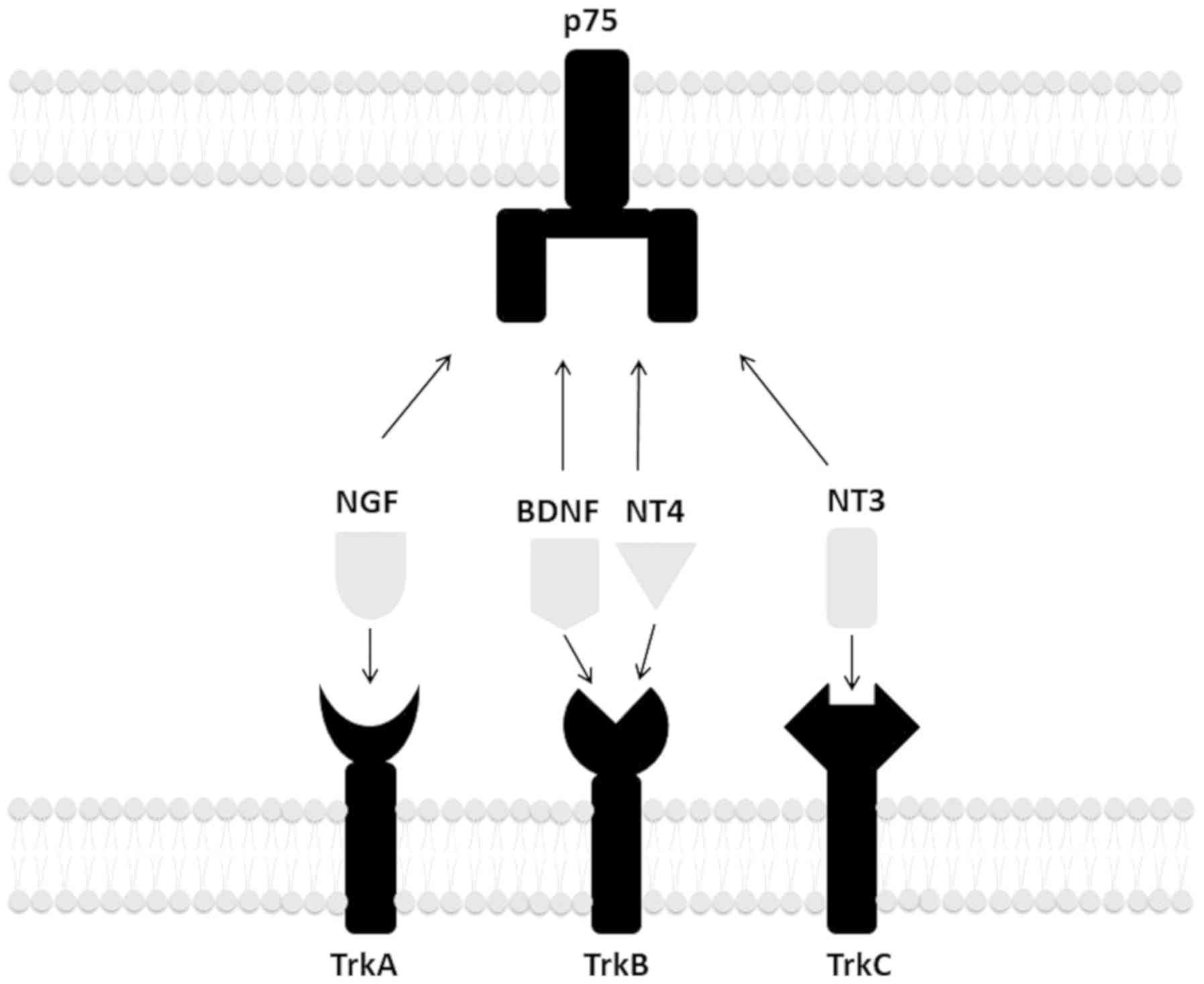
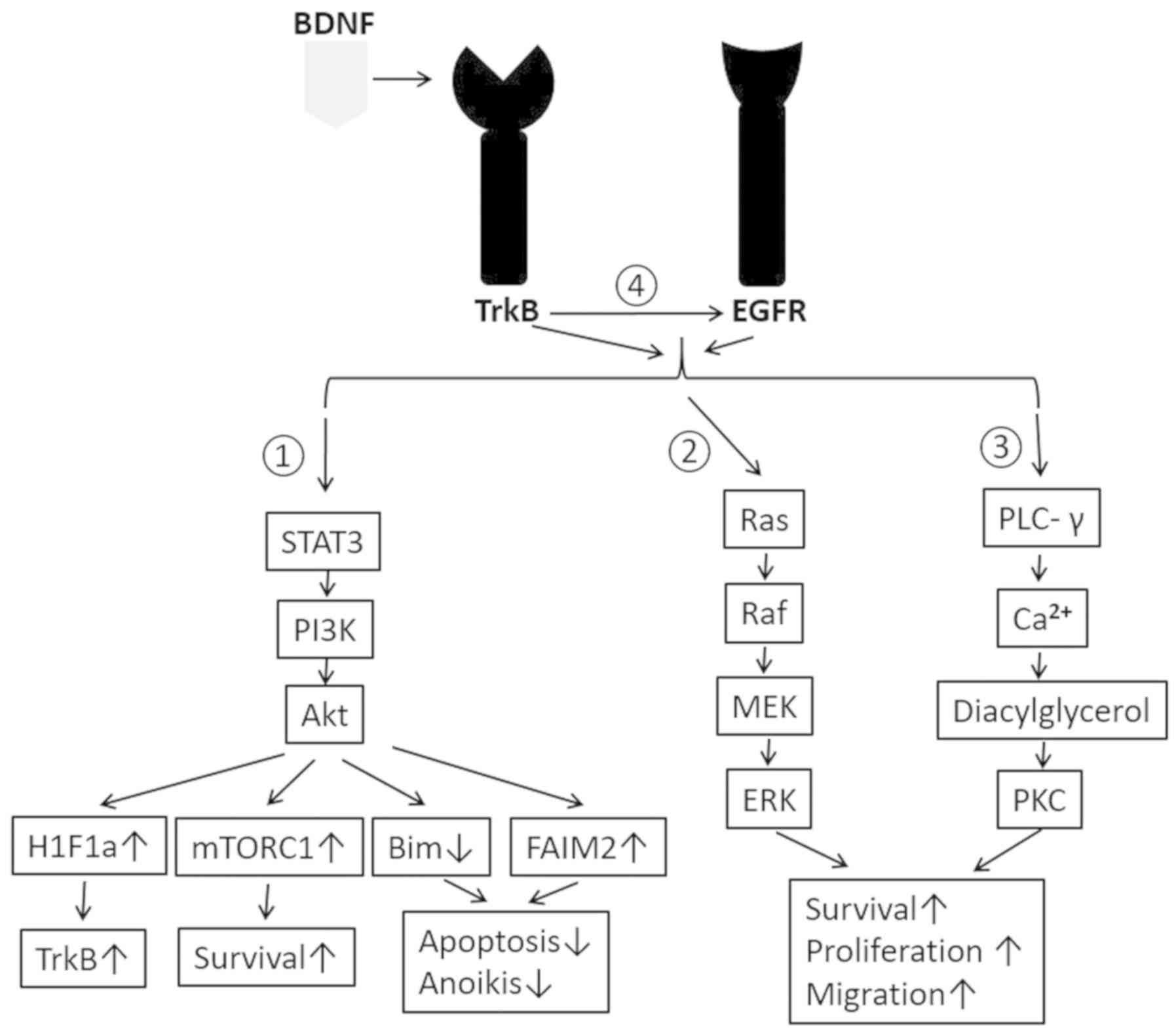
|
1
|
Bibel M and Barde YA: Neurotrophins: Key
regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous
system. Genes Dev. 14:2919–2937. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang EJ and Reichardt LF: Neurotrophins:
Roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci.
24:677–736. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meldolesi J: Neurotrophin receptors in the
pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of neurodegenerative diseases.
Pharmacol Res. 121:129–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reichardt LF: Neurotrophin-regulated
signalling pathways. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 361:1545–1564.
2006.
|
|
5
|
Meldolesi J: Neurotrophin Trk receptors:
New targets for cancer therapy. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol.
174:67–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vanhecke E, Adriaenssens E, Verbeke S,
Meignan S, Germain E, Berteaux N, Nurcombe V, Le Bourhis X and
Hondermarck H: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and
neurotrophin-4/5 are expressed in breast cancer and can be targeted
to inhibit tumor cell survival. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1741–1752.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ricci A, Graziano P, Mariotta S, Cardillo
G, Sposato B, Terzano C and Bronzetti E: Neurotrophin system
expression in human pulmonary carcinoid tumors. Growth Factors.
23:303–312. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moon A, Won KY, Lee JY, Kang I, Lee SK and
Lee J: Expression of BDNF, TrkB, and p53 in early-stage squamous
cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Pathology. 43:453–458. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brunetto de Farias C, Rosemberg DB, Heinen
TE, Koehler-Santos P, Abujamra AL, Kapczinski F, Brunetto AL,
Ashton-Prolla P, Meurer L, Reis Bogo M, et al: BDNF/TrkB content
and interaction with gastrin-releasing peptide receptor blockade in
colorectal cancer. Oncology. 79:430–439. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gilbertson RJ and Rich JN: Making a
tumour's bed: Glioblastoma stem cells and the vascular niche. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:733–736. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tanaka K, Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y,
Saigusa S, Kawamura M, Araki T, Uchida K, Mohri Y and Kusunoki M:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-induced
tropomyosin-related kinase B (Trk B) signaling is a potential
therapeutic target for peritoneal carcinomatosis arising from
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e964102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Okamura K, Harada T, Wang S, Ijichi K,
Furuyama K, Koga T, Okamoto T, Takayama K, Yano T and Nakanishi Y:
Expression of TrkB and BDNF is associated with poor prognosis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 78:100–106. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lange AM and Lo HW: Inhibiting TRK
proteins in clinical cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 10(pii):
E1052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tanaka J, Horiike Y, Matsuzaki M, Miyazaki
T, Ellis-Davies GC and Kasai H: Protein synthesis and
neurotrophin-dependent structural plasticity of single dendritic
spines. Science. 319:1683–1687. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Horch HW and Katz LC: BDNF release from
single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons. Nat
Neurosci. 5:1177–1184. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Figurov A, Pozzo-Miller LD, Olafsson P,
Wang T and Lu B: Regulation of synaptic responses to high-frequency
stimulation and LTP by neurotrophins in the hippocampus. Nature.
381:706–709. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu B, Goulding EH, Zang K, Cepoi D, Cone
RD, Jones KR, Tecott LH and Reichardt LF: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of
melanocortin-4 receptor. Nat Neurosci. 6:736–742. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao L, Lin EJ, Cahill MC, Wang C, Liu X
and During MJ: Molecular therapy of obesity and diabetes by a
physiological autoregulatory approach. Nat Med. 15:447–454. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng L, Huang T, Sun C, Hill DL and Krimm
R: BDNF is required for taste axon regeneration following
unilateral chorda tympani nerve section. Exp Neurol. 293:27–42.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng L, Ohman-Gault L, Ma L and Krimm RF:
Taste bud-derived BDNF is required to maintain normal amounts of
innervation to adult taste buds. eNeuro. 2(pii):
ENEURO.0097-15.2015. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meng L, Jiang X and Ji R: Role of
neurotrophin in the taste system following gustatory nerve injury.
Metab Brain Dis. 30:605–613. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ji R, Meng L, Li Q and Lu Q: TAM receptor
deficiency affects adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Metab Brain Dis.
30:633–644. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji R, Meng L, Jiang X, Cvm NK, Ding J, Li
Q and Lu Q: TAM receptors support neural stem cell survival,
proliferation and neuronal differentiation. PLoS One.
9:e1151402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Q, Ford MC, Lavik EB and Madri JA:
Modeling the neurovascular niche: VEGF- and BDNF-mediated
cross-talk between neural stem cells and endothelial cells: An in
vitro study. J Neurosci Res. 84:1656–1668. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blurton-Jones M, Kitazawa M,
Martinez-Coria H, Castello NA, Müller FJ, Loring JF, Yamasaki TR,
Poon WW, Green KN and LaFerla FM: Neural stem cells improve
cognition via BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13594–13599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pearse RN, Swendeman SL, Li Y, Rafii D and
Hempstead BL: A neurotrophin axis in myeloma: TrkB and BDNF promote
tumor-cell survival. Blood. 105:4429–4436. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakagawara A: Trk receptor tyrosine
kinases: A bridge between cancer and neural development. Cancer
Lett. 169:107–114. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brodeur GM, Minturn JE, Ho R, Simpson AM,
Iyer R, Varela CR, Light JE, Kolla V and Evans AE: Trk receptor
expression and inhibition in neuroblastomas. Clin Cancer Res.
15:3244–3250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Porter AC and Vaillancourt RR: Tyrosine
kinase receptor-activated signal transduction pathways which lead
to oncogenesis. Oncogene. 17:(11 Reviews). 1343–1352. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakagawara A, Azar CG, Scavarda NJ and
Brodeur GM: Expression and function of TRK-B and BDNF in human
neuroblastomas. Mol Cell Biol. 14:759–767. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yin B, Ma ZY, Zhou ZW, Gao WC, Du ZG, Zhao
ZH and Li QQ: The TrkB+ cancer stem cells contribute to
post-chemotherapy recurrence of triple-negative breast cancers in
an orthotopic mouse model. Oncogene. 34:761–770. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang SY, Hui LP, Li CY, Gao J, Cui ZS and
Qiu XS: More expression of BDNF associates with lung squamous cell
carcinoma and is critical to the proliferation and invasion of lung
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 16:1712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Radin DP and Patel P: BDNF: An oncogene or
tumor suppressor? Anticancer Res. 37:3983–3990. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hwang JJ, Park MH, Choi SY and Koh JY:
Activation of the Trk signaling pathway by extracellular zinc. Role
of metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 280:11995–12001. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hempstead BL: Dissecting the diverse
actions of pro-and mature neurotrophins. Curr Alzheimer Res.
3:19–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Johnston AL, Lun X, Rahn JJ, Liacini A,
Wang L, Hamilton MG, Parney IF, Hempstead BL, Robbins SM, Forsyth
PA, et al: The p75 neurotrophin receptor is a central regulator of
glioma invasion. PLoS Biol. 5:e2122007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Herrmann JL, Menter DG, Hamada J,
Marchetti D, Nakajima M and Nicolson GL: Mediation of
NGF-stimulated extracellular matrix invasion by the human melanoma
low-affinity p75 neurotrophin receptor: melanoma p75 functions
independently of trkA. Mol Biol Cell. 4:1205–1216. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Marchetti D, Aucoin R, Blust J, Murry B
and Greiter-Wilke A: p75 neurotrophin receptor functions as a
survival receptor in brain-metastatic melanoma cells. J Cell
Biochem. 91:206–215. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Khwaja F and Djakiew D: Inhibition of
cell-cycle effectors of proliferation in bladder tumor epithelial
cells by the p75NTR tumor suppressor. Mol Carcinog. 36:153–160.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yuanlong H, Haifeng J, Xiaoyin Z, Jialin
S, Jie L, Li Y, Huahong X, Jiugang S, Yanglin P, Kaichun W, et al:
The inhibitory effect of p75 neurotrophin receptor on growth of
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 268:110–119.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jin H, Pan Y, He L, Zhai H, Li X, Zhao L,
Sun L, Liu J, Hong L, Song J, et al: p75 neurotrophin receptor
inhibits invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
5:423–433. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ji R, Tian S, Lu HJ and Lu Q, Zheng Y,
Wang X, Ding J, Li Q and Lu Q: TAM receptors affect adult brain
neurogenesis by negative regulation of microglial cell activation.
J Immunol. 191:6165–6177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Puehringer D, Orel N, Lüningschrör P,
Subramanian N, Herrmann T, Chao MV and Sendtner M: EGF
transactivation of Trk receptors regulates the migration of newborn
cortical neurons. Nat Neurosci. 16:407–415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Park JR, Eggert A and Caron H:
Neuroblastoma: Biology, prognosis, and treatment. Hematol Oncol
Clin North Am. 24:65–86. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kermani P and Hempstead B: Brain-derived
neurotrophic factor: A newly described mediator of angiogenesis.
Trends Cardiovasc Med. 17:140–143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kermani P, Rafii D, Jin DK, Whitlock P,
Schaffer W, Chiang A, Vincent L, Friedrich M, Shido K, Hackett NR,
et al: Neurotrophins promote revascularization by local recruitment
of TrkB+ endothelial cells and systemic mobilization of
hematopoietic progenitors. J Clin Invest. 115:653–663. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ho R, Eggert A, Hishiki T, Minturn JE,
Ikegaki N, Foster P, Camoratto AM, Evans AE and Brodeur GM:
Resistance to chemotherapy mediated by TrkB in neuroblastomas.
Cancer Res. 62:6462–6466. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Brierley GV, Priebe IK, Purins L, Fung KY,
Tabor B, Lockett T, Nice E, Gibbs P, Tie J, McMurrick P, et al:
Serum concentrations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
are decreased in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Biomark.
13:67–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xiong L, Deng X, Wen Y, Yang Z and Miao X:
Association of BDNF and BMPR1A with clinicopathologic parameters in
benign and malignant gallbladder lesions. World J Surg Oncol.
11:802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Choi B, Lee EJ, Shin MK, Park YS, Ryu MH,
Kim SM, Kim EY, Lee HK and Chang EJ: Upregulation of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor in advanced gastric cancer contributes to bone
metastatic osteolysis by inducing long pentraxin 3. Oncotarget.
7:55506–55517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Götz R and Sendtner M: Cooperation of
tyrosine kinase receptor TrkB and epidermal growth factor receptor
signaling enhances migration and dispersal of lung tumor cells.
PLoS One. 9:e1009442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Qiu L, Zhou C, Sun Y, Di W, Scheffler E,
Healey S, Kouttab N, Chu W and Wan Y: Crosstalk between EGFR and
TrkB enhances ovarian cancer cell migration and proliferation. Int
J Oncol. 29:1003–1011. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
de Farias CB, Heinen TE, dos Santos RP,
Abujamra AL, Schwartsmann G and Roesler R: BDNF/TrkB signaling
protects HT-29 human colon cancer cells from EGFR inhibition.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 425:328–332. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Heinen TE, dos Santos RP, da Rocha A, Dos
Santos MP, Lopez PL, Silva Filho MA, Souza BK, Rivero LF, Becker
RG, Gregianin LJ, et al: Trk inhibition reduces cell proliferation
and potentiates the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in Ewing
sarcoma. Oncotarget. 7:348602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yee CL, Jones KR and Finger TE:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is present in adult mouse taste
cells with synapses. J Comp Neurol. 459:15–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Makino K, Kawamura K, Sato W, Kawamura N,
Fujimoto T and Terada Y: Inhibition of uterine sarcoma cell growth
through suppression of endogenous tyrosine kinase B signaling. PLoS
One. 7:e410492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Iyer R, Evans AE, Qi X, Ho R, Minturn JE,
Zhao H, Balamuth N, Maris JM and Brodeur GM: Lestaurtinib enhances
the antitumor efficacy of chemotherapy in murine xenograft models
of neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1478–1485. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Iyer R, Wehrmann L, Golden RL, Naraparaju
K, Croucher JL, MacFarland SP, Guan P, Kolla V, Wei G, Cam N, et
al: Entrectinib is a potent inhibitor of Trk-driven neuroblastomas
in a xenograft mouse model. Cancer Lett. 372:179–186. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jaboin J, Kim CJ, Kaplan DR and Thiele CJ:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB protects
neuroblastoma cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase pathway. Cancer Res. 62:6756–6763.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bao W, Qiu H, Yang T, Luo X, Zhang H and
Wan X: Upregulation of TrkB promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and anoikis resistance in endometrial carcinoma. PLoS
One. 8:e706162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kupferman M, Jiffar T, El-Naggar A, Yilmaz
T, Zhou G, Xie T, Feng L, Wang J, Holsinger FC, Yu D and Myers JN:
TrkB induces EMT and has a key role in invasion of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 29:2047–2059. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ricci A, De Vitis C, Noto A, Fattore L,
Mariotta S, Cherubini E, Roscilli G, Liguori G, Scognamiglio G,
Rocco G, et al: TrkB is responsible for EMT transition in malignant
pleural effusions derived cultures from adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Cell Cycle. 12:1696–1703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Smit MA, Geiger TR, Song JY, Gitelman I
and Peeper DS: A Twist-Snail axis critical for TrkB-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like transformation, anoikis
resistance, and metastasis. Mol Cell Biol. 29:3722–3737. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lee J, Jiffar T and Kupferman ME: A novel
role for BDNF-TrkB in the regulation of chemotherapy resistance in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e302462012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xia H, Li Y and Lv X: MicroRNA-107
inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the BDNF-mediated
PI3K/AKT pathway in human non-small lung cancer. Int J Oncol.
49:1325–1333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
DeWitt J, Ochoa V, Urschitz J, Elston M,
Moisyadi S and Nishi R: Constitutively active TrkB confers an
aggressive transformed phenotype to a neural crest-derived cell
line. Oncogene. 33:977–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen B, Liang Y, He Z, An Y, Zhao W and Wu
J: Autocrine activity of BDNF induced by the STAT3 signaling
pathway causes prolonged TrkB activation and promotes human
non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation. Sci Rep. 6:304042016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Navé BT, Ouwens M, Withers DJ, Alessi DR
and Shepherd PR: Mammalian target of rapamycin is a direct target
for protein kinase B: Identification of a convergence point for
opposing effects of insulin and amino-acid deficiency on protein
translation. Biochem J. 344:427–431. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Aoki M, Blazek E and Vogt PK: A role of
the kinase mTOR in cellular transformation induced by the
oncoproteins P3k and Akt. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:136–141. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Martens LK, Kirschner KM, Warnecke C and
Scholz H: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is a transcriptional
activator of the TrkB neurotrophin receptor gene. J Biol Chem.
282:14379–14388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li Z, Zhang J, Liu Z, Woo CW and Thiele
CJ: Downregulation of Bim by brain-derived neurotrophic factor
activation of TrkB protects neuroblastoma cells from paclitaxel but
not etoposide or cisplatin-induced cell death. Cell Death Differ.
14:318–326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Radin D, Lippa A, Patel P and Leonardi D:
Lifeguard inhibition of Fas-mediated apoptosis: A possible
mechanism for explaining the cisplatin resistance of
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
77:161–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Voldborg BR, Damstrup L, Spang-Thomsen M
and Poulsen HS: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and EGFR
mutations, function and possible role in clinical trials. Ann
Oncol. 8:1197–1206. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hunter T and Pines J: Cyclins and cancer.
II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 79:573–582.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bos JL: Ras oncogenes in human cancer: A
review. Cancer Res. 49:4682–4689. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Davis RJ: The mitogen-activated protein
kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 268:14553–14556.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sinkevicius KW, Kriegel C, Bellaria KJ,
Lee J, Lau AN, Leeman KT, Zhou P, Beede AM, Fillmore CM, Caswell D,
et al: Neurotrophin receptor TrkB promotes lung adenocarcinoma
metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:10299–10304. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Davis NM, Sokolosky M, Stadelman K, Abrams
SL, Libra M, Candido S, Nicoletti F, Polesel J, Maestro R, D'Assoro
A, et al: Deregulation of the EGFR/PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTORC1 pathway in
breast cancer: Possibilities for therapeutic intervention.
Oncotarget. 5:4603–4650. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Morris LG, Taylor BS, Bivona TG, Gong Y,
Eng S, Brennan CW, Kaufman A, Kastenhuber ER, Banuchi VE, Singh B,
et al: Genomic dissection of the epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR)/PI3K pathway reveals frequent deletion of the EGFR
phosphatase PTPRS in head and neck cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:19024–19029. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lee DH, Szczepanski MJ and Lee YJ:
Magnolol induces apoptosis via inhibiting the EGFR/PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
106:1113–1122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Cowley S, Paterson H, Kemp P and Marshall
CJ: Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for
PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell.
77:841–852. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Huang EJ and Reichardt LF: Trk receptors:
Roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem.
72:609–642. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Siu MK, Wong OG and Cheung AN: TrkB as a
therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
13:1169–1178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yuan Y, Ye HQ and Ren QC: Upregulation of
the BDNF/TrKB pathway promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition,
as well as the migration and invasion of cervical cancer. Int J
Oncol. 52:461–472. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cazorla M, Jouvenceau A, Rose C, Guilloux
JP, Pilon C, Dranovsky A and Prémont J: Cyclotraxin-B, the first
highly potent and selective TrkB inhibitor, has anxiolytic
properties in mice. PLoS One. 5:e97772010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Cazorla M, Prémont J, Mann A, Girard N,
Kellendonk C and Rognan D: Identification of a low-molecular weight
TrkB antagonist with anxiolytic and antidepressant activity in
mice. J Clin Invest. 121:1846–1857. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Light JE, Koyama H, Minturn JE, Ho R,
Simpson AM, Iyer R, Mangino JL, Kolla V, London WB and Brodeur GM:
Clinical significance of NTRK family gene expression in
neuroblastomas. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 59:226–232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Bertrand T, Kothe M, Liu J, Dupuy A, Rak
A, Berne PF, Davis S, Gladysheva T, Valtre C, Crenne JY and Mathieu
M: The crystal structures of TrkA and TrkB suggest key regions for
achieving selective inhibition. J Mol Biol. 423:439–453. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Drilon A, Siena S, Ou SI, Patel M, Ahn MJ,
Lee J, Bauer TM, Farago AF, Wheler JJ, Liu SV, et al: Safety and
antitumor activity of the multitargeted pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK
inhibitor entrectinib: Combined results from two phase I trials
(ALKA-372-001 and STARTRK-1). Cancer Discov. 7:400–409. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ardini E, Menichincheri M, Banfi P,
Bosotti R, De Ponti C, Pulci R, Ballinari D, Ciomei M, Texido G,
Degrassi A, et al: Entrectinib, a pan-TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor
with activity in multiple molecularly defined cancer indications.
Mol Cancer Ther. 15:628–639. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Burris HA, Shaw AT, Bauer TM, Farago AF,
Doebele RC, Smith S, Nanda N, Cruickshank S, Low JA and Brose MS:
Pharmacokinetics (PK) of LOXO-101 during the first-in-human phase I
study in patients with advanced solid tumors: Interim update.
Cancer Res. 75:45292015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Drilon A, Laetsch TW, Kummar S, DuBois SG,
Lassen UN, Demetri GD, Nathenson M, Doebele RC, Farago AF, Pappo
AS, et al: Efficacy of larotrectinib in TRK fusion-positive cancers
in adults and children. N Engl J Med. 378:731–739. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Al-Salama ZT and Keating GM: Cabozantinib:
A review in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Drugs. 76:1771–1778.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Abdelaziz A and Vaishampayan U:
Cabozantinib for renal cell carcinoma: Current and future
paradigms. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 18:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Schiff D, Desjardins A, Cloughesy T,
Mikkelsen T, Glantz M, Chamberlain MC, Reardon DA and Wen PY: Phase
1 dose escalation trial of the safety and pharmacokinetics of
cabozantinib concurrent with temozolomide and radiotherapy or
temozolomide after radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with
high-grade gliomas. Cancer. 122:582–587. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Radin DP, Zhong S, Purcell R and Lippa A:
Acute ampakine treatment ameliorates age-related deficits in
long-term potentiation. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:806–809. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Morgensztern D, Campo MJ, Dahlberg SE,
Doebele RC, Garon E, Gerber DE, Goldberg SB, Hammerman PS, Heist
RS, Hensing T, et al: Molecularly targeted therapies in
non-small-cell lung cancer annual update 2014. J Thorac Oncol.
10:(1 Suppl 1). S1–S63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cao L, Liu X, Lin EJ, Wang C, Choi EY,
Riban V, Lin B and During MJ: Environmental and genetic activation
of a brain-adipocyte BDNF/leptin axis causes cancer remission and
inhibition. Cell. 142:52–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Liu X, McMurphy T, Xiao R, Slater A, Huang
W and Cao L: Hypothalamic gene transfer of BDNF inhibits breast
cancer progression and metastasis in middle age obese mice. Mol
Ther. 22:1275–1284. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Xiao R, Bergin SM, Huang W, Slater AM, Liu
X, Judd RT, Lin ED, Widstrom KJ, Scoville SD, Yu J, et al:
Environmental and genetic activation of hypothalamic BDNF modulates
T-cell immunity to exert an anticancer phenotype. Cancer Immunol
Res. 4:488–497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Garofalo S, D'Alessandro G, Chece G, Brau
F, Maggi L, Rosa A, Porzia A, Mainiero F, Esposito V, Lauro C, et
al: Enriched environment reduces glioma growth through immune and
non-immune mechanisms in mice. Nat Commun. 6:66232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Linker RA, Lee DH, Flach AC, Litke T, van
den Brandt J, Reichardt HM, Lingner T, Bommhardt U, Sendtner M,
Gold R, et al: Thymocyte-derived BDNF influences T-cell maturation
at the DN3/DN4 transition stage. Eur J Immunol. 45:1326–1338. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Jaboin J, Hong A, Kim CJ and Thiele CJ:
Cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity is blocked by brain-derived
neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB signal transduction path in
neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 193:109–114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ochs G, Penn RD, York M, Giess R, Beck M,
Tonn J, Haigh J, Malta E, Traub M, Sendtner M and Toyka KV: A phase
I/II trial of recombinant methionyl human brain derived
neurotrophic factor administered by intrathecal infusion to
patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral
Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 1:201–206. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Apfel SC, Kessler JA, Adornato BT, Litchy
WJ, Sanders C and Rask CA: Recombinant human nerve growth factor in
the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy. NGF Study Group.
Neurology. 51:695–702. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Kordower JH, Palfi S, Chen EY, Ma SY,
Sendera T, Cochran EJ, Cochran EJ, Mufson EJ, Penn R, Goetz CG and
Comella CD: Clinicopathological findings following intraventricular
glial-derived neurotrophic factor treatment in a patient with
Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 46:419–424. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Radin DP, Purcell R and Lippa AS:
Oncolytic properties of ampakines in vitro. Anticancer Res.
38:265–269. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|