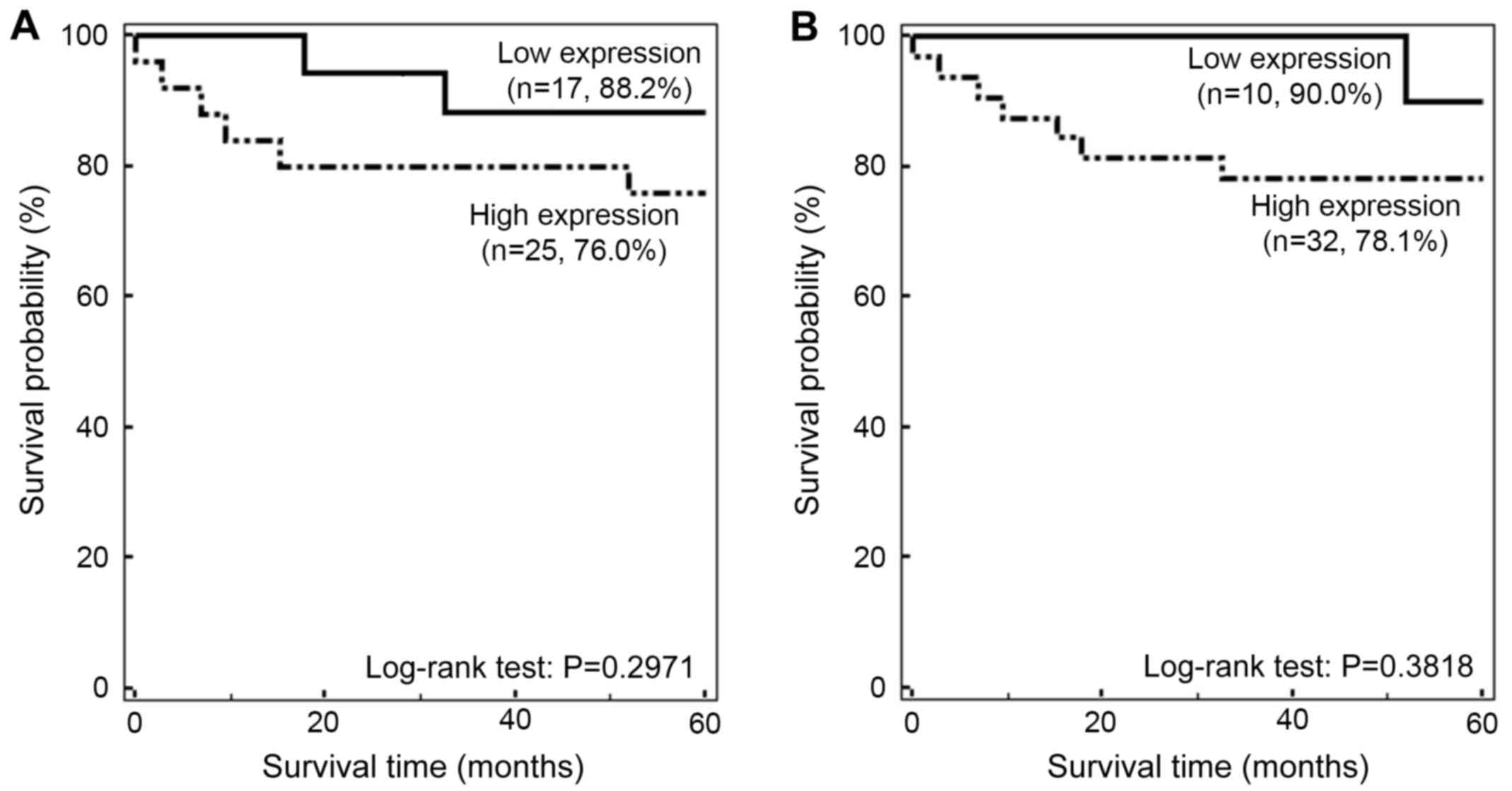
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Evans T, Sany O, Pearmain P, Ganesan R,
Blann A and Sundar S: Differential trends in the rising incidence
of endometrial cancer by type: Data from a UK population-based
registry from 1994 to 2006. Br J Cancer. 104:1505–1510. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fei LY: Fast Stats: An interactive tool
for access to SEER cancer statistics. Surveillance Research
Program, National Cancer Institute; http://seer.cancer.gov/faststatsFebruary
2–2013
|
|
4
|
Smith-Bindman R, Kerlikowske K, Feldstein
VA, Subak L, Scheidler J, Segal M, Brand R and Grady D: Endovaginal
ultrasound to exclude endometrial cancer and other endometrial
abnormalities. JAMA. 280:1510–1517. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Committee on Practice
Bulletins-Gynecology, . Practice bulletin no. 128: Diagnosis of
abnormal uterine bleeding in reproductive-aged women. Obstet
Gynecol. 120:197–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berek JS: Novak's Gynecology. 13th.
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2002
|
|
7
|
Ueda Y, Enomoto T and Kimura T, Miyatake
T, Yoshino K, Fujita M and Kimura T: Serum biomarkers for early
detection of gynecologic cancers. Cancers (Basel). 2:1312–1327.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gadducci A, Cosio S and Genazzani AR:
Tissue and serum biomarkers as prognostic variables in
endometrioid-type endometrial cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
80:181–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hakala A, Kacinski BM, Stanley ER, Kohorn
EI, Puistola U, Risteli J, Risteli L, Tomás C and Kauppila A:
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1, a clinically useful tumor
marker in endometrial adenocarcinoma: comparison with CA 125 and
the aminoterminal propeptide of type III procollagen. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 173:112–119. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takeshima N, Shimizu Y, Umezawa S, Hirai
Y, Chen JT, Fujimoto I, Yamauchi K and Hasumi K: Combined assay of
serum levels of CA125 and CA19-9 in endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol
Oncol. 54:321–326. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baser E, Gungor T, Togrul C, Turkoglu O
and Celen S: Preoperative prediction of poor prognostic parameters
and adjuvant treatment in women with pure endometrioid type
endometrial cancer: What is the significance of tumor markers? Eur
J Gynaecol Oncol. 35:513–518. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yasa C, Takmaz O, Dural O and Akhan SE:
The value of tumor markers in endometrial carcinoma: Review of
literature. Sci Res. 4:966–970. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Price FV, Chambers SK, Carcangiu ML,
Kohorn EI, Schwartz PE and Chambers JT: CA 125 may not reflect
disease status in patients with uterine serous carcinoma. Cancer.
82:1720–1725. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim K, Kim I, Lee KY, Rhee S and Stadtman
E: The isolation and purification of a specific ‘protector’ protein
which inhibits enzyme inactivation by a thiol/Fe (III)/O2
mixed-function oxidation system. J Biol Chem. 263:4704–4711.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rhee SG: Cell signaling. H2O2, a necessary
evil for cell signaling. Scienc e. 312:1882–1883. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Hall A, Nelson K, Poole LB and Karplus PA:
Structure-based insights into the catalytic power and
conformational dexterity of peroxiredoxins. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:795–815. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Neumann CA, Cao J and Manevich Y:
Peroxiredoxin 1 and its role in cell signaling. Cell Cycle.
8:4072–4078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mu ZM, Yin XY and Prochownik EV: Pag, a
putative tumor suppressor, interacts with the Myc Box II domain of
c-Myc and selectively alters its biological function and target
gene expression. J Biol Chem. 277:43175–43184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yo YD, Chung YM, Park JK, Ahn CM, Kim SK
and Kim HJ: Synergistic effect of peroxiredoxin II antisense on
cisplatin-induced cell death. Exp Mol Med. 34:273–277. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Okoh V, Deoraj A and Roy D:
Estrogen-induced reactive oxygen species-mediated signalings
contribute to breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1815:115–133.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Felty Q, Xiong WC, Sun D, Sarkar S, Singh
KP, Parkash J and Roy D: Estrogen-induced mitochondrial reactive
oxygen species as signal-transducing messengers. Biochemistry.
44:6900–6909. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Musarrat J, Arezina-Wilson J and Wani A:
Prognostic and aetiological relevance of 8-hydroxyguanosine in
human breast carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer. 32A:1–1214. 1996.
|
|
23
|
O'Leary PC, Terrile M, Bajor M, Gaj P,
Hennessy BT, Mills GB, Zagozdzon A, O'Connor DP, Brennan DJ, Connor
K, et al: Peroxiredoxin-1 protects estrogen receptor alpha from
oxidative stress-induced suppression and is a protein biomarker of
favorable prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
16:R792014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Karihtala P, Kauppila S, Soini Y and
Arja-Jukkola-Vuorinen: Oxidative stress and counteracting
mechanisms in hormone receptor positive, triple-negative and
basal-like breast carcinomas. BMC Cancer. 11:2622011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elamin A, Zhu H, Hassan AM, Xu N and
Ibrahim ME: Peroxiredoxin V: A candidate breast tumor marker of
population specificity. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:541–549. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pecorelli S: Revised FIGO staging for
carcinoma of the vulva, cervix, and endometrium. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 105:103–104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han S, Shen H, Jung M, Hahn BS, Jin BK,
Kang I, Ha J and Choe W: Expression and prognostic significance of
human peroxiredoxin isoforms in endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett.
3:1275–1279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rhee SG, Chae HZ and Kim K:
Peroxiredoxins: A historical overview and speculative preview of
novel mechanisms and emerging concepts in cell signaling. Free
Radic Biol Med. 38:1543–1552. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wonsey DR, Zeller KI and Dang CV: The
c-Myc target gene PRDX3 is required for mitochondrial homeostasis
and neoplastic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:pp.
6649–6654. 2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Knoops B, Clippe A, Bogard C, Arsalane K,
Wattiez R, Hermans C, Duconseille E, Falmagne P and Bernard A:
Cloning and characterization of AOEB166, a novel mammalian
antioxidant enzyme of the peroxiredoxin family. J Biol Chem.
274:30451–30458. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Whitaker HC, Patel D, Howat WJ, Warren AY,
Kay JD, Sangan T, Marioni JC, Mitchell J, Aldridge S, Luxton HJ, et
al: Peroxiredoxin-3 is overexpressed in prostate cancer and
promotes cancer cell survival by protecting cells from oxidative
stress. Br J Cancer. 109:983–993. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kinnula VL, Lehtonen S, Sormunen R,
Kaarteenaho-Wiik R, Kang SW, Rhee SG and Soini Y: Overexpression of
peroxiredoxins I, II, III, V, and VI in malignant mesothelioma. J
Pathol. 196:316–323. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Noh DY, Ahn SJ, Lee RA, Kim SW, Park IA
and Chae HZ: Overexpression of peroxiredoxin in human breast
cancer. Anticancer Res. 21:2085–2090. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choi JH, Kim TN, Kim S, Baek SH, Kim JH,
Lee SR and Kim JR: Overexpression of mitochondrial thioredoxin
reductase and peroxiredoxin III in hepatocellular carcinomas.
Anticancer Res. 22:3331–3335. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nonn L, Berggren M and Powis G: Increased
expression of mitochondrial peroxiredoxin-3 (Thioredoxin
Peroxidase-2) protects cancer cells against hypoxia and
drug-induced hydrogen peroxide-dependent. Mol Cancer Res.
1:682–689. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kropotov A, Gogvadze V, Shupliakov O,
Tomilin N, Serikov VB, Tomilin NV and Zhivotovsky B: Peroxiredoxin
V is essential for protection against apoptosis in human lung
carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 312:2806–2815. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song IS, Kim HK, Jeong SH, Lee SR, Kim N,
Rhee BD, Ko KS and Han J: Mitochondrial peroxiredoxin III is a
potential target for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 12:7163–7185.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Riddell JR, Wang XY, Minderman H and
Gollnick SO: Peroxiredoxin 1 stimulates secretion of
proinflammatory cytokines by binding to TLR4. J Immunol.
184:1022–1030. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Creasman WT, Odicino F, Maisonneuve P,
Quinn MA, Beller U, Benedet JL, Heintz AP, Ngan HY and Pecorelli S:
Carcinoma of the corpus uteri. FIGO 26th annual report on the
results of treatment in gynecological cancer. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 95 Suppl 1:S105–S143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|